Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 118-126.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0140
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on pyrolysis behavior and mechanism of calcium carbide slag/magnesium carbonate system
QI Xingzhao1,3( ), WANG Feng1(
), WANG Feng1( ), WU Jie1,2(
), WU Jie1,2( ), ZHANG Qi1,3, TANG Zhongfeng3
), ZHANG Qi1,3, TANG Zhongfeng3
- 1.School of Energy and Power Engineering,Inner Mongolia University of Technology,Hohhot 010051,China
2.Inner Mongolia Power Research Institute Branch,Inner Mongolia Power(Group) Co. ,Ltd. ,Hohhot 010020,China
3.Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 201204,China
-
Received:2024-03-11Online:2024-10-10Published:2024-11-05 -
Contact:WANG Feng, WU Jie E-mail:q15147159224@163.com;wangfeng@imut.edu.cn;wujiegongda@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
QI Xingzhao, WANG Feng, WU Jie, ZHANG Qi, TANG Zhongfeng. Study on pyrolysis behavior and mechanism of calcium carbide slag/magnesium carbonate system[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 118-126.
share this article
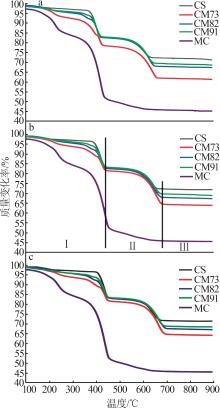
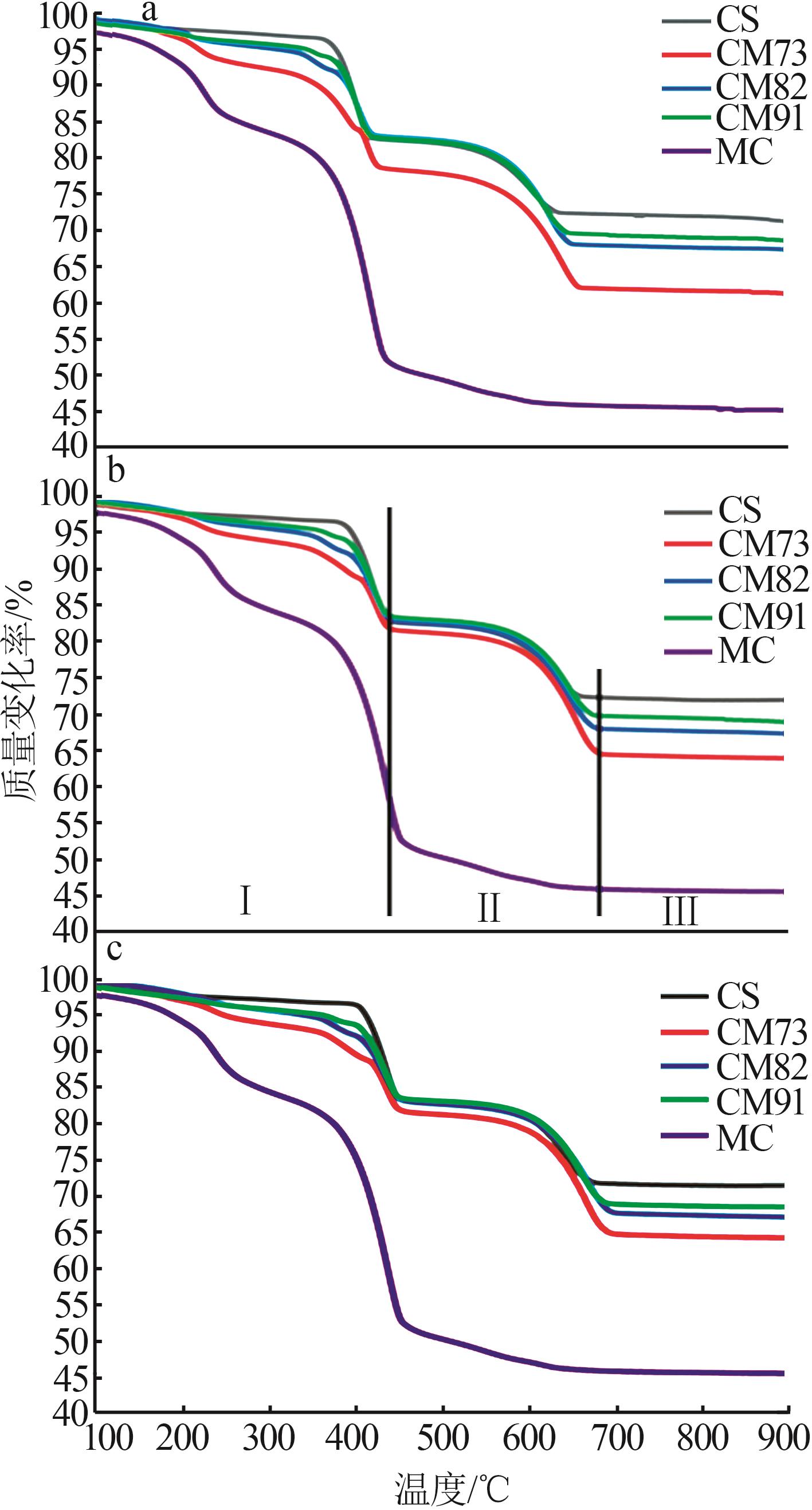
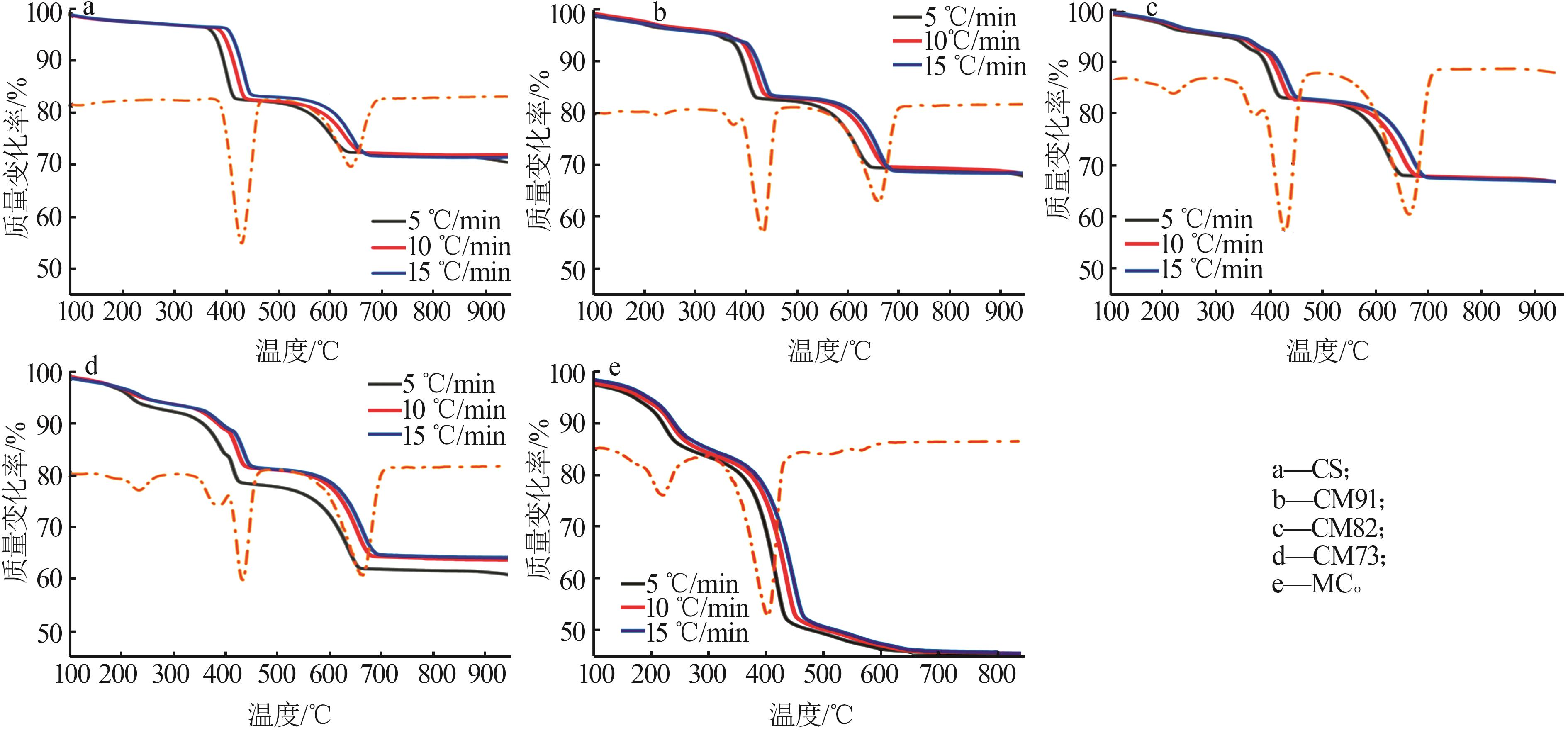
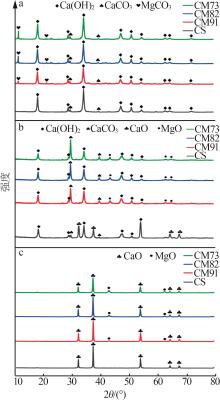
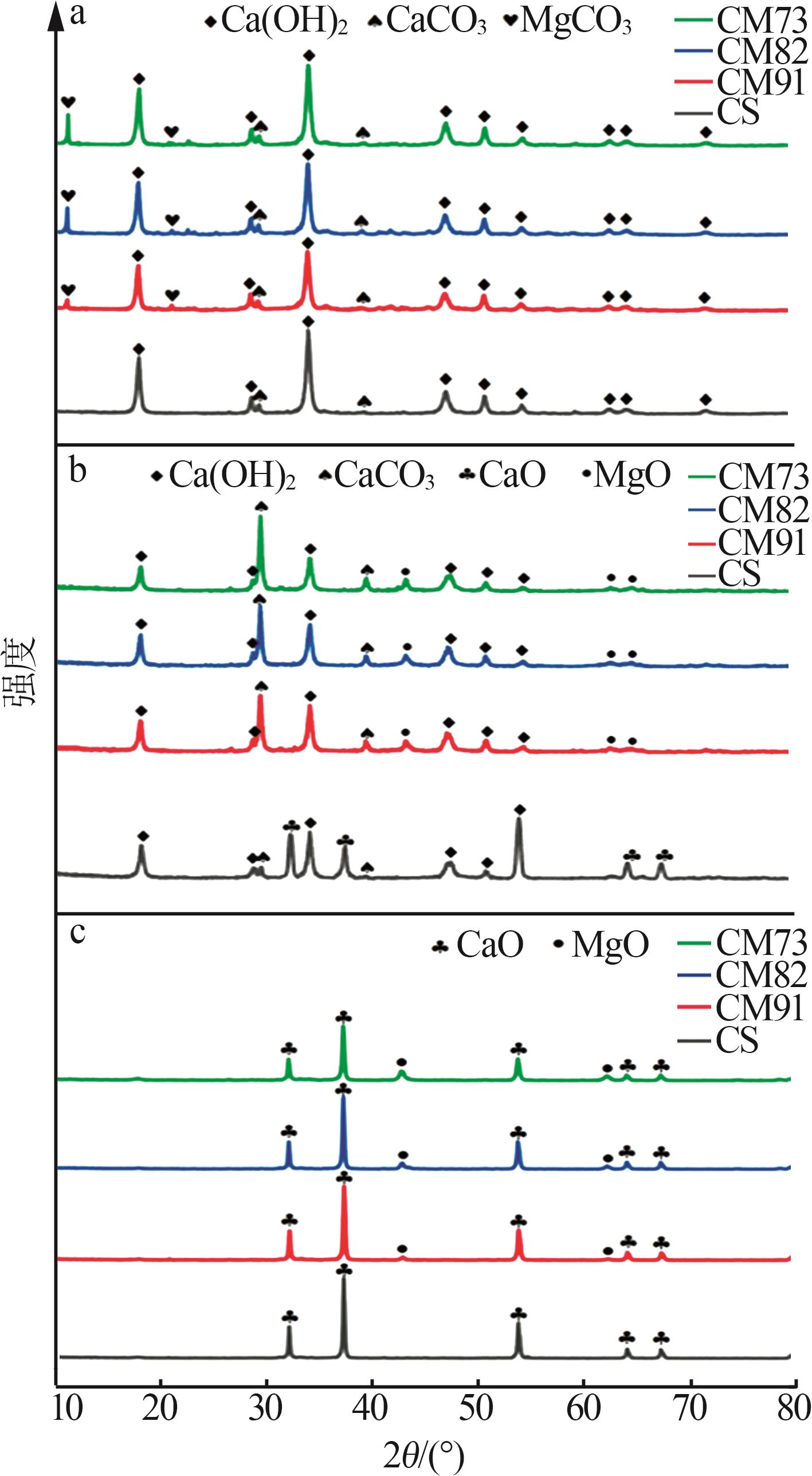
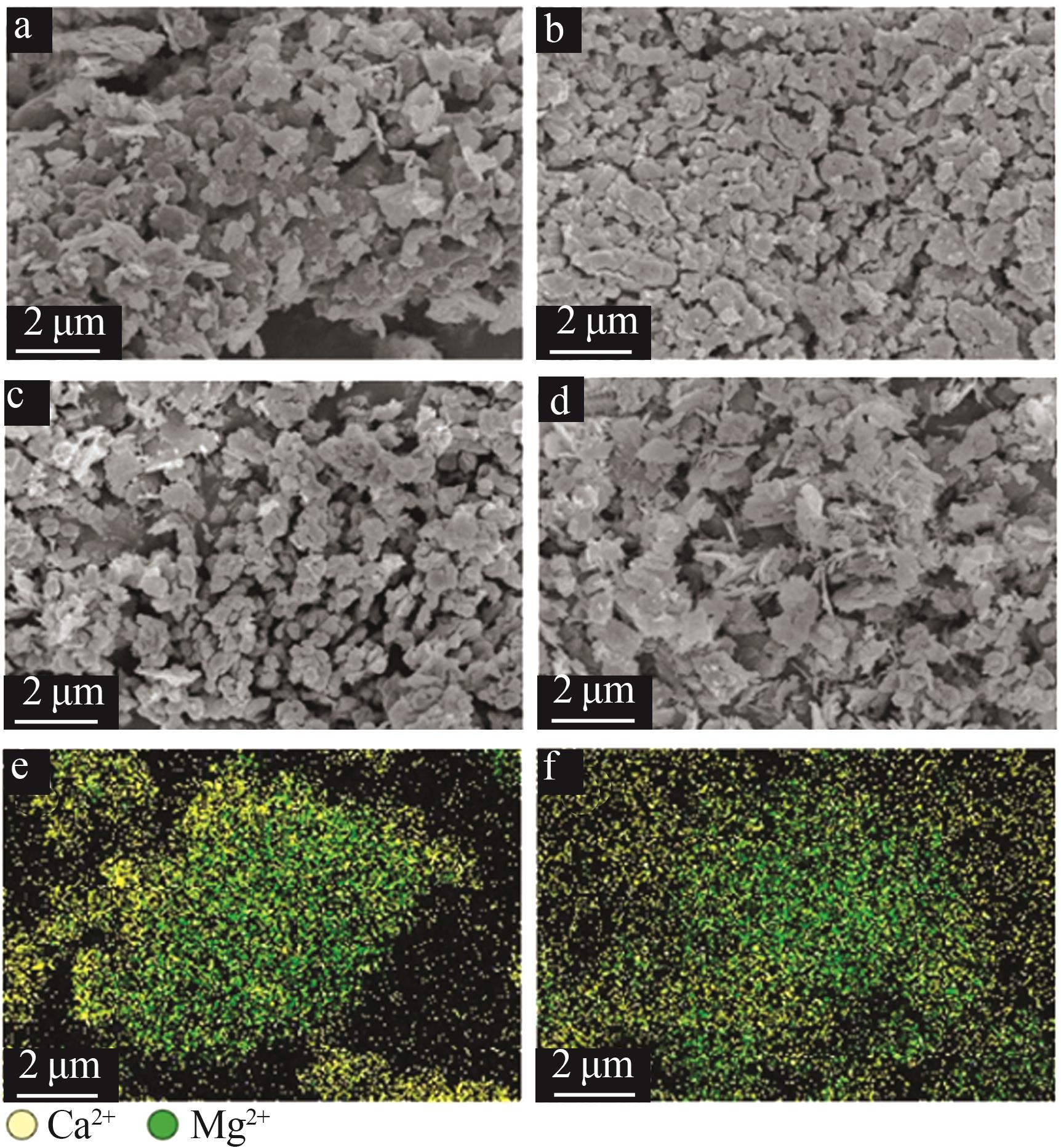
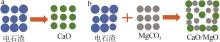
Table 2
Experimental conditions and parameters of samples"
| 名称 | 主要成分 | m(电石渣)/ m(MgCO3) | 实验条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | Ca(OH)2 | 烘干后CS在N2气氛下以5、10、15 ℃/min的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃;在CO2气氛下以10 ℃/min 的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃ | |
| CM91 | Ca(OH)2/MgCO3 | 9∶1 | 烘干后的电石渣和MgCO3按照质量比为9∶1机械混合,在N2气氛下以5、10、15 ℃/min的升温速率 由25 ℃升温至950 ℃;在CO2气氛下以10 ℃/min的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃ |
| CM82 | Ca(OH)2/MgCO3 | 8∶2 | 烘干后的电石渣和MgCO3按照质量比为8∶2机械混合,在N2气氛下以5、10、15 ℃/min的升温速率 由25 ℃升温至950 ℃;在CO2气氛下以10 ℃/min的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃ |
| CM73 | Ca(OH)2/MgCO3 | 7∶3 | 烘干后的电石渣和MgCO3按照质量比为7∶3机械混合,在N2气氛下以5、10、15 ℃/min的升温速率 由25 ℃升温至950 ℃;在CO2气氛下以10 ℃/min的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃ |
| MC | MgCO3 | 烘干后MC在N2气氛下以5、10、15 ℃/min的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃;在CO2气氛下以10 ℃/min 的升温速率由25 ℃升温至950 ℃ |
| 1 | 邵岚,马丽萍,杨杰,等.电石渣的资源化利用现状[J].现代化工,2024,44(3):79-83. |
| SHAO Lan, MA Liping, YANG Jie,et al.Re⁃utilization status of carbide slag[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2024,44(3):79-83. | |
| 2 | 赵珂萍,李晓玉,李瑞红,等.固废源CaO基CO2捕集材料的制备与捕集性能研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报,2023,42(2):520- 530. |
| ZHAO Keping, LI Xiaoyu, LI Ruihong,et al.Research progress on preparation and capture performance of CaO-based CO2 capture materials from solid wastes[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2023,42(2):520-530. | |
| 3 | 季洪峰,李灿华,都刚,等.固废源钙基碳捕集剂制备及抗烧结性研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(3):28-35. |
| JI Hongfeng, LI Canhua, DU Gang,et al.Research progress of preparation and sintering resistance of calcium⁃based CO2 trapping materials from solid waste sources[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(3):28-35. | |
| 4 | GENG Yiqi, GUO Yanxia, FAN Biao,et al.Research progress of calcium⁃based adsorbents for CO2 capture and anti⁃sintering modification[J].Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2021,49(7):998-1013. |
| 5 | LING Changjian, WANG Zirui, TANG Zhongfeng.Performance improvement of Na4SiO4 doped with Li2CO3-K2CO3 for high⁃temperature CO2 capture and thermochemical energy storage[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,476:146921. |
| 6 | WANG Zirui, LIU Weihua, LING Changjian,et al.CO2 capture behavior and chemical structure of the alkali zirconate⁃silicate hybrid sorbent from ZrSiO4 by alkali activation method[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2021,51:101639. |
| 7 | BIAN Zhiguo, LI Yingjie, ZHANG Chunxiao,et al.CaO/Ca(OH)2 heat storage performance of hollow nanostructured CaO-based material from Ca-looping cycles for CO2 capture[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2021,217:106834. |
| 8 | 匡盛铎,陈炜,林文升,等.Mg/Y改性Ca基吸附剂强化吸附CO2试验[J].洁净煤技术,2022,28(10):195-202. |
| KUANG Shengduo, CHEN Wei, LIN Wensheng,et al.Enhanced adsorption of CO2 by Mg/Y modified Ca-based adsorbents[J].Clean Coal Technology,2022,28(10):195-202. | |
| 9 | 王久衡,荣鼐,刘开伟,等.水蒸气强化纤维素模板改性钙基吸附剂固碳性能及强度[J].化工进展,2023,42(6):3217-3225. |
| WANG Jiuheng, RONG Nai, LIU Kaiwei,et al.Enhanced CO2 capture performance and strength of cellulose⁃templated CaO-based pellets with steam reactivation[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2023,42(6):3217-3225. | |
| 10 | LI Ping, CHEN Ran, LIN Yunan,et al.General approach to facile synthesis of MgO-based porous ultrathin nanosheets enabling high⁃efficiency CO2 capture[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,404:126459. |
| 11 | 吴爽,刘瑞,丁巍巍,等.Al2O3掺杂CaO吸附剂长周期CO2捕集性能研究[J].低碳化学与化工,2024(5):81-87. |
| WU Shuang, LIU Rui, DING Weiwei,et al.Long⁃term CO2 capture performance of Al2O3-doped CaO adsorbent[J].Low Carbon Chemistry and Chemical Industry,2024(5):81-87. | |
| 12 | 许春辉,王峰,凌长见,等.熔盐改性的金属氧化物捕获二氧化碳研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(5):1-7,23. |
| XU Chunhui, WANG Feng, LING Changjian,et al.Research progress of CO2 capture by metal oxides modified by molten sa⁃lts[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(5):1-7,23. | |
| 13 | PARK J, YI K B.Effects of preparation method on cyclic stability and CO2 absorption capacity of synthetic CaO-MgO absorbent for sorption⁃enhanced hydrogen production[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2012,37(1):95-102. |
| 14 | LI Keke, SUN Jian, ZHANG Yuxuan,et al.Cigarette butt⁃assisted combustion synthesis of dolomite⁃derived sorbents with enhanced cyclic CO2 capturing capability for direct solar⁃driven calcium looping[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2023,311:123269. |
| 15 | 唐玉婷,陈晓斌,马晓茜.Zr-Mg改性吸附剂捕集热解气中CO2的实验研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(7):118-125,143. |
| TANG Yuting, CHEN Xiaobin, MA Xiaoqian.Experiment study of capturing CO2 from pyrolysis gases by Zr-Mg modified sorbents[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(7):118-125,143. | |
| 16 | 彭李佳,王银龙,翟宸,等.白云石可控碳化联产氢氧化镁和碳酸钙及其改性[J].化工进展,2024(4):1981-1991. |
| PENG Lijia, WANG Yinlong, ZHAI Chen,et al.Controlled carbonization of dolomite for co⁃production of magnesium hydroxide and calcium carbonate and its modification[J].Progress in Che⁃mical Engineering,2024(4):1981-1991. | |
| 17 | 桂昌青,王雅静,凌长见,等.氧化镁基二氧化碳吸附剂的制备及改性研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(8):77-83. |
| GUI Changqing, WANG Yajing, LING Changjian,et al.Research progress of preparation and modification of MgO-based CO2 adsorbents[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(8):77-83. | |
| 18 | ZHANG Jianyu, CAO Qi, LIU Hongpan,et al.Thermal decomposition kinetics of carbide slag in air atmosphere[J].IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2019,227:052065. |
| 19 | 张雷,田园,路春美.工业废弃物煅烧动力学的热重分析与研究[J].煤炭学报,2011,36(4):681-686. |
| ZHANG Lei, TIAN Yuan, LU Chunmei.Thermogravimetric analysis and study on calcination kinetics of industrial wastes[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2011,36(4):681-686. | |
| 20 | 马晓宇,刘波,陈功,等.N2、CO2气氛下菱镁矿热分解的动力学机理[J].过程工程学报,2024.Doi:10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.223345. |
| MA Xiaoyu, LIU Bo, CHEN Gong,et al.Kinetic mechanism of thermal decomposition of magnesite under N2 and CO2 atmosphere[J].Journal of Process Engineering,2024.Doi:10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.223345. | |
| 21 | 张星,徐杰,王子兵,等.原料粒径对石灰石热分解反应动力学影响[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(2):79-84. |
| ZHANG Xing, XU Jie, WANG Zibing,et al.Effect of feedstock particle size on kinetics of limestone thermal decomposition reaction[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(2):79-84. | |
| 22 | SCHAUBE F, KOCH L, WÖRNER A,et al.A thermodynamic and kinetic study of the de⁃and rehydration of Ca(OH)2 at high H2O partial pressures for thermo⁃chemical heat storage[J].Thermochimica Acta,2012,538:9-20. |
| 23 | CHEN Dun, GAO Xiang, DOLLIMORE D.The application of non⁃isothermal methods of kinetic analysis to the decomposition of calcium hydroxide[J].Thermochimica Acta,1993,215:65-82. |
| [1] | ZHANG Jinjun, GUO Linlin, MIAO Chengpeng, LI Xingyu, PANG Yaheng, YANG Rongkai, YU Yasen. Study on preparation of spherical calcium carbonate for coating fillers based on carbide slag as raw materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 113-119. |
| [2] | YAN Xin, LIU Hailu, LIU Baolin, LIU Yi, LIU Yanyang. Research on key technologies and mechanisms of green nano calcium carbonate production [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 71-76. |
| [3] | ZHANG Bangcheng, WANG Li. Preparation and adsorption properties of waste polyester⁃based activated carbon activated by ZnCl2 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 126-134. |
| [4] | YANG Hanshuo, WANG Dexi, YU Honglei, YANG Yali, JIANG Jiuchuang. Experimental study on hydrodynamic cavitation⁃enhanced carbothermic reduction process for production of magnesium carbonate hydromagnesite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 74-79. |
| [5] | HU Dian, GUO Ze, ZHANG Hanquan, LU Manman. Research on effects of roasting process and typical impurities on reduction and decomposition process of phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 88-95. |
| [6] | ZHANG Jinjun, GUO Linlin, LIU Bojing, FENG Shuang, SHI Qi. Study on preparation of needle-like shaped CaCO3 from calcium carbide slag [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(7): 103-108. |
| [7] | YANG Yue, ZHU Ganyu, ZHANG Jianbo, MENG Ziheng, LIU Xinhui, YANG Jing, YAN Kun, PENG Zonggui, WANG Qiujian, LI Huiquan. Study on preparation of desulfurizer and byproduct gypsum from calcium carbide slag by cyclone separation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(5): 78-84. |
| [8] | ZHOU Qiang, WU Bin, CHEN Kui, JI Lijun, WU Yanyang. Study on thermal decomposition kinetic mechanism and calcination process of phosphorus tailings [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 47-54. |
| [9] | TIAN Xiaoli, LI Zhixun, FENG Runtang, ZHANG Jie, ZHENG Quanfu, SHI Xuwu, DU Yongbin. Study on thermal decomposition behavior of Tibetan Kamado microcrystalline magnesite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 60-65. |
| [10] | YANG Fengling,ZHAI Min,REN Lei,ZHANG Yuanyuan,CHENG Fangqin,DONG Hongyu. Influencing factors of crystallization products in wet desulfurization of carbide slag [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 92-98. |
| [11] | DU Guanggang, HE Tong, XU Zehui, LIU Lei. Study on properties of calcium oxide in SCA under different calcination conditions [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 35-41. |
| [12] | CHEN Xiaoqing, ZHOU Jian′an, WANG Yi, HAN Juan, WANG Bao, PEI Peiyan. Study on decomposition characteristic of limestone powder in high temperature flue gas of converter [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 70-77. |
| [13] | WU Di, LI Laishi, WANG Junkai, WU Yusheng, WANG Yuzheng, LI Mingchun. Study on decomposition process and thermal decomposition kinetics of ammonium sulfate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 86-92. |
| [14] | XU Ruilin,ZHAO Lipeng,LIU Xingwei,LIU Huan,WANG Hao,XU Xiaoming,ZENG Tao. Improvement of high temperature cycling performance of LiFePO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(9): 108-112. |
| [15] | LIANG Hai,YUAN Tianlong,WANG Wanting,YANG Yunhong,LIANG Wenjie,WANG Xiaomin,DENG Xinzhong. Synthesis of micron?tubular?magnesium oxide clusters and its adsorption performance for phosphate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(9): 77-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||