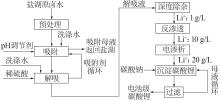
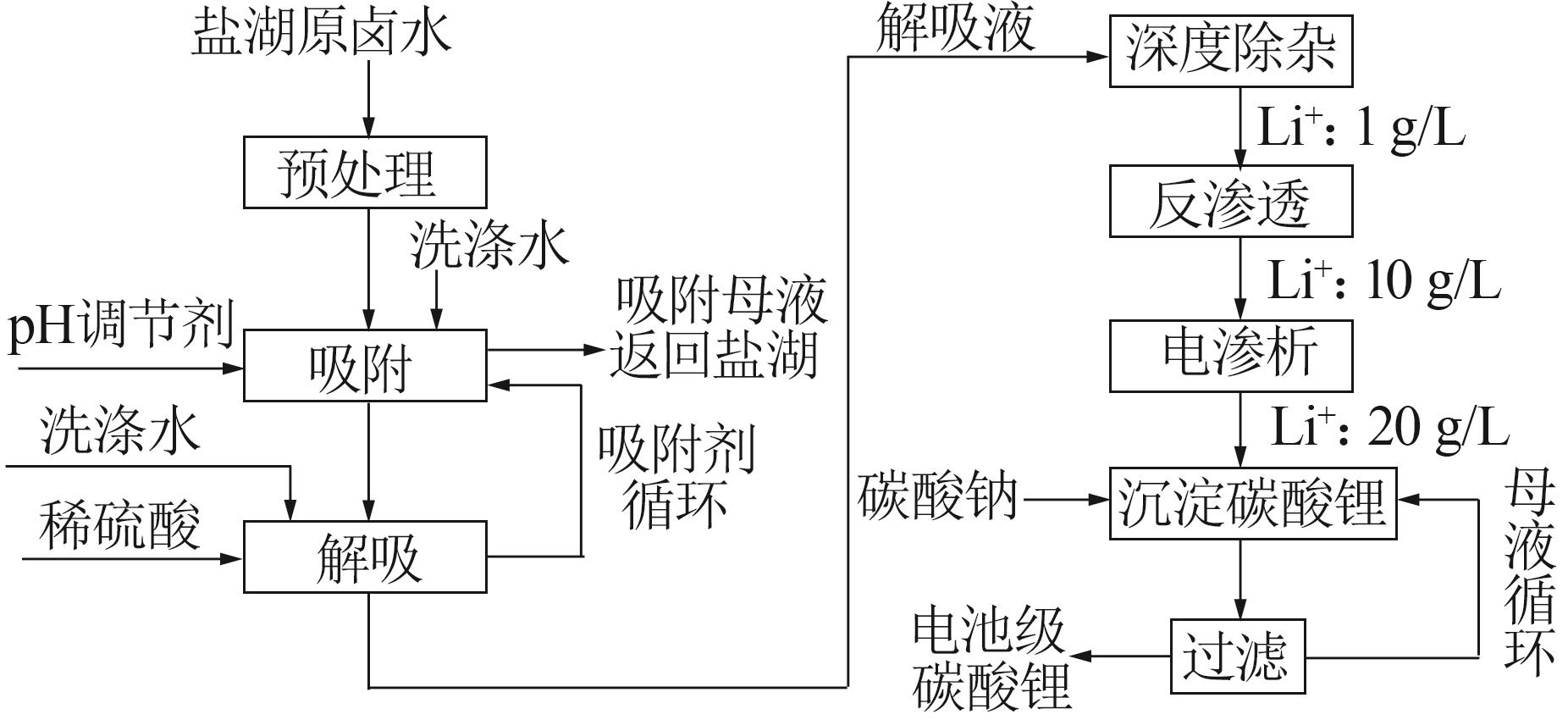
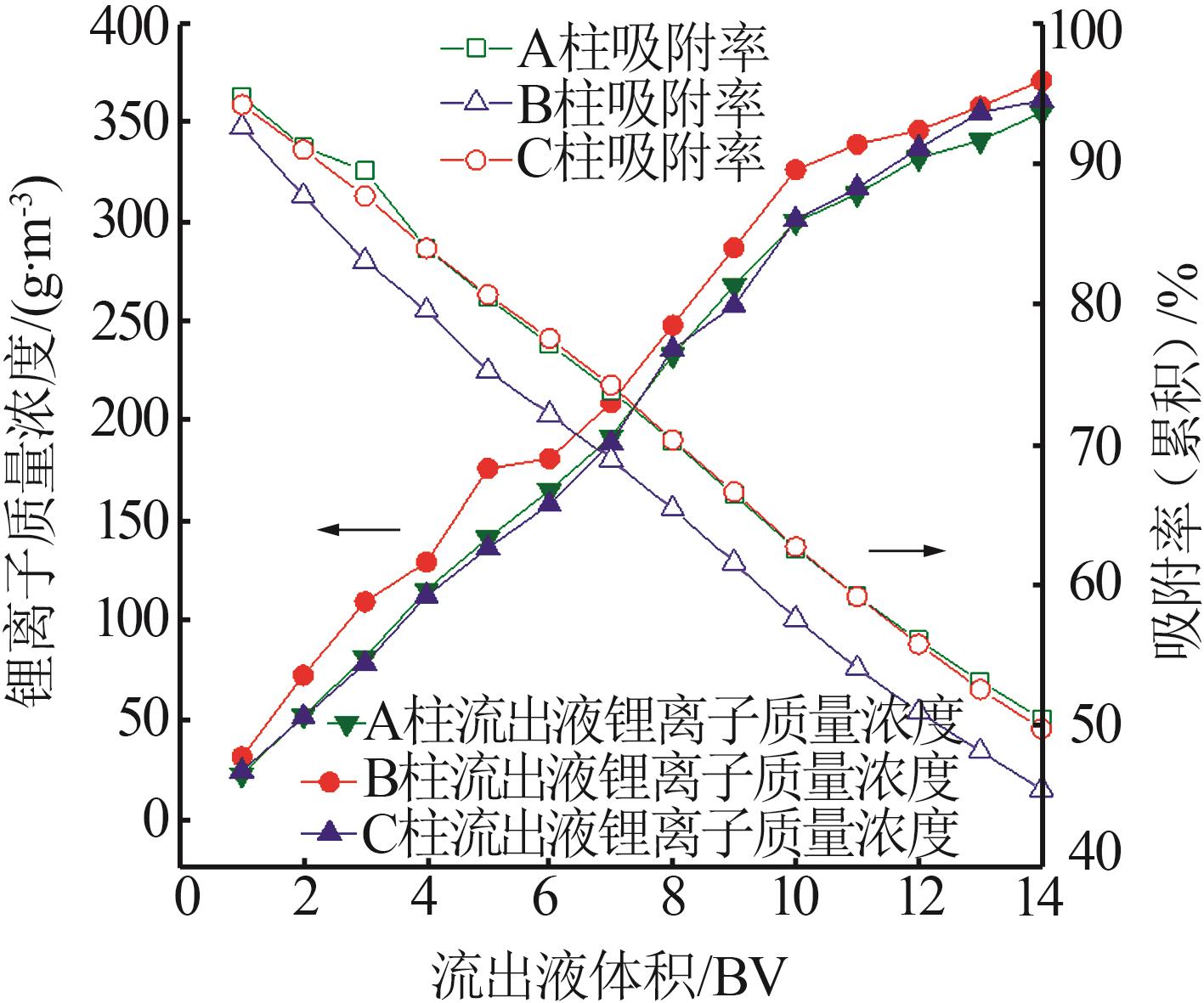
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 86-92.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0142
• Industrial Techniques • Previous Articles Next Articles
Pilot study on lithium extraction by adsorption from raw brine of magnesium sulfate subtype salt lakes in Tibet
LAI Xianrong( ), CHEN Zhouqin, SUN Hao, YANG Chao
), CHEN Zhouqin, SUN Hao, YANG Chao
- Sichuan Fanyu Lithium New Material Technology Co.,Ltd.,Deyang 618000,China
-
Received:2023-03-14Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-11-16
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LAI Xianrong, CHEN Zhouqin, SUN Hao, YANG Chao. Pilot study on lithium extraction by adsorption from raw brine of magnesium sulfate subtype salt lakes in Tibet[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 86-92.
share this article
Table 2
Performance parameters of manganese-based adsorbents"
| 项目 | 外观 | 生产 年份 | 粒度*/ (mm×mm) | 堆积密度/ (g·mL-1) | 抗压强度/ (N·颗-1) | 含水率/ % | 静态吸附容量/ (mg·g-1) | 操作吸附容量/ (mg·g-1) | 溶损率 (单次)/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
指 标 | I型 | 黑褐色不 规则颗粒 | 2020 | 2×(2~4) | 0.60~0.65 | 15~30 | 0.1~1.00 | 20~32 | 3~8 | 0.01~0.05 |
| II型 | 2021 | 2×(2~4) | 0.69~0.71 | 15~30 | 0.1~1.00 | 18~30 | 3~7 | 0.01~0.05 | ||
| III型 | 2021 | 1.7×(1~3) | 0.77~0.78 | 5~20 | 0.1~1.00 | 18~30 | 3~7 | 0.01~0.05 | ||
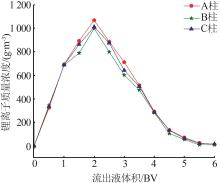
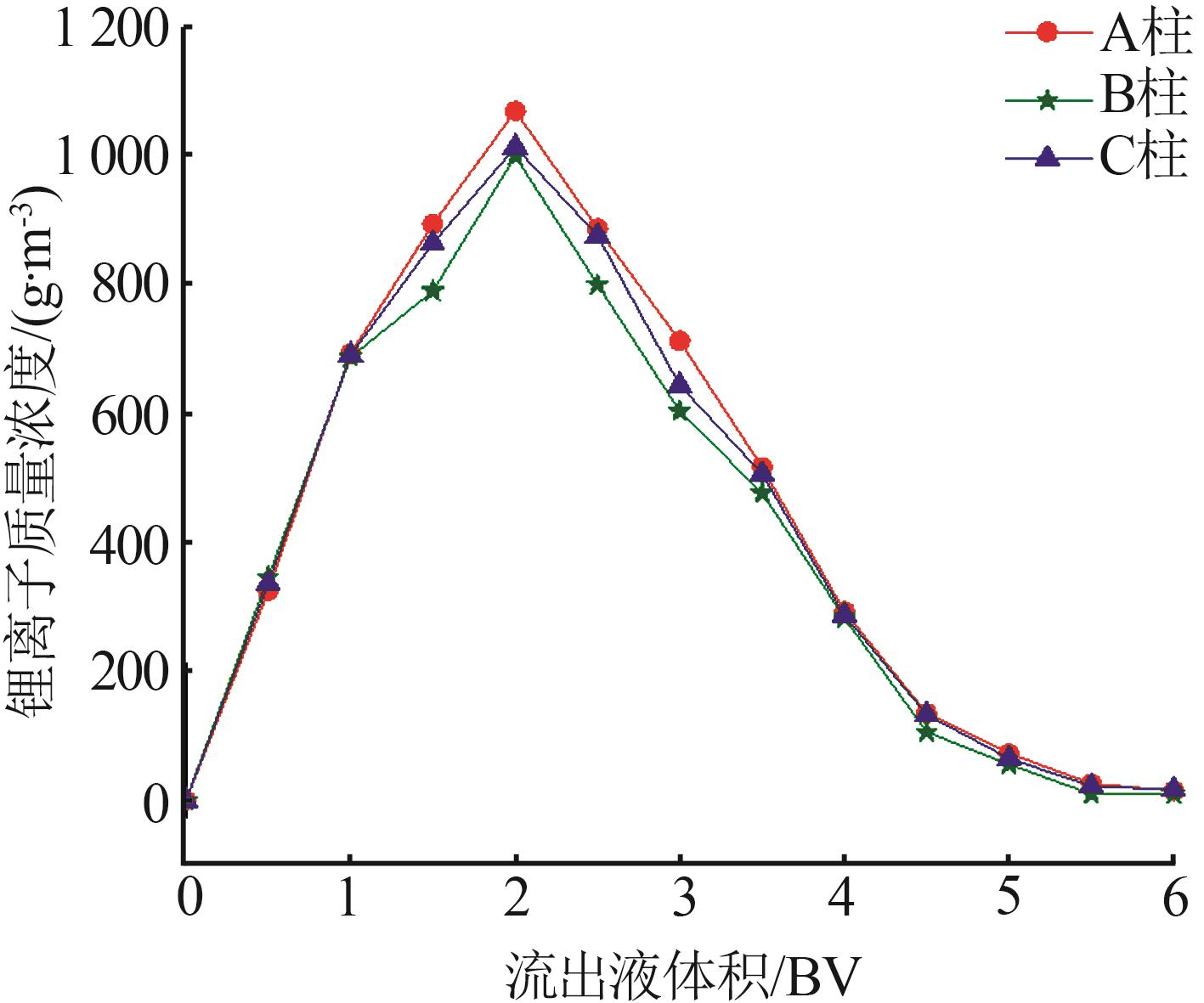
Table 5
Summary of key experimental data of A/B/C tower(30 d)"
| 编号 | 卤水中离子质量浓度/(mg·L-1) | 吸附母液中离子质量 浓度/(mg·L-1) | 吸附率/ % | 吸附容量/ (mg·g-1) | 脱镁率/ % | 解吸液中离子质量浓度/ (mg·L-1) | 解吸率/% | 溶损率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Mg2+ | Li+ | Mg2+ | Li+ | Mg2+ | Mn2+ | |||||||
| A塔 | 149.7 | 7.43 | 36.2 | 7.38 | 75.8 | 4.05 | 99.3 | 495.9 | 79.7 | 15.7 | 99.5 | 0.04 | |
| B塔 | 383.3 | 7.63 | 153.9 | 7.58 | 59.8 | 4.09 | 99.3 | 524.5 | 74.3 | 14.7 | 99.4 | 0.02 | |
| C塔 | 391.2 | 7.60 | 166.5 | 7.55 | 57.4 | 4.01 | 99.3 | 509.2 | 75.2 | 15.8 | 99.6 | 0.03 | |
Table 8
Lithium carbonate product test report"
| 检测项目 | 外观 | w(Li2CO3)/ % | w(Na+)/ % | w(Fe2+)/ % | w(Ca2+)/ % | w(SO42-)/ % | w(Cl-)/ % | w(盐酸不 溶物)/% | w(Mg2+)/ % | w(水分)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li2CO3-1质检要求 | 白色粉末,具有流动性,无肉眼可见杂质 | ≥99.0 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.003 5 | ≤0.040 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.020 | ≤0.015 | — | ≤0.3 |
| 实测值 | 白色粉末,具有流动性,无颗粒杂质 | 99.8 | 0.12 | 0.001 8 | 0.015 | 0.21 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.021 | 0.3 |
| 单项结论 | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | — | 合格 |
Table 11
Production cost estimate of lithium carbonate per ton (capacity:lithium carbonate 10 000 t/a)"
| 项目 | 名称 | 规格 | 单耗/ t | 单价* (万元·t-1) | 总价/ 万元 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
原 材 料 | 原卤水 | m3 | 670 | — | — | — |
| 吸附剂 | 颗粒 | 0.01 | 35.0 | 0.350 | 含运费 | |
| 碳酸钠 | 工业一级 | 1.650 | 0.25 | 0.412 | 含运费 | |
| 硫酸 | 工业一级 | 1.500 | 0.20 | 0.300 | 含运费 | |
| 调节剂 | 工业一级 | 1.600 | 0.30 | 0.480 | 含运费 | |
| 地下水 | — | 300 | 0.000 1 | 0.030 | 当地 | |
| 包装袋 | — | 1 | 0.01 | 0.010 | 吨袋 | |
离子膜 及其他 | — | — | — | 0.300 | — | |
| 能耗 | 电 | — | 10 000度 | 0.80元/度 | 0.800 | — |
| 设备折旧 | 总设备投资3.0亿元,10年折旧期 | 0.300 | — | |||
| 财务成本人工费用管理销售 | 资金利息:5%/a,总投资6.0亿元 | 0.300 | — | |||
| 120人,10 000元/(人·月) | 0.144 | 西藏 | ||||
| — | 0.120 | — | ||||
| 合计 | — | 3.546 | ||||
| 1 | 陈宋波,徐川,严新星,等.矿石和盐湖提锂研究进展[J].新能源科技,2022(10):31-34. |
| CHEN Songbo, XU Chuan, YAN Xinxing,et al.Research progress of lithium extraction from ores and salt lakes[J].New Energy Technology,2022(10):31-34. | |
| 2 | 李立平.碳酸锂和氯化钾价格齐升[EB/OL].(2023-01-30).https://www.sohu.com/a/635680404_121118712. |
| 3 | 伍倩,刘喜方,郑绵平,等.我国盐湖锂资源开发现状、存在问题及对策[J].现代化工,2017,37(5):1-5. |
| WU Qian, LIU Xifang, ZHENG Mianping,et al.Present situation,existing problems and countermeasures of development of salt lake lithium resources in China[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2017,37(5):1-5. | |
| 4 | 姜贞贞,刘高令,卓玛曲西,等.我国锂资源供需现状下西藏盐湖锂产业现状及对策建议[J].盐湖研究,2021,29(3):104- 110. |
| JIANG Zhenzhen, LIU Gaoling, ZHUO Maquxi,et al.Present situation and suggestions of saline lake lithium resource in Tibet under the current situation of supply and demand of lithium resources in China[J].Journal of Salt Lake Research,2021,29(3):104-110. | |
| 5 | 乜贞,伍倩,丁涛,等.中国盐湖卤水提锂产业化技术研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(10):1-12. |
| NIE Zhen, WU Qian, DING Tao,et al.Research progress on industrialization technology of lithium extraction from salt lake brine in China[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(10):1-12. | |
| 6 | 刘东帆,孙淑英,于建国.盐湖卤水提锂技术研究与发展[J].化工学报,2018,69(1):141-155. |
| LIU Dongfan, SUN Shuying, YU Jianguo.Research and development on technique of lithium recovery from salt lake brine[J].CIESC Journal,2018,69(1):141-155. | |
| 7 | 杨建元,程温莹,邓天龙,等.东台吉乃尔湖晶间卤水综合利用研究(煅烧法提锂工艺)[J].无机盐工业,1996,28(2):29-32. |
| YANG Jianyuan, CHENG Wenying, DENG Tianlong,et al.Study on comprehensive utilization of intergranular brine in Jinaier Lake,Dongtai(lithium extraction process by calcination)[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,1996,28(2):29-32. | |
| 8 | 曾小毛,樊磊.高镁锂比盐湖老卤萃取提锂工艺研究[J].矿冶工程,2017,37(6):95-96. |
| ZENG Xiaomao, FAN Lei.Extraction of lithium from salt-lake brine with high Mg/Li ratio[J].Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2017,37(6):95-96. | |
| 9 | 罗清龙,董明哲,李军,等.吸附法分离盐湖卤水中锂的研究进展[J].盐湖研究,2023,31(1):106-115. |
| LUO Qinglong, DONG Mingzhe, LI Jun,et al.Research progress of lithium separation from salt lake brine by adsorption method[J].Journal of Salt Lake Research,2023,31(1):106-115. | |
| 10 | 林钰青,张以任,邱宇隆,等.膜技术在盐湖提锂中的进展和展望[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(1):33-45. |
| LIN Yuqing, ZHANG Yiren, QIU Yulong,et al.Progress and prospect of membrane technology in lithium extraction from salt lake brine[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(1):33- 45. | |
| 11 | 何雪.一种掺硫富锂锰系锂吸附剂及其制备方法和应用:中国,110180489A[P].2021-12-07. |
| 12 | 钟辉,陈周秦,赖先熔,等.一种纳米单晶锰系锂吸附剂的合成方法:中国,113617327B[P].2022-07-15. |
| 13 | LAI Xianrong, YUAN Yijia, CHEN Zhouqin,et al.Adsorption-desorption properties of granular EP/HMO composite and its application in lithium recovery from brine[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2020,59(16):7913-7925. |
| 14 | 孙建科,陈进,易大伟.离子筛型锂吸附剂的成型及研究进展[J].化工新型材料,2022,50(2):293-297. |
| SUN Jianke, CHEN Jin, YI Dawei.Research progress on molding of ionic sieve type Li adsorbent[J].New Chemical Materials,2022,50(2):293-297. | |
| 15 | 佚名.新能源产业迎重大利好!碳酸锂价格三个月大跌40%[EB/OL].(2023-3-20).https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1760838161931516256&wfr=spider&for=pc. |
| 16 | 佚名.盐湖股份去年净利156亿元,未来或与王磊团队合作“盐湖提锂”[EB/OL].(2023-3-13).https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1760251170586412269&wfr=spider&for=pc. |
| [1] | LI Chao, WANG Liping, GAO Guimei, ZHANG Yunfeng, HONG Yu, LIU Darui, XU Lijun, CUI Yongjie. Study on reaction mechanism of acid leaching lithium from circulating fluidized bed fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 101-107. |
| [2] | BAI Xingxing, LI Hanfei, TANG Yong, ZHANG Jun, ZHU Guangkai, LI Lishuo, TONG Zhangfa. Study on preparation of cellulose based hydrogel doped with nano-calcium carbonate and its adsorption properties of copper ions [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 83-91. |
| [3] | KONG Lingjie, LI Guangbi, XIE Jiahao, YANG Xinhui, BAI Xiaoqin. Research progress on lithium extraction technology from salt lake brine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 14-26. |
| [4] | ZHOU Wanji, LI Sixia. Study on extraction lithium from brine with high magnesium using ionic liquid/metal salt extraction system [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 54-59. |
| [5] | WANG Ping, XU Rongsheng, SUN Dong, SHI Xiaohong, XU Wei, LI Mei. Study on preparation of nitrogen-doped biochar and its adsorption properties for methylene blue [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 117-127. |
| [6] | SONG Zhaoxia, LIU Yongkang, GUO Yaokun, WANG Tengfei. Study on adsorption performance of wheat straw biochar on malachite green [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 128-135. |
| [7] | XIONG Chengrong, CHEN Yan, TANG Miao, ZHANG Fengze, ZHOU Tianxiang, OUYANG Ruifeng, DONG Gang, SHI Wei, ZENG Tao, CHEN Yunxia, SU Xiaoli. Research progress on preparation of 2D vermiculite nanosheets and their environmental adsorption of pollutants [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 19-26. |
| [8] | ZHANG Bangcheng, WANG Li. Preparation and adsorption properties of waste polyester⁃based activated carbon activated by ZnCl2 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 126-134. |
| [9] | ZHANG Lijin, LÜ Qing, CHEN Xiaolang, LI Qingxin, SHI Hongyu, QIN Jun. Preparation of Ca-based LDO composite material and its adsorption performance for phosphate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 37-45. |
| [10] | ZHAO Chuang, ZHANG Boyu, LI Ben, JIN Fengying, LI Bin, SUN Zhenhai, GUO Chunlei. Study on adsorption and separation technology of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by adsorbent [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 61-68. |
| [11] | LIU Kailong, ZHU Kongyi, GUO Chunlei, MA Xiaobiao, WANG Yujian, SHENG Qiang, LI Xiang, WANG Yinbin, JIN Fengying. Effects of process condition on performance of diesel aromatic to light aromatic [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 139-146. |
| [12] | ZHU Zenghu, WANG Min, PENG Zhengjun, JIA Guofeng, LI Yan. Study on adsorption of potassium ions in lithium chloride solution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 61-66. |
| [13] | XU Mengyao, ZHANG Xin, HE Kunpeng, HE Jian, JIANG Wei. Preparation of yttrium oxide and zirconium phosphate adsorbents from zirconium-yttrium waste and evaluation of their performance [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 116-124. |
| [14] | LI Qiaoyun, HUANG Xiuxing, WEI Wenye, CHEN Zhen. Study on adsorption of methylene blue by activated carbon with acid/alkali synergistically modified fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 131-136. |
| [15] | LI Yang, LOU Feijian, SUI Xin, LI Keyan, LIU Fei, GUO Xinwen. Preparation of amine-functionalized fumed SiO2 materials and their performance for CO2 adsorption [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 38-43. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||