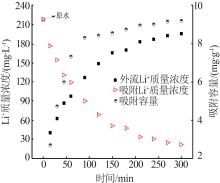
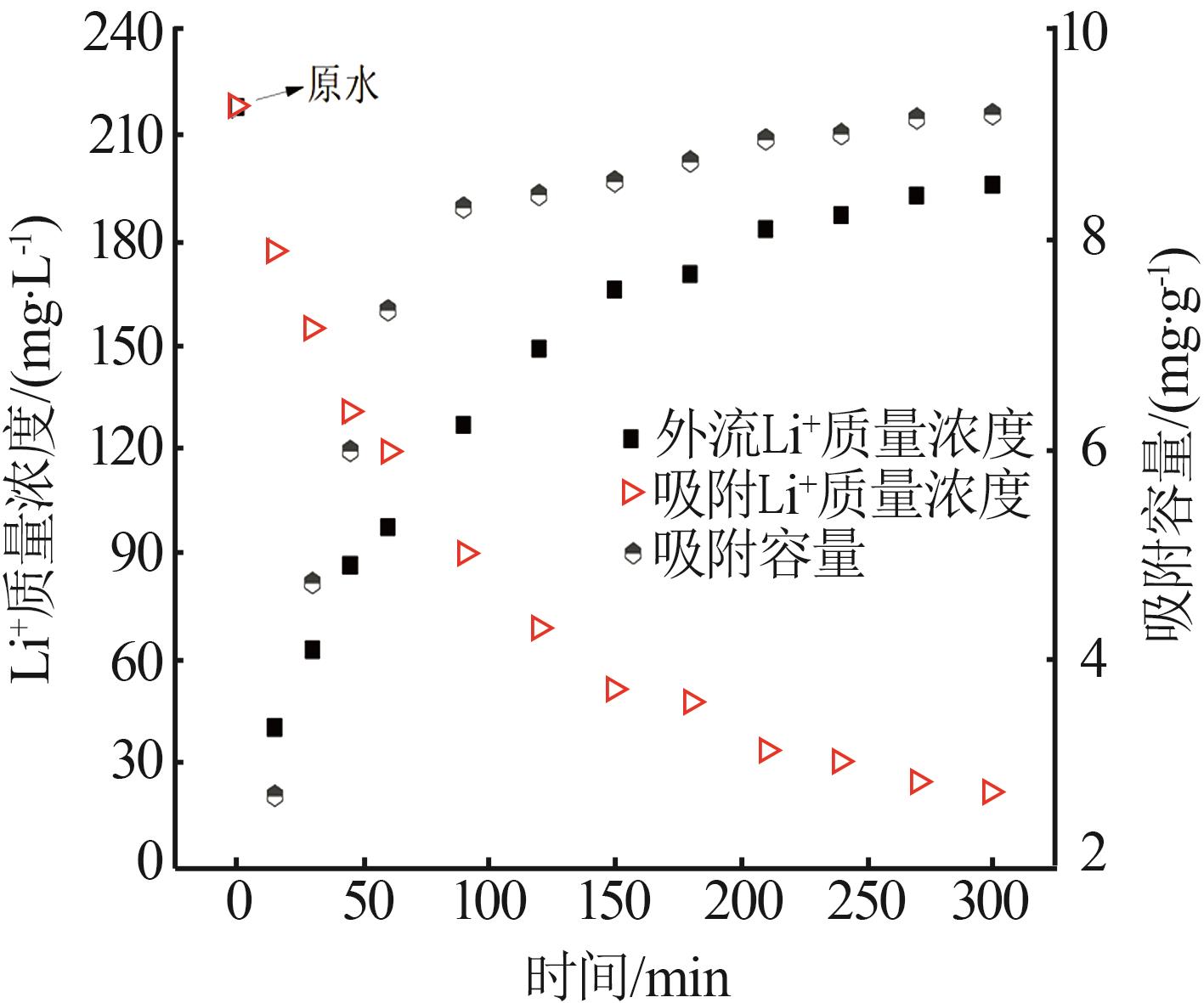
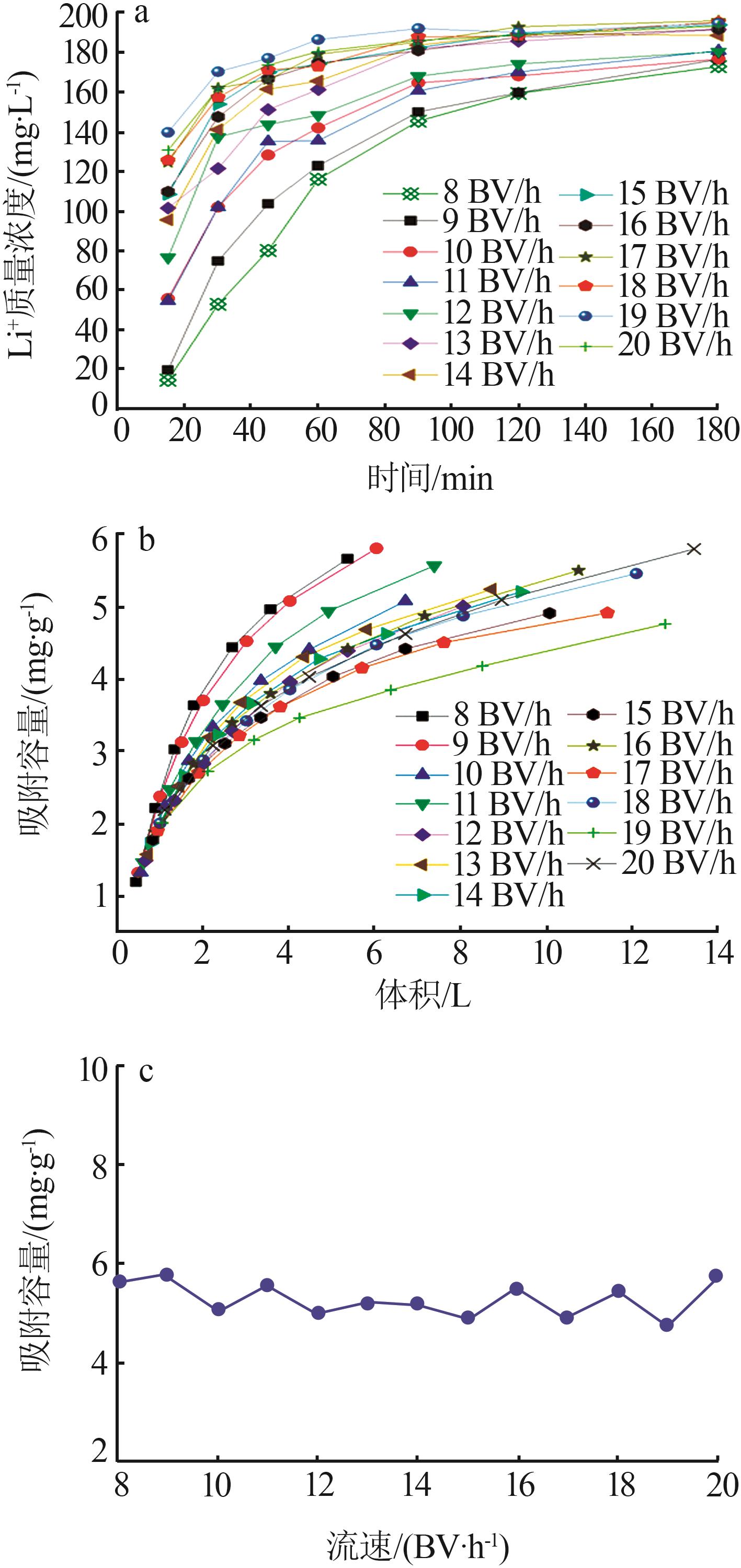
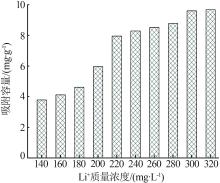
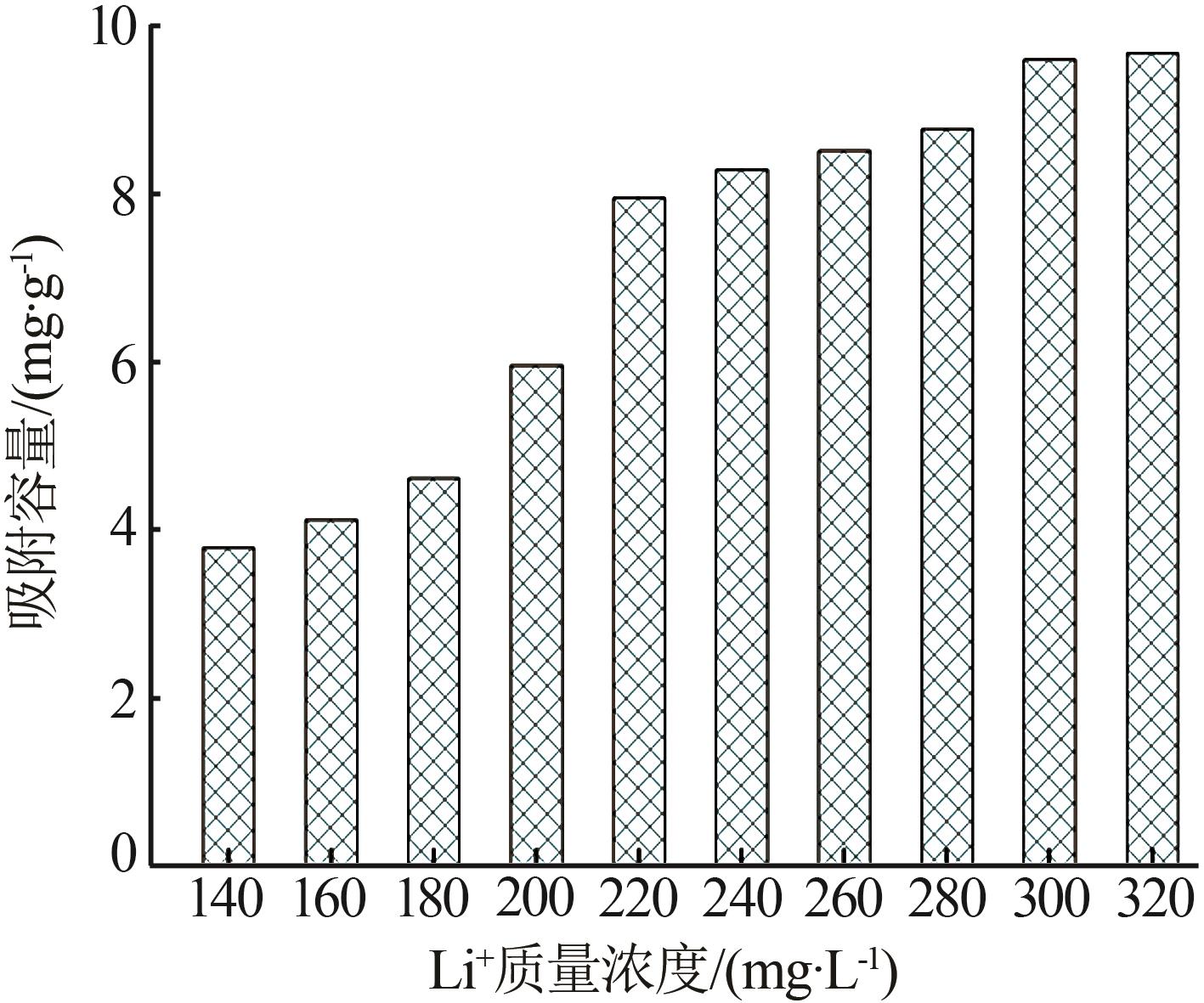
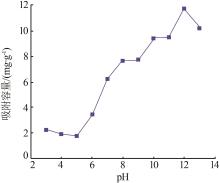
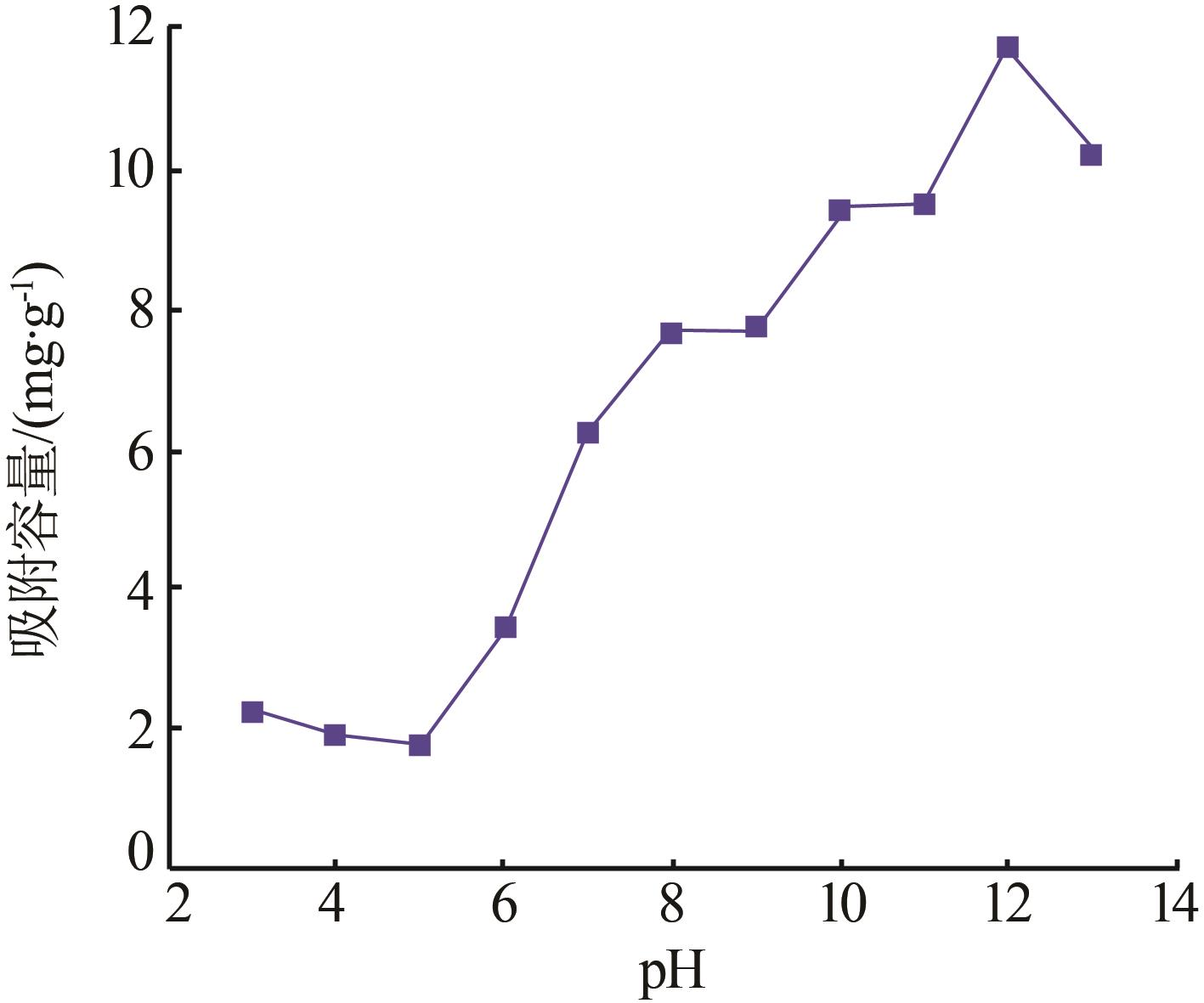
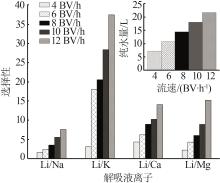
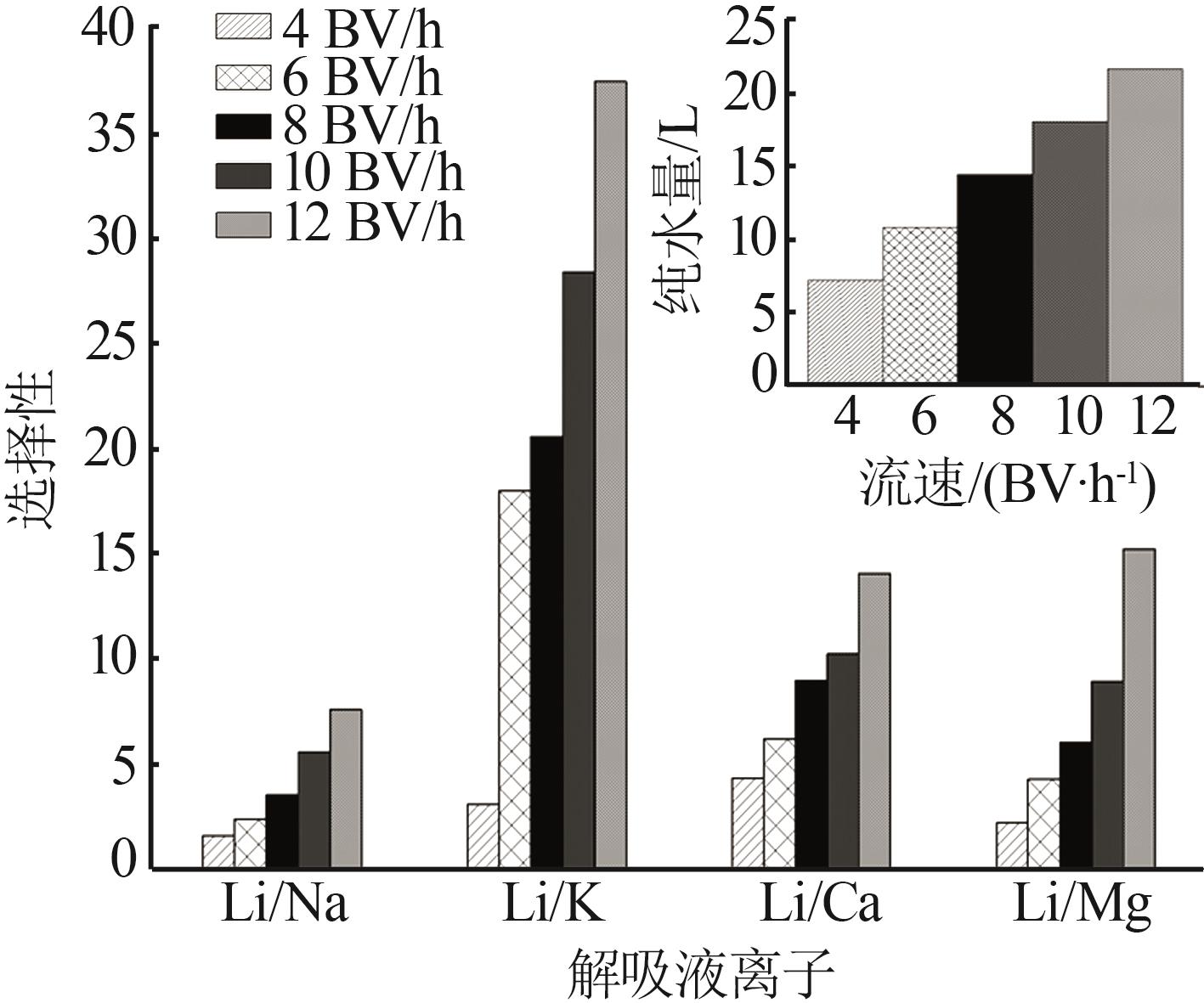
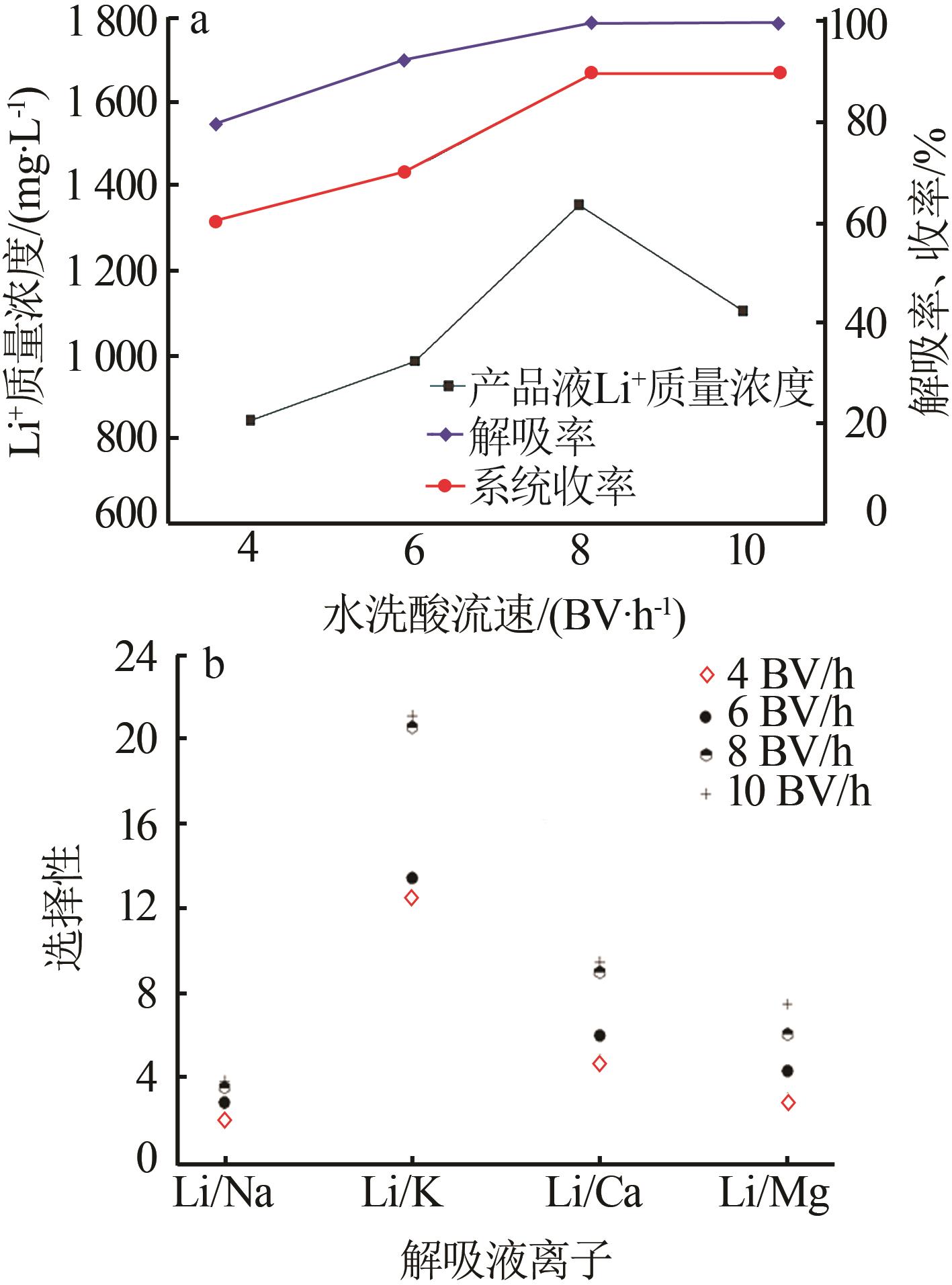
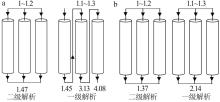
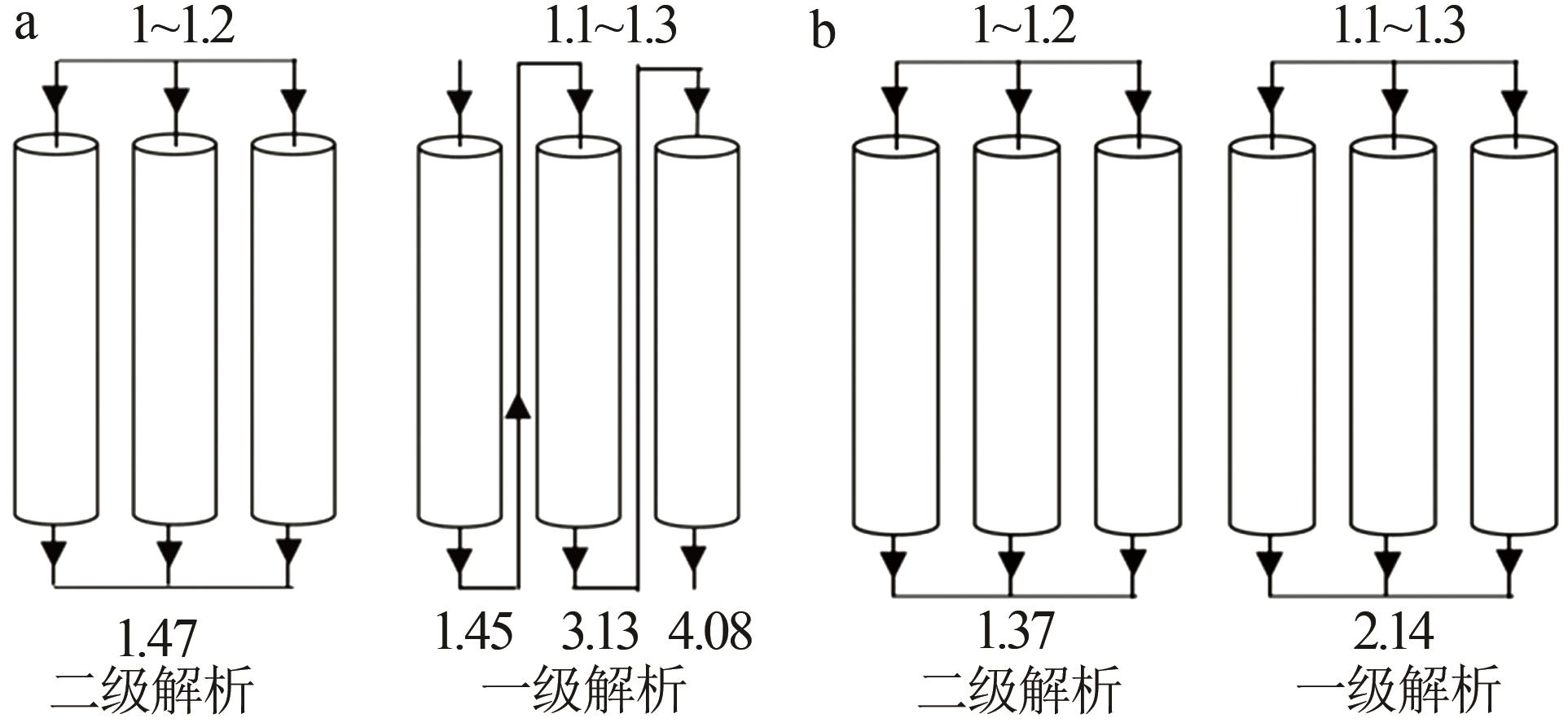
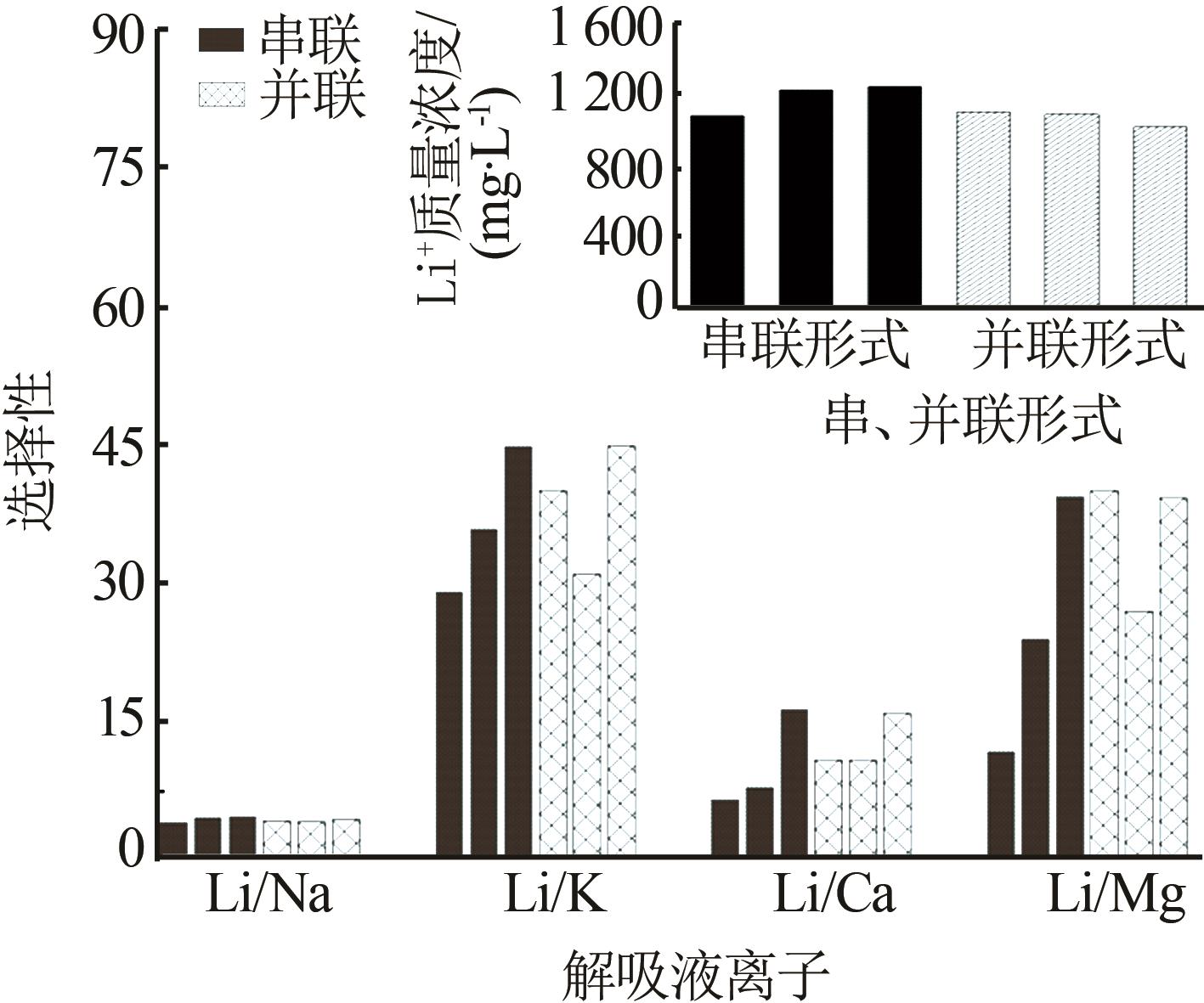
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 70-77.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0226
• Industrial Techniques • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application research of titanium adsorbent of carbonate-type salt lake in Tibet
JI Ying1( ), ZHANG Ying2, HOU Xuechao1, ZHU Xiaofeng1, JIANG Run1, PENG Wenjuan1, SUN Guangdong1, LÜ Long1(
), ZHANG Ying2, HOU Xuechao1, ZHU Xiaofeng1, JIANG Run1, PENG Wenjuan1, SUN Guangdong1, LÜ Long1( )
)
- 1.Beijing Origin Water Membrane Technology Co. , Ltd. , Beijing 101400, China
2.Beijing Huateyuan Technology Co. , Ltd. , Beijing 100080, China
-
Received:2023-04-21Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-11-16 -
Contact:Lü Long E-mail:18244606382@139.com;lvlong612@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JI Ying, ZHANG Ying, HOU Xuechao, ZHU Xiaofeng, JIANG Run, PENG Wenjuan, SUN Guangdong, LÜ Long. Application research of titanium adsorbent of carbonate-type salt lake in Tibet[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 70-77.
share this article
| 1 | 李康,王建平.中国锂资源开发利用现状及对策建议[J].资源与产业,2016,18(1):82-86. |
| LI Kang, WANG Jianping.China′s lithium resource development actuality and approaches[J].Resources & Industries,2016,18(1):82-86. | |
| 2 | 罗清平,郭朋成,李存增,等.我国锂资源分布及提取工艺研究现状[J].湿法冶金,2012,31(2):67-70. |
| LUO Qingping, GUO Pengcheng, LI Cunzeng,et al.Distribution of lithium resources and research status on lithium extraction technology[J].Hydrometallurgy of China,2012,31(2):67-70. | |
| 3 | SUN Ying, WANG Qi, WANG Yunhao,et al.Recent advances in magnesium/lithium separation and lithium extraction technologies from salt lake brine[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2021,256:117807. |
| 4 | GUO Xiaoyu, HU Shaofang, WANG Chenxi,et al.Highly efficient separation of magnesium and lithium and high-valued utilization of magnesium from salt lake brine by a reaction-coupled separation technology[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(19):6618-6626. |
| 5 | XU Shanshan, SONG Jianfeng, BI Qiuyan,et al.Extraction of lithium from Chinese salt-lake brines by membranes:Design and practice[J].Journal of Membrane Science,2021,635:119441. |
| 6 | ZHANG Ye, SUN Wei, XU Rui,et al.Lithium extraction from water lithium resources through green electrochemical-battery approaches:A comprehensive review[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,285:124905. |
| 7 | 柏春,郭敏,张慧芳,等.离子筛型锂吸附剂吸附法从盐湖卤水/海水中提锂的研究进展[J].化工进展,2017,36(3):802-809. |
| BAI Chun, GUO Min, ZHANG Huifang,et al.The research progress of extracting lithium from brine by lithium ion sieve[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2017,36(3):802-809. | |
| 8 | 路青强,陈琳琳,巢艳红,等.钛系锂离子筛用于盐湖提锂的研究进展[J].化工进展,2021,40(S1):1-12. |
| LU Qingqiang, CHEN Linlin, CHAO Yanhong,et al.Research progress of titanium-based lithium ion sieve for extracting lithium from salt lake brine[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(S1):1-12. | |
| 9 | 卞维柏,潘建明.选择性吸附提锂材料的研究进展[J].化工进展,2020,39(6):2206-2217. |
| BIAN Weibai, PAN Jianming.Research progress in selective adsorption materialsfor lithium extraction[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020,39(6):2206-2217. | |
| 10 | 许鑫.高效锂离子选择性吸附材料的设计、制备及性能研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2017. |
| 11 | 张理元,沈如倩,阳金菊,等.锂离子筛研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(5):28-37. |
| ZHANG Liyuan, SHEN Ruqian, YANG Jinju,et al.Research progress on lithium ion sieves[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(5):28-37. | |
| 12 | ZHANG Liyuan, HE Gang, ZHOU Dali,et al.Study on transformation mechanism of lithium titanate modified with hydrochloric acid[J].Ionics,2016,22(11):2007-2014. |
| 13 | SHI Xichang, ZHANG Zhibing, ZHOU Dingfang,et al.Synthesis of Li+ adsorbent(H2TiO3) and its adsorption properties[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2013,23(1):253-259. |
| 14 | 王卓,黄冉笑,吴大天,等.盐湖卤水型锂矿基本特征及其开发利用潜力评价[J].中国地质,2023,50(1):102-117. |
| WANG Zhuo, HUANG Ranxiao, WU Datian,et al.The basic characteristics and development potential evaluation of salt lake brine-type lithium deposits[J].Geology in China,2023,50(1):102-117. | |
| 15 | 乜贞,伍倩,丁涛,等.中国盐湖卤水提锂产业化技术研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(10):1-12. |
| NIE Zhen, WU Qian, DING Tao,et al.Research progress on industrialization technology of lithium extraction from salt lake brine in China[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(10):1-12. | |
| 16 | 刘成林,余小灿,袁学银,等.世界盐湖卤水型锂矿特征、分布规律与成矿动力模型[J].地质学报,2021,95(7):2009-2029. |
| LIU Chenglin, YU Xiaocan, YUAN Xueyin,et al.Characteristics,distribution regularity and formation model of brine-type Li deposits in salt lakes in the world[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,95(7):2009-2029. | |
| 17 | 姜贞贞,刘高令,卓玛曲西,等.我国锂资源供需现状下西藏盐湖锂产业现状及对策建议[J].盐湖研究,2021,29(3):104-110. |
| JIANG Zhenzhen, LIU Gaoling, ZHUO Maquxi,et al.Present situation and suggestions of saline lake lithium resource in Tibet under the current situation of supply and demand of lithium resources in China[J].Journal of Salt Lake Research,2021, 29(3):104-110. | |
| 18 | 袁俊生,杨树娥,邓会宁.连续离子交换技术及其在海水提钾的应用[J].盐业与化工,2007,36(3):27-30. |
| YUAN Junsheng, YANG Shue, DENG Huining.The technology of continuous ionic exchange and its application in extracting potassium from seawater[J].Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry,2007,36(3):27-30. | |
| 19 | 黄根树,徐美娟,杨套伟,等.连续离子交换法分离发酵液中的L-精氨酸[J].食品与发酵工业,2017,43(6):1-7. |
| HUANG Genshu, XU Meijuan, YANG Taowei,et al.Recovery of L-arginine in the fermentation broth by continuous ion exchange[J].Food and Fermentation Industries,2017,43(6):1-7. | |
| 20 | 李小为.钛系锂离子筛的构筑及其锂吸附性能研究[D].镇江:江苏大学,2021. |
| 21 | 顾俊杰,李增荣,唐发满,等.用于盐湖卤水吸附法提锂的连续离子交换工艺研究[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(7):46-51. |
| GU Junjie, LI Zengrong, TANG Faman,et al.Study on continuous ion exchange process applied in lithium extraction from salt lake brine with adsorption method[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(7):46-51. | |
| 22 | 周喜诚.吸附法从盐湖卤水中提锂及制备碳酸锂的工艺研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013. |
| 23 | 颜辉.新型锂吸附剂的吸附性能及提锂工艺的研究[D].成都:成都理工大学,2014. |
| 24 | 陈旺,蒋磊,潘巧珍,等.钛系锂离子筛的制备及其吸附性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(10):47-51. |
| CHEN Wang, JIANG Lei, PAN Qiaozhen,et al.Research on preparation and adsorption performance of titanium lithium ion sieve[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(10):47-51. | |
| 25 | 张丽芬.偏钛酸型锂吸附剂的制备及性能研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2010. |
| [1] | LIU Jie, SHI Xueru, WEI Shubing, CAO Xinxin. Artificial interface layer construction and sodium storage performance of P2-type layered oxide cathode [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 39-44. |
| [2] | CHEN Haixia, YAN Hong, SUN Yunlong, MA Guoqiang. Research progress of lithium resource extraction technology [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(1): 9-22. |
| [3] | FU Yu, DENG Mi, HUANG Donggen, WAN Jinbao. Research progress of lithium extraction technology from salt lake brine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 9-16. |
| [4] | WANG Yansu, LIU Guozhu, YU Haibin. Research progress of platinum-based propane dehydrogenation catalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(7): 1-9. |
| [5] | HAN Hongjing, ZHANG Jingze, LAMAO Zhuoma, HAN Jizhe, WU Yongmin, TANG Weiping. Preparation of Al-Co co-doped lithium manganese oxide and its adsorption performance of lithium [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(7): 38-44. |
| [6] | TIAN Yuling, CHENG Yang, HAN Rong, ZHOU Mei, WANG Chengjie, GE Qiangru. Effect of CaO on heavy metals stability and adsorption properties of sludge-derived biochar [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 124-129. |
| [7] | LUO Zhibo, WANG Huaiyou, WANG Min, DU Baoqiang. Effect of purity on thermo-physical properties of 60% NaNO3-40% KNO3 binary molten salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 43-49. |
| [8] | WANG Yansu, LIU Guozhu, YU Haibin. Research progress of non-precious metal catalysts for propane dehydrogenation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(12): 1-11. |
| [9] | ZHU Ruisong, CAO Jing, LIU Taoran, LI Yingwen, GAO Fei, HU Xuesheng. Research progress of lithium extraction technology and industrialization of unconventional brines in global [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 1-11. |
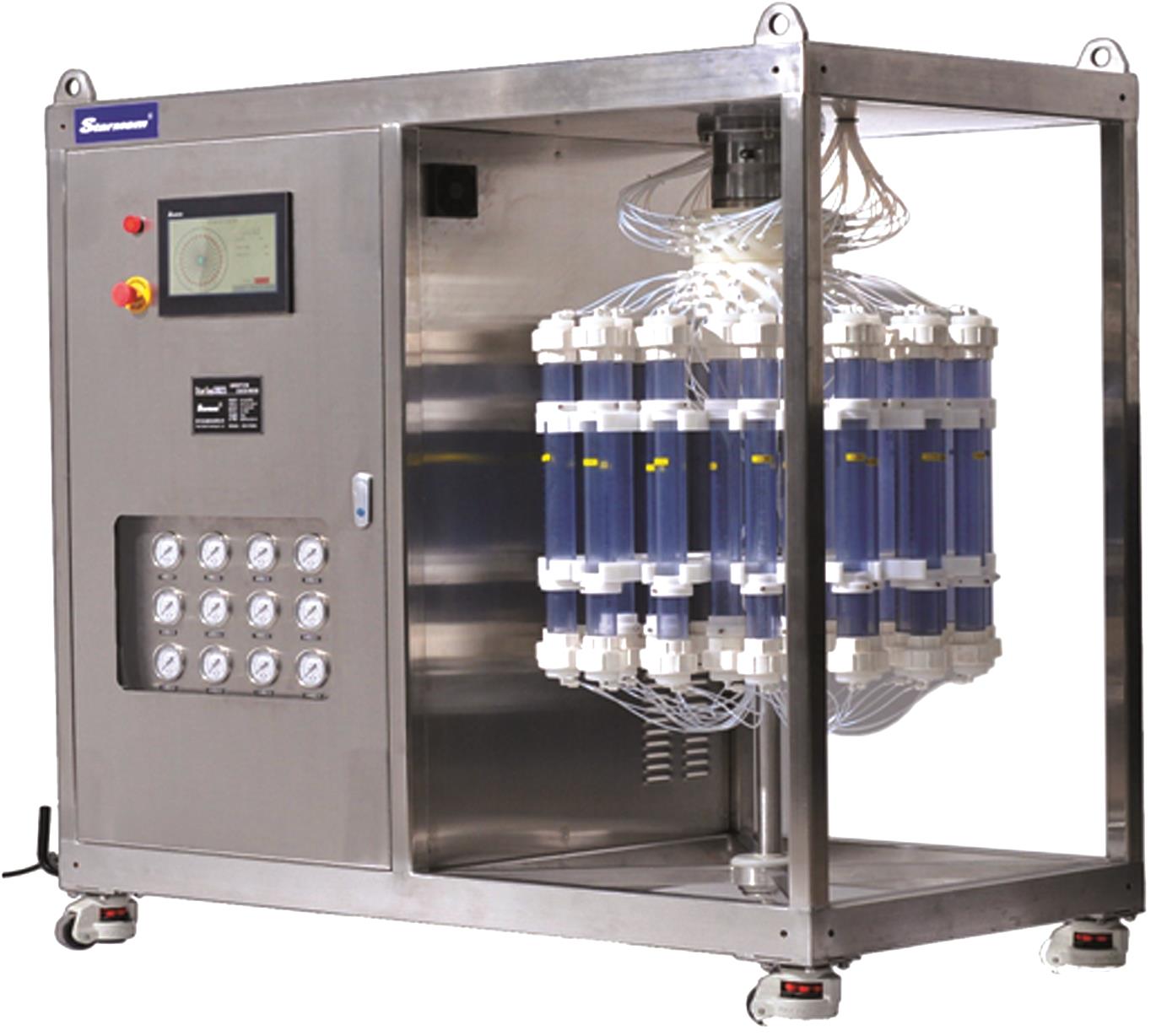
| [10] | HU Yue, MO Hengliang, LI Tianyu, PENG Wenjuan, SUN Guangdong, XIAO Hongkang, CHEN Yili, LI Suoding, TANG Yang. Study on spinning molding and performance of Ti-based lithium ion sieve powder and PVDF resin [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 58-63. |
| [11] | LAI Xianrong, CHEN Zhouqin, SUN Hao, YANG Chao. Pilot study on lithium extraction by adsorption from raw brine of magnesium sulfate subtype salt lakes in Tibet [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 86-92. |
| [12] | LI Huifang, WANG Xiao, BAI Youpeng, ZHANG Shixiang. Study on extraction of lithium from low grade high clay leaching solution by solvent extraction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 63-69. |
| [13] | LIN Yuqing,ZHANG Yiren,QIU Yulong,ZHANG Jiayu,YU Jianguo. Progress and prospect of membrane technology in lithium extraction from salt lake brine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 33-45. |
| [14] | WANG Ping. Quantitative analysis of linkage between lithium supply and demand and lithium price [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(9): 1-13. |
| [15] | HAN Hongjing,WU Yongmin,CAO Yongsheng,HAN Tingting,TANG Weiping. Preparation of nano?flake polyhedral manganese based lithium ion sieve and its adsorption and desorption characteristic for Li+ [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(8): 59-65. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||