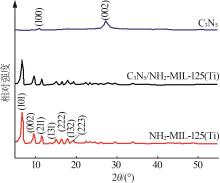
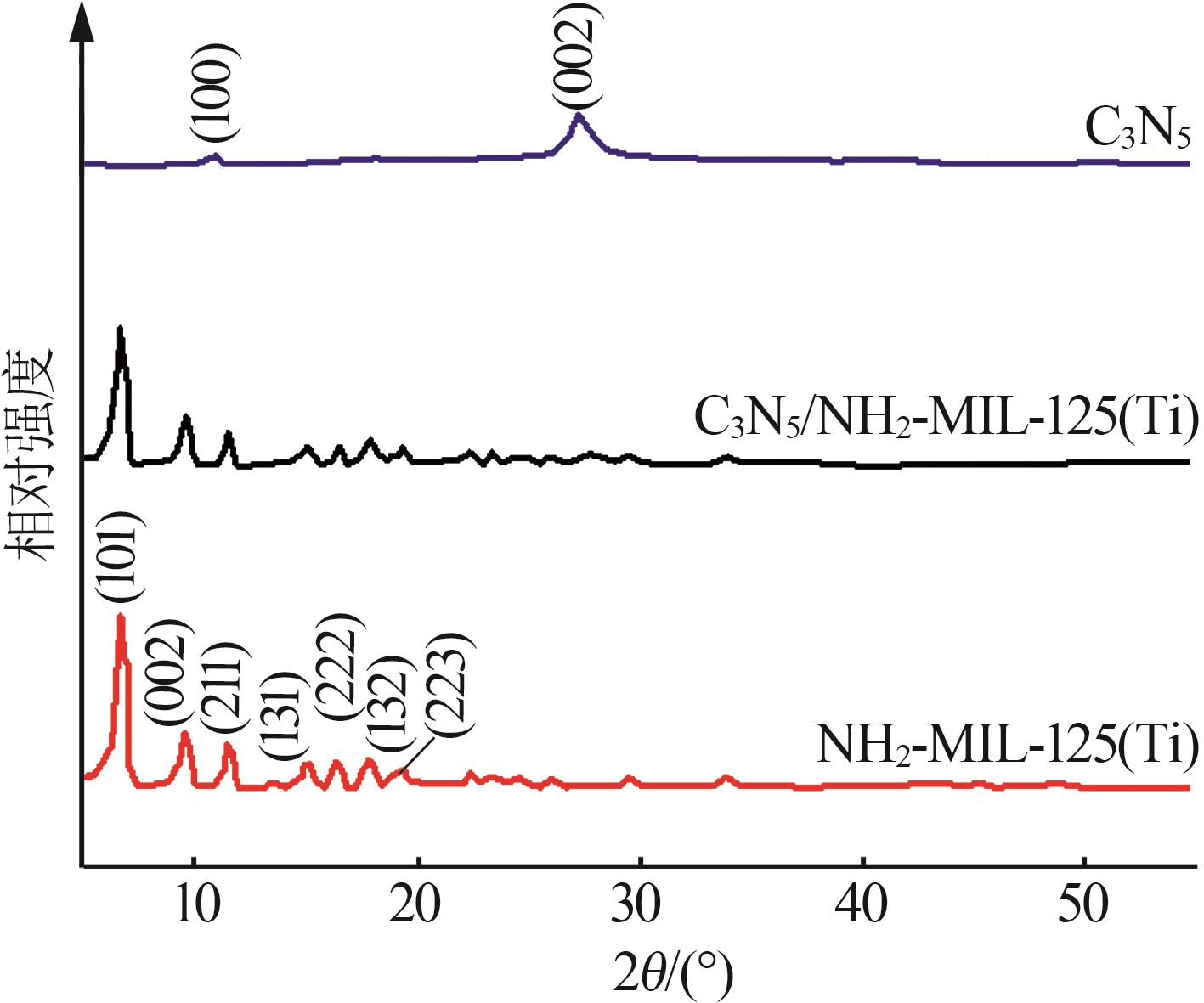
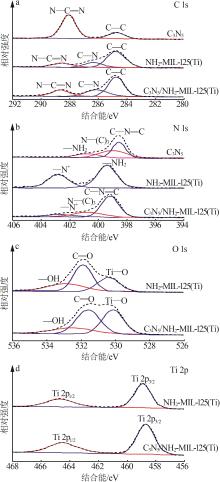
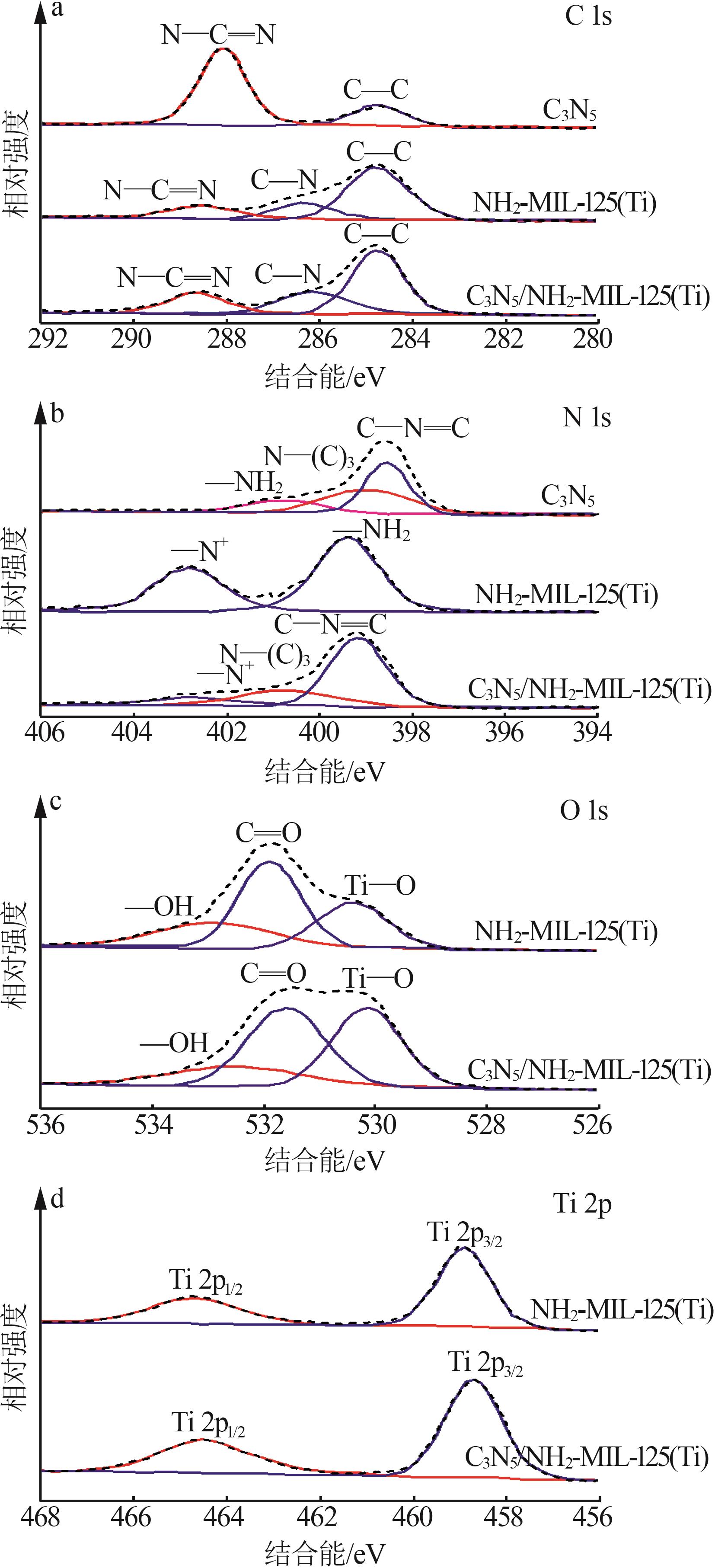
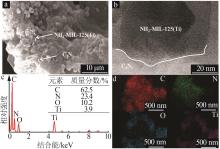
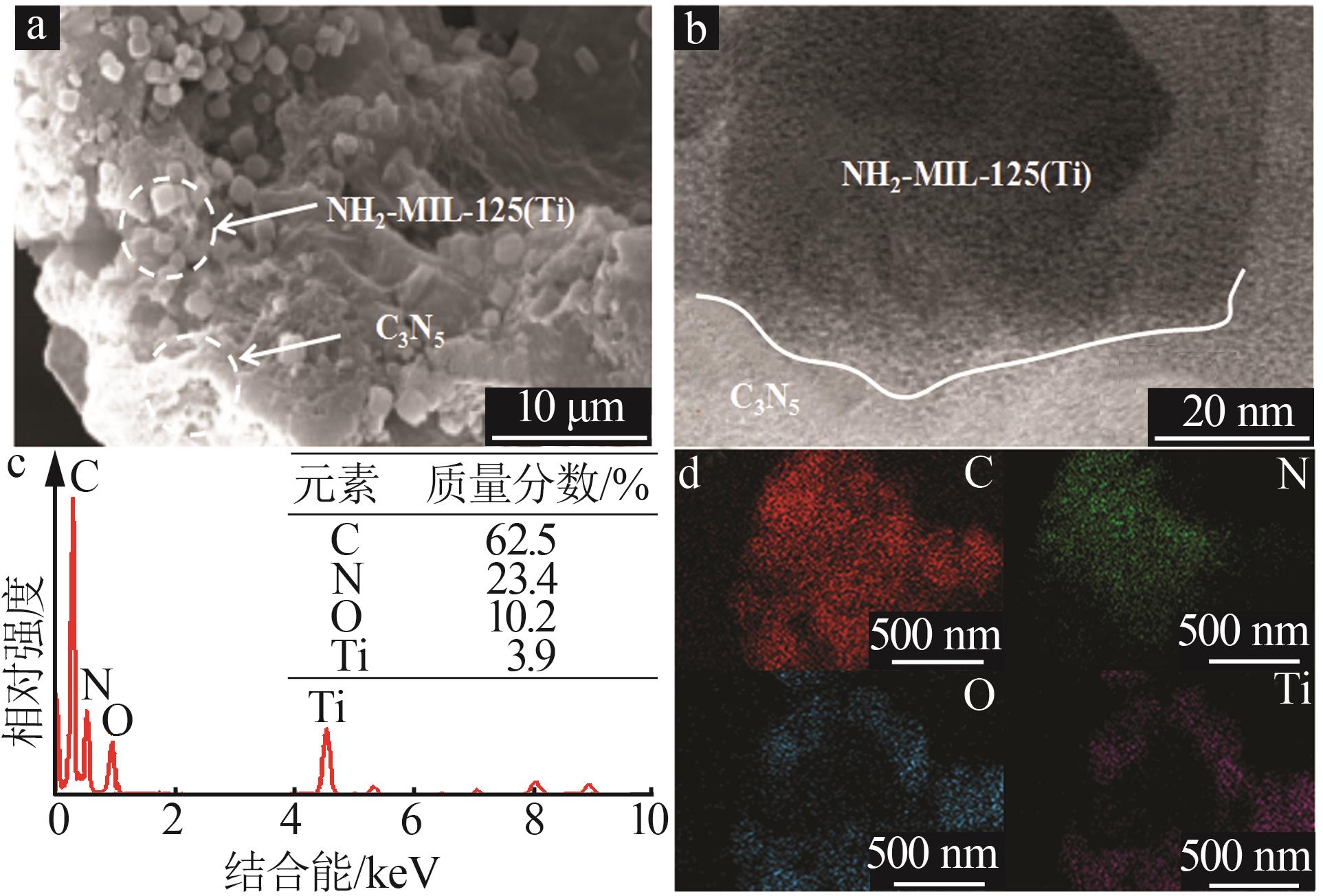
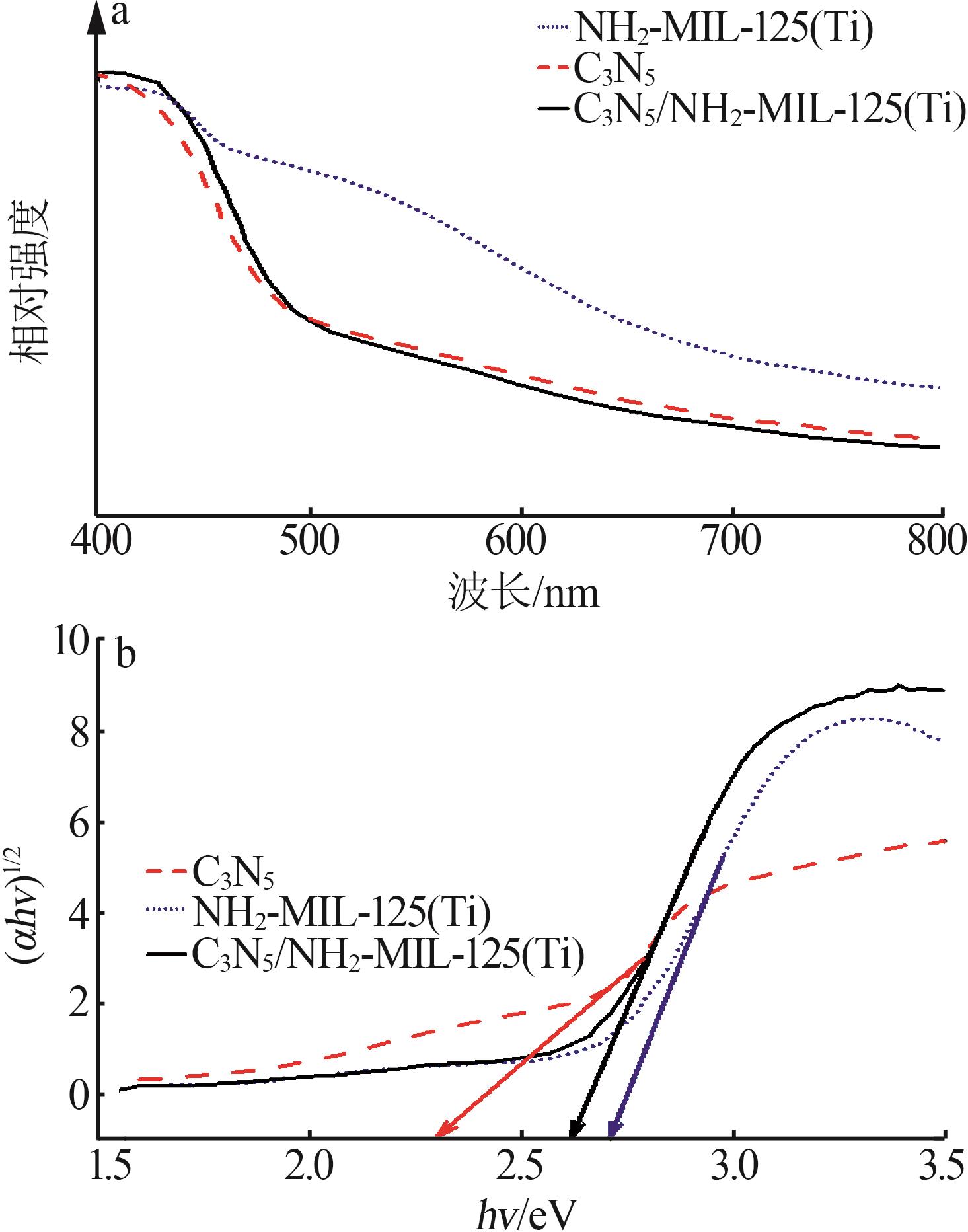
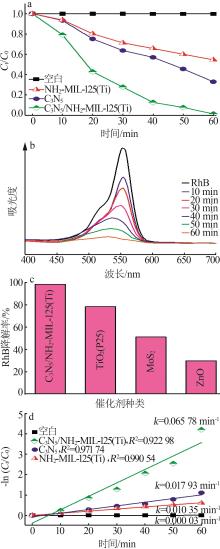
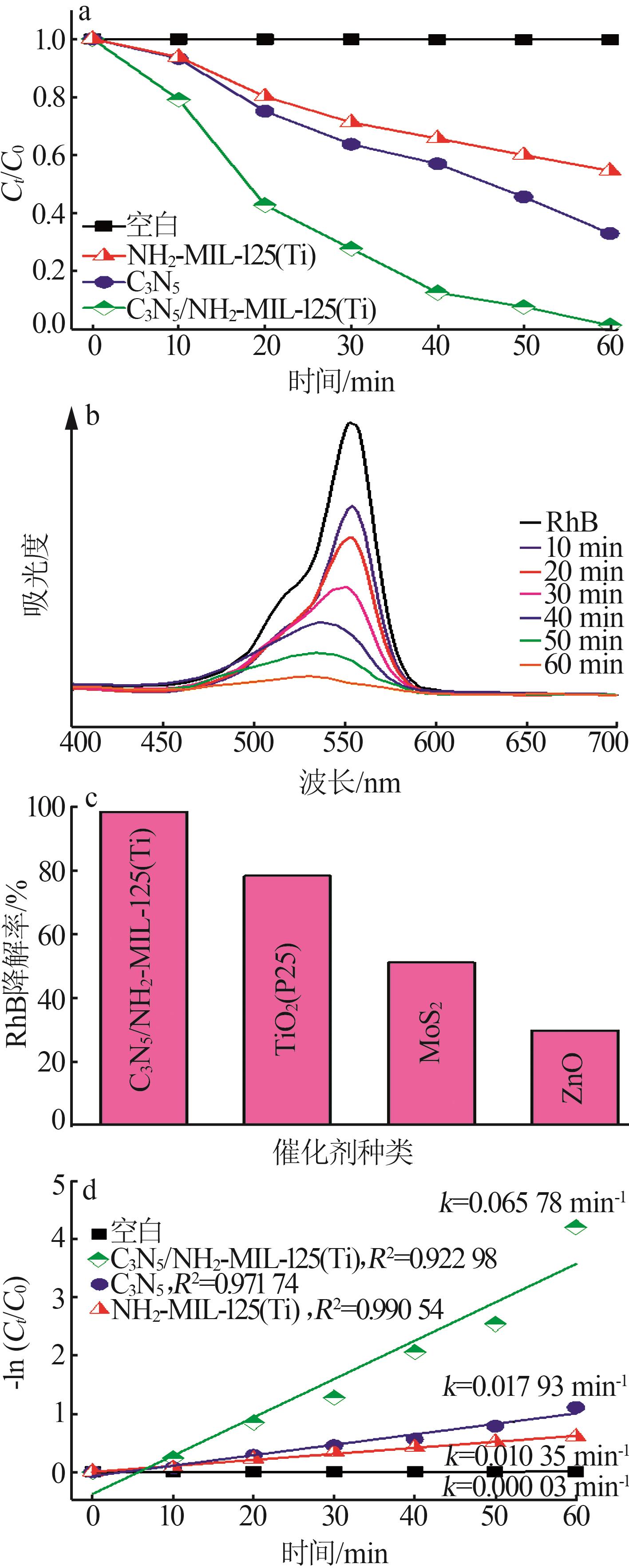
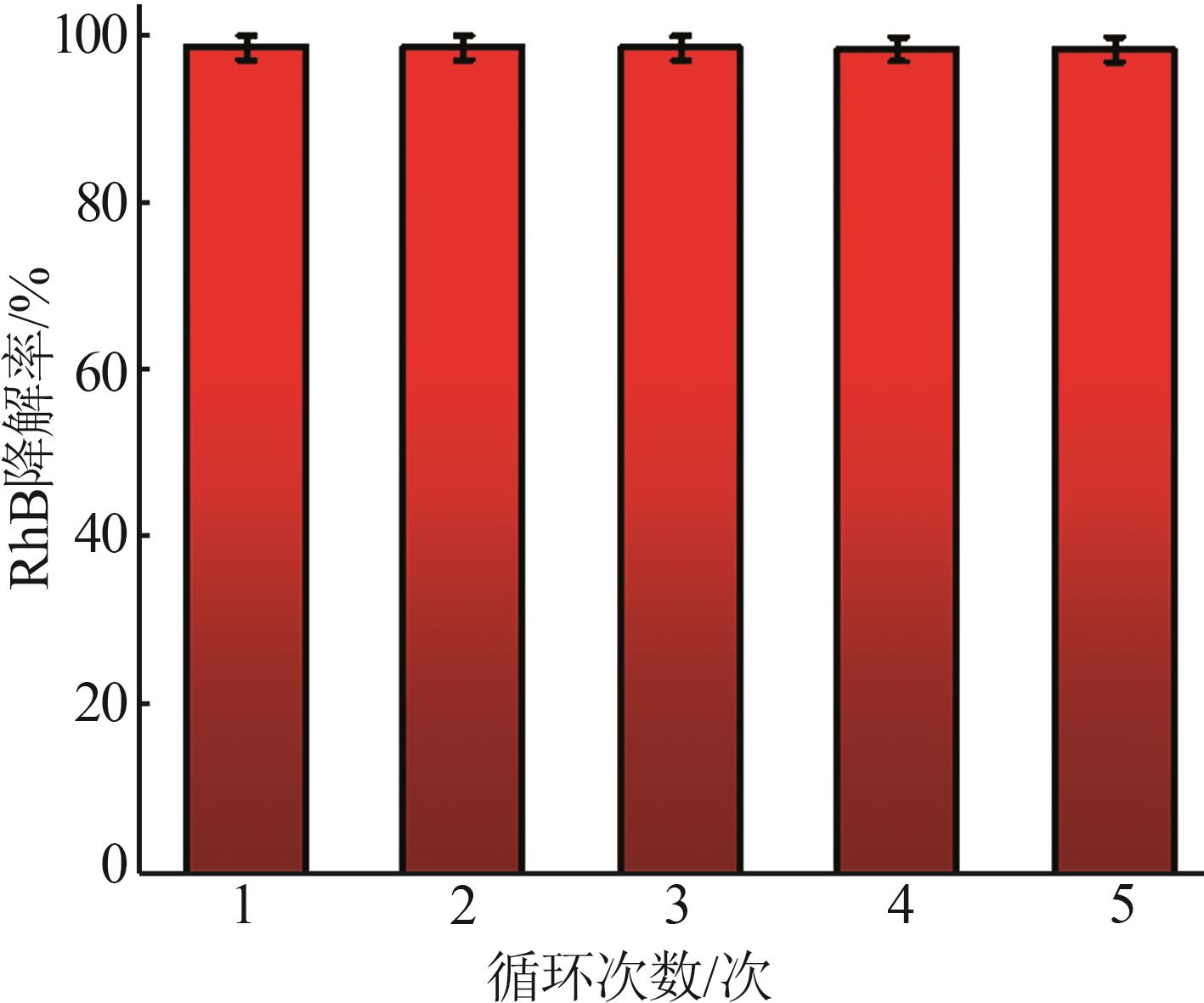
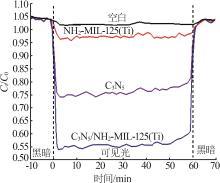
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 120-128.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0201
• Catalytic Materials • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on photocatalytic and mechanical properties of C3N5/NH2-MIL-125(Ti) modified concrete mortar
- China Railway Urban Construction Group First Engineering Company Limited,Taiyuan 030000,China
-
Received:2024-04-09Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-01-24
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Guangming. Study on photocatalytic and mechanical properties of C3N5/NH2-MIL-125(Ti) modified concrete mortar[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 120-128.
share this article
| 1 | 《“十四五” 工业绿色发展规划》发布绿色低碳转型方向[J].印染,2022,48(1):84-85. |
| The “14th Five-Year Plan for Industrial Green Development” released the direction of green and low-carbon transformation[J].China Dyeing & Finishing,2022,48(1):84-85. | |
| 2 | 工信部等六部门印发《工业水效提升行动计划》提高有色等行业工业废水循环利用水平[J].中国有色冶金,2022,51(3): 72. |
| The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other six departments issued the ‘Industrial Water Efficiency Improvement Action Plan’ to improve the recycling level of industrial wastewater in non-ferrous and other industries [J].China Nonferrous Metallurgy,2022,51(3):72. | |
| 3 | 刘思乐,卜义夫,陶洋,等.g-C3N4掺杂TiO2/活性炭复合光催化剂的制备及其光催化性能[J].印染,2022,48(3):16-20. |
| LIU Sile, BU Yifu, TAO Yang,et al.Preparation and photocatalytic performance of g-C3N4 doped TiO2/activated carbon composite photocatalyst[J].China Dyeing & Finishing,2022,48(3):16-20. | |
| 4 | 陈彰旭,朱丹琛,傅明连.g-C3N4/TiO2复合材料制备及其处理罗丹明B研究[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(7):130-136. |
| CHEN Zhangxu, ZHU Danchen, FU Minglian.Study on preparation of g-C3N4/TiO2 composites and application for rhodamine B removal[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(7):130-136. | |
| 5 | 洪雪丽,焦芬,刘维.印染废水处理技术综述[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版),2023,54(4):1219-1229. |
| HONG Xueli, JIAO Fen, LIU Wei.Review on dyeing wastewater treatment technology[J].Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology),2023,54(4):1219-1229. | |
| 6 | 刘桂梅,吕海钦,曾玉彬,等.TiO2光催化选择性还原氮氧化物的应用研究进展[J].化工新型材料,2021,49(6):61-65. |
| LIU Guimei, Haiqin LÜ, ZENG Yubin,et al.Progress on TiO2 photo-catalytic selective reduction of nitrogen oxide[J].New Che-Materials mical,2021,49(6):61-65. | |
| 7 | 季雨晴,傅敏,杨凌,等.硅藻泥/TiO2/g-C3N4光催化涂料的制备及净化NO性能研究[J].现代化工,2021,41(2):172-176, 182. |
| JI Yuqing, FU Min, YANG Ling,et al.Preparation of diatom mud/TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalytic coatings and its purification performance to NO[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2021,41(2):172-176,182. | |
| 8 | 赵文璞,赵晓东,季惠明,等.SiO2/g-C3N4复合材料的3D打印制备及对染料废水的处理性能[J].工业水处理,2024,44(3):64-73. |
| ZHAO Wenpu, ZHAO Xiaodong, JI Huiming,et al.Preparation of SiO2/g-C3N4 composite material by 3D printing and its treatment properties for wastewater containing dyes[J].Industrial Water Treatment,2024,44(3):64-73. | |
| 9 | RAJENDRAN S, CHELLAPANDI T, USHAVIPINACHANDRAN V,et al.Sustainable 2D Bi2WO6/g-C3N5 heterostructure as visible light-triggered abatement of colorless endocrine disruptors in waste-water[J].Applied Surface Science,2022,577:151809. |
| 10 | LIU Tianyu, YANG Guojiang, WANG Wei,et al.Preparation of C3N5 nanosheets with enhanced performance in photocatalytic methylene blue(MB) degradation and H2-evolution from water splitting[J].Environmental Research,2020,188:109741. |
| 11 | KUMAR P, VAHIDZADEH E, THAKUR U K,et al.C3N5:A low bandgap semiconductor containing an azo-linked carbon nitride framework for photocatalytic,photovoltaic and adsorbent applications[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019,141(13):5415-5436. |
| 12 | WANG Lei, CHEN Ruijie, ZHANG Zhiqiang,et al.Constructing direct Z-scheme heterojunction g-C3N5/BiOBr for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction with H2O[J].Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2023,11(2):109345. |
| 13 | ZHANG Junlei, TAO Hengcong, WU Shanshan,et al.Enhanced durability of nitric oxide removal on TiO2(P25) under visible light:Enabled by the direct Z-scheme mechanism and enhanced structure defects through coupling with C3N5 [J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2021,296:120372. |
| 14 | YANG Jing, LONG Jieqing, HUANG Haizan,et al.Synthesis of visible-light driven CeO2/g-C3N5 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic performance for organic dyes[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2023,660:130846. |
| 15 | LIU Sile, BU Yifu, CHENG Song,et al.Preparation of g-C3N5/g-C3N4 heterojunction for methyl orange photocatalytic degradation:Mechanism analysis[J].Journal of Water Process Engineering,2023,54:104019. |
| 16 | 刘思乐,洪雯雯,单译,等.Zr基MOFs材料UiO-66-NH2负载g-C3N4催化剂的制备及光催化性能[J].印染,2024,50(3):15-19. |
| LIU Sile, HONG Wenwen, SHAN Yi,et al.Preparation of Zr-based MOFs material UiO-66-NH2 supported g-C3N4 catalyst and its photocatalytic property[J].China Dyeing & Finishing,2024,50(3):15-19. | |
| 17 | 李菲.海藻酸钠/MOFs复合微球制备及其在印染废水中的应用[J].印刷与数字媒体技术研究,2024(1):107-112. |
| LI Fei.Preparation of sodium alginate/MOFs composite microspheres and the application in printing and dyeing wastewater[J].Printing and Digital Media Technology Study,2024(1):107- 112. | |
| 18 | IKREEDEEGH R R, TASLEEM S, HOSSEN M A.Facile fabrication of binary g-C3N4/NH2-MIL-125(Ti) MOF nanocomposite with Z-scheme heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic H2 production and CO2 reduction under visible light[J].Fuel,2024,360:130561. |
| 19 | 贺晓宇.基于氮化碳的光催化水泥混凝土制备与性能研究[J].公路,2020,65(10):292-296. |
| HE Xiaoyu.Preparation and properties of photocatalytic cement concrete based on carbon nitride[J].Highway,2020,65(10):292-296. | |
| 20 | 王玲玲,陈佰岩,韦志强,等.光催化混凝土物理力学性能研究[J].混凝土,2020(4):29-31,35. |
| WANG Lingling, CHEN Baiyan, WEI Zhiqiang,et al.Study on physical properties and mechanical behaviors of photocatalytic concrete[J].Concrete,2020(4):29-31,35. | |
| 21 | 周晓兵,丁思晴,高莉宁,等.掺杂改性石墨相氮化碳水泥基复合材料的光催化作用研究[J].公路,2022,67(10):368- 373. |
| ZHOU Xiaobing, DING Siqing, GAO Lining,et al.Study on the photocatalytic effect of doped modified graphite phase carbon nitride cement-based composites[J].Highway,2022,67(10):368-373. | |
| 22 | 林淑瑾,罗盛洋,熊晓立.负载S-g-C3N4/MgAl-CLDH光催化砂浆的去污及水化性能研究[J].硅酸盐通报,2024,43(1):44-51. |
| LIN Shujin, LUO Shengyang, XIONG Xiaoli.Decontamination and hydration performance of photocatalytic mortar loaded with S-g-C3N4/MgAl-CLDH[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2024,43(1):44-51. | |
| 23 | 林元明,林佳福,熊晓立,等.TiO2改性钢渣基透水混凝土的力学和NO x 降解性能研究[J].硅酸盐通报,2024,43(1):191- 199. |
| LIN Yuanming, LIN Jiafu, XIONG Xiaoli,et al.Mechanical and NO x degradation performance of TiO2 modified steel slag-based permeable concrete[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2024,43(1):191-199. | |
| 24 | 贾霞,王彦敏,张文凯,等.纳米TiO2降解汽车尾气在道路工程中的应用研究进展[J].市政技术,2024,42(1):10-16,29. |
| JIA Xia, WANG Yanmin, ZHANG Wenkai,et al.Research on nano-TiO2 degradation of automobile exhaust in road engineer-ing[J].Journal of Municipal Technology,2024,42(1):10-16, 29. | |
| 25 | 谭玉简,刘民,郭新闻,等.溶剂和微波辅助对NH2-MIL-125-Ti制备及其光催化性能的影响[J].石油学报(石油加工),2021,37(4):744-756. |
| TAN Yujian, LIU Min, GUO Xinwen,et al.Effects of solvent and microwave assistance on synthesis of NH2-MIL-125-Ti and its photocatalytic performance[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing Section),2021,37(4):744-756. | |
| 26 | YIN Hongfei, YUAN Chunyu, LV Huijun,et al.The interface design of(0D/2D/1D) AgI/BiOI/C3N5 dual Z-scheme heterostructures with efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2023,308:122815. |
| 27 | 智芳芳.PVC/g-C3N4复合材料的制备及其光催化净化污水的研究[J].塑料科技,2024,52(2):69-71. |
| ZHI Fangfang.Preparation of PVC/g-C3N4 composites and its photocatalytic purification of wastewater[J].Plastics Science and Technology,2024,52(2):69-71. | |
| 28 | 李明辉,谷二艳,邹星宇,等.N-CDs@Nb2O5-AMMC纳米材料的制备及其可见光催化性能研究[J].功能材料,2024,55(1):1203-1211. |
| LI Minghui, GU Eryan, ZOU Xingyu,et al.Preparation of N-CDs@Nb2O5-AMMC nanomaterial and study of visible light photocatalytic property[J].Journal of Functional Materials,2024,55(1):1203-1211. |
| [1] | SHI Wangfang, ZHANG Yongsheng. Study on NO x degradation performance of concrete-based non-metallic boron doped nitrogen-rich carbon nitride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 116-123. |
| [2] | LI Zihan, ZHANG Jiaqi, LI Shizhuo, LI Xinyu, LIU Shaozhuo, WANG Yihao, HAO Yucui, LIU Jian, LI Yanhua. Study on synthesis and catalytic mechanism of CdS/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 124-132. |
| [3] | SUN Qinghao, LI Keyan, GUO Xinwen. Study on photocatalytic benzyl alcohol oxidation coupled with hydrogen production over Pd/ZnIn2S4 nanosheets [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 113-119. |
| [4] | ZHANG Guoqiang, RONG Xilin, XIAO Zhenfang, XUE Ziran, CHENG Hao, FENG Jun, LIU Quan, LU Yao, HUANG Wenyi. Study on preparation and photocatalytic properties of bagasse carbon aerogels loaded with zinc oxide nanoparticles [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 131-138. |
| [5] | WANG Yawen, WANG Fangfang, GENG Siyu, JU Jia, CHEN Lei, CHEN Changdong. Study on preparation and photocatalytic performance of SrTiO3-SrWO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 143-149. |
| [6] | LIU Min, HUANG Xiu, ZHANG Liyuan. Research progress of S-type heterojunction photocatalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 18-27. |
| [7] | LI Jiangpeng, ZHANG Huibin. Synergistic degradation of methylene blue by photo-Fenton and photocatalytic with 3D porous LaFeO3/CeO2/SrTiO3 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 141-148. |
| [8] | TANG Bei. Preparation of ZnO/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalytic material and its degradation of pyridine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 133-142. |
| [9] | HUANG Jianan, LU Xiaoyu, WANG Mitang. Effect of Ba-La co-doping on degradation of methylene blue dye by TaON [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 146-151. |
| [10] | ZUO Guangling, WANG Minghui, PENG Yunying, DU Jia, YE Hongyong. Study on hnoneycomb-like LaVO4/Bi2O3 heterojunction for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 158-164. |
| [11] | CUI Xiangdong, LIU Sile. Study on photoelectric performance analysis of g-C3N5 nanorods and removal of Cr(Ⅵ) and methylene blue [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 159-168. |
| [12] | YAN Yu, ZHOU Wenyuan, YANG Yunfei, WU Junshu, WANG Jinshu, SUN Lingmin. Study on surface regulation of sodium ferric silicate photocatalyst and its enhanced Cr(Ⅵ) photoreduction properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 141-150. |
| [13] | MA Yihong, CHEN Xingtao, TANG Lei. Treatment of printing wastewater by chemical coagulation-TiO2/g-C3N5 photocatalytic degradation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 151-158. |
| [14] | YANG Bo, LIANG Zhiyan, LIU Wenyuan, CAO Jiazhen, LIU Xinyue, XING Mingyang. Research progress of application of molybdenum-based catalytic materials for water pollution control [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 1-12. |
| [15] | YU Hongchao, ZHANG Mengmeng, JIN Tianxiang. Research progress of microstructure and crystal surface effect of Ag3PO4 photocatalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 13-20. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||