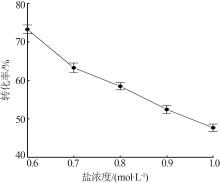
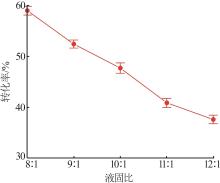
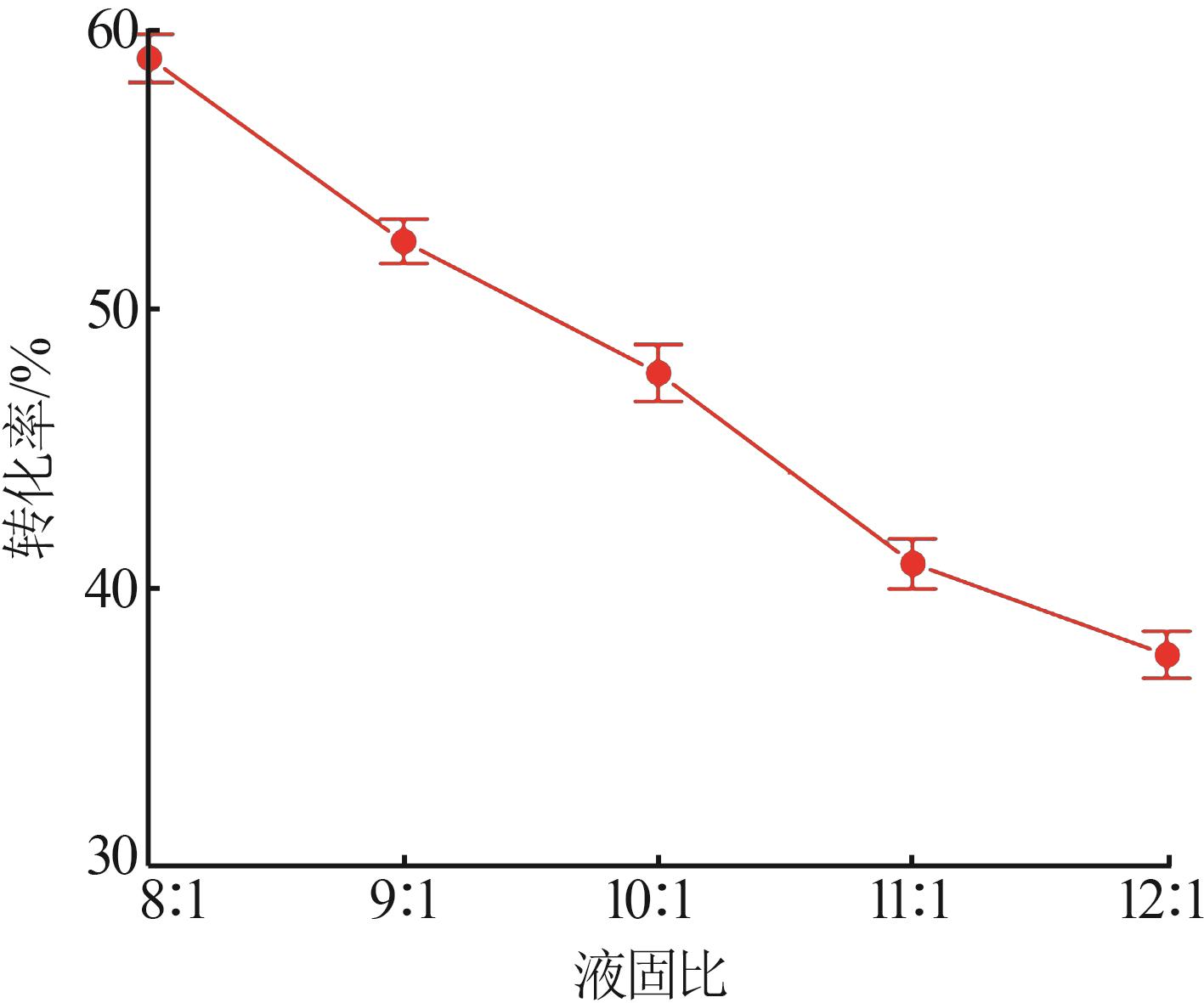
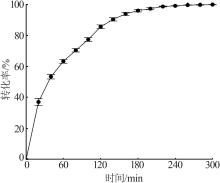
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 64-69.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0364
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
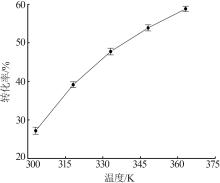
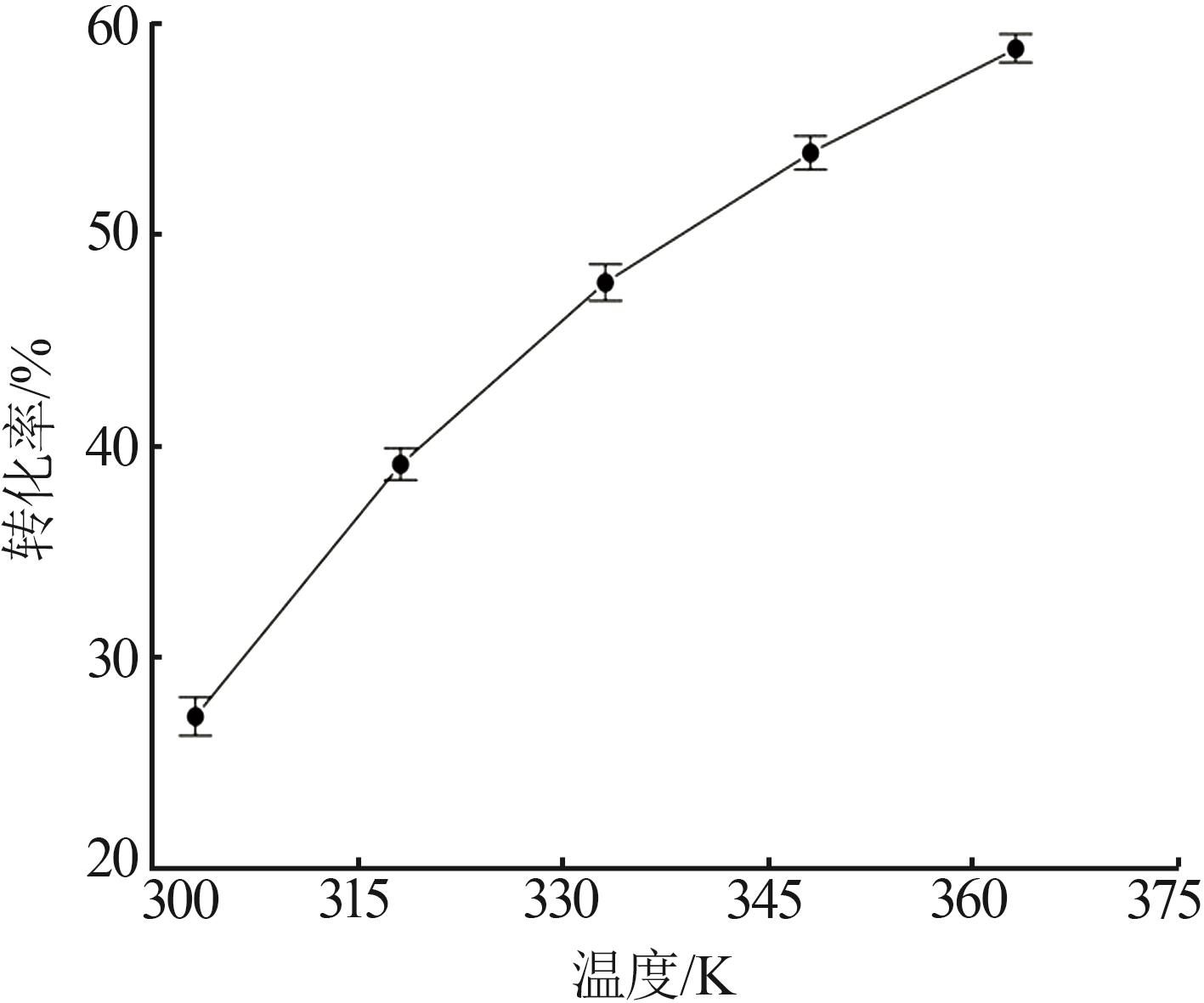
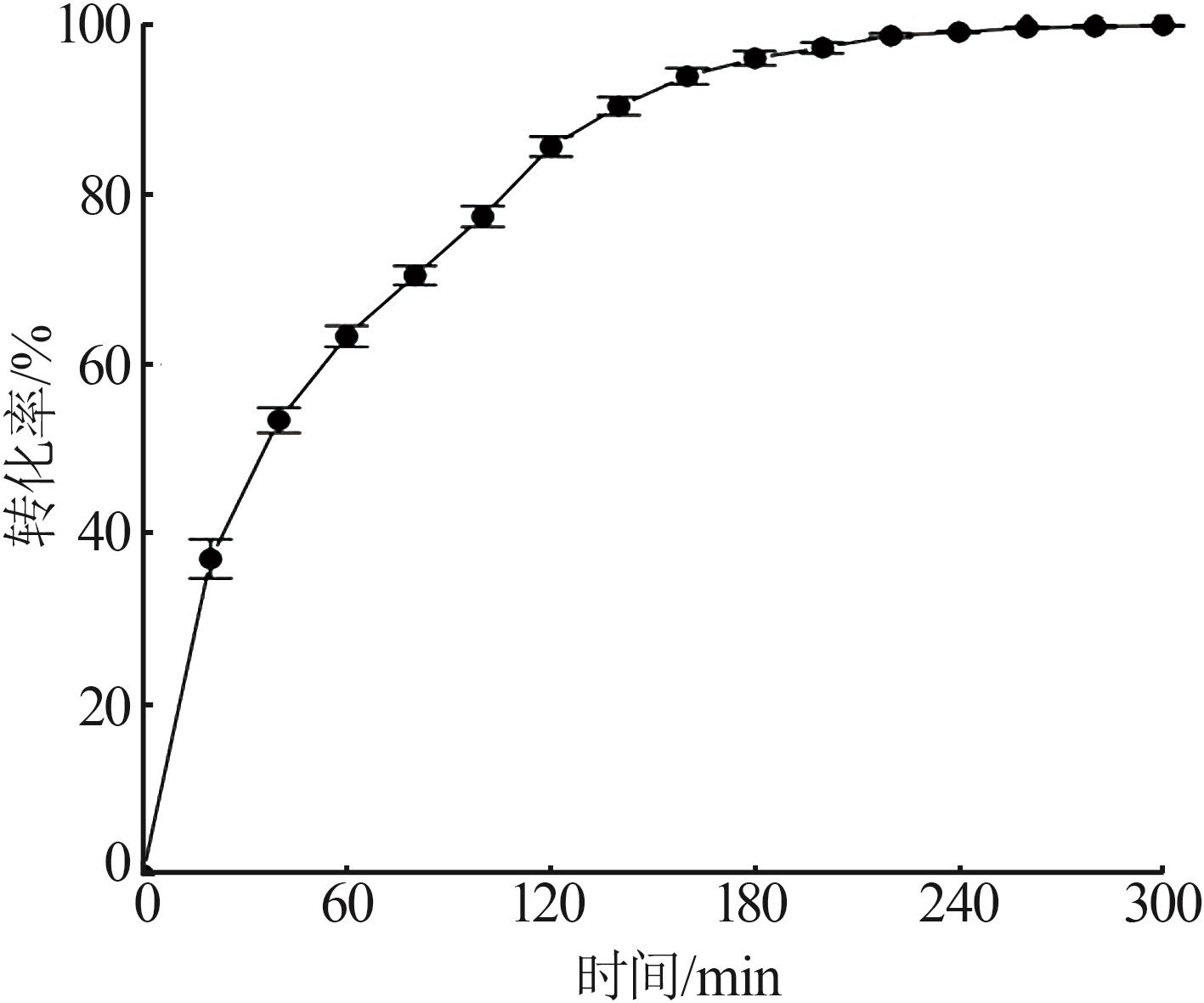
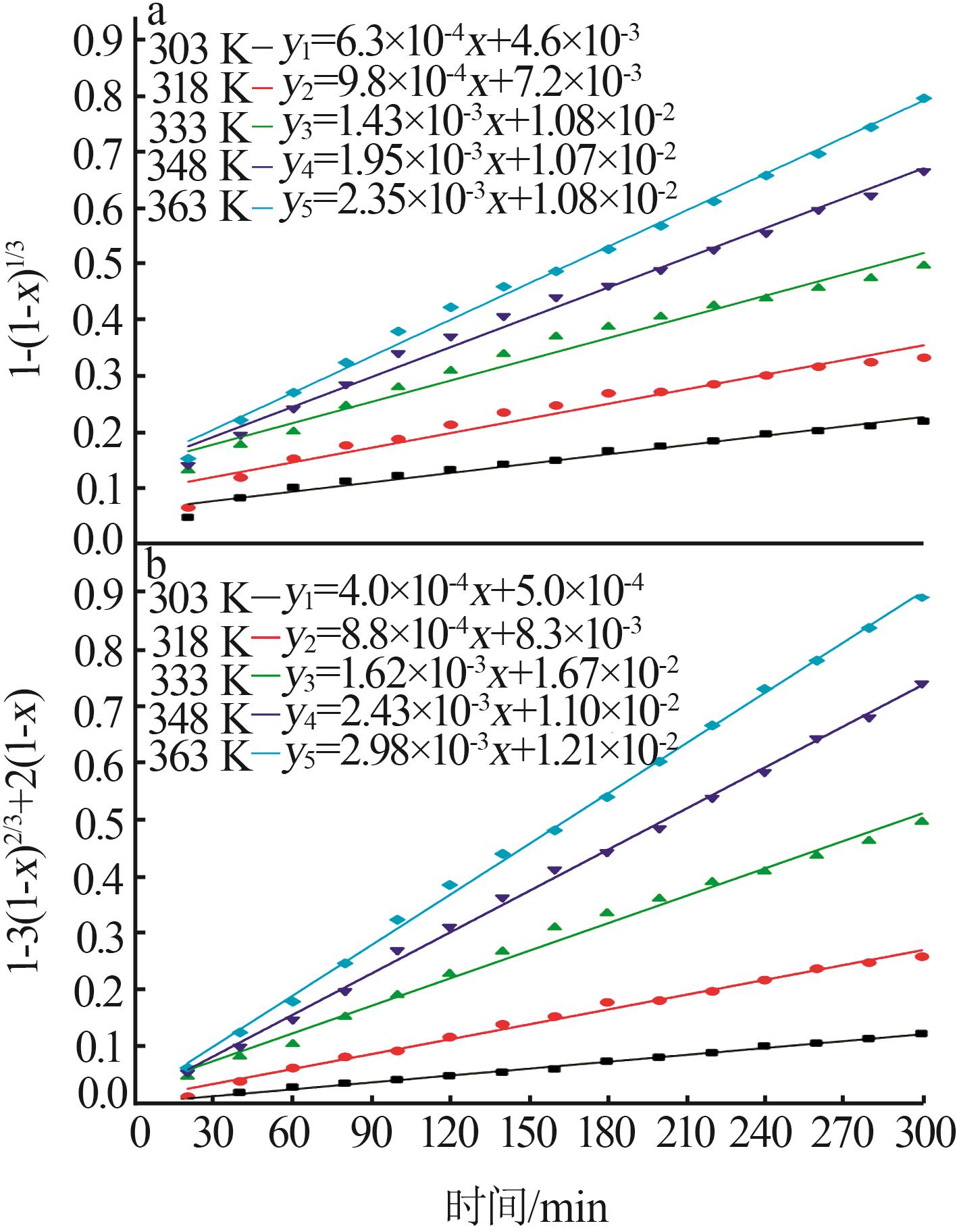
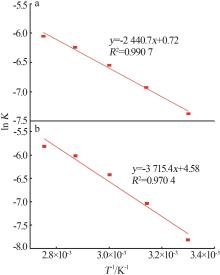
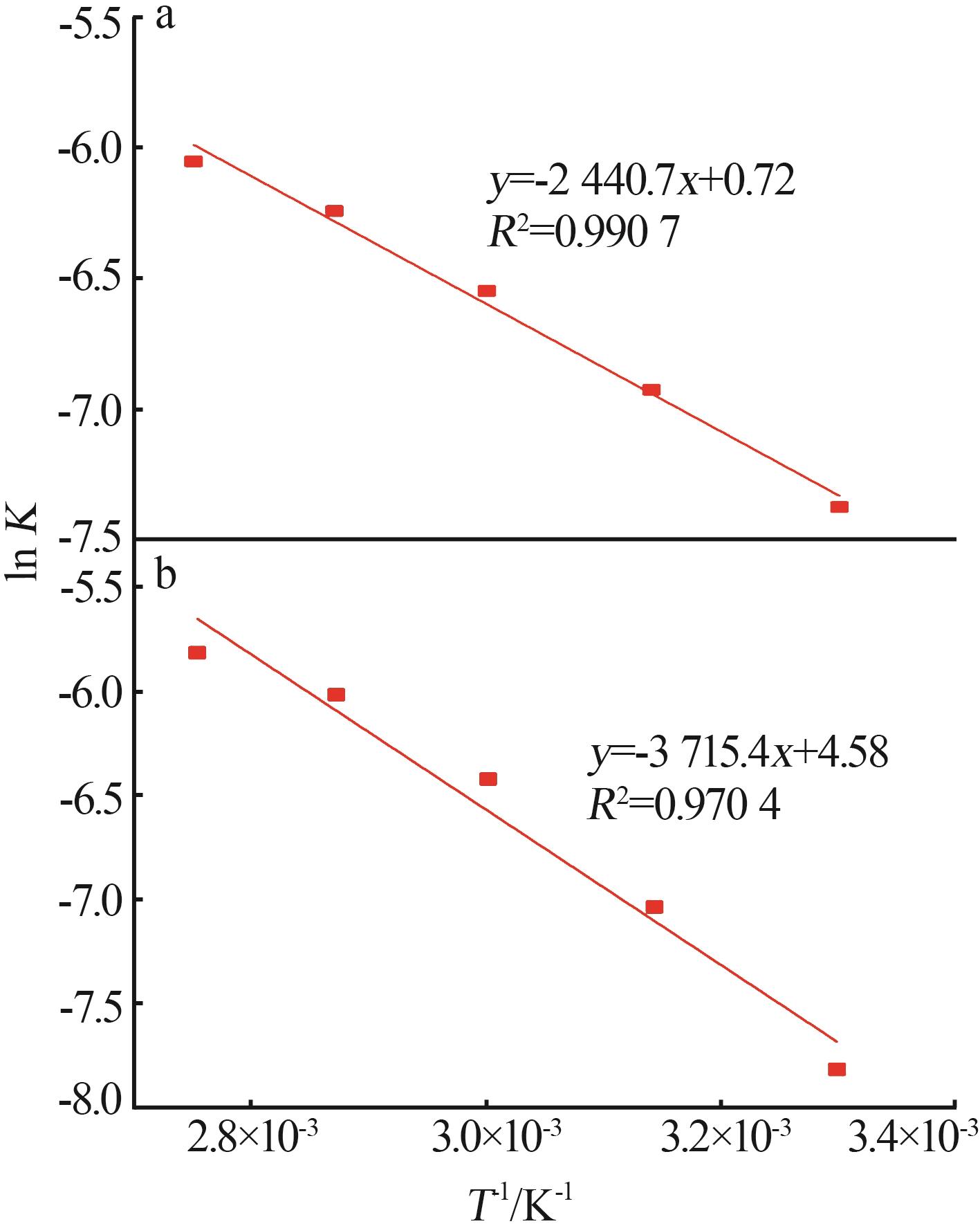
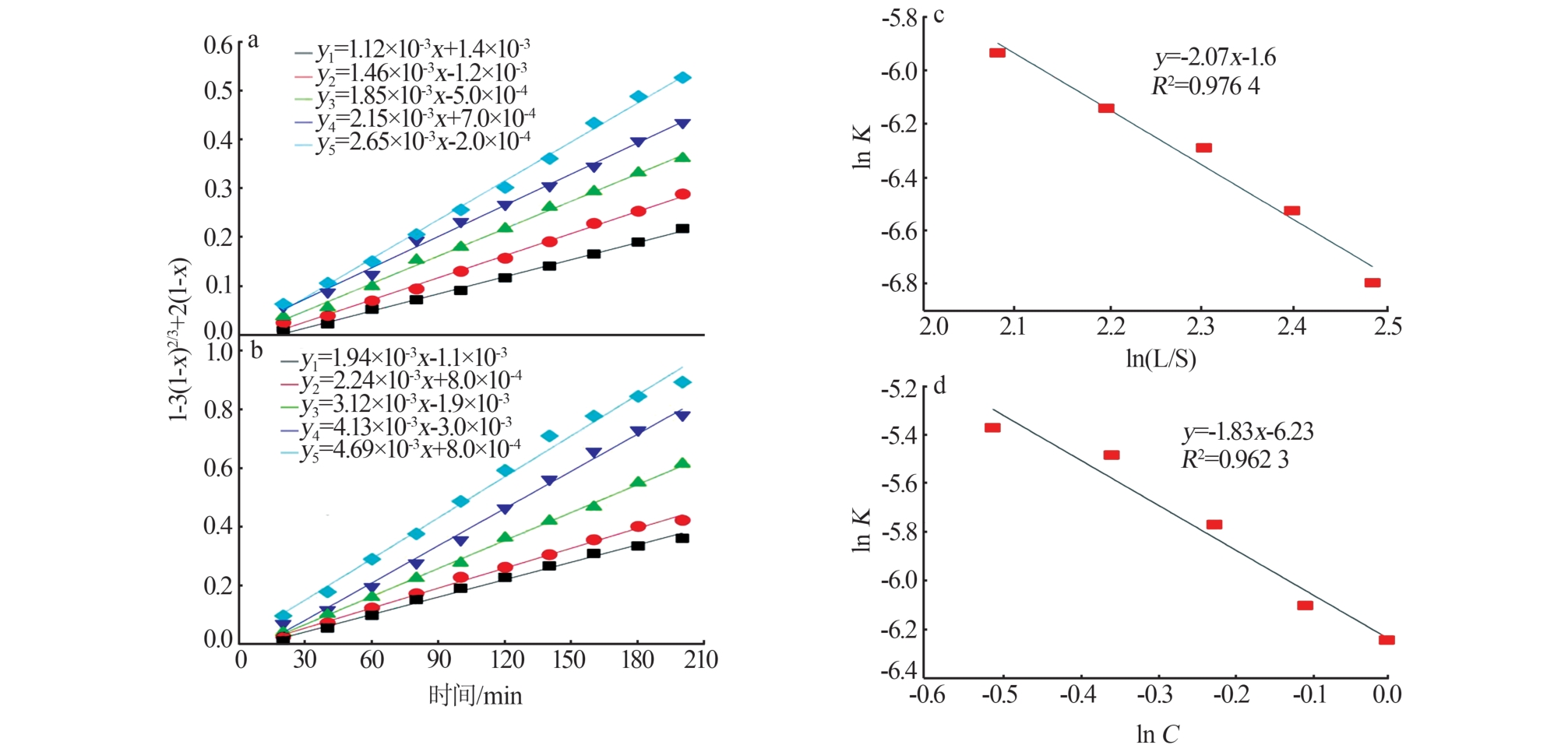
Reaction kinetics of ethylenediamine hydrochloride with calcium hydroxide
ZHANG Yu1( ), ZHAO Guiyan1, TIAN Yongchang1, QIU Xiaokui2, SUN Jiali2, XU Lixin3(
), ZHAO Guiyan1, TIAN Yongchang1, QIU Xiaokui2, SUN Jiali2, XU Lixin3( )
)
- 1.Graduate School of Engineering,Anhui University of Technology,Ma'anshan 243002,China
2.GBXF Silicones Co. ,Ltd. ,Ma'anshan 238251,China
3.College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Anhui University of Technology,Ma'anshan 243032,China
-
Received:2023-07-11Online:2024-05-10Published:2024-05-15 -
Contact:XU Lixin E-mail:1398357442@qq.com;lxxu@ahut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Yu, ZHAO Guiyan, TIAN Yongchang, QIU Xiaokui, SUN Jiali, XU Lixin. Reaction kinetics of ethylenediamine hydrochloride with calcium hydroxide[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 64-69.
share this article
| 1 | 李超,王继琼.乙撑胺生产技术及市场现状[J].天津化工,2017,31(4):10-11. |
| LI Chao, WANG Jiqiong.乙撑胺生产技术及市场现状[J].Tianjin Chemical Industry,2017,31(4):10-11. | |
| 2 | 周晶,邱俊.乙二胺合成工艺及催化剂的研究进展[J].化学世界,2016,57(9):583-589. |
| ZHOU Jing, QIU Jun.Research progress of the synthetic process of ethylenediamine and its catalysts[J].Chemical World,2016,57(9):583-589. | |
| 3 | 杨溢,兰昭洪,田保亮,等.乙二胺合成工艺进展[J].石油化工,2012,41(5):603-608. |
| YANG Yi, LAN Zhaohong, TIAN Baoliang,et al.Progress in research of ethylenediamine synthesis[J].Petrochemical Technology,2012,41(5):603-608. | |
| 4 | 刘玉普,邸友莹,何东华,等.乙二胺盐酸盐的低温热容和热化学性质[J].高等学校化学学报,2010,31(6):1227-1230. |
| LIU Yupu, DI Youying, HE Donghua,et al.Low-temperature heat capacities and thermochemistry properties of ethylene diamine dihydrochloride[J].Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2010,31(6):1227-1230. | |
| 5 | 罗娟,胡忠于,仇明华.脱除乙二胺盐酸盐中HCl的新方法[J].吉首大学学报(自然科学版),2004,25(1):92-93. |
| LUO Juan, HU Zhongyu, QIU Minghua.Research about how to extract hydrochloride existing in ethylenediamine[J].Journal of Jishou University(Natural Science Edition),2004,25(1):92-93. | |
| 6 | BUDDE F J.Process for the recovery of ethylene amines:US,5072048[P].1991-12-10. |
| 7 | 王伟,毛伟,吕婧,等.萃取精馏法分离乙二胺和H2O的共沸物[J].化学工程,2014,42(10):25-28. |
| WANG Wei, MAO Wei, Jing LÜ,et al.Separation of EDA and H2O azeotrope by extractive distillation[J].Chemical Engineering (China),2014,42(10):25-28. | |
| 8 | JAYARAMAN K, VELAYUTHAM D, SRINIVASAN R K,et al.Isolation of ethylenediamine from industrial solution of ethylenediamine hydrochloride by electrodialysis[J].Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology,2003,78(6):626-631. |
| 9 | CESAS R, ZAJACK T.Neutralization of Ethylenediamine Hydrochloride and recovery of Ethylenediamine:US,20100069673[P]. 2010-03-18. |
| 10 | 胡江华,罗晗晗,甘俊,等.一种从双胺基硅烷副产物乙二胺盐酸盐中制取无水乙二胺的方法:中国,110172024B[P].2022-03-04. |
| 11 | 赵锋伟,惠丰,袁俊,等.乙醇胺缩合胺化反应合成乙二胺研究进展[J].化工进展,2020,39(S2):212-220. |
| ZHAO Fengwei, HUI Feng, YUAN Jun,et al.Progress in selective synthesis of ethylenediamine via condensation amination of monoethanolamine[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020,39(S2):212-220. | |
| 12 | 张海江.管道化反应器合成乙二胺的工艺研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2008. |
| ZHANG Haijiang.Study on the synthesis of ethylenediamine with a tubular reactor[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2008. | |
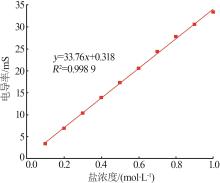
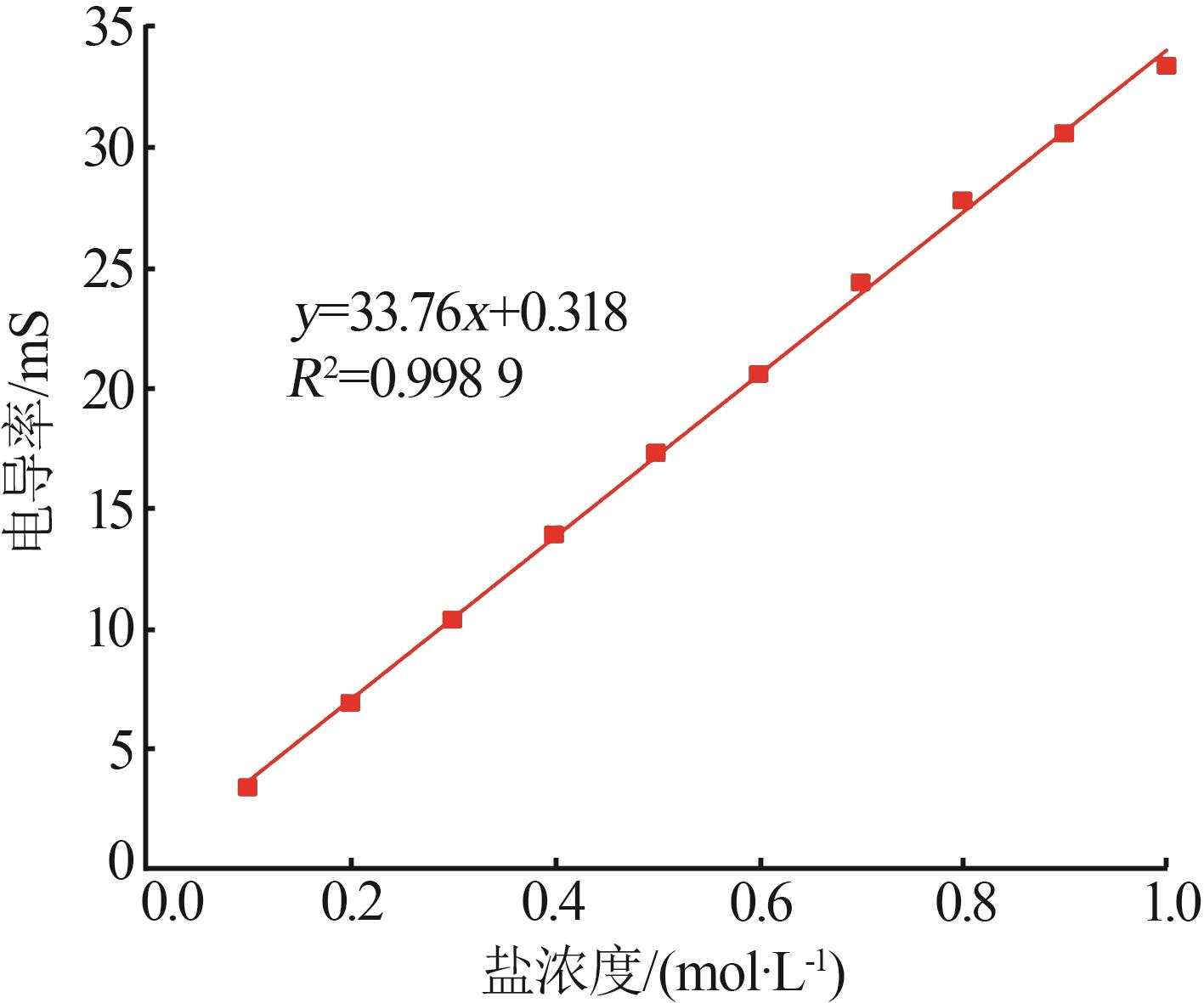
| 13 | 彭嘉伟,邓德华,刘赞群.电导率法测定氯氧镁水泥中醇可抽提氯离子含量[J].建筑材料学报,2022,25(8):877-884. |
| PENG Jiawei, DENG Dehua, LIU Zanqun.Determination of alcohol leachable chloride ion content of magnesium oxychloride cement by conductivity method[J].Journal of Building Materials,2022,25(8):877-884. | |
| 14 | 王浩森,任柄臣,许德华,等.硝酸分解磷钾矿的浸出工艺及动力学[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(5):45-51. |
| WANG Haosen, REN Bingchen, XU Dehua,et al.Leaching process and kinetics of phosphorus-potassium ore decomposition by nitric acid[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(5):45- 51. | |
| 15 | 王智玉,廖玮婷,谢雷,等.超临界乙醇中木质素解聚的宏观动力学模型[J].林产工业,2021,58(6):55-60. |
| WANG Zhiyu,LIAO Weiting,XIE Lei,et alMacro[P].kinetics model of lignin depolymerization in supercritical ethanol[J].China Forest Products Industry,2021,58(6):55-60. | |
| 16 | 孟留洋,李解,苏文柔,等.白云鄂博钾长石微波碱浸反应等温动力学分析[J].稀有金属,2020,44(10):1113-1120. |
| MENG Liuyang, LI Jie, SU Wenrou,et al.Isothermal kinetics of alkaline leaching of potassium feldspar from Bayan obo under microwave irradiation[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2020,44(10):1113-1120. | |
| 17 | 高新愿.磷石膏制硫酸钾第一阶段反应动力学研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2018. |
| GAO Xinyuan.Study on the First Stage Reaction Kinetics of Potassium Sulfate from Phosphogypsum[D].Nanchang:Nanchang University,2018. | |
| 18 | 周海,杨三可,解田.磷酸分解磷矿的动力学及影响因素研究[J].应用化工,2021,50(6):1472-1477. |
| ZHOU Hai, YANG Sanke, XIE Tian.Study on the dissolution kinetics of phosphate ore in phosphoric acid and its influencing factors[J].Applied Chemical Industry,2021,50(6):1472-1477. | |
| 19 | HOMMA S, OGATA S, KOGA J,et al.Gas-solid reaction model for a shrinking spherical particle with unreacted shrinking core[J].Chemical Engineering Science,2005,60(18):4971-4980. |
| 20 | KAVCı E, ÇALBAN T, ÇOLAK S,et al.Leaching kinetics of ulexite in sodium hydrogen sulphate solutions[J].Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2014,20(5):2625-2631. |
| [1] | HAN Wei, SONG Yongming, LIU Qi, XU Jinling, XU Rong, LI Chunquan, YIN Shuaijun, SUN Zhiming. Study on performance of calcium chloride assisted thermal activation of coal gangue and its peroxymonosulfate activation toward benzo(a)pyrene degradation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 103-112. |
| [2] | ZENG Yijun, JIANG Ziwen, JIAN Chengzong, QUAN Xuejun. Study on deep extraction of chromium from calcium-free roasting slag of chromite ore [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 90-96. |
| [3] | MA Shuqing, LI Changwen, SHI Chenglong, QIN Yaru. Kinetic study of lithium extraction from solution with iron-based ionic liquid system [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 60-66. |
| [4] | FANG Fan, YAO Benlin, XIAO Yiqun, JIA Yanhong, CHEN Hui, LI Bin, HE Hui. Research progress on dissolution behavior and mechanism of uranium dioxide in nitric acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 34-43. |
| [5] | ZOU Yang, LU Zhiyan, HU Zhilin, SUN Ze. Study on metastable zone width and primary nucleation kinetics for cooling crystallization of KNO3 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 67-74. |
| [6] | CHENG Ziyang, CHEN Guofu. Early hydration kinetics research of nano-SiO2 and cement composite cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 80-87. |
| [7] | ZHAO Shiyong, XIAO Yuchen, MA Qingqing, YANG Zhenni, WANG Jizhen, FAN Xiaoping. Study on adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) on 4A zeolite synthesized by aluminum extraction residue by fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 127-134. |
| [8] | DENG Yinxiang, CHEN Chaoyi, WANG Shiyu, GAO Yingxue, PENG Shuang. Effect of cell voltage on electrochemical conversion of CO2 to carbon materials in CaCl2 based molten salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(1): 40-46. |
| [9] | FAN Fangfang, TONG Zhongkai, ZUO Weiyuan. Study on adsorption of tetracycline from wastewater by calcium modified peanut shell biochar [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 109-115. |
| [10] | ZHOU Qiang, WU Bin, CHEN Kui, JI Lijun, WU Yanyang. Study on thermal decomposition kinetic mechanism and calcination process of phosphorus tailings [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 47-54. |
| [11] | TIAN Xiaoli, LI Zhixun, FENG Runtang, ZHANG Jie, ZHENG Quanfu, SHI Xuwu, DU Yongbin. Study on thermal decomposition behavior of Tibetan Kamado microcrystalline magnesite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 60-65. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xing,XU Jie,WANG Zibing,HOU Peng,HE Long,LIU Huan. Effect of feedstock particle size on kinetics of limestone thermal decomposition reaction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 79-84. |
| [13] | DING Ning, ZHANG Jian, PING Qingwei, SHENG Xueru, LI Na. Study on adsorption and release properties of matrine by magnesium-modified diatomite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 37-46. |
| [14] | LI Xiyan, ZHANG Hong, LIU Xuejing, YANG Hao, XU Shuai, LI Jiaxin, XIE Jiaqi, XU Guangwen. Study on decomposition characteristic and kinetics of magnesite in inhibitory atmosphere [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 50-55. |
| [15] | PENG Jiaoyu, TAN Yuqin, YANG Keli, DONG Yaping, ZHANG Bo, LI Wu. Study on crystallization mechanism and kinetics of macallisterite synthesized with bischofite from salt lake [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 56-62. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||