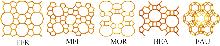
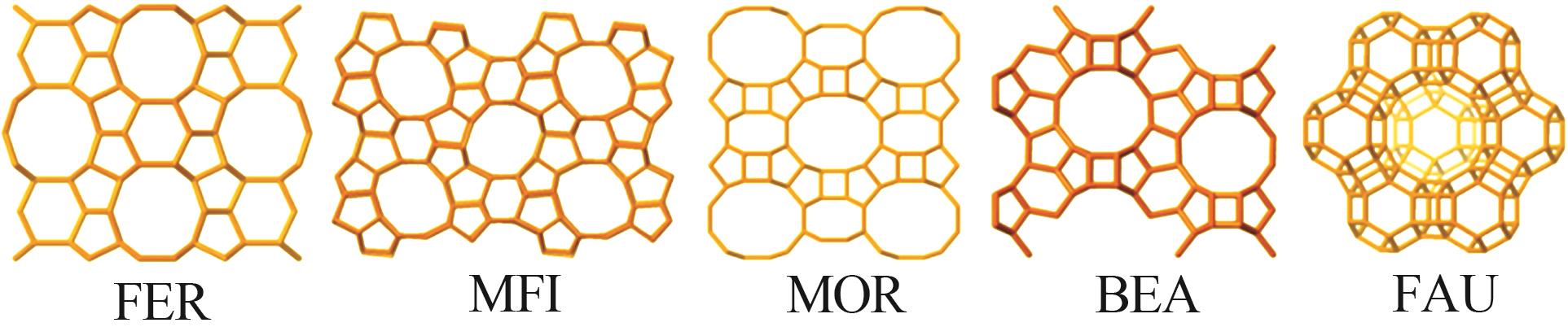
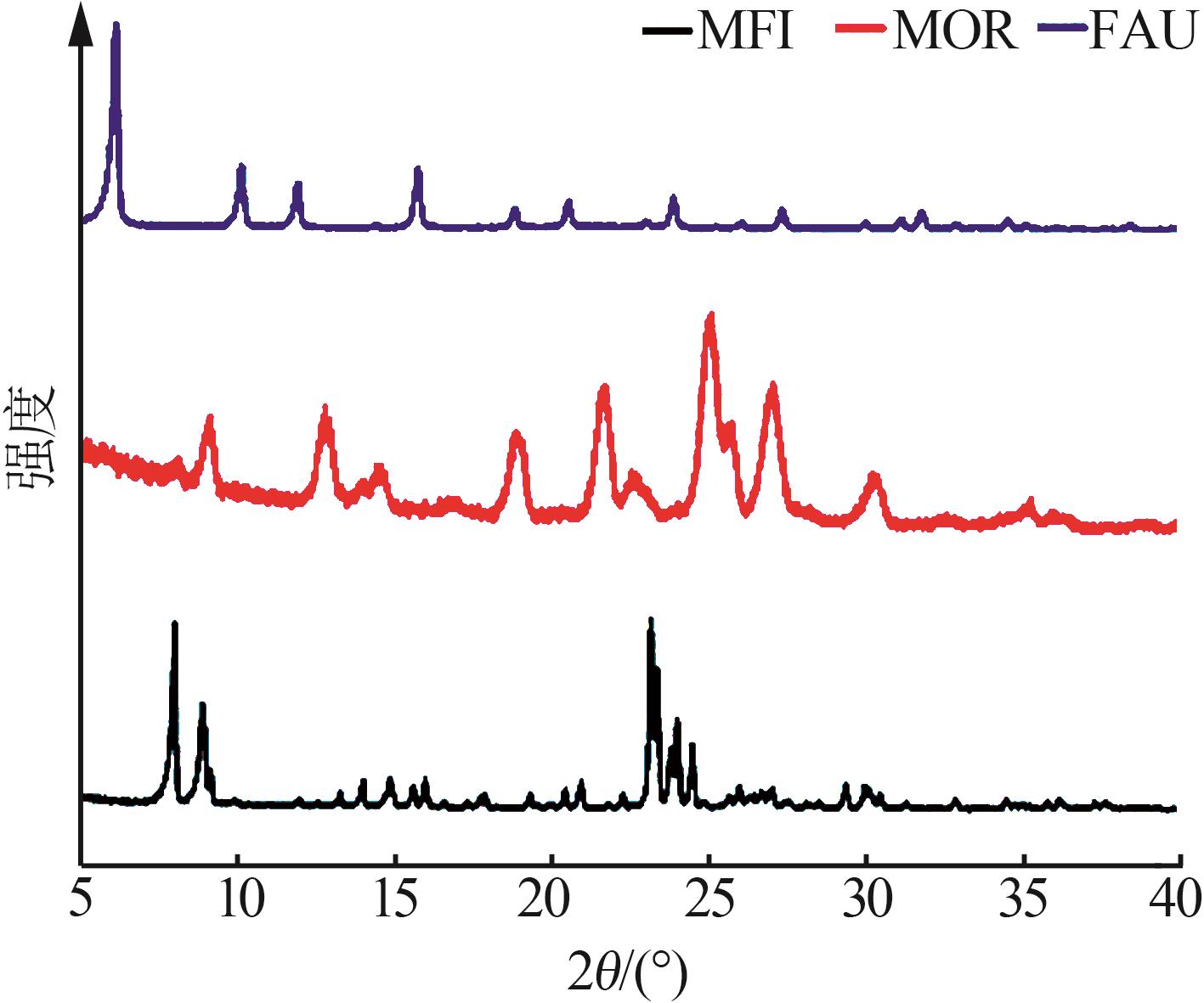
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 71-78.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0204
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
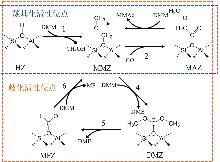
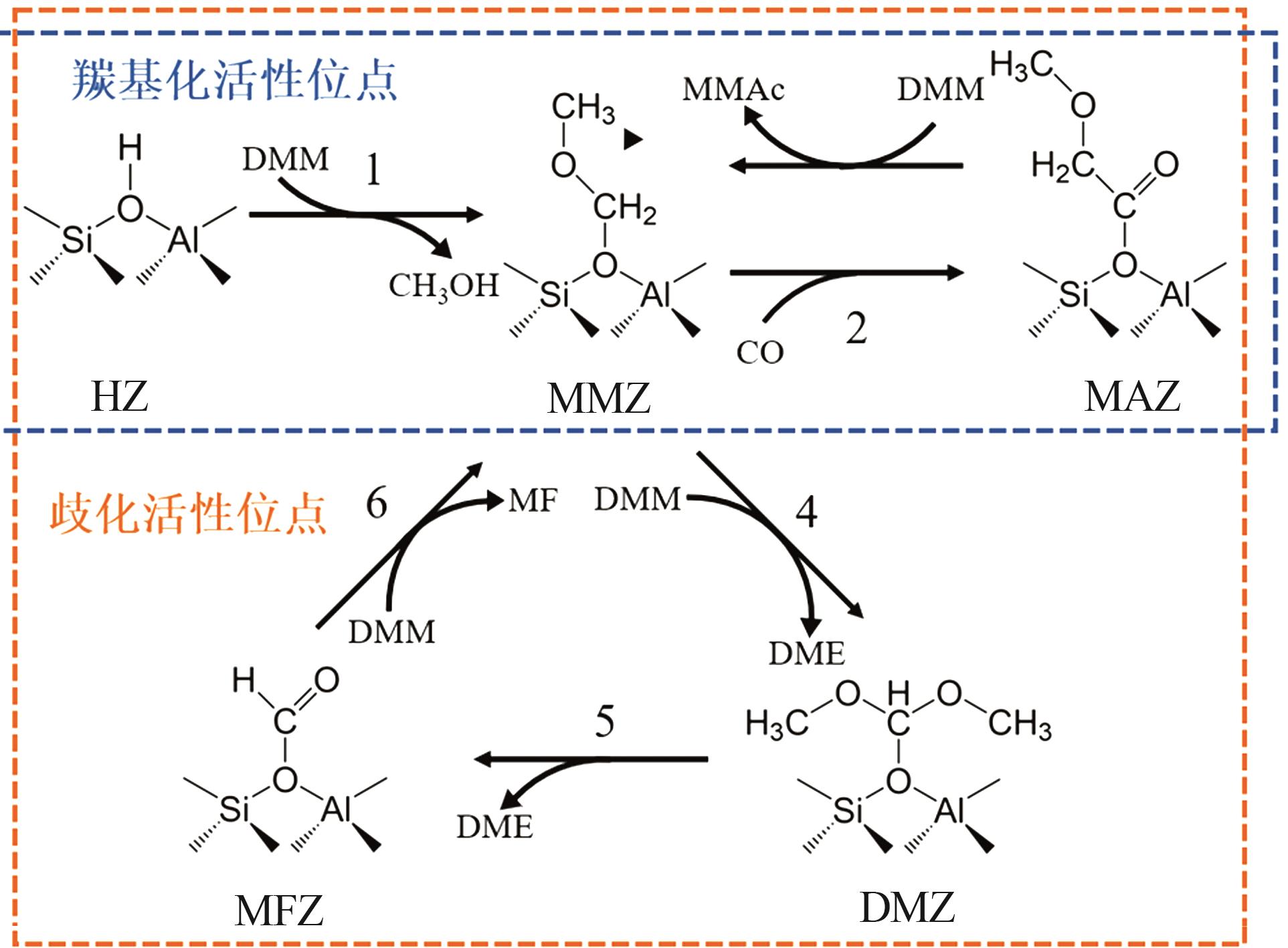
Mechanism study on influence of zeolite topology on dimethoxymethane carbonylation reaction
GAO Shaolei1,2( ), WANG Yingli1, QI Liang1(
), WANG Yingli1, QI Liang1( )
)
- 1. National Engineering Research Center of Lower?Carbon Catalysis Technology,Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics,Chi? nese Academy of Sciences,Dalian 116023,China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2024-04-09Online:2025-05-10Published:2024-06-18 -
Contact:QI Liang E-mail:gaoshaolei@dicp.ac.cn;qlyanfei920@dicp.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GAO Shaolei, WANG Yingli, QI Liang. Mechanism study on influence of zeolite topology on dimethoxymethane carbonylation reaction[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(5): 71-78.
share this article
| 1 | 倪友明.甲缩醛羰基化制甲氧基乙酸甲酯及水解制乙醇酸甲酯技术[Z].大连:中国科学院大连化学物理研究所,2022-12-01. |
| 2 | HENDRIKSEN D.Intermediates to ethylene glycol:Carbonylation of formaldehyde catalyzed by Nafion solid perfluorosulfonic acid resin[J].Preprint Papers,American Chemical Society,Division of Fuel Chemistry,1983,28:176. |
| 3 | SHI Qiqi, GUO Heqin, CHEN Congbiao,et al.An efficient Brønsted acidic polymer resin for the carbonylation of formaldehyde to glycolic acid[J].Reaction Kinetics,Mechanisms and Catalysis,2020,130(2):1027-1042. |
| 4 | CAO Xuemin, ZHANG Kun, WANG Yu,et al.Boosting the production of glycolic acid from formaldehyde carbonylation via the bifunctional PdO/ZSM-5 catalyst[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2023,62(43):17671-17680. |
| 5 | ZHU Zhihao, SUN Ying, YU Haijun,et al.Effect of polytetrafluoroethylene hollow fiber microstructure on formaldehyde carbonylation performance in membrane contactor[J].Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2023,55:148-155. |
| 6 | WANG Di, LV Jiangang.Synthesis of precursors to ethylene glycol via the acid⁃catalyzed carbonylation of formaldehyde[J].Catalysts,2023,13(10):1327. |
| 7 | CELIK F E, KIM T J, BELL A T.Vapor-phase carbonylation of dimethoxymethane over H-faujasite[J].Angewandte Chemie,2009,48(26):4813-4815. |
| 8 | CHEUNG P, BHAN A, SUNLEY G J,et al.Selective carbonylation of dimethyl ether to methyl acetate catalyzed by acidic zeolites[J].Angewandte Chemie,2006,45(10):1617-1620. |
| 9 | CHEUNG P, BHAN A, SUNLEY G J,et al.Site requirements and elementary steps in dimethyl ether carbonylation catalyzed by aci⁃dic zeolites[J].Journal of Catalysis,2007,245(1):110-123. |
| 10 | XIE Mingguan, FANG Xudong, LIU Hongchao,et al.Cyclic oxygenate⁃based deactivation mechanism in dimethyl ether carbonylation reaction over a pyridine⁃modified H-MOR catalyst[J].ACS Catalysis,2023,13(21):14327-14333. |
| 11 | XIE Mingguan, FANG Xudong, CHEN Zhiyang,et al.Insights into the CO-mediated deactivation mechanism for dimethyl ether carbonylation reaction over a H-MOR catalyst[J].Applied Catalysis A:General,2024,677:119701. |
| 12 | FAN Dong, CHEN Nan, HAN Songyue,et al.H2-promoted benign coke strategy for dimethyl ether carbonylation with long⁃term stability and high activity[J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2024,16(15):18745-18753. |
| 13 | LIU Junlong, XUE Huifu, HUANG Xiumin,et al.Stability enhancement of H-mordenite in dimethyl ether carbonylation to methyl acetate by pre⁃adsorption of pyridine[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2010,31(7):729-738. |
| 14 | CELIK F E, KIM T J, BELL A T.Effect of zeolite framework type and Si/Al ratio on dimethoxymethane carbonylation[J].Journal of Catalysis,2010,270(1):185-195. |
| 15 | SHAPOVALOV V, BELL A.Theoretical study of zeolite⁃catalyzed dimethoxymethane carbonylation to methyl methoxyaceta⁃te[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2010,114:17753-17760. |
| 16 | RASMUSSEN D B, CHRISTENSEN J M, TEMEL B,et al.Ketene as a reaction intermediate in the carbonylation of dimethyl ether to methyl acetate over mordenite[J].Angewandte Chemie,2015,54(25):7261-7264. |
| 17 | LIU Shiping, ZHU Wenliang, SHI Lei,et al.A highly efficient Nafion-H catalyst for vapour phase carbonylation of dimethoxymethane[J].RSC Advances,2014,4(77):40999-41002. |
| 18 | LIU Shiping, ZHU Wenliang, SHI Lei,et al.Activity enhancement of nafion resin:Vapor⁃phase carbonylation of dimethoxymethane over nafion⁃silica composite[J].Applied Catalysis A:General,2015,497:153-159. |
| 19 | CHEN Fei, SHI Lei, YAO Jie,et al.A highly efficient sulfonic acid resin for liquid⁃phase carbonylation of dimethoxymethane[J].Catalysis Science & Technology,2018,8(2):580-590. |
| 20 | YAO Jie, WANG Yan, BELLO S S,et al.Regulation of Brønsted acid sites in H-MOR for selective methyl methoxyacetate synthesis[J].Applied Organometallic Chemistry,2020,34(11):e5925. |
| 21 | SHEIKH K A, ZAGHINI FRANCESCONI V, ZEVACO T A,et al.Carbonylation of dimethoxymethane:A study on the reactivity of different solid acid catalysts[J].Catalysis Science & Technology,2024,14(5):1148-1166. |
| 22 | CHEN Fei, SHI Lei, BELLO S,et al.Excellent prospects in methyl methoxyacetate synthesis with a highly active and reusable sulfonic acid resin catalyst[J].New Journal of Chemistry,2020,44(4):1346-1353. |
| 23 | ZHANG Dongxi, SHI Lei, WANG Yan,et al.Effect of mass⁃transfer control on HY zeolites for dimethoxymethane carbonylation to methyl methoxyacetate[J].Catalysis Today,2018,316:114-121. |
| 24 | CHEN Fei, ZHANG Dongxi, SHI Lei,et al.Optimized pore structures of hierarchical HY zeolites for highly selective production of methyl methoxyacetate[J].Catalysts,2019,9(10):865. |
| 25 | XIE Zhiqiang, CHEN Congbiao, HOU Bo,et al.Study of the nature of high⁃silica H-Y acid sites in dimethoxymethane carbonylation by NH3 poisoning[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2018,122(18):9909-9917. |
| 26 | 梁瑞康,刘卓,孙泽平,等.铝源对HZSM-5分子筛中骨架铝落位及其甲缩醛气相羰基化性能的影响[J].工业催化,2023,31(7):23-31. |
| LIANG Ruikang, LIU Zhuo, SUN Zeping,et al.Effects of aluminium sources on the framework aluminum siting of HZSM-5 zeolite and its catalytic performance in dimethoxymethane carbonylation[J].Industrial Catalysis,2023,31(7):23-31. | |
| 27 | 孙泽平,武建兵,李鹏,等.柠檬酸处理对ZSM-5分子筛甲缩醛气相羰基化性能的影响[J].分子催化,2021,35(1):22-30. |
| SUN Zeping, WU Jianbing, LI Peng,et al.Effect of citric acid modification of ZSM-5 zeolite on vapor⁃phase dimethoxymethane carbonylation[J].Journal of Molecular Catalysis(China),2021,35(1):22-30. | |
| 28 | WU Jianbing, ZHANG Xiaoyan, SUN Zeping,et al.Effect of NaOH content in the synthesis gel on the catalytic performance of H-ZSM-5 zeolites in the gas phase carbonylation of dimethoxymethane[J].Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2019,47(10):1226-1234. |
| 29 | 张晓艳,武建兵,周玮,等.ZSM-5分子筛形貌及硅铝比对甲缩醛气相羰基化反应性能的影响[J].工业催化,2019,27(8):52-59. |
| ZHANG Xiaoyan, WU Jianbing, ZHOU Wei,et al.Effect of morphology and Si/Al ratio of ZSM-5 on gas phase carbonylation of dimethoxymethane[J].Industrial Catalysis,2019,27(8):52-59. | |
| 30 | ZHU Dali, WANG Linying, ZHANG Wenna,et al.Realizing fast synthesis of high⁃silica zeolite Y with remarkable catalytic performance[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2022,61(23):e202117698. |
| 31 | EMEIS C A.Determination of integrated molar extinction coefficients for infrared absorption bands of pyridine adsorbed on solid acid catalysts[J].Journal of Catalysis,1993,141(2):347-354. |
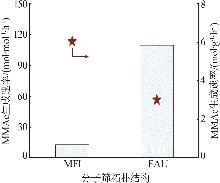
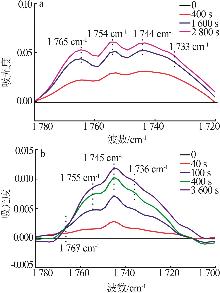
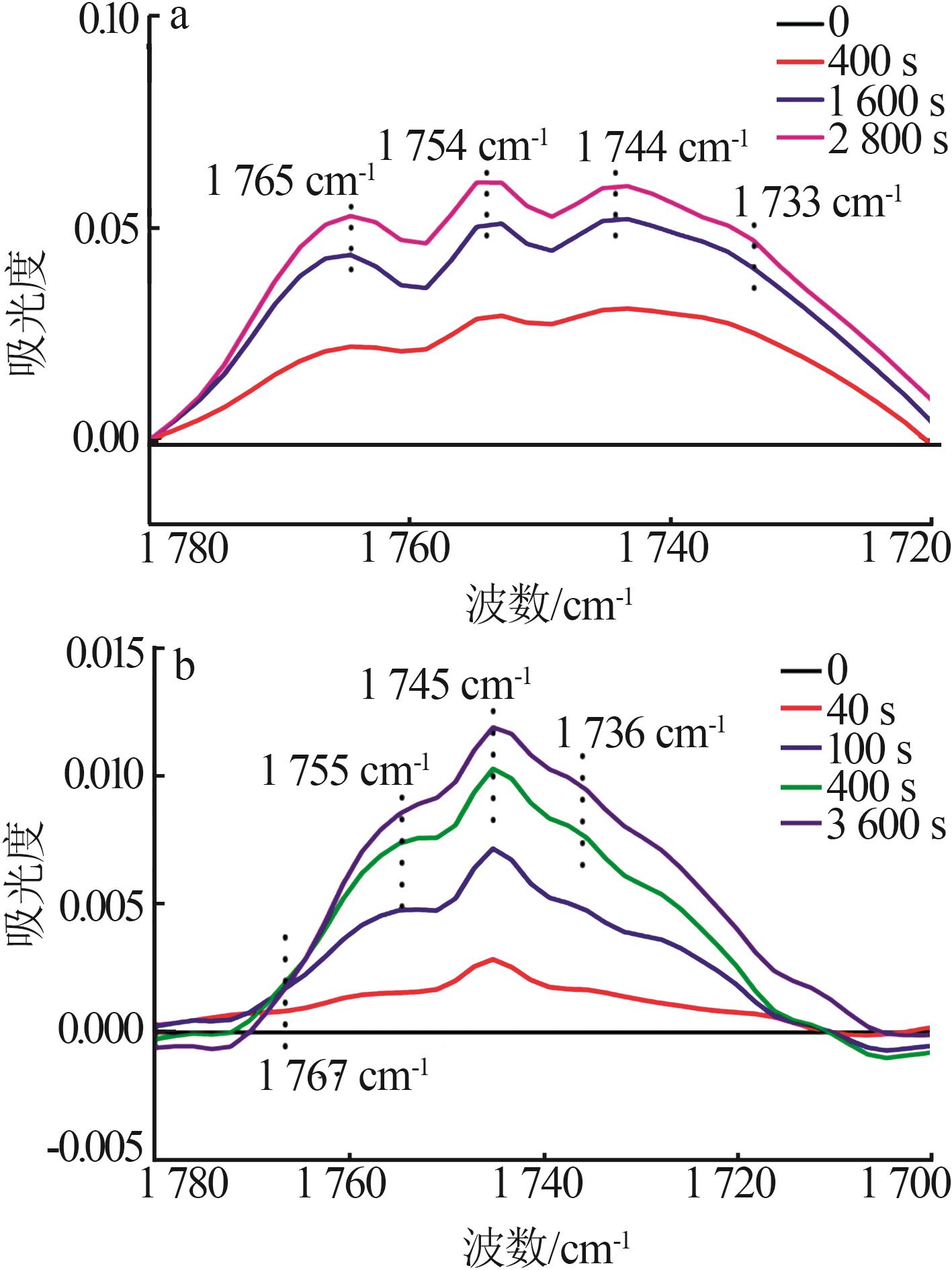
| 32 | CELIK F E, KIM T, MLINAR A N,et al.An investigation into the mechanism and kinetics of dimethoxymethane carbonylation over FAU and MFI zeolites[J].Journal of Catalysis,2010,274(2):150-162. |
| [1] | LIU Xinlong, YANG Zhenyu, HAO He, LIU Shuxin, WU Chenyang, WANG Xingli, MA Qingqing. Study on shaped 4A zeolite synthesized with aluminum extraction residue by fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 78-85. |
| [2] | TAN Shanyi, WEN Huizi, HE Shuyu, ZHANG Liwen, CHEN Shaohua, XI Benjun. Study on leaching behavior and kinetics of phosphorus from phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 105-112. |
| [3] | GUO Yingjun, WU Songsong, DING Chunyan, ZHAO Shikai, SONG Tao, WEN Guangwu. Preparation of SSZ-13 zeolite membrane from glass-ceramics-strontium feldspar by crystal transformation method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 76-82. |
| [4] | FAN Jingxin, LI Bin, HONG Luwei, HONG Meihua, GONG Xin. Research status and prospects of olefin removal catalyst from aromatic reforming oil [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 14-25. |
| [5] | ZHU Jicheng, YANG Qixin, LIANG Haoquan, WANG Zengkun, OUYANG Fugui, DI Jing, GAI Xikun. Effect of confined catalyst Ni@S2 on performance of methane dry reforming reaction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 138-146. |
| [6] | LIU Huangfei, ZHANG Li, LIU Tao. Research progress of fast synthesis technologies of zeolites [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 36-43. |
| [7] | ZENG Yijun, JIANG Ziwen, JIAN Chengzong, QUAN Xuejun. Study on deep extraction of chromium from calcium-free roasting slag of chromite ore [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 90-96. |
| [8] | MA Shuqing, LI Changwen, SHI Chenglong, QIN Yaru. Kinetic study of lithium extraction from solution with iron-based ionic liquid system [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 60-66. |
| [9] | FANG Fan, YAO Benlin, XIAO Yiqun, JIA Yanhong, CHEN Hui, LI Bin, HE Hui. Research progress on dissolution behavior and mechanism of uranium dioxide in nitric acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 34-43. |
| [10] | ZOU Yang, LU Zhiyan, HU Zhilin, SUN Ze. Study on metastable zone width and primary nucleation kinetics for cooling crystallization of KNO3 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 67-74. |
| [11] | WANG Jianjie, SHU Xiaolong, XIAO Xia, WANG Peng, FAN Xiaoqiang, KONG Lian, XIE Zean, ZHAO Zhen. Study on synthesis of hierarchical flower⁃like ZSM-5 zeolite and its catalytic performance for n-octane cracking [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 139-146. |
| [12] | CHENG Ziyang, CHEN Guofu. Early hydration kinetics research of nano-SiO2 and cement composite cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 80-87. |
| [13] | ZHANG Yu, ZHAO Guiyan, TIAN Yongchang, QIU Xiaokui, SUN Jiali, XU Lixin. Reaction kinetics of ethylenediamine hydrochloride with calcium hydroxide [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 64-69. |
| [14] | DI Lu, WANG Weiguo, CHEN Juexian, WU Chuanshu. Study on preparation of transition metal-supported Silicalite-1 zeolite catalyst and its catalytic performance for furfural hydrogenation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 125-132. |
| [15] | LAI Huilong, YU fei, YANG Dongxia, MA Jiangli, YIN Xuemei, CHANG Shiying. Research on NH3-SCR performance and ammonia storage characteristics based on different Cu-CHA catalyst schemes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 159-166. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||