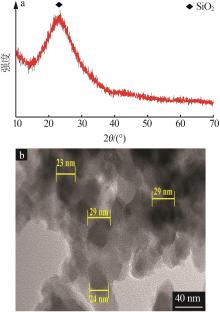
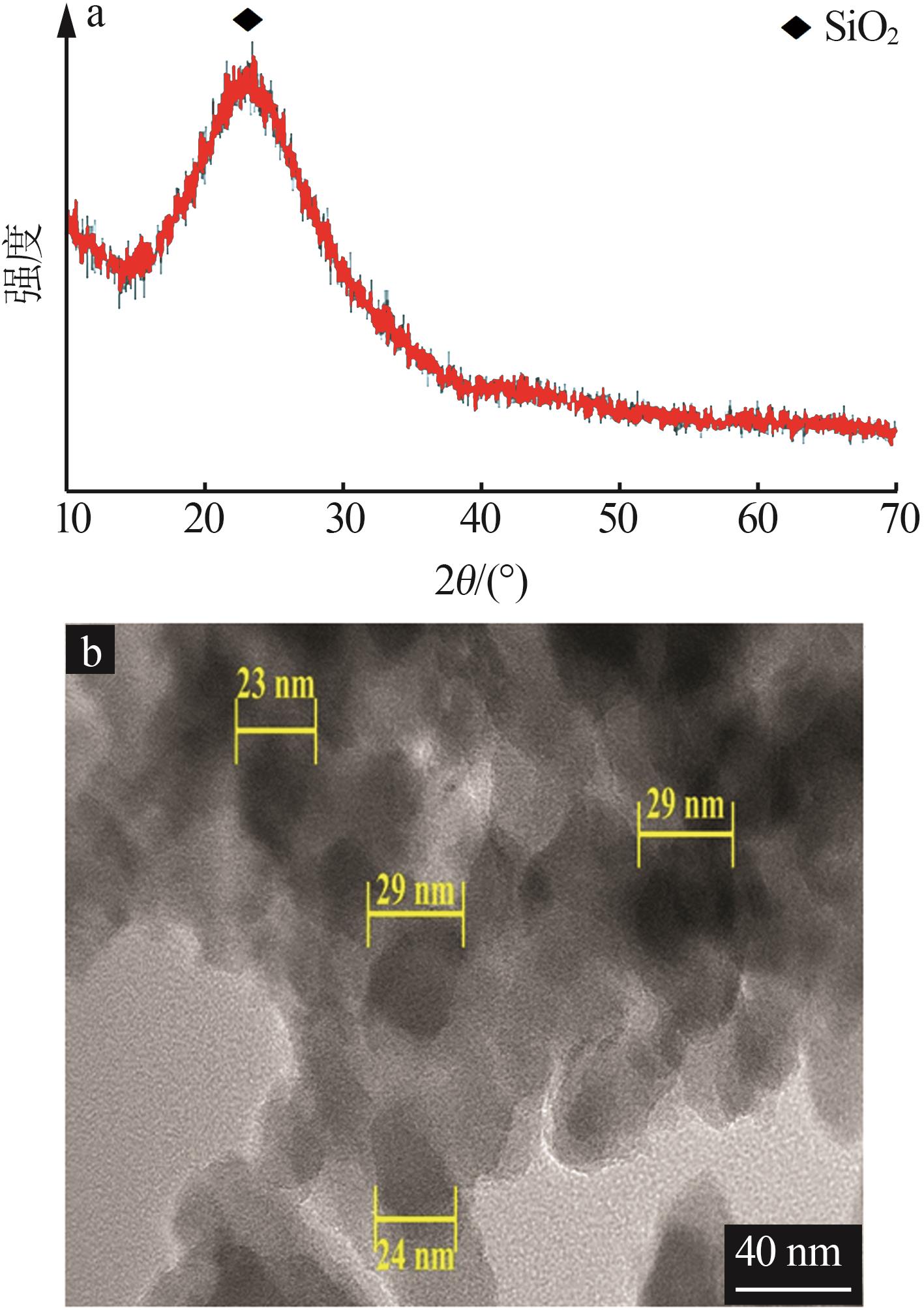
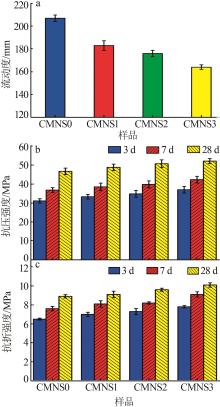
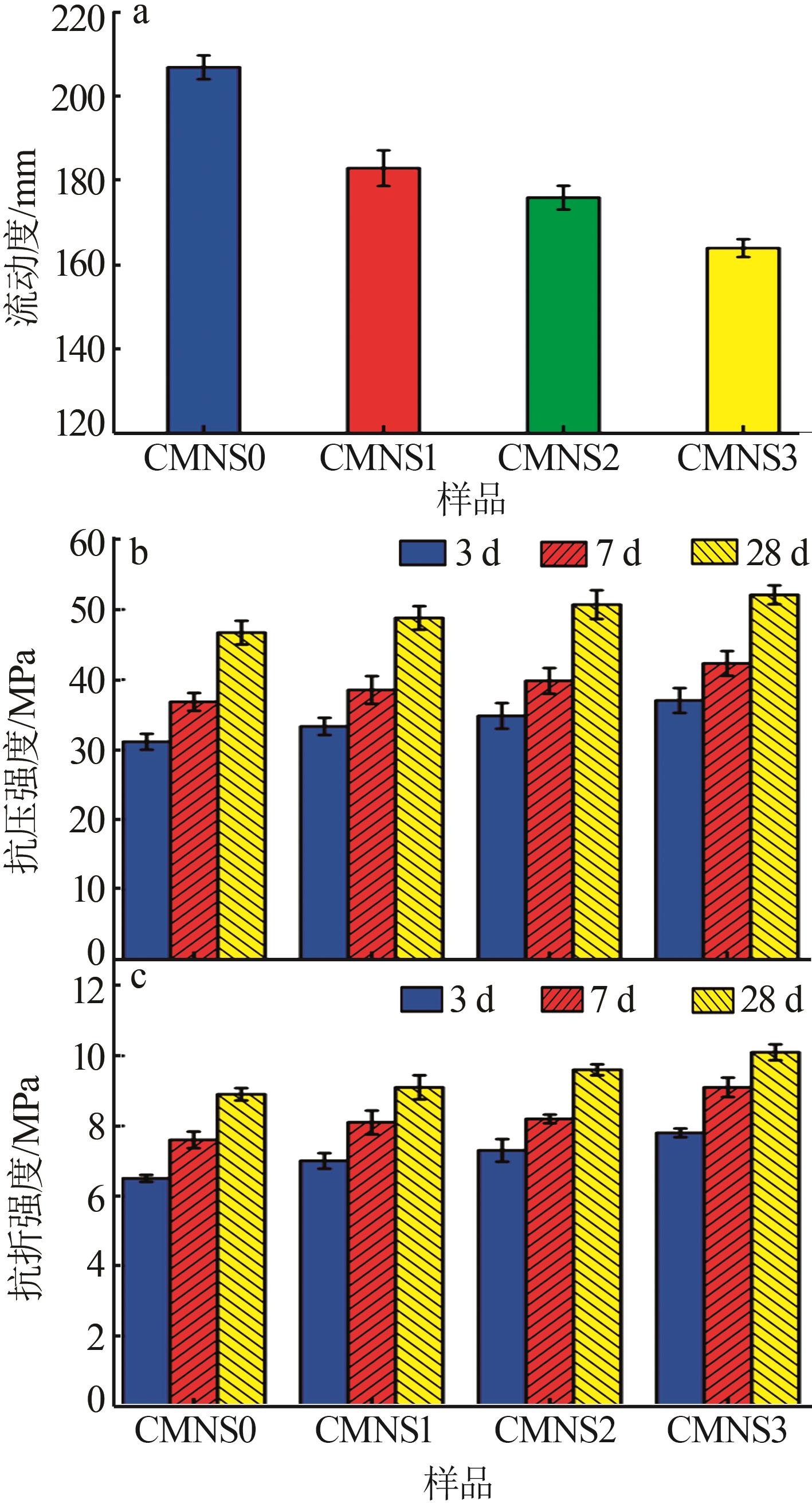
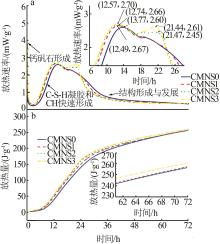
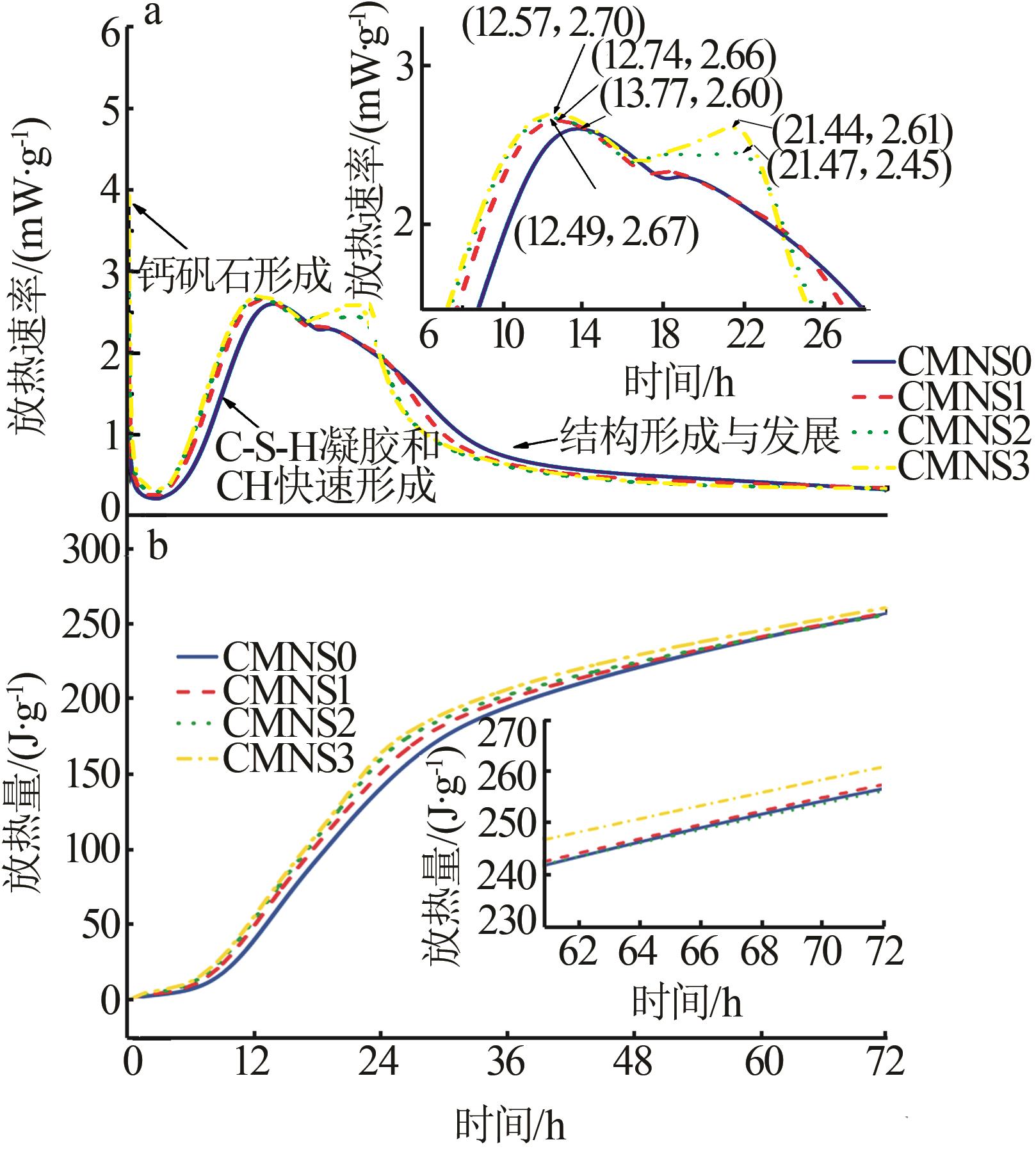
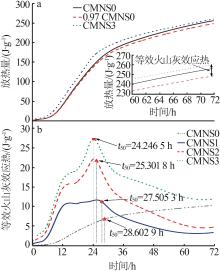
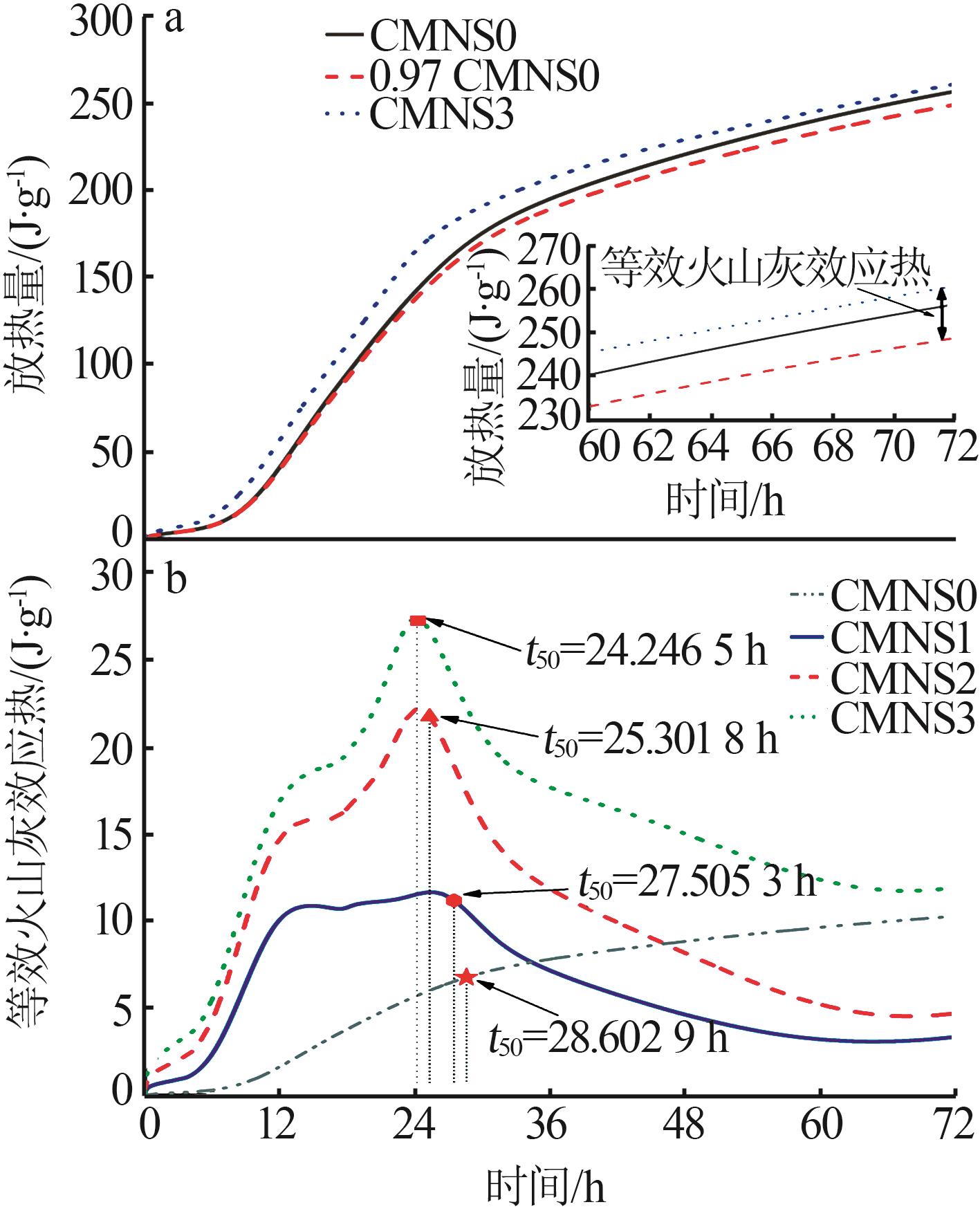
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 80-87.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0435
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Early hydration kinetics research of nano-SiO2 and cement composite cementitious materials
- 1.Hubei Communications Investment Technology Development Co. ,Ltd. ,Wuhan 430000,China
2.Guang′an;Vocational & Technical College,Guang′an 638500,China
-
Received:2023-09-01Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-08-01
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHENG Ziyang, CHEN Guofu. Early hydration kinetics research of nano-SiO2 and cement composite cementitious materials[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 80-87.
share this article
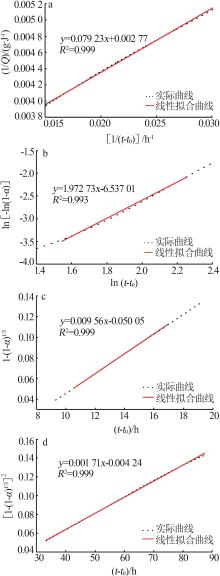
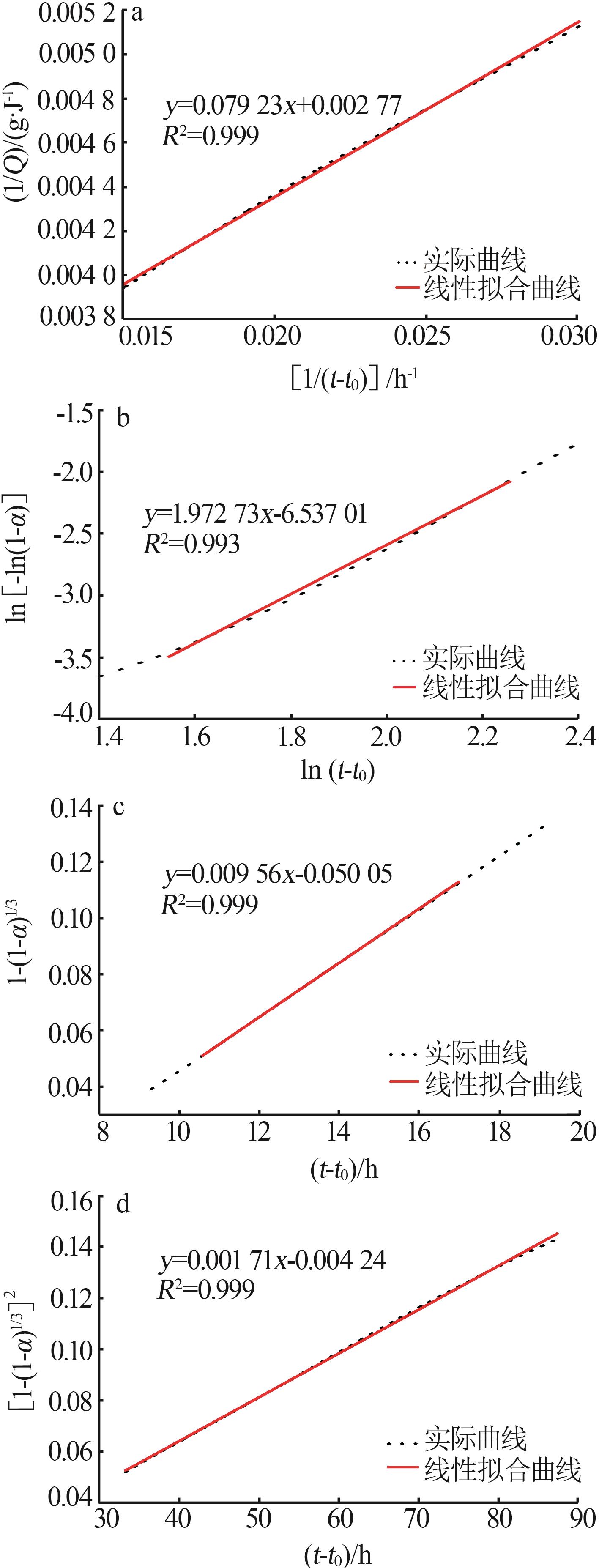
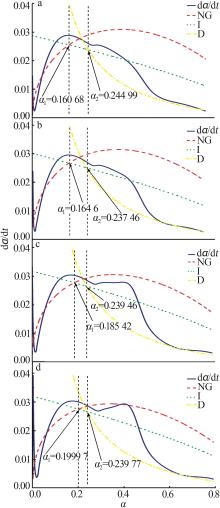
Table 5
Hydration kinetic parameters of different gelling systems"
| 样品 | n | K1′ | K2′ | K3′ | 类型 | α1 | α2 | α2-α1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMNS0 | 1.972 7 | 0.036 4 | 0.009 6 | 0.001 71 | NG-I-D | 0.160 7 | 0.245 0 | 0.084 3 |
| CMNS1 | 1.873 7 | 0.038 2 | 0.010 2 | 0.001 79 | NG-I-D | 0.164 6 | 0.237 6 | 0.072 9 |
| CMNS2 | 1.772 1 | 0.038 4 | 0.010 6 | 0.001 85 | NG-I-D | 0.185 4 | 0.239 5 | 0.054 1 |
| CMNS3 | 1.703 9 | 0.037 5 | 0.010 7 | 0.001 86 | NG-I-D | 0.200 0 | 0.239 8 | 0.039 8 |
Table 5
| 1 | 王丹,张丽娜,侯鹏坤,等.纳米SiO2在水泥基材料中的应用研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报,2020,39(4):1003-1015. |
| WANG Dan, ZHANG Lina, HOU Pengkun,et al.Research progress in modification of cement⁃based materials using nano⁃sili⁃ca[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,39(4):1003-1015. | |
| 2 | SHI Tao, LI Zexin, GUO Jian,et al.Research progress on CNTs/CNFs⁃modified cement⁃based composites:A review[J].Construction and Building Materials,2019,202(30):290-307. |
| 3 | YOUSUF F, WEI Xiaosheng.Investigation of the early⁃age microstructural development of hydrating cement pastes through electrical resistivity measurements[J].Case Studies in Construction Materials,2020,13:e00391. |
| 4 | ZHANG Jianwu, GUAN Xuemao, LI Haiyan,et al.Performance and hydration study of ultra⁃fine sulfoaluminate cement⁃based double liquid grouting material[J].Construction and Building Materials,2017,132:262-270. |
| 5 | POLAT R, DEMIRBOGA R, KARAGÖL F.The effect of nano⁃MgO on the setting time,autogenous shrinkage,microstructure and mechanical properties of high performance cement paste and mortar[J].Construction and Building Materials,2017,156:208- 218. |
| 6 | 陈旭勇,程子扬,詹旭,等.纳米SiO2-橡胶粉再生混凝土力学性能试验研究及数值模拟[J].材料导报,2021,35(23):23235-23240,23245. |
| CHEN Xuyong, CHENG Ziyang, ZHAN Xu,et al.Experimental and numerical research on mechanical properties of recycled concrete with nano⁃SiO2-rubber powder[J].Materials Reports,2021,35(23):23235-23240,23245. | |
| 7 | AGARWAL A, BHUSNUR S, SHANMUGA PRIYA T.Experimental investigation on recycled aggregate with laboratory concrete waste and nano⁃silica[J].Materials Today:Proceedings,2020,22:1433-1442. |
| 8 | 戎志丹,姜广,孙伟.纳米SiO2和CaCO3对超高性能水泥基复合材料的影响[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版),2015,45(2):393-398. |
| RONG Zhidan, JIANG Guang, SUN Wei.Effects of nano⁃SiO2 and nano⁃CaCO3 on properties of ultra⁃high performance cementitious composites[J].Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition),2015,45(2):393-398. | |
| 9 | SUN Jinfeng, XU Zhiqiang, LI Weifeng,et al.Effect of nano⁃SiO₂ on the early hydration of alite⁃sulphoaluminate cement[J].Nanomaterials,2017,7(5):102. |
| 10 | 徐晶,王先志.纳米二氧化硅对混凝土界面过渡区的改性机制及其多尺度模型[J].硅酸盐学报,2018,46(8):1053-1058. |
| XU Jing, WANG Xianzhi.Effect of nano⁃silica modification on interfacial transition zone in concrete and its multiscale modell⁃ing[J].Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,46(8):1053-1058. | |
| 11 | 朱靖塞,许金余,白二雷,等.复合纳米材料对混凝土动态力学性能的影响[J].复合材料学报,2016,33(3):597-605. |
| ZHU Jingsai, XU Jinyu, BAI Erlei,et al.Effects of composite nanomaterials on dynamic mechanical properties of concretes[J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(3):597-605. | |
| 12 | LI Long, XUAN D, SOJOBI A,et al.Development of nano⁃silica treatment methods to enhance recycled aggregate concrete[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2021,118(6):103963. |
| 13 | NUAKLONG P, SATA V, WONGSA A,et al.Recycled aggregate high calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete with inclusion of OPC and nano⁃SiO2 [J].Construction and Building Materials,2018,174(6):244-252. |
| 14 | XU Zhenhai, ZHOU Zonghui, DU Peng,et al.Effects of nano⁃silica on hydration properties of tricalcium silicate[J].Construction and Building Materials,2016,125(30):1169-1177. |
| 15 | ZHOU Yingwu, ZHENG Shuyue, HUANG Xiaoxu,et al.Performance enhancement of green high⁃ductility engineered cementitious composites by nano⁃silica incorporation[J].Construction and Building Materials,2021,281:122618. |
| 16 | NAZARI A, RIAHI S.Microstructural,thermal,physical and mechanical behavior of the self compacting concrete containing SiO2 nanoparticles[J].Materials Science and Engineering A,2010,527(29):7663-7672. |
| 17 | NILI M, EHSANI A.Investigating the effect of the cement paste and transition zone on strength development of concrete containing nanosilica and silica fume[J].Materials & Design,2015,75:174-183. |
| 18 | KRSTULOVIĆ R, DABIĆ P.A conceptual model of the cement hydration process[J].Cement and Concrete Research,2000, 30(5):693-698. |
| 19 | 阎培渝,郑峰.水泥基材料的水化动力学模型[J].硅酸盐学报,2006,34(5):555-559. |
| YAN Peiyu, ZHENG Feng.Kinetics model for the hydration mechanism of cementitious materials[J].Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2006,34(5):555-559. | |
| 20 | 彭小芹,兰聪,王淑萍,等.水化硅酸钙粉体对水泥水化反应过程及机理的影响[J].建筑材料学报,2015,18(2):195-201. |
| PENG Xiaoqin, LAN Cong, WANG Shuping,et al.Effects of the C-S-H powder on the hydration process and mechanism of cement[J].Journal of Building Materials,2015,18(2):195-201. | |
| 21 | HE Zhen, HU Lingling.Hydration mechanism of cement⁃based materials with different Si-rich mineral admixtures[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology:Materials Science,2018,33(3):654-660. |
| 22 | 陈杰,水中和,孙涛,等.活化煤矸石在水泥基材料中的早期水化动力学研究[J].硅酸盐通报,2019,38(7):1983-1990. |
| CHEN Jie, SHUI Zhonghe, SUN Tao,et al.Early hydration kinetics research of calcined coal gangue in cement⁃based materi⁃als[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2019,38(7):1983-1990. | |
| 23 | MA Baoguo, MEI Junpeng, TAN Hongbo,et al.Effect of nano silica on hydration and microstructure characteristics of cement high volume fly ash system under steam curing[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology:Ma terials Science,2019,34(3):604-613. |
| 24 | LIU Xiaohai, MA Baoguo, TAN Hongbo,et al.Effects of colloidal nano⁃SiO2 on the immobilization of chloride ions in cement-fly ash system[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2020,110:103596. |
| 25 | RUPASINGHE M, NICOLAS R S, MENDIS P,et al.Investigation of strength and hydration characteristics in nano⁃silica incorporated cement paste[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2017,80(7):17-30. |
| [1] | SHI Wangfang, ZHANG Yongsheng. Study on NO x degradation performance of concrete-based non-metallic boron doped nitrogen-rich carbon nitride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 116-123. |
| [2] | TU Yanping, BAI Dengxian, CHENG Shukai, XIE Junjie, HUANG Zhiliang, CHEN Guofu. Effect of high temperature modification of mineral powder and quicklime on properties of phosphogypsum cement based materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 94-101. |
| [3] | DAI Hongtao, SHEN Fangfang, YANG Wentao. Experimental study on preparation of ceramic permeable pavement brick from waste incineration slag [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 121-127. |
| [4] | ZHONG Binyang, LIANG Yulan, CHEN Zhijie, LIAO Qihua, WANG Jingui. Study on properties and microstructure of cement⁃based fillers modified by oyster shell powder [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 135-140. |
| [5] | LI Qiang, YOU Xiaomin, SHE Xuefeng, JIANG Zeyi, XUE Qingguo, WANG Jingsong. Effect of calcination temperature and carbon structure on compressive strength of CaO-containing carbon pellets [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 43-49. |
| [6] | DENG Changhong. Preparation of nano silica microemulsion and its water control performance [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(5): 71-77. |
| [7] | LI Peng, WANG Likun, MENG Qiuyan. Study on effect of α-hemihydrate gypsum on performance of cement mortar and its hydration mechanism [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 98-103. |
| [8] | GUO Jianye, WANG Dong, SU Lijun, LI Wenjing. Effect of aerogel doping on thermal insulation performance of glass fiber felt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 53-57. |
| [9] | HE Wenchao,XUE Jing,WANG Wei. Research on strength and creep characteristics of concrete containing fly ash microbead [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 124-128. |
| [10] | FU Rusong,LU Yuexian,AN Hongfang,KONG Dewen,FU Rubin. Study on preparation of cementitious materials from raw phosphogypsum cured by hemihydrate phosphogypsum and their properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(6): 109-114. |
| [11] | LIU Yingqiang,GUO Runhua,LIU Xijie. Influence of silica fume and metakaolin on properties of slag?fly ash microbead cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(6): 102-108. |
| [12] | ZHANG Farong,FAN Tiantian,GUO Yanyun,LI Lu,LIU Bingguang,LI Jiansheng. Research progress on self-cleaning film materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 74-80. |
| [13] | LI Zirui,XING Dongxian,TANG Jianwei,WANG Baoming,HUA Quanxian,LIU Li,LIU Yong. Study on preparation and heat storage performance of phosphogypsum-based composite phase change materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 34-39. |
| [14] | FU Dejin,GOU Bibo,LI Mingdong,WANG Haifeng,WANG Jiawei. Study on effect of reinforcement on properties of phosphogypsum non-burning building materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(2): 90-94. |
| [15] | PAN Zude,LIU Qi,CAO Yang,CHEN Qianlin,YANG Min,XIE Yan. Study on preparation and properties of phosphogypsum based mine filling materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(11): 90-95. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||