Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 105-110.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0269
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on optimization of COD and fluoride removal on waste salt carbonization process by response surface method
LI Jun( ), ZHOU Zhaoan, LIU Xiaowen, MAO Anzhang, ZHOU Aiqing
), ZHOU Zhaoan, LIU Xiaowen, MAO Anzhang, ZHOU Aiqing
- Guangdong Feinan Resources Recycling Co.,Ltd.,Zhaoqing 526233,China
-
Received:2024-05-13Online:2025-04-10Published:2025-04-21
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Jun, ZHOU Zhaoan, LIU Xiaowen, MAO Anzhang, ZHOU Aiqing. Study on optimization of COD and fluoride removal on waste salt carbonization process by response surface method[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 105-110.
share this article
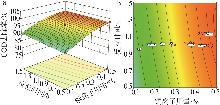
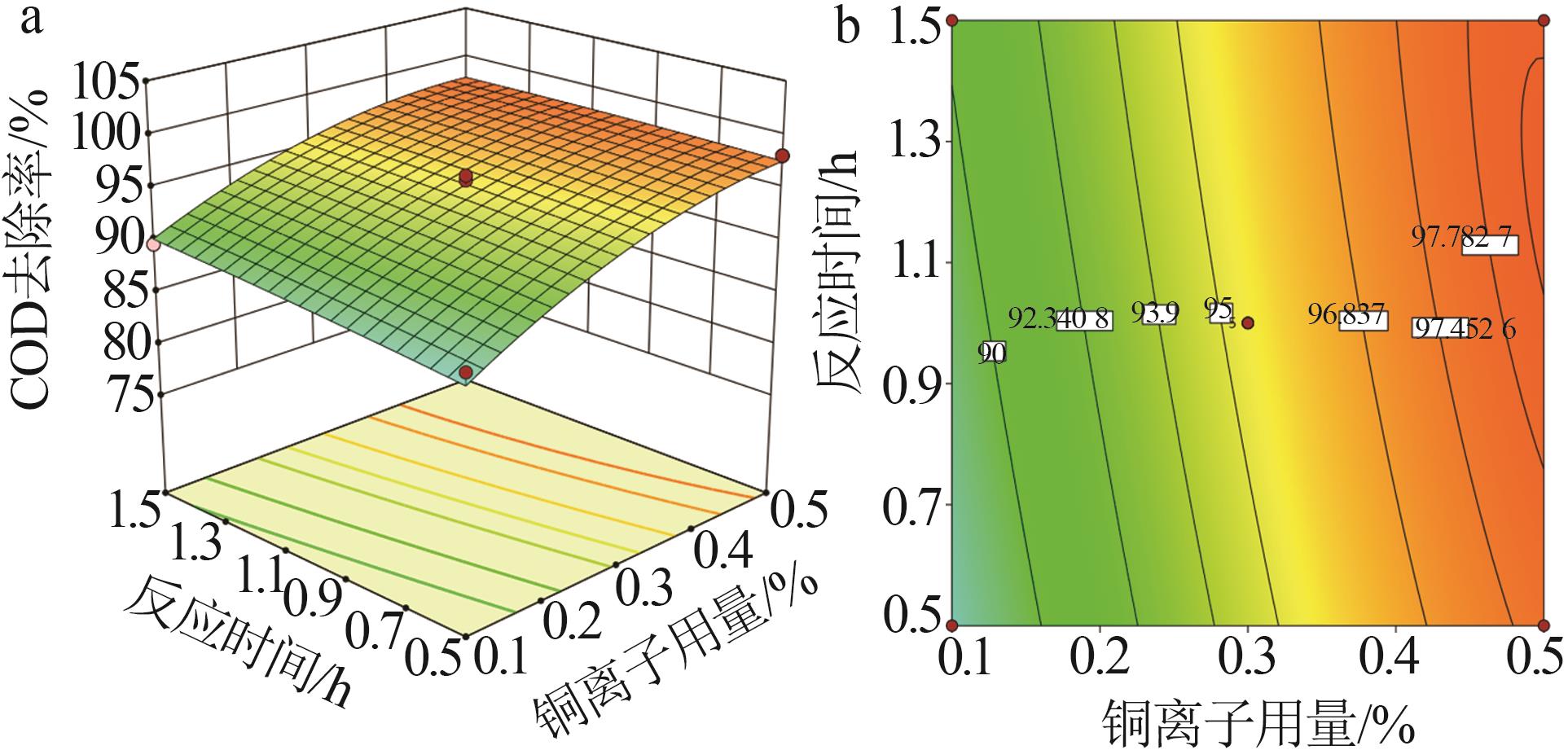
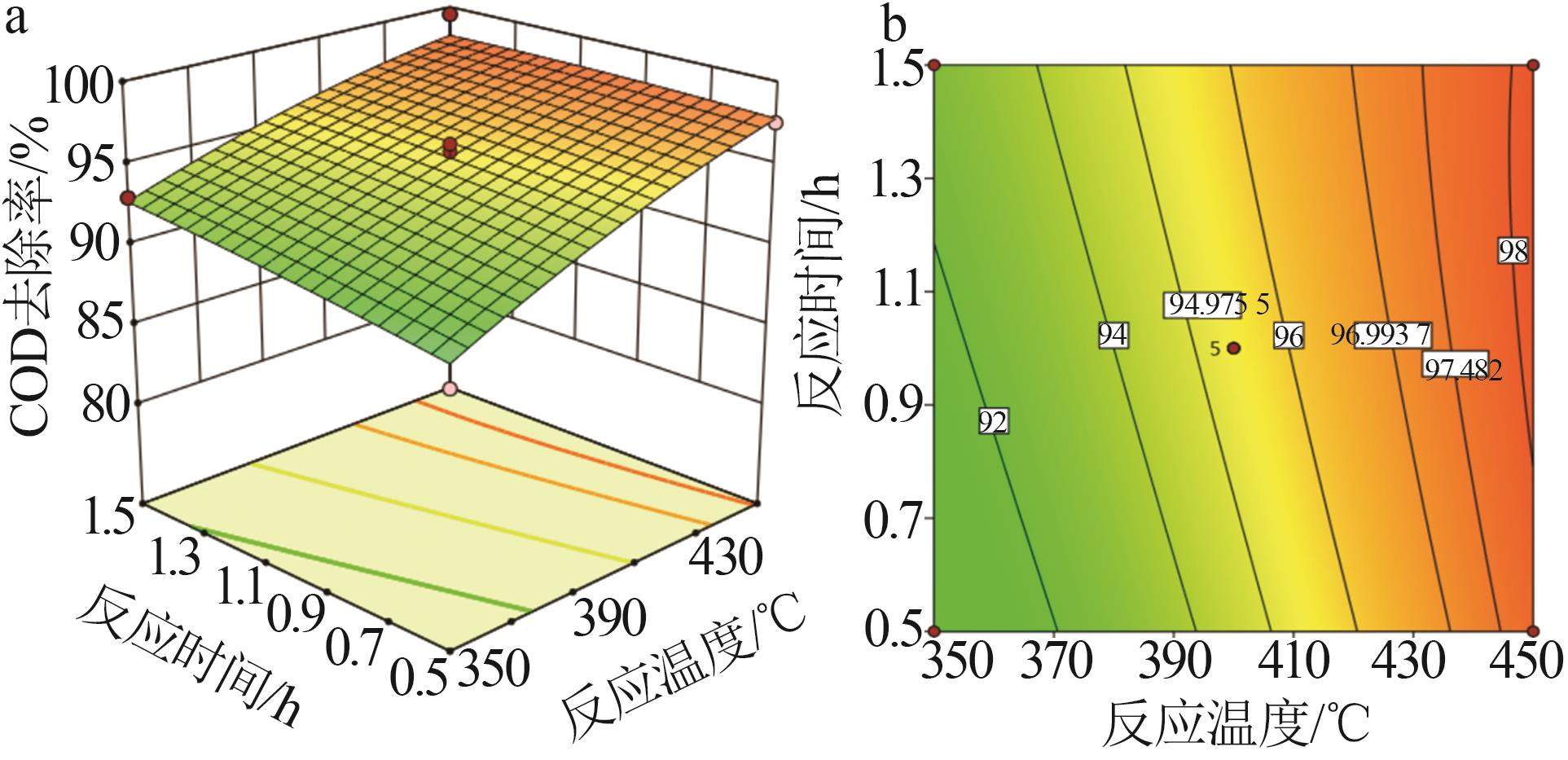
Table 3
BBD model and calculation results"
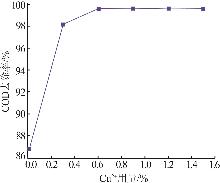
| 编号 | Cu2+用量/% | 反应温度/℃ | 反应时间/h | COD去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验值 | 预测值 | ||||
| 1 | 0.1 | 400 | 1.5 | 89.73 | 90.24 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 400 | 0.5 | 88.61 | 87.47 |
| 3 | 0.3 | 400 | 1.0 | 95.33 | 95.41 |
| 4 | 0.3 | 450 | 0.5 | 97.53 | 97.78 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 450 | 1.0 | 97.66 | 97.92 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 400 | 1.5 | 96.74 | 97.88 |
| 7 | 0.3 | 350 | 0.5 | 88.59 | 89.99 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 350 | 1.0 | 97.53 | 96.64 |
| 9 | 0.5 | 400 | 0.5 | 98.10 | 97.59 |
| 10 | 0.3 | 400 | 1.0 | 95.32 | 95.41 |
| 11 | 0.3 | 400 | 1.0 | 96.25 | 95.41 |
| 12 | 0.1 | 350 | 1.0 | 82.71 | 82.45 |
| 13 | 0.3 | 400 | 1.0 | 95.79 | 95.41 |
| 14 | 0.3 | 350 | 1.5 | 92.98 | 92.73 |
| 15 | 0.3 | 450 | 1.5 | 99.51 | 98.11 |
| 16 | 0.1 | 450 | 1.0 | 93.44 | 94.33 |
| 17 | 0.3 | 400 | 1.0 | 94.38 | 95.41 |
Table 4
Variance analysis of quadratic model"
方差 来源 | 平方和 | 自由度 | 均方 | F值 | P值 (Prob>F) | 显著性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 299.15 | 9 | 33.24 | 21.45 | 0.000 3 | 显著 |
| A | 157.89 | 1 | 157.89 | 101.86 | <0.000 1 | 显著 |
| B | 86.66 | 1 | 86.66 | 55.91 | 0.000 1 | 显著 |
| C | 4.70 | 1 | 4.70 | 3.03 | 0.125 3 | 不显著 |
| AB | 28.09 | 1 | 28.09 | 18.12 | 0.003 8 | 显著 |
| AC | 1.54 | 1 | 1.54 | 0.992 0 | 0.352 4 | 不显著 |
| BC | 1.45 | 1 | 1.45 | 0.936 8 | 0.365 3 | 不显著 |
| A² | 16.31 | 1 | 16.31 | 10.52 | 0.014 2 | 显著 |
| B² | 1.57 | 1 | 1.57 | 1.01 | 0.347 6 | 不显著 |
| C² | 0.095 7 | 1 | 0.095 7 | 0.061 7 | 0.810 9 | 不显著 |
| 残差 | 10.85 | 7 | 1.55 | |||
| 失拟项 | 8.92 | 3 | 2.97 | 6.18 | 0.055 4 | 不显著 |
| 纯误差 | 1.93 | 4 | 0.481 3 | |||
| 总和 | 310 | 16 |
| [1] | 高润,殷进,张楠,等.化工行业废盐产生现状及资源化利用研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(11):25-31. |
| GAO Run, YIN Jin, ZHANG Nan,et al.Current situation of waste salt generation and research progress on resource utilization in chemical industry [J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(11):25-31. | |
| [2] | 李彦伟,陈洪法,张树立,等.废盐处置工艺与设备解析[J].中国新技术新产品,2021(2):122-124. |
| LI Yanwei, CHEN Hongfa, ZHANG Shuli,et al.Analysis of waste salt disposal process and equipment[J].New Technology & New Products of China,2021(2):122-124. | |
| [3] | 丁志广,郭键柄,卢超.化工废盐无害化处理的实验研究[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(2):58-61. |
| DING Zhiguang, GUO Jianbing, LU Chao.Experimental study on harmless disposal of chemical waste salts[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(2):58-61. | |
| [4] | 黄和风,余华清,王明,等.废盐资源化的组合处理工艺研究[J].中国资源综合利用,2022,40(7):1-3. |
| HUANG Hefeng, YU Huaqing, WANG Ming,et al.Research on combined treatment process of waste salt recycling[J].China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2022,40(7):1-3. | |
| [5] | 陈齐新,魏佳.工业废盐资源化利用典型工艺及前景分析[J].节能与环保,2021(6):78-80. |
| CHEN Qixin, WEI Jia.Typical technology and prospect analysis of industrial waste salt resource utilization[J].Energy Conservation & Environmental Protection,2021(6):78-80. | |
| [6] | 刘铮,党春阁,宋丹娜,等.精细化工业园区化工废盐处理问题探究[J].化工管理,2019(6):153-154. |
| LIU Zheng, DANG Chunge, SONG Danna,et al.Exploration into the treatment of chemical waste salt in fine industrial parks[J].Chemical Enterprise Management,2019(6):153-154. | |
| [7] | 周海云,鲍业闯,邹明璟,等.农药废盐回转窑高温熔融处理技术实践与分析[J].工业水处理,2021,41(8):140-145. |
| ZHOU Haiyun, BAO Yechuang, ZOU Mingjing,et al.Practice and analysis of high temperature melting treatment technology for pesticide waste salt in rotary kiln[J].Industrial Water Treatment,2021,41(8):140-145. | |
| [8] | 姜海超,申银山,陈晓飞,等.含氰工业废盐中杂质的高温氧化脱除实验研究[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(2):62-64. |
| JIANG Haichao, SHEN Yinshan, CHEN Xiaofei,et al.Experimental study on high temperature oxidation removal of impurities in cyanide-contained industrial waste salts[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(2):62-64. | |
| [9] | 赵宗文,王忠兵,郭杏林,等.工业废盐中有机物杂质脱除技术综述[J].化工环保,2021,41(6):673-677. |
| ZHAO Zongwen, WANG Zhongbing, GUO Xinglin,et al.Review on technologies for organic impurities removal from industrial waste salt[J].Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry,2021,41(6):673-677. | |
| [10] | 张森,王军,陈天虎,等.农药行业NaCl-KCl型废盐热处理研究[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(2):106-112. |
| ZHANG Sen, WANG Jun, CHEN Tianhu,et al.Research on heat treatment of NaCl-KCl waste salt in pesticide industry[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(2):106-112. | |
| [11] | 周兆安,李俊,刘小文,等.高化学需氧量工业废盐炭化除杂及精制工艺研究[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(9):100-105. |
| ZHOU Zhaoan, LI Jun, LIU Xiaowen,et al.Study on carbonization and purification process of high COD industrial waste salt[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(9):100-105. | |
| [12] | 张以飞.高温炭化法处理工业废盐工程方案研究[J].环境与发展,2020,32(4):48-49,51. |
| ZHANG Yifei.Study on the project scheme of high-temperature carbonization for industrial waste salt treatment[J].Environment and Development,2020,32(4):48-49,51. | |
| [13] | 梁国强,崔咪芬,乔旭,等.Cu-Mo/Al2O3复合金属催化剂的制备及其催化裂解草甘膦副产废盐[J].南京工业大学学报(自然科学版),2023,45(6):600-609. |
| LIANG Guoqiang, CUI Mifen, QIAO Xu,et al.Preparation of Cu-Mo/Al2O3 composite metal catalyst and its catalytic cracking of glyphosate by-product waste salt[J].Journal of Nanjing Tech University(Natural Science Edition),2023,45(6):600-609. | |
| [14] | 刘金淼,姚瑶,马欣欣,等.不同金属离子对生物质热解特性的研究综述[J].现代化工,2016,36(6):32-36. |
| LIU Jinmiao, YAO Yao, MA Xinxin,et al.Influence of different metal ions on biomass pyrolysis:A review[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2016,36(6):32-36. | |
| [15] | 张志强,崔康平,陈星,等.响应曲面法优化碳热还原重铬酸钠制备超细氧化铬[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(10):136- 144. |
| ZHANG Zhiqiang, CUI Kangping, CHEN Xing,et al.Optimization of preparation of ultrafine chromium oxide by carbothermal reduction of sodium dichromate by response surface methodolo-gy[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(10):136-144. | |
| [16] | 王文亮,时宇杰,党泽攀,等.Cu-Zn氯化盐对生物质催化热裂解失重行为的影响[J].石油化工,2018,47(2):127-132. |
| WANG Wenliang, SHI Yujie, DANG Zepan,et al.Influence on the pyrolysis behavior of catalytic pyrolysis from larch impregnated with Cu-Zn chlorides[J].Petrochemical Technology,2018,47(2):127-132. |
| [1] | BAI Xingxing, LI Hanfei, TANG Yong, ZHANG Jun, ZHU Guangkai, LI Lishuo, TONG Zhangfa. Study on preparation of cellulose based hydrogel doped with nano-calcium carbonate and its adsorption properties of copper ions [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 83-91. |
| [2] | TANG Dongwu, YE Changwen, DENG Jie, AO Fang. Study on leaching rate of calcium and magnesium from phosphorus tailings based on thermodynamic analysis and response surface method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 98-106. |
| [3] | CHEN Junhui, LIU Xiang, HU Qingxi, TIAN Bangxin, CHEN Jiale. Study on leaching extraction of high purity potassium chloride from sintering machine head ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 102-108. |
| [4] | LIU Xiaowen, LI Jun, ZHOU Zhaoan, MAO Anzhang, ZHOU Aiqing. Study on response surface methodology optimization of PAC for deep purification of fluorine ion in high concentration sodium sulfate solution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 67-72. |
| [5] | LI Chunli, ZHANG Huanhuan, CHENG Zhuo, TANG Xiuhua, ZHANG Fengzhen, YE Yuling. Anti-solvent crystallization process of NH4VO3 in NaVO3-NH4Cl-H2O solution system [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 39-44. |
| [6] | YAO Jiankang, HU Shuozhen, NIU Dongfang, WU Jianping, ZHANG Xinsheng. Study on electrochemical treatment of sodium chloride organic waste salt in spice industry [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 105-115. |
| [7] | LI Hongyuan, ZHANG Jianhua. Study on removal process of total organic carbon from industrial waste salts by pyrolysis [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 95-102. |
| [8] | ZHOU Zhaoan, LI Jun, LIU Xiaowen, ZHOU Aiqing, MAO Anzhang. Study on carbonization and purification process of high COD industrial waste salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 100-105. |
| [9] | ZHANG Conghua, YAN Wenbin, XIAO Jiajun, ZHAO Ke, PENG Shangquan, WEI Yuhong. Reductive leaching technology of manganese anode slag using tartaric acid as reducing agent optimized by RSM [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 106-113. |
| [10] | WANG Yingnan, SHENG Linlin, HUANG Juan, HUANG Zhanbin. Study on adsorption performance of lead from water by coal-fired slag [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 109-115. |
| [11] | CUI Gengyin, XIE Lang, LU Yuexian, KONG Dewen, WANG Lingling. Optimization of mechanical properties of basalt fiber reinforced phosphogypsum-based composites based on RSM [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 116-123. |
| [12] | LI Xun, JIA Yanhong, DOU Qiang, YANG Yang. Study on vacuum distillation purification technology for radioactive waste salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(7): 97-102. |
| [13] | WU Yulin, WU Junhu, YANG Xiushan, XU Dehua, ZHANG Zhiye. Study on optimization of decalcification process of calcium and magnesium nitrate solution by response surface method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 50-56. |
| [14] | ZHANG Sen,WAN Jun,CHEN Tianhu,DONG Shiwei,XU Liang,LI Yaqian,ZHAO Yueling. Research on heat treatment of NaCl-KCl waste salt in pesticide industry [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 106-112. |
| [15] | TENG Jiayang, FENG Qingge, ZHANG Xuan, QIN Fanghong, FENG Jinghang, HU Jiawen, CHEN Chaohong. Study on preparation of pseudo-boehmite from aluminum dross resource treatment [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 130-138. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||