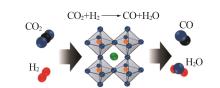
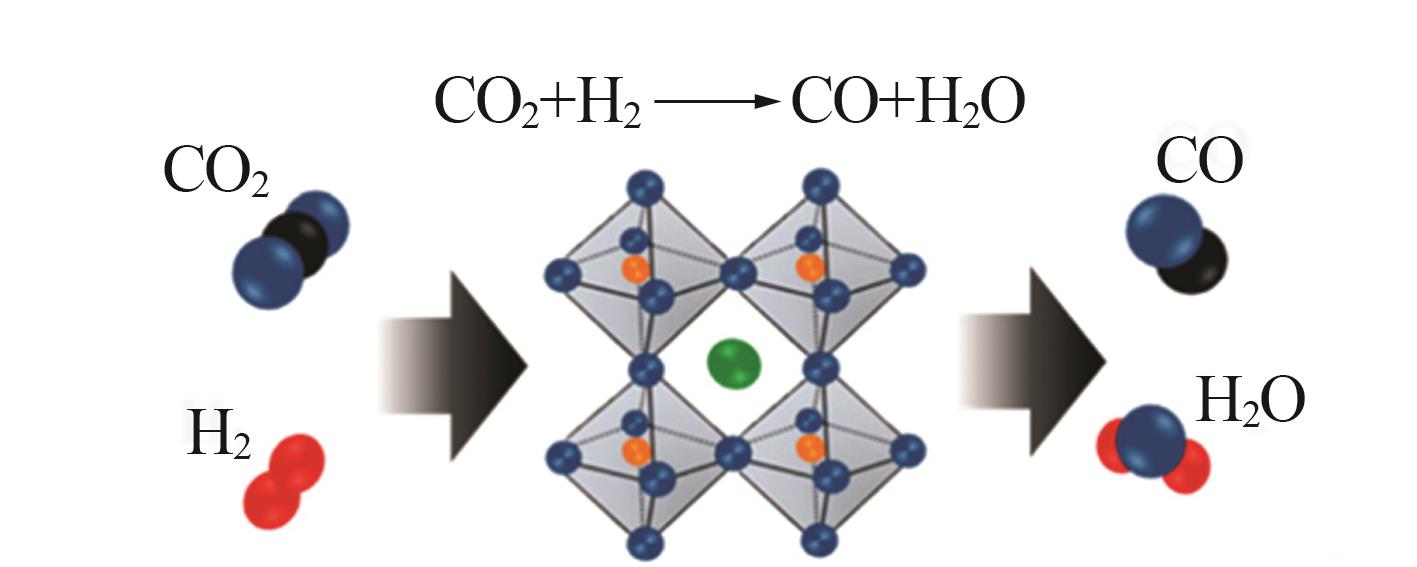
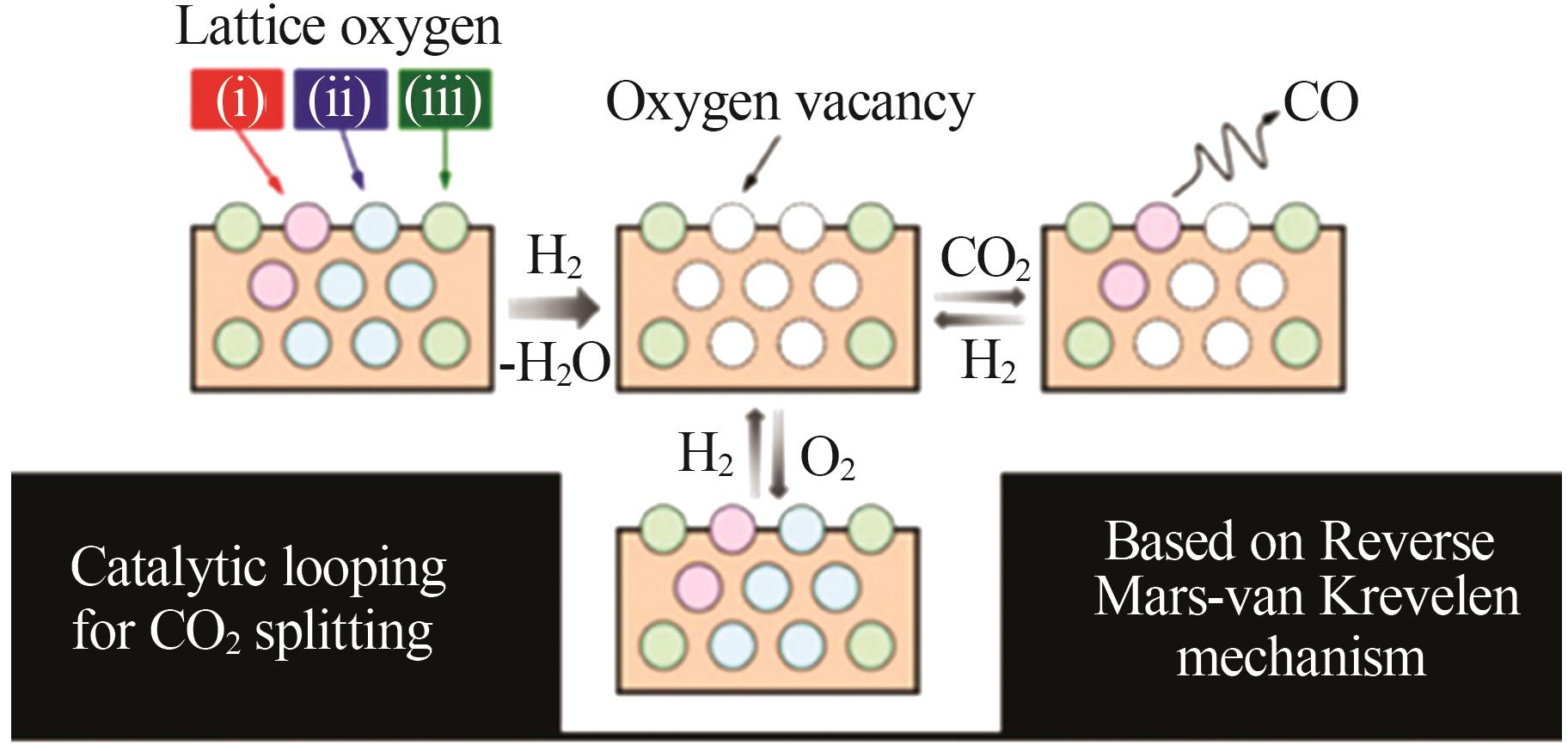
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 105-115.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0445
• Reviews and Special Topics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of CO2 conversion via Reverse Water-Gas Shift reaction
HOU Zhanggui( ), WU Chongchong(
), WU Chongchong( ), ZHANG Siran
), ZHANG Siran
- CNOOC Institute of Chemicals & Advanced Materials,Beijing 102209,China
-
Received:2024-08-09Online:2024-11-10Published:2024-11-27 -
Contact:WU Chongchong E-mail:houzhg2@cnooc.com.cn;wuchch6@cnooc.com.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HOU Zhanggui, WU Chongchong, ZHANG Siran. Research progress of CO2 conversion via Reverse Water-Gas Shift reaction[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 105-115.
share this article
Table 1
Catalytic performance of supported catalysts in RWGS reaction"
| 催化剂 | 反应 温度/℃ | n(CO2)∶ n(H2) | 空速/ [mL·(g·h)-1] | CO2转化率/% | CO选择性/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt/CeO2[ | 450 | 1∶3 | 43 200 | 35 | 98 |
| Pt/TiO2[ | 600 | 1∶3 | 12 000 | 56 | 100 |
| PtW/Al2O3[ | 450 | 1∶3 | 34 200 | 42 | 78 |
| Cu/CeO2[ | 500 | 1∶3 | 300 000 | 41 | 100 |
| NiCo/SiO2[ | 500 | 1∶4 | 15 000 | 50 | 47 |
| Ni12P5-SiO2[ | 600 | 1∶4 | 6 000 | 44.8 | 91.8 |
| CuIn/ZrO2[ | 600 | 1∶4 | 3 000 | 48 | 100 |
| NiMo/Al2O3[ | 600 | 1∶1 | 30 000 | 34 | |
| Ni/CeO2[ | 650 | 1∶1 | 6 000 | 38 | 94 |
| RuFe/CeO2[ | 800 | 1∶1 | 6 000 | 47.5 | 100 |
| PtCs/TiO2[ | 500 | 1∶4 | 30 000 | 44 | 98 |
| Ni/NiCeZr[ | 550 | 1∶3 | 50 000 | 48 | 87.5 |
Table 2
Catalytic performance of oxide catalysts in RWGS reaction"
| 催化剂 | 反应温度/℃ | n(CO2)∶n(H2) | 空速/[mL·(g·h)-1] | CO2转 化率/% | CO选择性/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RuNi/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2[ | 700 | 1∶4 | 24 000 | 72 | 91 |
| In2O3-CeO2[ | 500 | 1∶1 | 24 000 | 19.98 | 100 |
| Ni/Ce-Zr-O[ | 750 | 1∶1 | 30 000 | 49.66 | 99.65 |
| Ga2O3-CeO2[ | 500 | 1∶1 | 4 800 | 15 | 100 |
| BaZr0.8Y0.2O3[ | 600 | 1∶1 | 2 400 | 26.7 | 93 |
| BaZr0.8Y0.16Zn0.04O3[ | 600 | 1∶1 | 2 400 | 37.5 | 97 |
| BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.16Zn0.04O3[ | 600 | 1∶1 | 2 400 | 10.8 | 74 |
| CuAl2O4-α[ | 400 | 1∶3 | 9 960 | 37 | 100 |
| Co3-x Al x O4[ | 500 | 1∶5 | 55 000 | 53 | 98 |
| K3CuAlFe[ | 550 | 1∶1 | 1 830 | 35 | |
| CeO2-CaO[ | 650 | 20 000 | 49 | 100 |
Table 3
Catalytic performance of carbide catalysts in RWGS reaction"
| 催化剂 | 反应 温度/℃ | n(CO2)∶ n(H2) | 空速/[mL·(g·h)-1] | CO2转 化率/% | CO选 择性/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu/β-Mo2C[ | 500 | 1∶2 | 300 000 | 28.9 | 99.0 |
| Cu/β-Mo2C[ | 600 | 1∶2 | 300 000 | 40.0 | 99.2 |
| α-Mo2C[ | 400 | 1∶1 | 2 000 | 15.9 | 99.3 |
| 介孔MoC[ | 400 | 1∶4 | 12 000 | 16 | 100 |
| Mo2C/Al2O3[ | 400 | 1∶3 | 3 000 | 24 | 94.5 |
| Mo2C/SiO2[ | 400 | 1∶3 | 3 000 | 27.5 | 98.5 |
| Mo2C/TiO2[ | 400 | 1∶3 | 3 000 | 8.5 | 97 |
| Mo x C-B[ | 350 | 1∶3 | 3 000 | 18 | ~98 |
| α-MoC1-x[ | 600 | 1∶4 | 36 000 | 60 | 99 |
| β-Mo2C[ | 600 | 1∶4 | 36 000 | 60 | 98 |
| 1 | 王挺,章文文,毛庆,等.二氧化碳电还原制乙醇催化体系与材料研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2024,56(7):1-10,68. |
| WANG Ting, ZHANG Wenwen, MAO Qing,et al.Research progress of catalytic system and materials for electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to ethanol[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2024,56(7):1-10,68. | |
| 2 | WU Qing, WU Chongchong.Mechanism insights on single-atom catalysts for CO2 conversion[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2023,11(10):4876-4906. |
| 3 | GONZÁLEZ-CASTAÑO M, DORNEANU B, ARELLANO-GARCÍA H.The reverse water gas shift reaction:A process systems engineering perspective[J].Reaction Chemistry & Engineering,2021,6(6):954-976. |
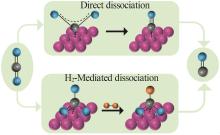
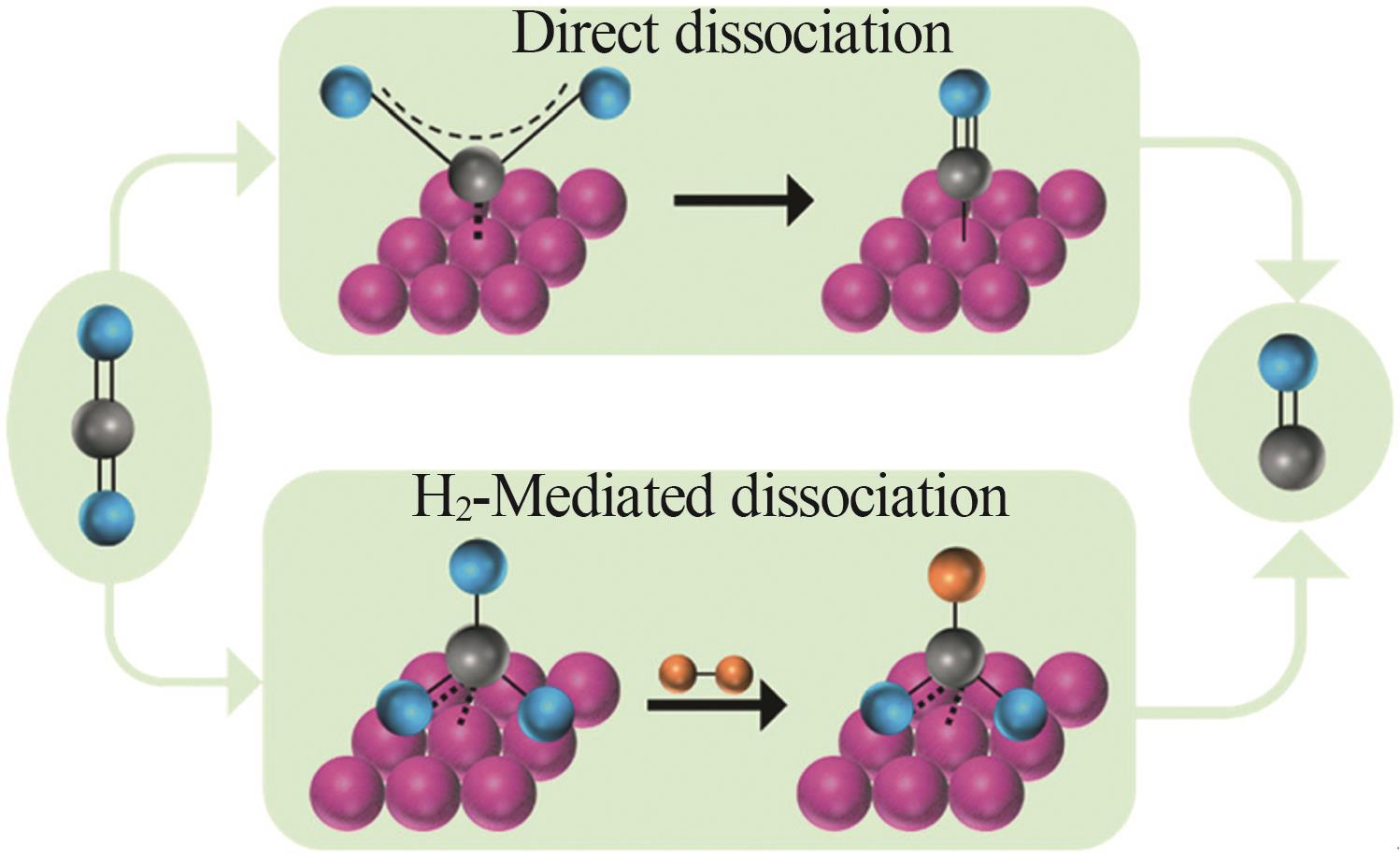
| 4 | WANG Huilin, BOOTHARAJU M S, KIM J H,et al.Synergistic interactions of neighboring platinum and iron atoms enhance reverse water-gas shift reaction performance[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2023,145(4):2264-2270. |
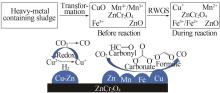
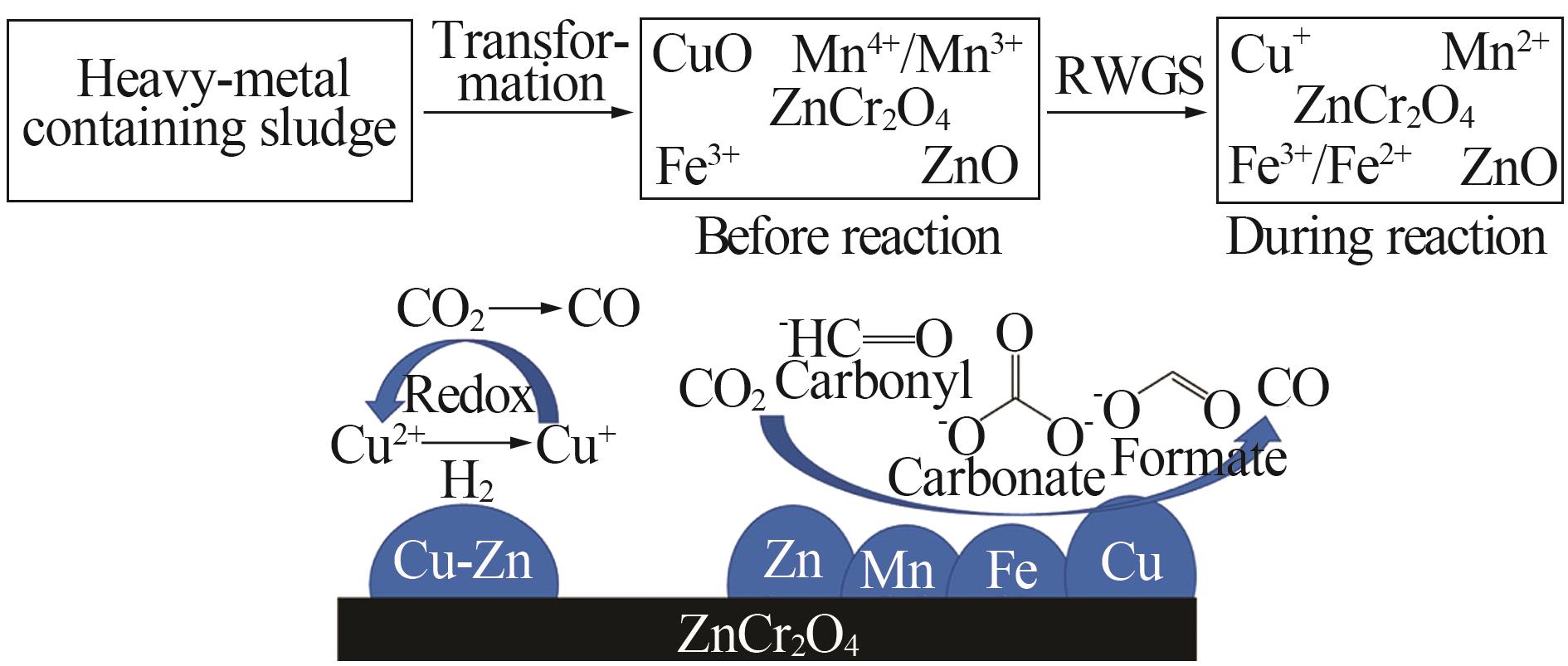
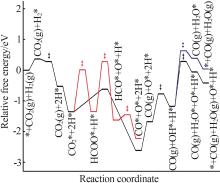
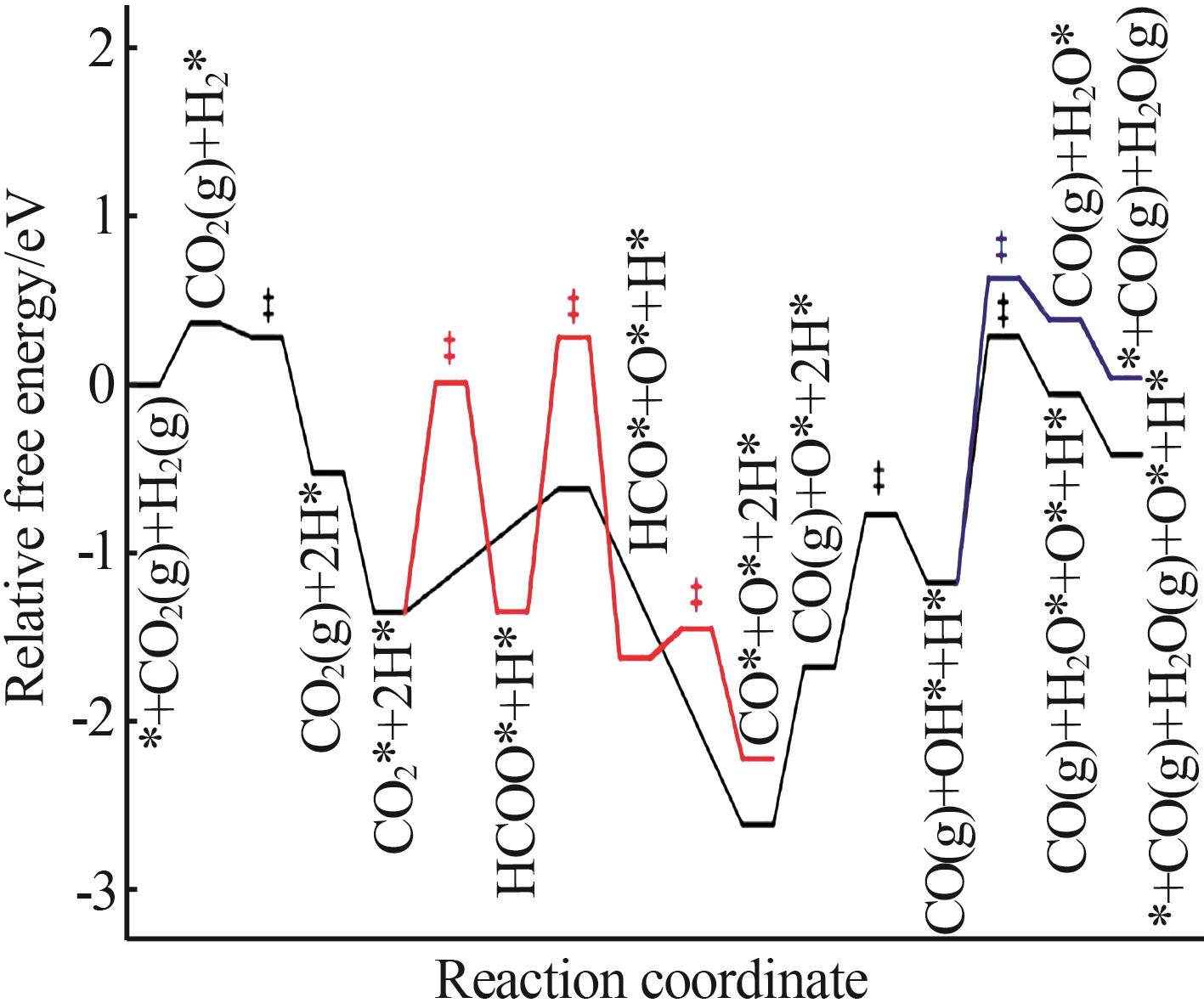
| 5 | HOU Hao, HOU Luman, YU Qiang,et al.Electroplating sludge-derived multiple-metal-doped spinel with superior CO selectivity in reverse water-gas-shift reaction[J].ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2022,10(6):2214-2223. |
| 6 | KHOSHOOEI M A, WANG Xijun, VITALE G,et al.An active,stable cubic molybdenum carbide catalyst for the high-temperature reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].Science,2024,384(6695):540-546. |
| 7 | 王晓月,张伟敏,姚正阳,等.逆水煤气变换反应研究进展[J].化工进展,2023,42(3):1583-1594. |
| WANG Xiaoyue, ZHANG Weimin, YAO Zhengyang,et al.Research progress of reverse water gas shift reaction[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2023,42(3):1583-1594. | |
| 8 | PANAGIOTOPOULOU P.Hydrogenation of CO2 over supported noble metal catalysts[J].Applied Catalysis A:General,2017,542:63-70. |
| 9 | TRIVIÑO M L T, ARRIOLA N C, KANG Y S,et al.Transforming CO2 to valuable feedstocks:Emerging catalytic and technological advances for the reverse water gas shift reaction[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2024,487:150369. |
| 10 | WANG Luhui, ZHANG Shaoxing, LIU Yuan.Reverse water gas shift reaction over co-precipitated Ni-CeO2 catalysts[J].Journal of Rare Earths,2008,26(1):66-70. |
| 11 | CHEN Xiaodong, CHEN Ya, SONG Chunyu,et al.Recent advances in supported metal catalysts and oxide catalysts for the reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].Frontiers in Chemistry,2020,8:709. |
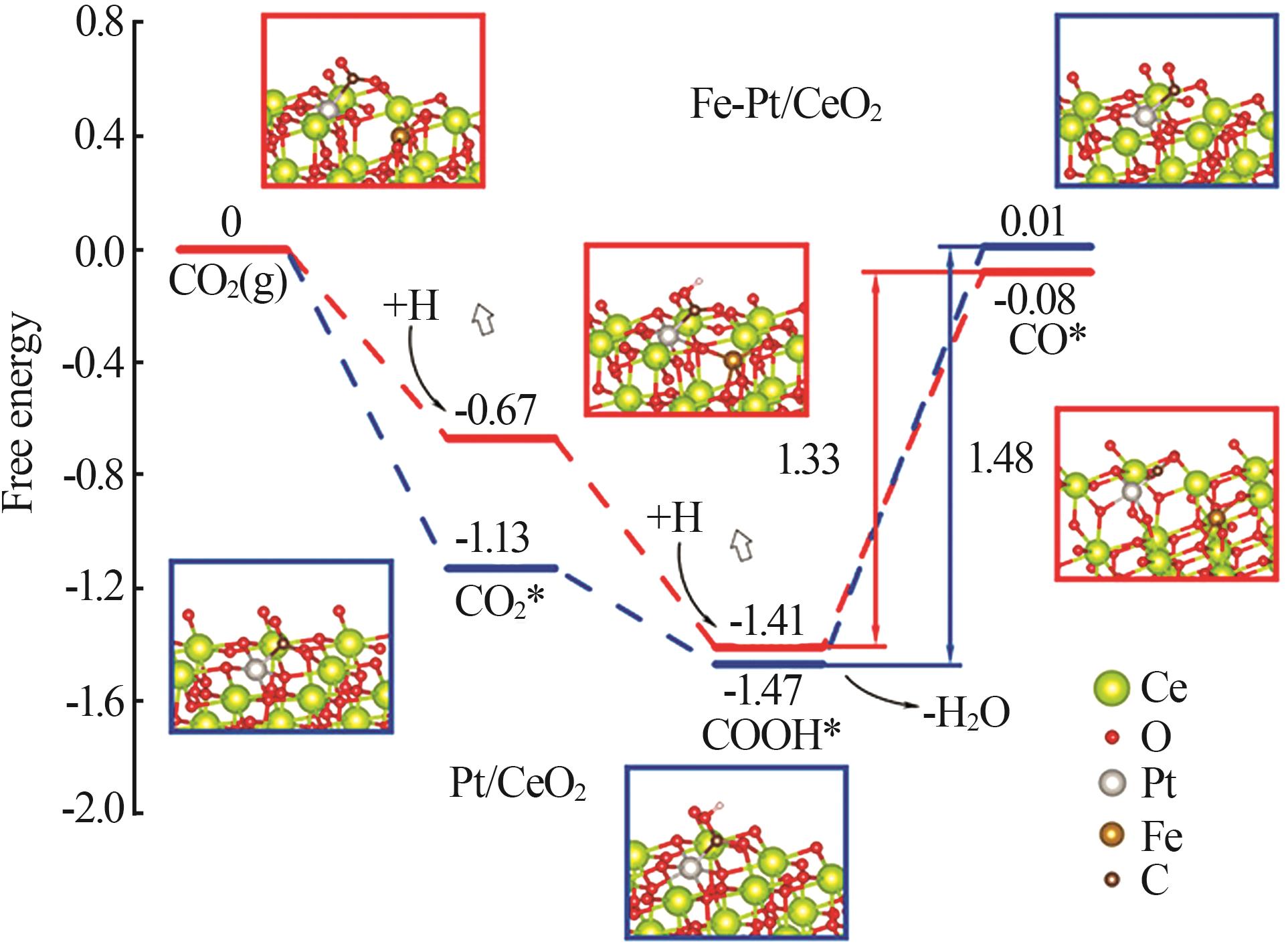
| 12 | ZHAO Zhiying, WANG Mingzhi, MA Peijie,et al.Atomically dispersed Pt/CeO2 catalyst with superior CO selectivity in reverse water gas shift reaction[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2021,291:120101. |
| 13 | KIM S S, PARK K H, HONG S C.A study of the selectivity of the reverse water-gas-shift reaction over Pt/TiO2 catalysts[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2013,108:47-54. |
| 14 | KOBAYASHI D, KOBAYASHI H, KUSADA K,et al.Boosting reverse water-gas shift reaction activity of Pt nanoparticles through light doping of W[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2021,9(28):15613-15617. |
| 15 | ZHANG Yudong, LIANG Long, CHEN Ziyang,et al.Highly efficient Cu/CeO2-hollow nanospheres catalyst for the reverse water-gas shift reaction:Investigation on the role of oxygen vacancies through in situ UV-Raman and DRIFTS[J].Applied Surface Science,2020,516:146035. |
| 16 | PRICE C A H, PASTOR-PEREZ L, REINA T R,et al.Yolk-Shell structured NiCo@SiO2 nanoreactor for CO2 upgrading via reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].Catalysis Today,2022,383:358-367. |
| 17 | HAMEED G, GOKSU A, MERKOURI L P,et al.Experimental optimization of Ni/P atomic ratio for nickel phosphide catalysts in reverse water-gas shift[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2023,77:102606. |
| 18 | LI Mo, PHAM T H MY,KO Y,et al.Support-dependent Cu-In bimetallic catalysts for tailoring the activity of reverse water gas shift reaction[J].ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2022,10(4):1524-1535. |
| 19 | KHARAJI A G, SHARIATI A, OSTADI M.Development of Ni-Mo/Al2O3 catalyst for reverse water gas shift(RWGS) reaction[J].Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2014,14(9):6841-6847. |
| 20 | WANG Luhui, LIU Hui, LIU Yuan,et al.Influence of preparation method on performance of Ni-CeO2 catalysts for reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].Journal of Rare Earths,2013,31(6):559-564. |
| 21 | PANARITIS C, EDAKE M, COUILLARD M,et al.Insight towards the role of ceria-based supports for reverse water gas shift reaction over RuFe nanoparticles[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2018,26:350-358. |
| 22 | TORRES-SEMPERE G, GONZÁLEZ-ARIAS J, PENKOVA A,et al.CO2 conversion via low-temperature RWGS enabled by multicomponent catalysts:Could transition metals outperform Pt?[J].Topics in Catalysis,2024.Doi:10.1007/s11244-024-01935-7. |
| 23 | ZONETTI P C, LETICHEVSKY S, GASPAR A B,et al.The Ni x Ce0.75Zr0.25- x O2 solid solution and the RWGS[J].Applied Catalysis A:General,2014,475:48-54. |
| 24 | SHEN Haidong, DONG Yujuan, YANG Shaowei,et al.Identifying the roles of Ce3+-OH and Ce-H in the reverse water-gas shift reaction over highly active Ni-doped CeO2 catalyst[J].Nano Research,2022,15(7):5831-5841. |
| 25 | GU Mengwei, DAI Sheng, QIU Runfa,et al.Structure-activity relationships of copper- and potassium-modified iron oxide catalysts during reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].ACS Catalysis,2021,11(20):12609-12619. |
| 26 | DAI Hui, ZHANG Anhang, XIONG Siqi,et al.The catalytic performance of Ga2O3-CeO2 composite oxides over reverse water gas shift reaction[J].ChemCatChem,2022,14(6):e202200049. |
| 27 | KANG Hefei, LIU Yajie, LU Ye,et al.Exploring the sustained release catalysis of CuAl2O4 spinel for highly effective CO2 conversion to CO[J].Journal of Catalysis,2024,432:115427. |
| 28 | KIM D H, PARK J L, PARK E J,et al.Dopant effect of barium zirconate-based perovskite-type catalysts for the intermediate-temperature reverse water gas shift reaction[J].ACS Catalysis,2014,4(9):3117-3122. |
| 29 | MATSUO H, KOBAYASHI M, NANIWA S,et al.Hydrogenation of CO2 over Mn-substituted SrTiO3 based on the reverse mars-van krevelen mechanism[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2023,127(19):8946-8952. |
| 30 | LE SACHÉ E, PASTOR-PÉREZ L, HAYCOCK B J,et al.Switchable catalysts for chemical CO2 recycling:A step forward in the methanation and reverse water-gas shift reactions[J].ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2020,8(11):4614-4622. |
| 31 | WANG Wei, ZHANG Yao, WANG Zongyuan,et al.Reverse water gas shift over In2O3-CeO2 catalysts[J].Catalysis Today,2016,259:402-408. |
| 32 | SUN Fengman, YAN Changfeng, WANG Zhida,et al.Ni/Ce-Zr-O catalyst for high CO2 conversion during reverse water gas shift reaction(RWGS)[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2015,40(46):15985-15993. |
| 33 | SPENNATI E, GARBARINO G, RIANI P,et al.Alumina-supported cobalt catalysts in the hydrogenation of CO2 at atmospheric pressure[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(64):25006-25015. |
| 34 | SUN Shuzhuang, ZHANG Chen, CHEN Sining,et al.Integrated CO2 capture and reverse water-gas shift reaction over CeO2-CaO dual functional materials[J].Royal Society Open Science,2023,10(4):230067. |
| 35 | ORTEGA-TRIGUEROS A, CACCIA M, NARCISO J.Tuning activity and selectivity in catalyzed reactions of environmental and industrial importance with a high-surface area,mesoporous Mo2C catalyst[J].Chemistry of Materials,2022,34(14):6232-6239. |
| 36 | ZHANG Xiao, ZHU Xiaobing, LIN Lili,et al.Highly dispersed copper over β-Mo2C as an efficient and stable catalyst for the reverse water gas shift(RWGS) reaction[J].ACS Catalysis,2017,7(1):912-918. |
| 37 | LIU Xianyun, KUNKEL C,RAMÍREZ DE LA PISCINA P,et al.Effective and highly selective CO generation from CO2 using a polycrystalline α-Mo2C catalyst[J].ACS Catalysis,2017,7(7):4323-4335. |
| 38 | PAJARES A, LIU Xianyun, BUSACKER J R,et al.Supported nanostructured Mo x C materials for the catalytic reduction of CO2 through the reverse water gas shift reaction[J].Nanomaterials,2022,12(18):3165. |
| 39 | LIU Xianyun, PAJARES A, CALINAO MATIENZO D D,et al.Preparation and characterization of bulk Mo x C catalysts and their use in the reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].Catalysis Today,2020,356:384-389. |
| 40 | GAO Jiajian, WU Yue, JIA Chunmiao,et al.Controllable synthesis of α-MoC1- x and β-Mo2C nanowires for highly selective CO2 reduction to CO[J].Catalysis Communications,2016,84:147- 150. |
| 41 | ZHANG Jiajun, FENG Kai, LI Zhengwen,et al.Defect-driven efficient selective CO2 hydrogenation with Mo-based clusters[J].JACS Au,2023,3(10):2736-2748. |
| 42 | KUHN A N, PARK R C, YU Siying,et al.Valorization of carbon dioxide into C1 product via reverse water gas shift reaction using oxide-supported molybdenum carbides[J].Carbon Future,2024,1(2):9200011. |
| 43 | 彭晓伟,王银斌,臧甲忠,等.金属改性甲醇芳构化催化剂的制备及性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(9):104-108. |
| PENG Xiaowei, WANG Yinbin, ZANG Jiazhong,et al.Research on preparation of metal modified catalysts and catalytic performances of methanol aromatization[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(9):104-108. | |
| 44 | 刘永存,肖寒,王帅,等.Ni-Mo-P/Beta-ZSM-5催化剂对四氢萘加氢裂化性能的研究[J].无机盐工业,2018,50(6):81-85. |
| LIU Yongcun, XIAO Han, WANG Shuai,et al.Study on hydrocracking performance of tetralin over Ni-Mo-P/Beta-ZSM-5 catalyst[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2018,50(6):81-85. | |
| 45 | 司智伟,丹少鹏,陈树伟,等.Co-Al2O3高效催化CO2氧化乙苯脱氢制苯乙烯[J].燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(11):1683-1690. |
| SI Zhiwei, DAN Shaopeng, CHEN Shuwei,et al.Highly efficient Co-Al2O3 catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene with CO2 [J].Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2023,51(11):1683-1690. | |
| 46 | WU Jiayi, ZHENG Yuhang, FU Jiali,et al.Synthetic Ni-CaO-CeO2 dual function materials for integrated CO2 capture and conversion via reverse water-gas shift reaction[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2023,317:123916. |
| [1] | LI Chao, WANG Liping, GAO Guimei, ZHANG Yunfeng, HONG Yu, LIU Darui, XU Lijun, CUI Yongjie. Study on reaction mechanism of acid leaching lithium from circulating fluidized bed fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 101-107. |
| [2] | YAN Xin, LIU Hailu, LIU Baolin, LIU Yi, LIU Yanyang. Research on key technologies and mechanisms of green nano calcium carbonate production [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 71-76. |
| [3] | CHEN Xue, OUYANG Quansheng, SHAO Jiaojing. Recent research progress of lithium-sulfur batteries based on solid-solid reaction mechanism [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 12-23. |
| [4] | WANG Chao, SONG Guoliang, XIAO Han. Industrial application of THFS-2 sulfurized reforming prehydrogenation catalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 94-100. |
| [5] | ZHAN Sijin, LIU Shike, LIU Fei, YAO Mengqin, CAO Jianxin. Study on preparation and catalytic performance of ZnO-CeO2 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 137-143. |
| [6] | REN Qixia, YANG Kun, LIU Fei, YAO Mengqin, CAO Jianxin. Effect of promoter on physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of ZnO/ZrO2 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 144-154. |
| [7] | YANG Kun, REN Qixia, DONG Yonggang, LIU Fei, YAO Mengqin, CAO Jianxin. Effect of calcination temperature on catalytic performance of ZnGaZrO x /SAPO-34 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 136-145. |
| [8] | LI Yang, LOU Feijian, SUI Xin, LI Keyan, LIU Fei, GUO Xinwen. Preparation of amine-functionalized fumed SiO2 materials and their performance for CO2 adsorption [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 38-43. |
| [9] | FENG Qing, WANG Yansu, ZHOU Wei, LIU Yang, SUN Yanmin, NAN Jun. Research progress on catalysts for relay-catalysis of CO2 to prepare high value-added chemicals [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 81-94. |
| [10] | JIN Shengshi, LIU Kaijie, LIU Qiuwen, ZHANG Yibo, YANG Xiangguang. Study on catalytic performance of phosphoric acid modified CeO2 nanorod supported Pt catalyst for propane combustion [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(1): 141-148. |
| [11] | ZHANG Conghua, YAN Wenbin, XIAO Jiajun, ZHAO Ke, PENG Shangquan, WEI Yuhong. Reductive leaching technology of manganese anode slag using tartaric acid as reducing agent optimized by RSM [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 106-113. |
| [12] | CHANG Chengbing, LIU Shengyu, ZHANG Lei, YANG Zhichao, GUO Jianying, LI Bao. Experimental study on carbon dioxide sequestration by wet carbonation of calcium silicate minerals [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 57-65. |
| [13] | ZHAO Yan, HAO Xuewei, SHI Hainan, LI Jiahui, LI Keyan, GUO Xinwen. Study on photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of Cu-doped TiO2/PCN heterojunction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 21-27. |
| [14] | SONG Zhijia, WANG Suisui, KUANG Qin. Hollow Cu-doped TiO2 for enhancing photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 45-50. |
| [15] | CHEN Junxue, MO Jianxin, ZHOU Zhiyu, LI Zhonglin, WANG Ding, LI Yuping, HU Yongjun, JIANG Xuexian, LI Yibing. Study on synthesis of NaFe x Cr y (SO4)2(OH)6 and their electrochemical properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 71-76. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||