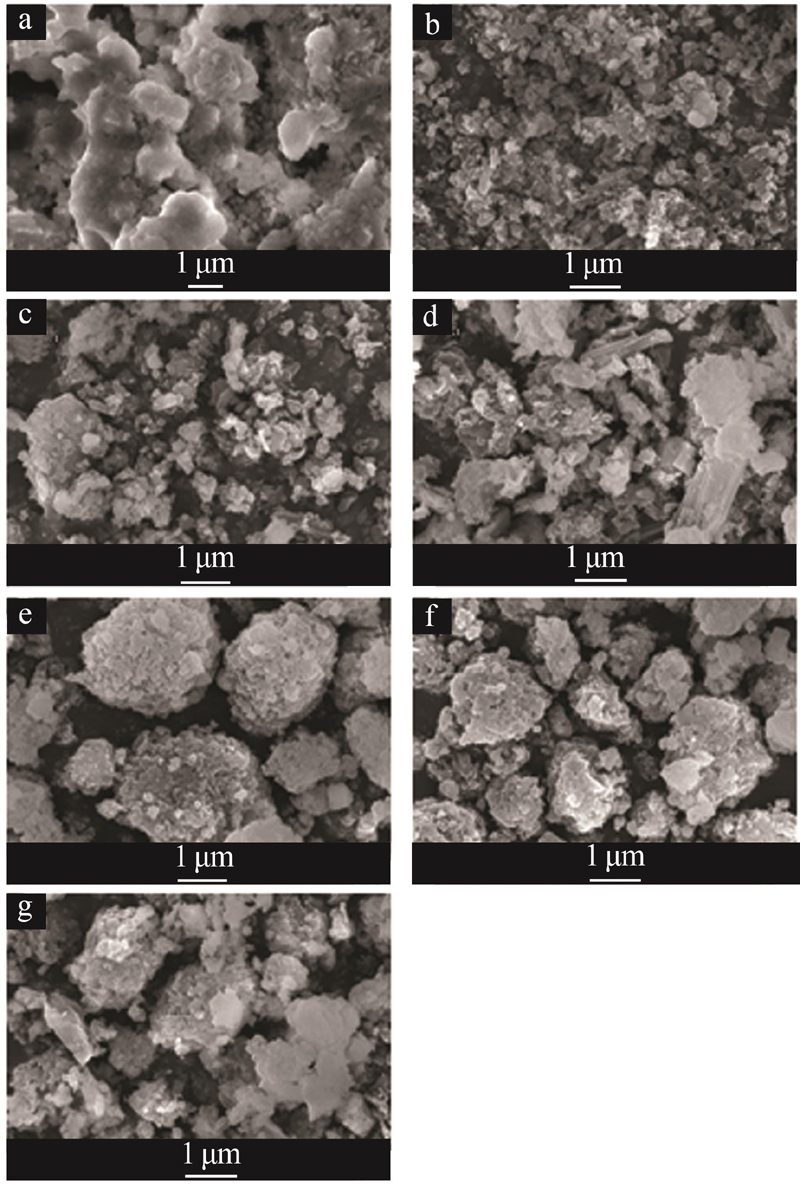
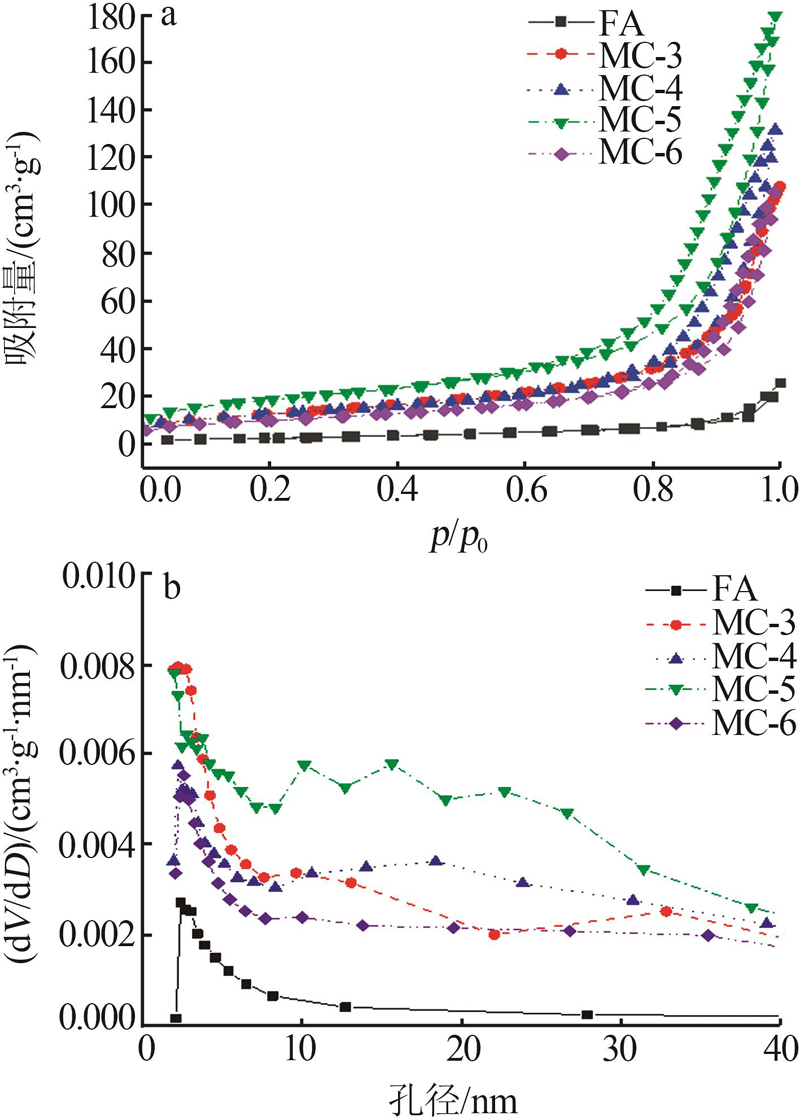
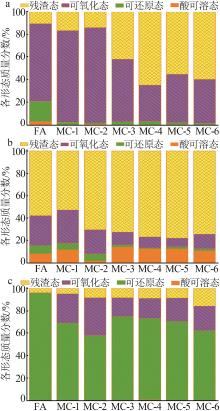
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 84-91.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0401
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on effect mechanism of silicon-aluminum additives on stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash by mechanochemical stabilization method
LI Wen1,2( ), WANG Wenxiang1,2(
), WANG Wenxiang1,2( ), FANG Hongsheng1,2, WU Pingxiao3
), FANG Hongsheng1,2, WU Pingxiao3
- 1. Guangdong Polytechnic of Environmental Protection and Engineering, Foshan 528216, China
2. Foshan Engineering Technology Research Center for Safe disposal and Comprehensive Utilization of Hazardous Waste, Foshan 528216, China
3. College of Environment and Energy, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
-
Received:2022-07-02Online:2023-04-10Published:2023-04-13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Wen, WANG Wenxiang, FANG Hongsheng, WU Pingxiao. Study on effect mechanism of silicon-aluminum additives on stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash by mechanochemical stabilization method[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 84-91.
share this article
Table 4
Heavy metal leaching toxicity and leachingcoefficient of FA and immobilized products"
| 样品编号 | 浸出浓度/(mg·L-1) | 浸出系数/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cr | Zn | Pb | Cr | Zn | ||
| FA | 16.04±0.80 | 2.15±0.04 | 1.28±0.04 | 5.94 | 1.34 | 0.13 | |
| MC-1 | 2.24±0.16 | 1.91±0.07 | 0.34±0.05 | 0.83 | 1.19 | 0.03 | |
| MC-2 | 1.71±0.25 | 1.20±0.23 | 0.41±0.04 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.04 | |
| MC-3 | 0.11±0.01 | 0.73±0.13 | <0.001 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 0.00 | |
| MC-4 | 0.05±0.01 | 2.34±0.47 | <0.001 | 0.02 | 2.09 | 0.00 | |
| MC-5 | 0.04±0.01 | 3.40±0.26 | <0.001 | 0.02 | 3.04 | 0.00 | |
| MC-6 | 0.02±0.01 | 0.17±0.08 | <0.001 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.00 | |
浓度限值(GB 5085.3—2007) | 5 | 15 | 100 | — | — | — | |
| 1 | 刘雪梅,罗思梦.固化稳定化技术对垃圾焚烧飞灰中重金属的研究[J].应用化工,2022,51(3):816-820. |
| LIU Xuemei, LUO Simeng.Study on heavy metals in MSWI fly ash by solidification stabilization technology[J].Applied Chemical Industry,2022,51(3):816-820. | |
| 2 | 马懿,郑仁栋,周志昊,等.生活垃圾焚烧飞灰处置技术与应用瓶颈[J].环境工程,2022,40(5):237-243. |
| MA Yi, ZHENG Rendong, ZHOU Zhihao,et al.Bottleneck and disposal technology of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration[J].Environmental Engineering,2022,40(5):237-243. | |
| 3 | 杨延梅,慕宗宇,王菲,等.螯合剂固化生活垃圾焚烧飞灰中重金属的机理研究进展[J].环境科学研究,2022,35(10):2388-2395. |
| YANG Yanmei, MU Zongyu, WANG Fei,et al.Review on mechanisms of chelating agents to solidify heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(10):2388-2395. | |
| 4 | 王文祥,李宝花,周海彪,等.水洗-球磨法降解飞灰中二噁英的研究[J].环境科学学报,2017,37(6):2232-2237. |
| WANG Wenxiang, LI Baohua, ZHOU Haibiao,et al.Degradation of dioxin in fly ash by water-ball milling process[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2017,37(6):2232-2237. | |
| 5 | CHEN Zhiliang, TANG Minghui, LU Shengyong,et al.Mechanochemical degradation of PCDD/Fs in fly ash within different milling systems[J].Chemosphere,2019,223:188-195. |
| 6 | HU Jun, HUANG Zhiyong, YU Jianming.Highly-effective mechanochemical destruction of hexachloroethane and hexachlorobenzene with Fe/Fe3O4 mixture as a novel additive[J].Science of the Total Environment,2019,659:578-586. |
| 7 | CHEN Zhiliang, LU Shengyong, TANG Minghui,et al.Mechanochemical stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash with additives[J].The Science of the Total Environment,2019,694.Doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133813 . |
| 8 | YUAN Qixin, ZHANG Yongsheng, WANG Tao,et al.Mechanochemical stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash from coal-fired power plants via dry milling and wet milling[J].Waste Management,2021,135:428-436. |
| 9 | SHI Dezhi, HU Chunyan, ZHANG Jinlu,et al.Silicon-aluminum additives assisted hydrothermal process for stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash from MSW incineration[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2017,165:44-53. |
| 10 | LI Xinying, CHEN Quanyuan, ZHOU Yasu,et al.Stabilization of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash using silica fume[J].Waste Management,2014,34(12):2494-2504. |
| 11 | 金会心,王尚杰夫,肖媛丹,等.赤泥与粉煤灰资源特性及其协同利用现状研究[J].贵州大学学报:自然科学版,2022,39(2):18-26. |
| JIN Huixin, WANG Shangjiefu, XIAO Yuandan,et al.Study on the characteristics and collaborative utilization of red mud and fly ash resources[J].Journal of Guizhou University:Natural Sciences,2022,39(2):18-26. | |
| 12 | YU Shuyao, DU Bing, BAHEIDUOLA A,et al.HCB dechlorination combined with heavy metals immobilization in MSWI fly ash by using n-Al/CaO dispersion mixture[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,392.Doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122510 . |
| 13 | ROJAS R.Copper,lead and cadmium removal by Ca Al layered double hydroxides[J].Applied Clay Science,2014,87:254-259. |
| 14 | LIU Qiang, LI Yajun, ZHANG Jia,et al.Effective removal of zinc from aqueous solution by hydrocalumite[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2011,175:33-38. |
| 15 | 向跟华,刘涛,张一敏,等.页岩提钒中和渣制备硫酸钙晶须填料的研究[J].无机盐工业,2018,50(10):48-53. |
| XIANG Genhua, LIU Tao, ZHANG Yimin,et al.Study on preparation of calcium sulfate whisker filler from shale vanadium neutralized slag[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2018,50(10):48-53. | |
| 16 | 朱莹,丁竑瑞,李艳,等.不同亚类硅酸盐矿物的中红外光谱学特征[J].矿物学报,2019,39(2):173-182. |
| ZHU Ying, DING Hongrui, LI Yan,et al.The middle-infrared spectroscopic characteristics of several common silicate minerals[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2019,39(2):173-182. | |
| 17 | 朱莹,丁竑瑞,李艳,等.含白云石天然碳酸盐岩在中红外波段的辐射特性研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2019,38(6):743-752. |
| ZHU Ying, DING Hongrui, LI Yan,et al.A study of the middle in-frared emission properties of dolomitic natural carbonate rock[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2019,38(6):743-752. | |
| 18 | 郭雪飞,宋华玲,龙泉树,等.不同亚类硅酸盐宝玉石矿物的近红外光谱研究[J].昆明理工大学学报:自然科学版,2019,44(3):22-25. |
| GUO Xuefei, SONG Hualing, LONG Quanshu,et al.A study on near-infrared spectroscopy of different subgroup silicate gemstone minerals[J].Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology:Natural Science,2019,44(3):22-25. | |
| 19 | 彭春元,赵辉.利用红外光谱技术分析水泥性能[J].水泥技术,2001(4):63-65. |
| PENG Chunyuan, ZHAO Hui.Analysis of cement properties by infrared spectroscopy[J].Cement Technology,2001(4):63-65. | |
| 20 | LI Mingguo, SUN C J, GAU S H,et al.Effects of wet ball milling on lead stabilization and particle size variation in municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,174(1/2/3):586-591. |
| 21 | 陈志良.机械化学法降解垃圾焚烧飞灰中二噁英及协同稳定化重金属的机理研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2019. |
| CHEN Zhiliang.Mechanism study of mechanochemistry on PCDD/Fs degradation and on heavy metals stabilization in MSWI fly ash[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2019. | |
| 22 | 黎雯.类水滑石/碳纳米管复合材料的构建及其对双酚A的催化降解研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2015. |
| LI Wen.Frabrication of hydrotalcite/carbon nanotube composites and its application in catalytic degradation of BPA[D].Guangzhou:South China University of Technology,2015. | |
| 23 | CHEN Qian, LONG Ling, LIU Xiaobo,et al.Low-toxic zeolite fabricated from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash via microwave-assisted hydrothermal process with fusion pretreatment[J].Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2020,22(4):1196-1207. |
| 24 | ELIANA GATTULLO C, D'ALESSANDRO C, ALLEGRETTA I,et al.Alkaline hydrothermal stabilization of Cr(Ⅵ) in soil using glass and aluminum from recycled municipal solid wastes[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,344:381-389. |
| 25 | ZHOU Xian, ZHOU Min, WU Xian,et al.Reductive solidification/stabilization of chromate in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by ascorbic acid and blast furnace slag[J].Chemosphere,2017,182:76-84. |
| 26 | WANG Wenxia, GAO Xiangpeng, LI Tinghao,et al.Stabilization of heavy metals in fly ashes from municipal solid waste incineration via wet milling[J].Fuel,2018,216:153-159. |
| 27 | 杨凤玲,李鹏飞,叶泽甫,等.城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰组成特性及重金属熔融固化处理技术研究进展[J].洁净煤技术,2021,27(1):169-180. |
| YANG Fengling, LI Pengfei, YE Zefu,et al.Study progress on the composition characteristics of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration and treatment technology of heavy metal melting and solidification[J].Clean Coal Technology,2021,27(1):169-180. | |
| 28 | SHI Huisheng, KAN Lili.Leaching behavior of heavy metals from municipal solid wastes incineration(MSWI) fly ash used in concrete[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,164(2/3):750-754. |
| 29 | ZHANG Haiying, ZHAO Youcai.Study on physicochemical characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration(MSWI) fly ash[C]//IEEE.2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology,2009:28-31. |
| 30 | ZHAO Xinyue, YANG Jinyan, NING Ning,et al.Chemical stabilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash:A review[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022,29(27):40384-40402. |
| 31 | 杨南如.机械力化学过程及效应(Ⅱ):机械力化学过程及应用[J].建筑材料学报,2000,3(2):93-97. |
| YANG Nanru.Processes and effects of mechanochemistry(Ⅱ)—Processes and application of mechanochemistry[J].Journal of Building Materials,2000,3(2):93-97. |
| [1] | ZHAO Feiyan, ZHANG Xiaodong, DU Yanxia, WANG Qiang, LI Xiaoyan. Preparation technology and research progress of fly ash ceramsite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 16-23. |
| [2] | LI Kuai, LI Zhaoshuai, DONG Tingxuan, LI Dan, GUO Shengwei, HAN Fenglan. Study on effect of wet magnetic separation on distribution of Fe and heavy metal in fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 98-104. |
| [3] | LI Qiaoyun, HUANG Xiuxing, WEI Wenye, CHEN Zhen. Study on adsorption of methylene blue by activated carbon with acid/alkali synergistically modified fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 131-136. |
| [4] | WANG Lijuan, YAN Kezhou, GUO Zhiqiang, ZHAO Zhonghe, GUO Yanxia, CHENG Fangqin. Preparation of poly-aluminum chloride from acid leaching liquor of red mud-coal gangue activated by sodium salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 76-83. |
| [5] | XU Wenzhen,LI Canhua,JI Hongfeng,LI Zimu,WU Zhaoyang,LI Minghui. Research progress of red mud in field of recycled metals and building materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 10-18. |
| [6] | LI Songhong,ZHOU Songhua,ZHAO Aiming,DONG Wenyan,JIANG Chunyan,CAO Yang,AO Xianquan. Study on catalytic gasification reaction of distillers′grains under H2O/CO2 atmosphere [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 132-140. |
| [7] | PAN Sicheng,XU Hongbin,ZHANG Hongling,DONG Yuming,ZHANG Hongjun,LOU Taiping. Study on preparation of metatitanic acid by hydrolysis of leaching solution of roasted mixture of red mud and ammonium sulfate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 85-91. |
| [8] | LU Jingjing,XIE Yan,LI Chen,MENG Mei,FENG Lunwei. Study on treatment of phosphorus-containing wastewater by lanthanum-loaded magnetized red mud [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 99-105. |
| [9] | YUE Yuansui, CHENG Guanwen, XU Min, XU Xiaoyu, ZHANG Zhenlin, NONG Guowu. Function and effect of ferric chloride solution in alkaline regulation of red mud [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 121-129. |
| [10] | SUN Zhigao, WU Yuan, YANG Xingchun, ZHANG Dongliang, WANG Mitang. Preparation and properties of high-magnesium nickel slag-fly ash based geopolymer [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 139-146. |
| [11] | YANG Hongjun, WANG Min, GE Haiwen, QIAO Youmin, QIAO Ziyang. Study on recycling process of potassium from calcium aluminate fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 121-127. |
| [12] | HE Wenchao,XUE Jing,WANG Wei. Research on strength and creep characteristics of concrete containing fly ash microbead [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 124-128. |
| [13] | LIU Darui,XU Lijun,LI Shichun,CAO Kun,TU Ya,LI Wenqing,LIU Qingliang. Research progress of recovery of strategic metal lithium from fly ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 56-63. |
| [14] | LEI Ming,ZHU Hanyu,LIU Zilong,CHEN Guopeng,YUAN Junsheng. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in hardened solid of net slurry co?disposed by cement kiln [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(8): 107-113. |
| [15] | CUI Jiaxin,WANG Lianyong,LU Simeng,SUN Yanwen,WANG Rui,HE Yan,HAN Jianli. Research on performance of hydrothermally synthesized zeolite with fly ash from different producing areas [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(5): 96-100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||