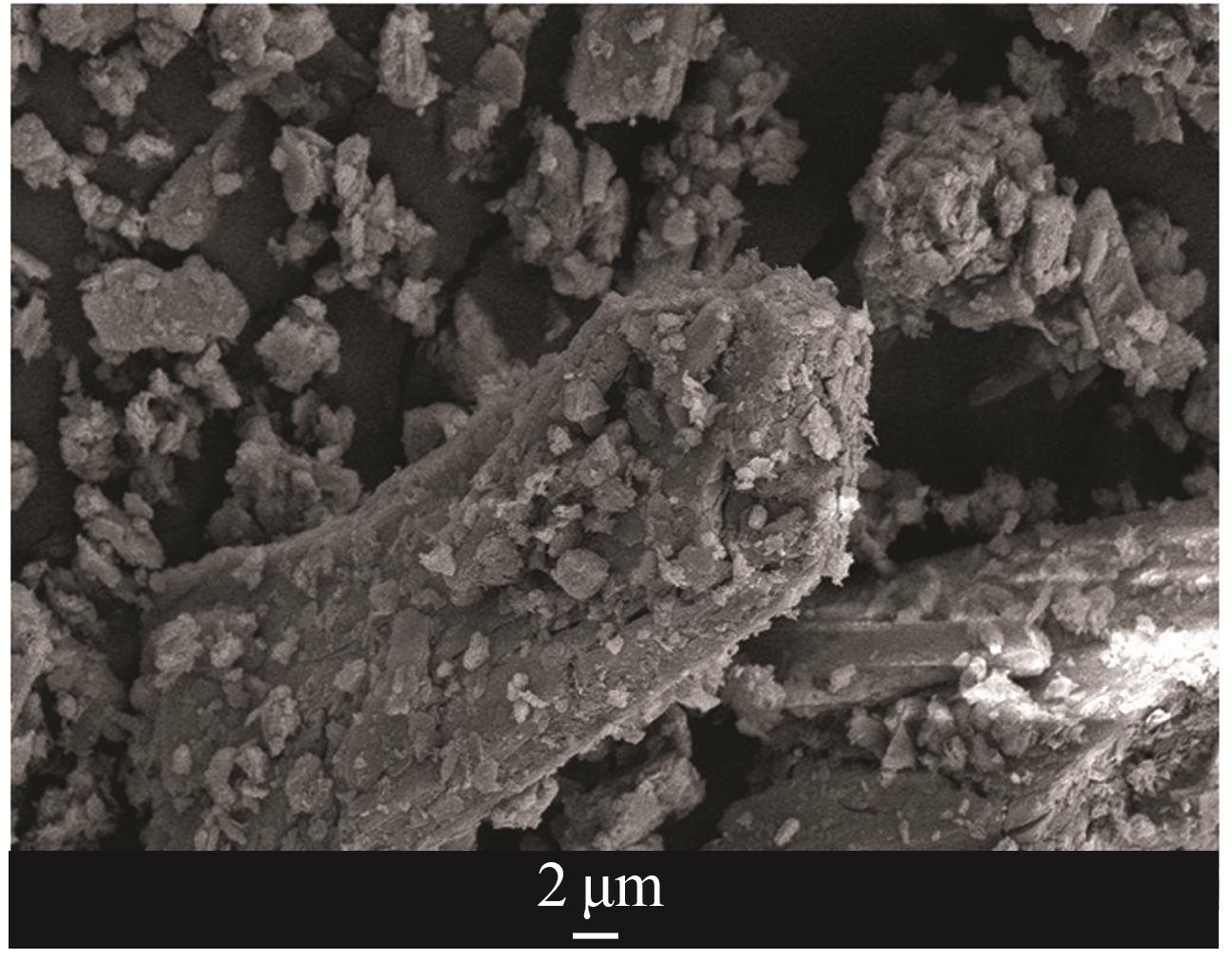
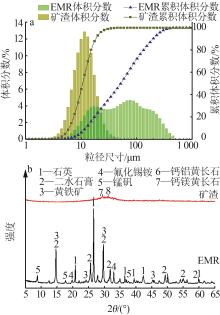
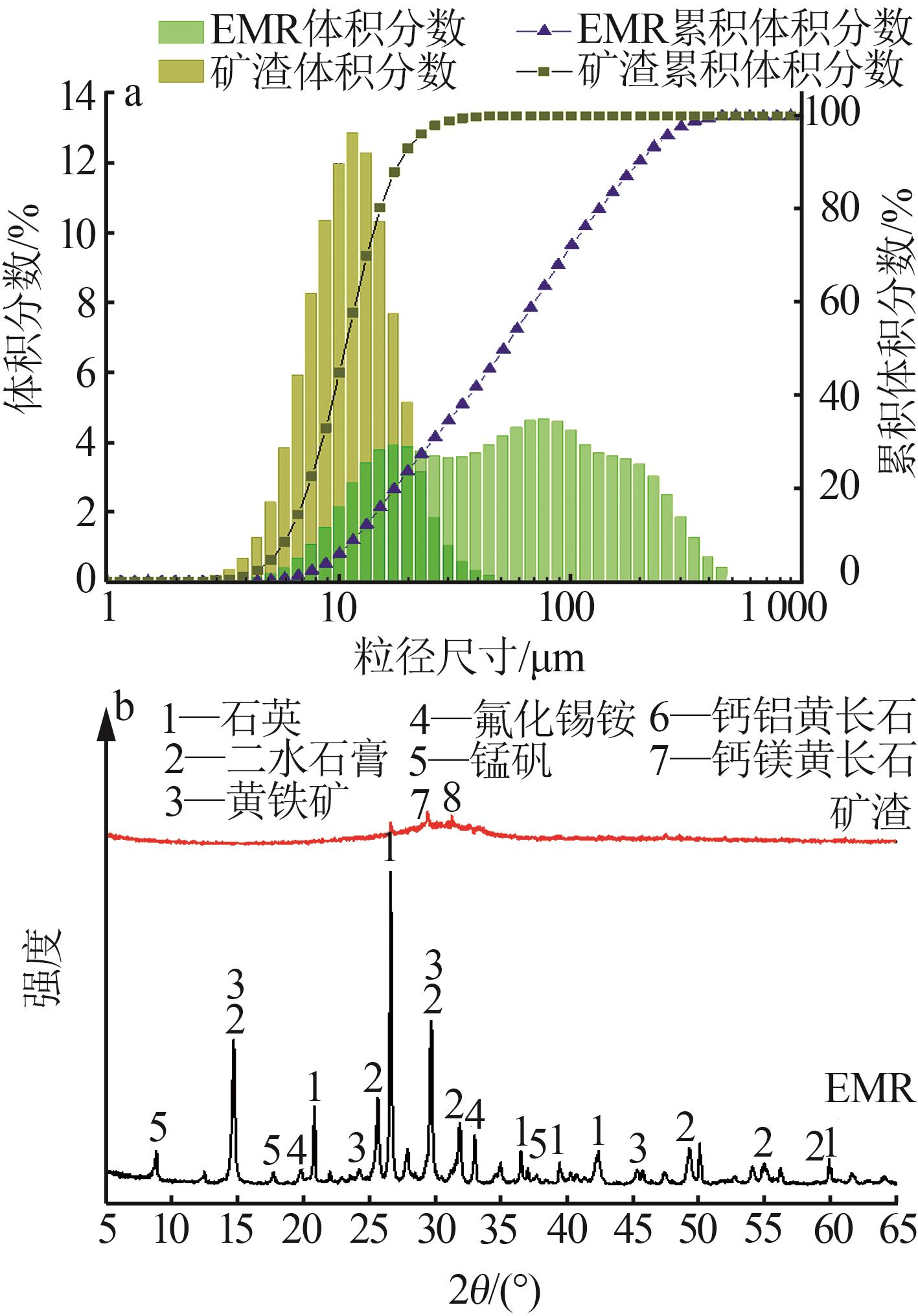
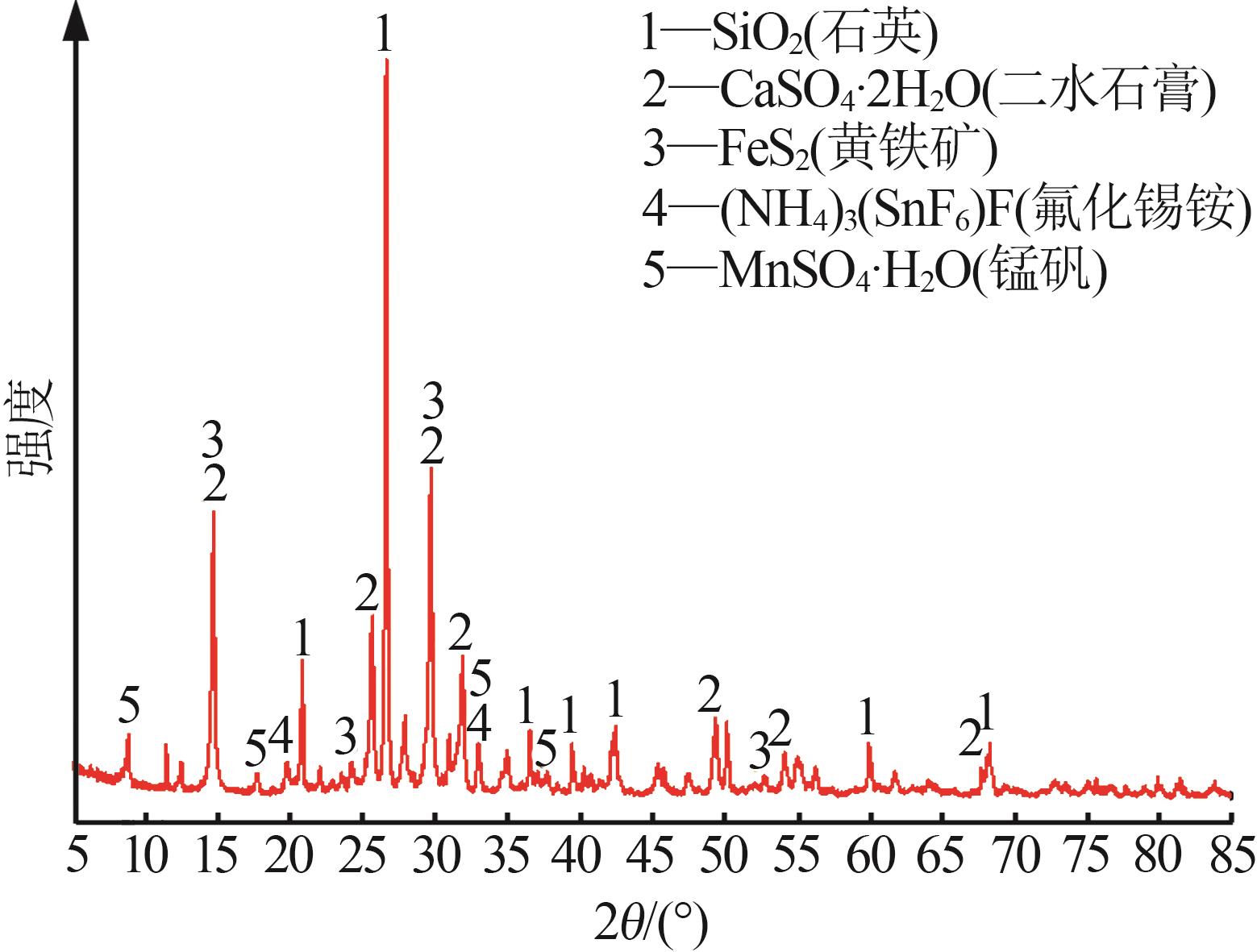
| 1 |
何德军,舒建成,陈梦君,等.电解锰渣建材资源化研究现状与展望[J].化工进展,2020,39(10):4227-4237.
|
|
HE Dejun, SHU Jiancheng, CHEN Mengjun,et al.Current status and future prospects of electrolytic manganese residue reused as building materials[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020,39(10):4227-4237.
|
| 2 |
梁宇廷,孟棒棒,林晔,等.多种固废协同处理电解锰渣固锰除氨的最优配比及效果分析[J].环境工程学报,2023,17(7):2342-2351.
|
|
LIANG Yuting, MENG Bangbang, LIN Ye,et al.Optimal ratio and effect analysis of solidified manganese and ammonia removal from electrolytic manganese residue treated with various solid wastes[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2023,17(7):2342-2351.
|
| 3 |
杨晓红,薛希仕,张露露,等.电解锰渣盐酸浸取钙的动力学研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(1):82-86.
|
|
YANG Xiaohong, XUE Xishi, ZHANG Lulu,et al.Kinetics study of calcium leaching from electrolytic manganese residue by hydrochloric acid[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(1):82-86.
|
| 4 |
董馨予,王海峰,贺跃,等.电解锰渣的浸出毒性分析及无害化处理[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(5):85-90.
|
|
DONG Xinyu, WANG Haifeng, HE Yue,et al.Exleaching toxicity analysis and harmless treatment of electrolytic manganese resid-ue[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(5):85-90.
|
| 5 |
吴霜,王家伟,刘利,等.电解锰渣综合利用评述[J].无机盐工业,2016,48(4):22-25.
|
|
WU Shuang, WANG Jiawei, LIU Li,et al.Review on comprehensive utilization of electrolytic manganese slag[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2016,48(4):22-25.
|
| 6 |
黄真江,赵瑜,侯俊宇,等.电解锰渣对混凝土抗压强度及孔结构的影响[J].混凝土与水泥制品,2023(10):100-102.
|
|
HUANG Zhenjiang, ZHAO Yu, HOU Junyu,et al.Effect of electrolytic manganese slag on compressive strength and pore structure of concrete[J].China Concrete and Cement Products,2023(10):100-102.
|
| 7 |
韩林沛.电解锰渣基缓释肥的制备及其性能研究[D].绵阳:西南科技大学,2023.
|
|
HAN Linpei.Preparation and properties of electrolytic manganese slag-based slow-release fertilizer[D].Mianyang:Southwest University of Science and Technology,2023.
|
| 8 |
HE Dejun, SHU Jiancheng, WANG Rong,et al.A critical review on approaches for electrolytic manganese residue treatment and disposal technology:Reduction,pretreatment,and reuse[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,418:126235.
|
| 9 |
母维宏,和森,周新涛,等.铜渣/电解锰渣基磷酸盐胶凝材料的制备及其形成机理探讨[J].化学工程,2020,48(10):23-28,51.
|
|
MU Weihong, HE Sen, ZHOU Xintao,et al.Preparation and mechanism of copper slag/electrolytic manganese residue-based phosphate cementitious materials[J].Chemical Engineering(China),2020,48(10):23-28,51.
|
| 10 |
张歆,刘方,朱健,等.基于电解锰渣-磷石膏复合胶凝材料的制备与表征[J].硅酸盐通报,2021,40(5):1610-1619.
|
|
ZHANG Xin, LIU Fang, ZHU Jian,et al.Preparation and characterization of composite cementitious material based on electrolytic manganese residue-phosphogypsum[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(5):1610-1619.
|
| 11 |
王亚光.粉煤灰/电解锰渣地质聚合物材料的制备及其性能研究[D].银川:北方民族大学,2018.
|
|
WANG Yaguang.Preparation and properties of fly ash/electrolytic manganese slag geopolymer material[D].Yinchuan:Beifang University of Nationalities,2018.
|
| 12 |
TANG Liang, HE Zhaoyi, PEI Shanshan,et al.Hydration characteristics and pollutant solidification mechanism of full solid waste electrolytic manganese residue super sulfate cement[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2024,84:108563.
|
| 13 |
周宏研,陈平,赵艳荣,等.电解锰渣对热焖钢渣活性的硫酸盐激发[J].无机盐工业,2019,51(5):66-69.
|
|
ZHOU Hongyan, CHEN Ping, ZHAO Yanrong,et al.Sulfate activation of electrolytic manganese residue on heat-stewed steel slag activity[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2019,51(5):66- 69.
|
| 14 |
王智,郭清春,蒋小花,等.电解锰渣对粉煤灰火山灰活性的硫酸盐激发[J].非金属矿,2011,34(4):5-8.
|
|
WANG Zhi, GUO Qingchun, JIANG Xiaohua,et al.Sulphate activating of electrolytic manganese residue to fly ash[J].Non-Metallic Mines,2011,34(4):5-8.
|
| 15 |
XU Yingtang, LIU Xiaoming, ZHANG Yuliang,et al.Investigation on sulfate activation of electrolytic manganese residue on early activity of blast furnace slag in cement-based cementitious material[J].Construction and Building Materials,2019,229:116831.
|
| 16 |
RAHMAN M M, BASSUONI M T.Thaumasite sulfate attack on concrete:Mechanisms,influential factors and mitigation[J].Construction and Building Materials,2014,73:652-662.
|
 ), TANG Liang2, HE Zhaoyi2, WANG Jian1, PEI Shanshan3, XIA Lei4
), TANG Liang2, HE Zhaoyi2, WANG Jian1, PEI Shanshan3, XIA Lei4