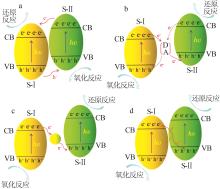
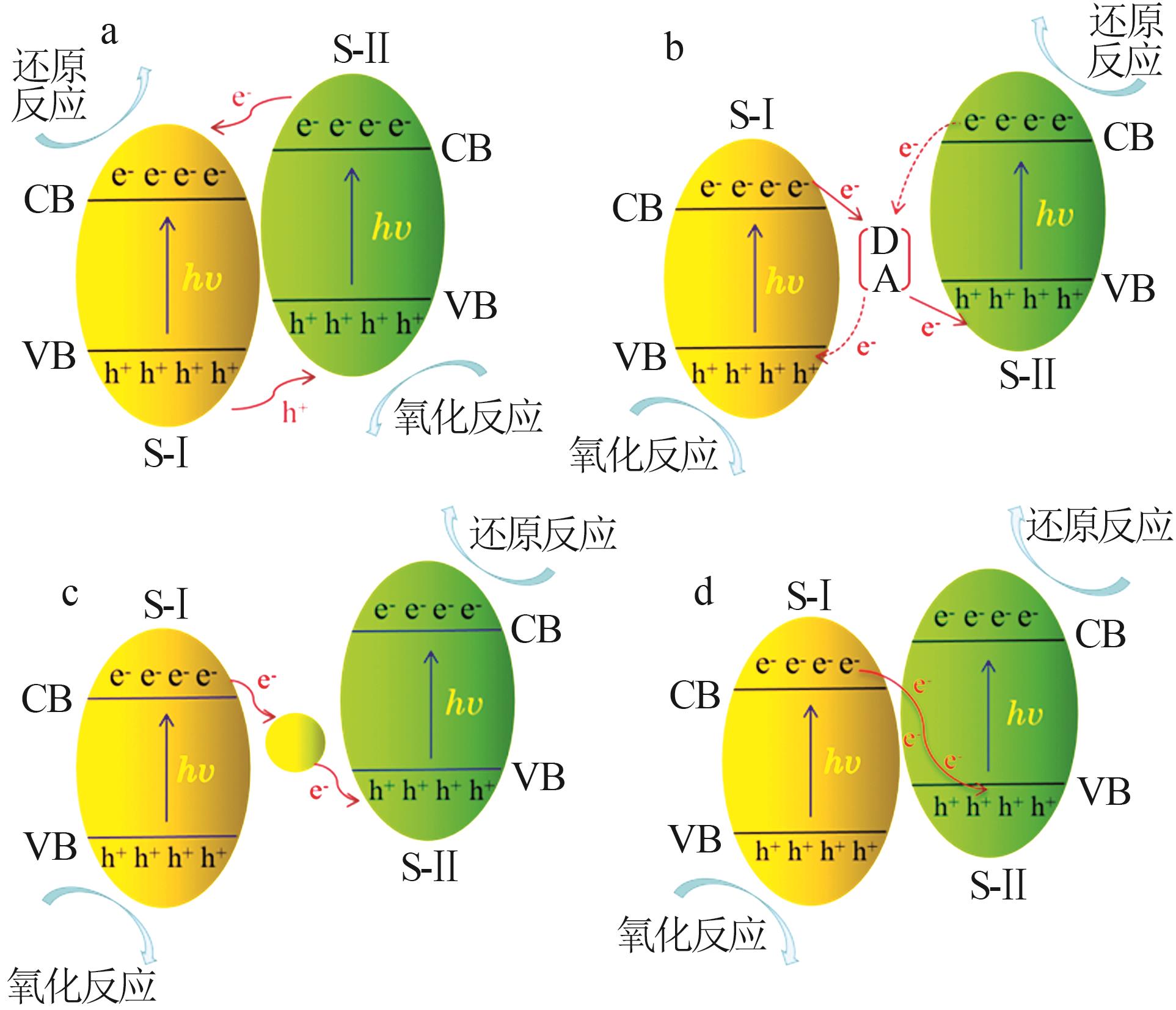
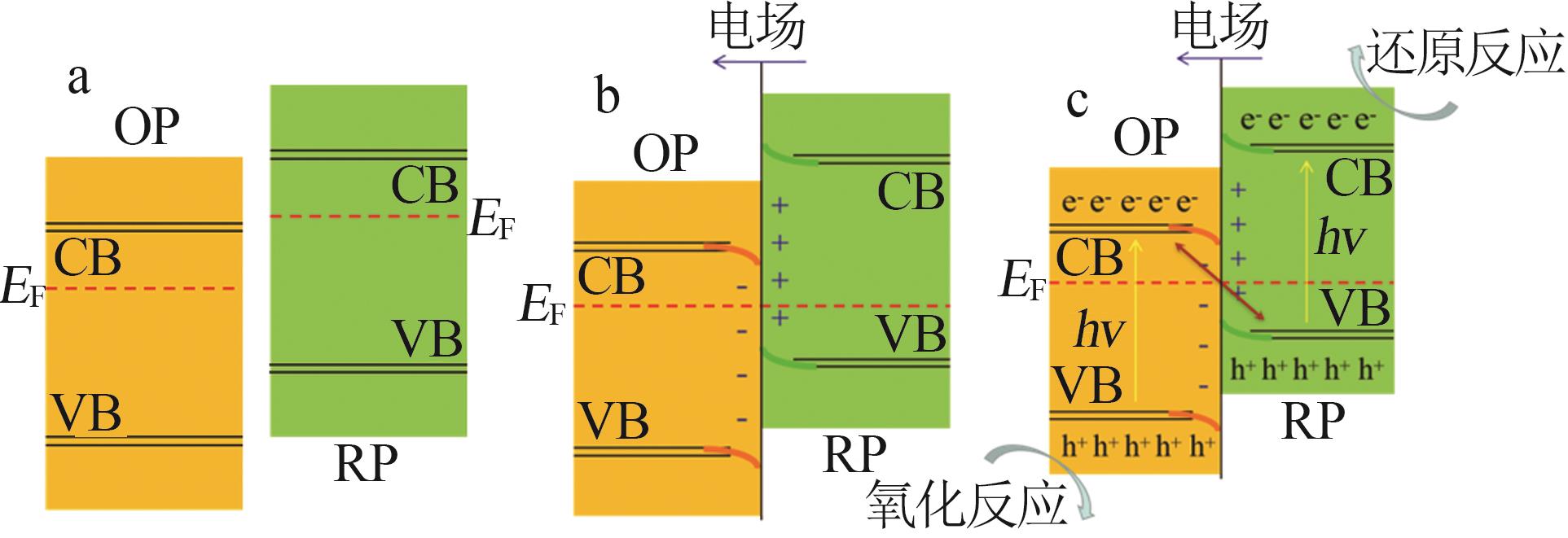
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 18-27.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0437
• Reviews and Special Topics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of S-type heterojunction photocatalysts
LIU Min1,2,3( ), HUANG Xiu1, ZHANG Liyuan1,2,3(
), HUANG Xiu1, ZHANG Liyuan1,2,3( )
)
- 1.College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Neijiang Normal University,Neijiang 641112,China
2.Key Laboratory of Fruit Waste Treatment and Resource Recycling of the Sichuan Provincial College,Neijiang 641112,China
3.Special Agricultural Resources in Tuojiang River Basin Sharing and Service Platform of Sichuan Province,Neijiang 641112,China
-
Received:2023-09-04Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:ZHANG Liyuan E-mail:liuminep@126.com;zhangliyuansir@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Min, HUANG Xiu, ZHANG Liyuan. Research progress of S-type heterojunction photocatalysts[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 18-27.
share this article
Table 2
Construction method of S-type heterojunction"
| 方法 | 定义 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 共沉淀法[ | 在溶液中含有两种或多种阳离子,其以均相存在于溶液中,加入沉淀剂,经沉淀反应后,可得到各种成分均一的沉淀 | 操作方便,条件简单 |
| 水热合成法[ | 以水或有机溶剂为介质,在密闭反应釜中进行高温化学反应 | 制备的催化剂尺寸均一、形貌可控、结晶良好且晶体团聚较轻 |
| 高温固相法[ | 在高温条件下,固体界面间经过接触、反应、成核、晶体生长反应而生成一大批复合氧化物 | 简洁,焙烧温度影响样品结构形貌 |
| 静电纺丝法[ | 利用电场作用克服表面张力形成纤维状从而改变其形貌 | 简单易操作;产量低,环境影响大 |
| 原位生长法[ | 在一定维度的材料上负载量子点 | 对材料尺寸有一定要求 |
| 微波水热法[ | 利用微波辐射的能量和水热反应的高温高压条件进行化学反应 | 成本低廉、操作简单、反应快速 |
| 热缩聚法[ | 在气氛炉中进行煅烧,高温高压条件下发生聚合反应 | 方便易操作;时间较长且需要稀有气体 |
| 静电自组装法[ | 在特定条件下,分子依赖非共价键分子间作用力自发连接成结构稳定的分子聚集体 | 对分子的尺寸及空间方向有特定要求 |
Table 3
H2-evolution of S-type heterojunction photocatalysts"
| S型异质结 | 助催化剂 (质量分 数/%) | 光源 波长/nm | H2放出 率/(μmol· h-1·g-1) | 增强 因子 | 表观量 子产率/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiTe2/g-C3N4[ | Pt(3) | 300 W Xe lamp | 2 540.4 | 23.4 | — |
| HCCN/ACN[ | Pt(1) | 300 W Xe lamp | 5 534 | 6.6 | 3.62 |
| W18O49/HCN[ | — | 300 W Xe lamp (λ>420 nm) | 892 | 3.4 | 6.21 |
| Au/g-C3N4[ | — | 500 W Xe lamp (λ>400 nm) | 552.6 | 5.3 | — |
| ZIS/CDs/CN[ | Pt(1) | 300 W Xe lamp (λ>420 nm) | 17 580 | 2 | 12.73 |
| MoS2/CdIn2S4[ | — | 300 W Xe lamp (λ>400 nm) | 1 868.19 | 2.26 | — |
ZIS/ZnSe HNSs[ | Pt(1) | 300 W Xe lamp (λ> 420 nm) | 3 332.2 | — | 10.9 |
WO3/TiO2/ rGO[ | — | 350 W Xe lamp | 245.8 | 3.5 | 1.4 |
| ZCS@DBTCN[ | — | 300 W Xe lamp | 8 870 | — | 14.9 |
| Co3O4/ZnO[ | Pt(0.5) | 500 W Xe lamp (420~700 nm) | 2 241 | 1 834 | — |
| ZnBi2O4/ZnO[ | — | 570 W Xe lamp | 3 340 | 12.7 | — |
| WO3/CoP[ | — | 5 W white light | 4 417.2 | 5.06 | 2.02 |
| Bi2O2CO2/HPR[ | — | 300 W Xe lamp | 3 144 | 3 | — |
| 1 | HASIJA V, RAIZADA P, SUDHAIK A,et al.Recent advances in noble metal free doped graphitic carbon nitride based nanohybrids for photocatalysis of organic contaminants in water:A review[J].Applied Materials Today,2019,15:494-524. |
| 2 | YANG Xi, TIAN Zhen, CHEN Yufang,et al. In situ synthesis of 2D ultrathin cobalt doped g-C3N4 nanosheets enhances photocatalytic performance by accelerating charge transfer[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,859:157754. |
| 3 | LI Kaining, ZHANG Sushu, LI Yuhan,et al.MXenes as noble⁃metal⁃alternative co⁃catalysts in photocatalysis[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2021,42(1):3-14. |
| 4 | FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K.Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode[J].Nature,1972,238(5358):37-38. |
| 5 | PEDANEKAR R S, SHAIKH S K, RAJPURE K Y.Thin film photocatalysis for environmental remediation:A status review[J].Current Applied Physics,2020,20(8):931-952. |
| 6 | THIMSEN E, BISWAS S, LO C S,et al.Predicting the band structure of mixed transition metal oxides:Theory and experiment[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2009,113(5):2014-2021. |
| 7 | ZAREZADEH S, HABIBI-YANGJEH A, MOUSAVI M.Fabrication of novel ZnO/BiOBr/C-Dots nanocomposites with considerable photocatalytic performances in removal of organic pollutants under visible light[J].Advanced Powder Technology,2019,30(6):1197-1209. |
| 8 | KANAKARAJU D, YAHYA M S, WONG S P.Removal of chemical oxygen demand from agro effluent by ZnO photocatalysis and photo-Fenton[J].SN Applied Sciences,2019,1(7):738. |
| 9 | ZHU Bangyao, ZHANG Qi, LI Xiuyan,et al.Facile synthesis of ZnS/ZnO nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J].Phy⁃ sica Status Solidi (a),2018,215(23):1800359. |
| 10 | DAFARE S, DESHPANDE P S, BHAVSAR R S.Photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye on combustion synthesised Fe2O3 [J].Indian Journal of Chemical Technology,2013,20(6):406-410. |
| 11 | WANG Qizhao, LIAN Juhong, MA Qiong,et al.Photodegradation of Rhodamine B over a novel photocatalyst of feather keratin decorated CdS under visible light irradiation[J].New Journal of Chemistry,2015,39(9):7112-7119. |
| 12 | ZHANG Xian, JIA Feifei, YANG Bingqiao,et al.Oxidation of molybdenum disulfide sheet in water under in situ atomic force microscopy observation[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2017,121(18):9938-9943. |
| 13 | WANG Xinchen, MAEDA K, THOMAS A,et al.A metal⁃free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visiblelight[J].Nature Materials,2009,8:76-80. |
| 14 | ZHAO Chen, WANG Jiasheng, CHEN Xi,et al.Bifunctional Bi12O17Cl2/MIL-100(Fe) composites toward photocatalytic Cr(Ⅵ) sequestration and activation of persulfate for bisphenol A degradation[J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,752:141901. |
| 15 | YU Jun, CAO Jiao, YANG Zhaohui,et al.One⁃step synthesis of Mn-doped MIL-53(Fe) for synergistically enhanced generation of sulfate radicals towards tetracycline degradation[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2020,580:470-479. |
| 16 | CHEN Shifu, YANG Yunguang, LIU Wei.Preparation,characterization and activity evaluation of TiN/F-TiO2 photocatalyst[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,186(2/3):1560-1567. |
| 17 | RESZCZYNSKA J, GRZYB T, SOBCZAK J W,et al.Visible light activity of rare earth metal doped(Er3+,Yb3+or Er3+/Yb3+)titania photocatalysts[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2015,163:40-49. |
| 18 | STUCCHI M, BIANCHI C L, ARGIRUSIS C,et al.Ultrasound assisted synthesis of Ag-decorated TiO2 active in visible light[J].Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2018,40(Pt A):282-288. |
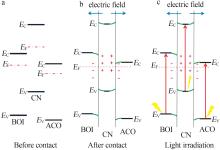
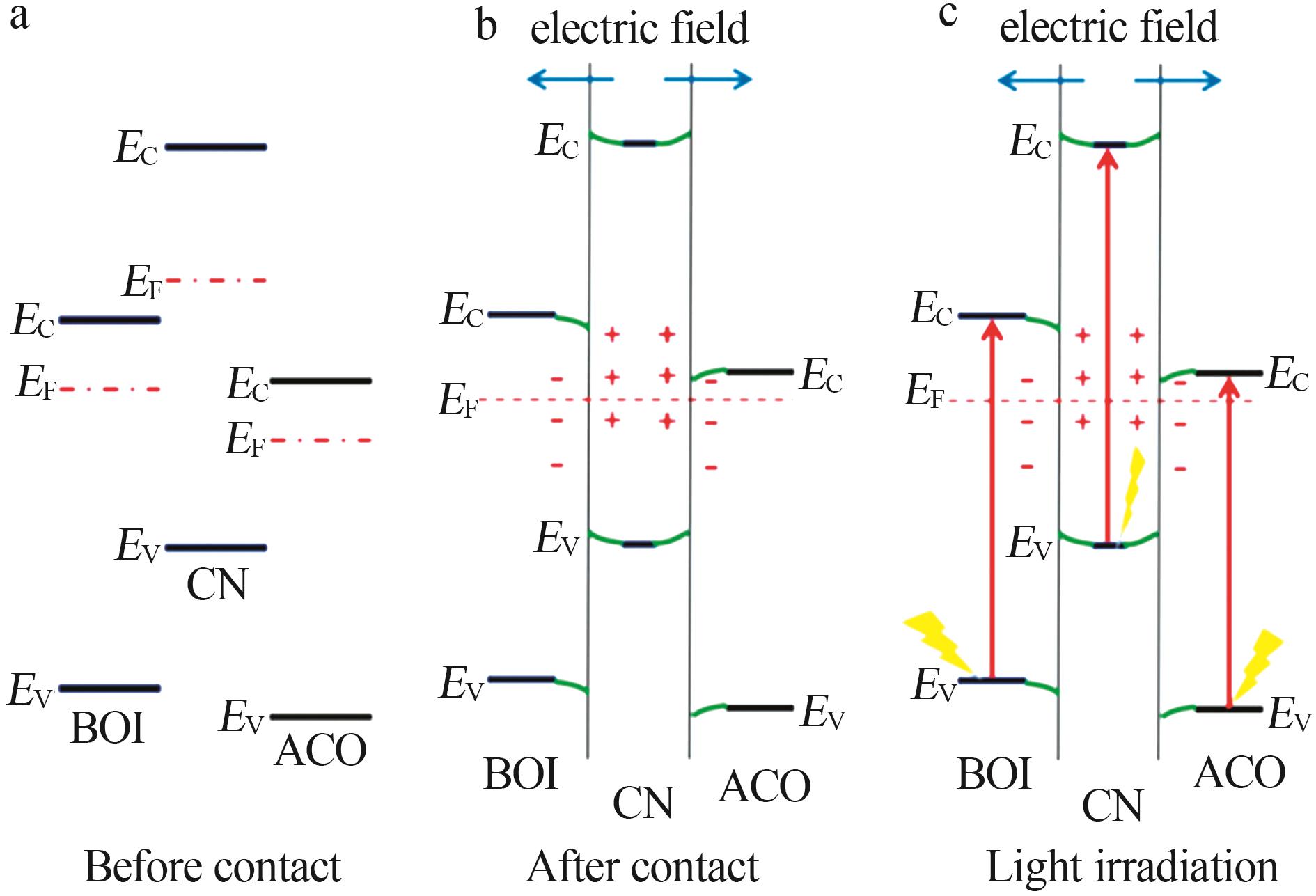
| 19 | QI Lifang, CHENG Bei, YU Jiaguo,et al.High⁃surface area mesoporous Pt/TiO₂ hollow chains for efficient formaldehyde decomposition at ambient temperature[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2016,301:522-530. |
| 20 | OHNO T.Development of visible light sensitive TiO2 photocatalysts and their sensitization using Fe3+ ions[J].Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute,2006,49(4):168-176. |
| 21 | BENTO R T, CORREA O V, PILLIS M F.On the surface chemistry and the reuse of sulfur⁃doped TiO2 films as photocatalysts[J].Materials Chemistry and Physics,2021,261:124231. |
| 22 | WU Ling, YU J C, FU Xianzhi.Characterization and photocatalytic mechanism of nanosized CdS coupled TiO2 nanocrystals under visible light irradiation[J].Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical,2006,244(1/2):25-32. ′ |
| 23 | ENESCA A, ANDRONIC L.Photocatalytic activity of S-scheme heterostructure for hydrogen production and organic pollutant removal:A mini⁃review[J].Nanomaterials,2021,11(4):871. |
| 24 | SERPONE N, BORGARELLO E, GRÄTZEL M.Visible light induced generation of hydrogen from H2S in mixed semiconductor dispersions;improved efficiency through inter⁃particle electron transfer[J].Journal of the Chemical Society,Chemical Communications,1984(6):342-344. |
| 25 | DANISH M, MUNEER M.Excellent visible⁃light⁃driven Ni-ZnS/g-C3N4 photocatalyst for enhanced pollutants degradation performance:Insight into the photocatalytic mechanism and adsorption isotherm[J].Applied Surface Science,2021,563:150262. |
| 26 | BEDJA I, KAMAT P V.Capped semiconductor colloids.Synthesis and photoelectrochemical behavior of TiO2-capped SnO2 nanocrystallites[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry,1995,99(22):9182-9188. |
| 27 | BARD A J.Photoelectrochemistry and heterogeneous photo⁃catalysis at semiconductors[J].Journal of Photochemistry,1979,10(1):59-75. |
| 28 | XU Quanlong, ZHANG Liuyang, CHENG Bei,et al.S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst[J].Chem,2020,6(7):1543-1559. |
| 29 | TADA H, MITSUI T, KIYONAGA T,et al.All⁃solid⁃state Z-scheme in CdS-Au-TiO2 three⁃component nanojunction syst⁃ em[J].Nature Materials,2006,5:782-786. |
| 30 | TACHIBANA Y, VAYSSIERES L, DURRANT J R.Artificial photosynthesis for solar water⁃splitting[J].Nature Photonics,2012,6:511-518. |
| 31 | LIU Jianjun, CHENG Bei, YU Jiaguo.A new understanding of the photocatalytic mechanism of the direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 heterostructure[J].Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics:PCCP,2016,18(45):31175-31183. |
| 32 | FU Junwei, XU Quanlong,LOW J,et al.Ultrathin 2D/2D WO3/g-C3N4 step⁃scheme H2-production photocatalyst[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2019,243:556-565. |
| 33 | JIANG Guoping, ZHENG Chaoyue, YAN Teng,et al.Cd0.8Mn0.2S/MoO3 composites with an S-scheme heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].Dalton Transactions,2021,50(15):5360-5369. |
| 34 | WANG Pengfei, LIU Yao, JIANG Ning,et al.Double S-scheme AgBr heterojunction co⁃modified with g-C3N4 and black phosphorus nanosheets greatly improves the photocatalytic activity and stability[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2021,329: 115540. |
| 35 | WANG Zhongliao, CHEN Yifan, ZHANG Liuyang,et al.Step⁃scheme CdS/TiO2 nanocomposite hollow microsphere with enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity[J].Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2020,56:143-150. |
| 36 | ZHANG Kailian, ZHOU Man, YU Changlin,et al.Construction of S-scheme g-C3N4/ZrO2 heterostructures for enhancing photocatalytic disposals of pollutants and electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].Dyes and Pigments,2020,180:108525. |
| 37 | ZHEN Yanzhong, YANG Chunming, SHEN Huidong,et al.Photocatalytic performance and mechanism insights of a S-scheme g-C3N4/Bi2MoO6 heterostructure in phenol degradation and hydrogen evolution reactions under visible light[J].Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics:PCCP,2020,22(45):26278-26288. |
| 38 | GE Haonan, XU Feiyan, CHENG Bei,et al.S-scheme heterojunction TiO2/CdS nanocomposite nanofiber as H2-production photocatalyst[J].ChemCatChem,2019,11(24):6301-6309. |
| 39 | HE Fei, ZHU Bicheng, CHENG Bei,et al.2D/2D/0D TiO2/C3N4/Ti3C2 MXene composite S-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced CO2 reduction activity[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2020,272:119006. |
| 40 | HUO Yao, ZHANG Jinfeng, WANG Zhongliao,et al.Efficient interfacial charge transfer of 2D/2D porous carbon nitride/bismuth oxychloride step⁃scheme heterojunction for boosted solar⁃driven CO2 reduction[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021, 585:684-693. |
| 41 | HUO Yao, ZHANG Jinfeng, DAI Kai,et al.Amine⁃modified S-scheme porous g-C3N4/CdSe⁃diethylenetriamine composite with enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity[J].ACS Applied Energy Materials,2021,4(1):956-968. |
| 42 | MEI Zihui, WANG Guohong, YAN Suding,et al.Rapid microwave⁃assisted synthesis of 2D/1D ZnIn2S4/TiO2 S-scheme heterojunction for catalyzing photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].Acta Physico Chimica Sinica,2021,37(6):2009097. |
| 43 | CHEN Yanli, SU Fengyun, XIE Haiquan,et al.One⁃step construction of S-scheme heterojunctions of N-doped MoS2 and S-doped g-C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,404:126498. |
| 44 | XU Feiyan, MENG Kai, CHENG Bei,et al.Unique S-scheme heterojunctions in self⁃assembled TiO2/CsPbBr3 hybrids for CO2 photoreduction[J].Nature Communications,2020,11:4613. |
| 45 | WANG Libo, CHENG Bei, ZHANG Liuyang,et al. In situ irradiated XPS investigation on S-scheme TiO2@ZnIn2S4 photocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction[J].Small,2021,17(41):2103447. |
| 46 | CHENG Chang, HE Bowen, FAN Jiajie,et al.An inorganic/organic S-scheme heterojunction H2-production photocatalyst and its charge transfer mechanism[J].Advanced Materials,2021,33(22):2100317. |
| 47 | CAO Shuang, ZHONG Bo, BIE Chuanbiao,et al.Insights into photocatalytic mechanism of H2 production integrated with organic transformation over WO3/Zn0.5Cd0.5S S-scheme heterojunction[J].Acta Physico Chimica Sinica,2024,40:2307016. |
| 48 | WEI Renbin, HUANG Zanling, GU Guanghui,et al.Dual⁃cocatalysts decorated rimous CdS spheres advancing highly⁃efficient visible⁃light photocatalytic hydrogen production[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2018,231:101-107. |
| 49 | LI Jinmao, WU Congcong, LI Jin,et al.1D/2D TiO2/ZnIn2S4 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2022,43(2):339-349. |
| 50 | ZHANG Bin, SHI Huanxian, HU Xiaoyun,et al.A novel S-scheme MoS2/CdIn2S4 flower⁃like heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic degradation and H2 evolution activity[J].Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics,2020,53(20):205101. |
| 51 | 薛晋波,高国翔,申倩倩,等.新型S型CdS-BiVO4异质结光电极的构筑及产氢性能研究[J].高等学校化学学报,2021,42(8):2493-2499. |
| XUE Jinbo, GAO Guoxiang, SHEN Qianqian,et al.Construction of a novel S-scheme CdS-BiVO4 heterojunction photoelectrodes and research on hydrogen production[J].Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2021,42(8):2493-2499. | |
| 52 | LI Teng, GUO Xin, ZHANG Lijun,et al.2D CoP supported 0D WO3 constructed S-scheme for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(39):20560-20572. |
| 53 | ZHANG Qiqi, BAI Xue, HU Xiaoyun,et al.Efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution over 2D/2D S-scheme NiTe2/g-C3N4 heterojunction with superhydrophilic surface[J].Applied Surface Science,2022,579:152224. |
| 54 | SUN Haoran, SHI Yuxing, SHI Weilong,et al.High⁃crystalline/amorphous g-C3N4 S-scheme homojunction for boosted photocatalytic H2 production in water/simulated seawater:Interfacial charge transfer and mechanism insight[J].Applied Surface Science,2022,593:153281. |
| 55 | LIU Qinqin, HE Xudong, PENG Jinjun,et al.Hot⁃electron⁃assisted S-scheme heterojunction of tungsten oxide/graphitic carbon nitride for broad⁃spectrum photocatalytic H2 generation[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2021,42(9):1478-1487. |
| 56 | MU Feihu, MIAO Xiaowei, CAO Jihui,et al.Integration of plasmonic effect and S-scheme heterojunction into gold decorated carbon nitride/cuprous oxide catalyst for photocatalysis[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,360:131948. |
| 57 | XU Zheng, SHI Weilong, SHI Yuxing,et al.Carbon dots as solid⁃state electron mediator and electron acceptor in S-scheme heterojunction for boosted photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].Applied Surface Science,2022,595:153482. |
| 58 | ZHONG Yueqi, LI Mengyuan, LUAN Xue,et al.Ultrathin ZnIn2S4/ZnSe heteronanosheets with modulated S-scheme enable high efficiency of visible⁃light⁃responsive photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2023,335:122859. |
| 59 | HE Fei, MENG Aiyun, CHENG Bei,et al.Enhanced photocatalytic H2-production activity of WO3/TiO2 step⁃scheme heterojunction by graphene modification[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2020,41(1):9-20. |
| 60 | LI Han, TAO Shanren, WAN S,et al.S-scheme heterojunction of ZnCdS nanospheres and dibenzothiophene modified graphite carbon nitride for enhanced H2 production[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2023,46:167-176. |
| 61 | MOHAMED R M, SHAWKY A.Visible⁃light⁃driven hydrogen production over ZIF-8 derived Co3O4/ZnO S-scheme based p-n heterojunctions[J].Optical Materials,2022,124:112012. |
| 62 | BAHADORAN A, MASUDY-PANAH S, DE LILE J R,et al.Novel 0D/1D ZnBi2O4/ZnO S-scheme photocatalyst for hydrogen production and BPA removal[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(47):24094-24106. |
| 63 | WANG Zhuanhu, BAI Yuexia, LI Yunpeng,et al.Bi2O2CO3/red phosphorus S-scheme heterojunction for H2 evolution and Cr(Ⅵ) reduction[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2022,609:320-329. |
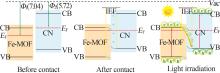
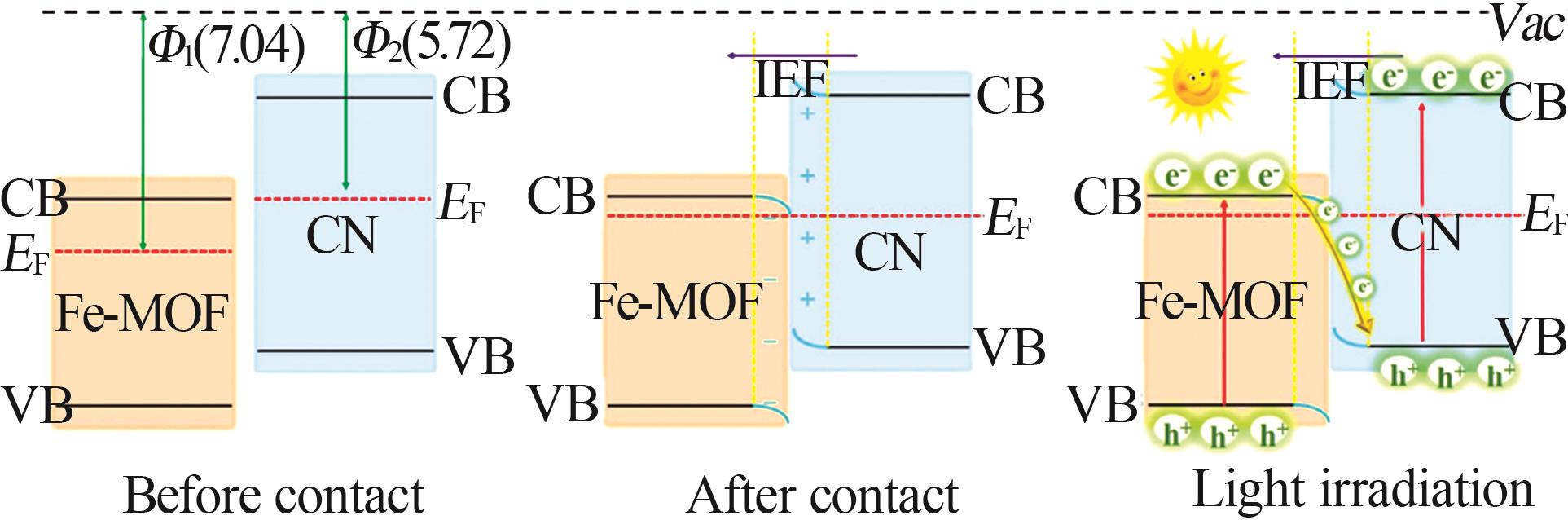
| 64 | ZHAO Xiaoxue, XU Mengyang, SONG Xianghai,et al.3D Fe-MOF embedded into 2D thin layer carbon nitride to construct 3D/2D S-scheme heterojunction for enhanced photoreduction ofCO2[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2022,43(10):2625-2636. |
| 65 | DONG Zhongliang, ZHOU Jiaxin, ZHANG Zhijie,et al.Construction of a p-n type S-scheme heterojunction by incorporating CsPbBr3 nanocrystals into mesoporous Cu2O microspheres for efficient CO2 photoreduction[J].ACS Applied Energy Materials,2022,5(8):10076-10085. |
| 66 | HE J, SHAO D W, ZHENG L C,et al.Construction of Z-scheme Cu2O/Cu/AgBr/Ag photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under visible light[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2017,203:917-926. |
| 67 | MALEFANE M E.Co3O4/Bi4O5I2/Bi5O7I C-scheme heterojunction for degradation of organic pollutants by light⁃emitting diode irradiation[J].ACS Omega,2020,5(41):26829-26844. |
| 68 | 马润东,郭雄,施凯旋,等.MoS2/g-C3N4 S型异质结的构建及光催化性能研究[J].无机材料学报,2023,38(10):1176-1182. |
| MA Rundong, GUO Xiong, SHI Kaixuan,et al.S-type heterojunction of MOS2/g-C3N4:Construction and photocatalysis[J].Journal of Inorganic Materials,2023,38(10):1176-1182. | |
| 69 | 徐凯旋,亢玉龙,高晓明,等.内电场增强S型异质结N-C3N4/BiOCl x I1- x 的制备及其光催化性能[J].复合材料学报,2023, 40(9):5134-5144. |
| XU Kaixuan, KANG Yulong, GAO Xiaoming,et al.Preparation of S-type heterojunction N-C3N4/BiOCl x I1- x with internal electric field and enhanced photocatalytic properties[J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2023,40(9):5134-5144. | |
| 70 | HU Xuecheng, WANG Guohong, WANG Juan,et al.Step⁃scheme NiO/BiOI heterojunction photocatalyst for rhodamine photodegradation[J].Applied Surface Science,2020,511:145499. |
| 71 | CHEN Zijun, GUO Hai, LIU Huiyun,et al.Construction of dual S-scheme Ag2CO3/Bi4O5I2/g-C3N4 heterostructure photocatalyst with enhanced visible⁃light photocatalytic degradation for tetracycline[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,438:135471. |
| [1] | SHI Wangfang, ZHANG Yongsheng. Study on NO x degradation performance of concrete-based non-metallic boron doped nitrogen-rich carbon nitride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 116-123. |
| [2] | LI Zihan, ZHANG Jiaqi, LI Shizhuo, LI Xinyu, LIU Shaozhuo, WANG Yihao, HAO Yucui, LIU Jian, LI Yanhua. Study on synthesis and catalytic mechanism of CdS/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 124-132. |
| [3] | CHENG Xiaoqiang, MA Jun, FENG Bin, BAI Liguang, ZHAO Xiaodong. Discussion on application of post-treatment process in fixed bed hydrogen peroxide production process [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 98-104. |
| [4] | SUN Qinghao, LI Keyan, GUO Xinwen. Study on photocatalytic benzyl alcohol oxidation coupled with hydrogen production over Pd/ZnIn2S4 nanosheets [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 113-119. |
| [5] | LIU Guangming. Study on photocatalytic and mechanical properties of C3N5/NH2-MIL-125(Ti) modified concrete mortar [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 120-128. |
| [6] | ZHANG Feigang, LIU Zhongli. Study on application of CuO/g-C3N4 composites in organic dye degradation and supercapacitors [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 129-136. |
| [7] | SUN Yanlong, YUAN Guangsheng, WANG Hongjun. Study on palladium modified mesoporous TiO2 nanorods for efficient photodegradation of tetracycline [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 147-153. |
| [8] | ZHANG Guoqiang, RONG Xilin, XIAO Zhenfang, XUE Ziran, CHENG Hao, FENG Jun, LIU Quan, LU Yao, HUANG Wenyi. Study on preparation and photocatalytic properties of bagasse carbon aerogels loaded with zinc oxide nanoparticles [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 131-138. |
| [9] | WANG Yawen, WANG Fangfang, GENG Siyu, JU Jia, CHEN Lei, CHEN Changdong. Study on preparation and photocatalytic performance of SrTiO3-SrWO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 143-149. |
| [10] | LI Jiangpeng, ZHANG Huibin. Synergistic degradation of methylene blue by photo-Fenton and photocatalytic with 3D porous LaFeO3/CeO2/SrTiO3 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 141-148. |
| [11] | TANG Bei. Preparation of ZnO/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalytic material and its degradation of pyridine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 133-142. |
| [12] | ZHOU Xuan, LI Mengrui, CHEN Yichen, FAN Huiqiang, WANG Bin, YUAN Gang. Research progress of nickel-based phosphide composites in improving of catalytic water electrolysis for hydrogen evolution performance [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 8-15. |
| [13] | YAO Jiankang, HU Shuozhen, NIU Dongfang, WU Jianping, ZHANG Xinsheng. Study on electrochemical treatment of sodium chloride organic waste salt in spice industry [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 105-115. |
| [14] | HUANG Jianan, LU Xiaoyu, WANG Mitang. Effect of Ba-La co-doping on degradation of methylene blue dye by TaON [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 146-151. |
| [15] | ZUO Guangling, WANG Minghui, PENG Yunying, DU Jia, YE Hongyong. Study on hnoneycomb-like LaVO4/Bi2O3 heterojunction for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 158-164. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||