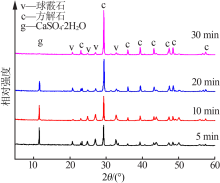
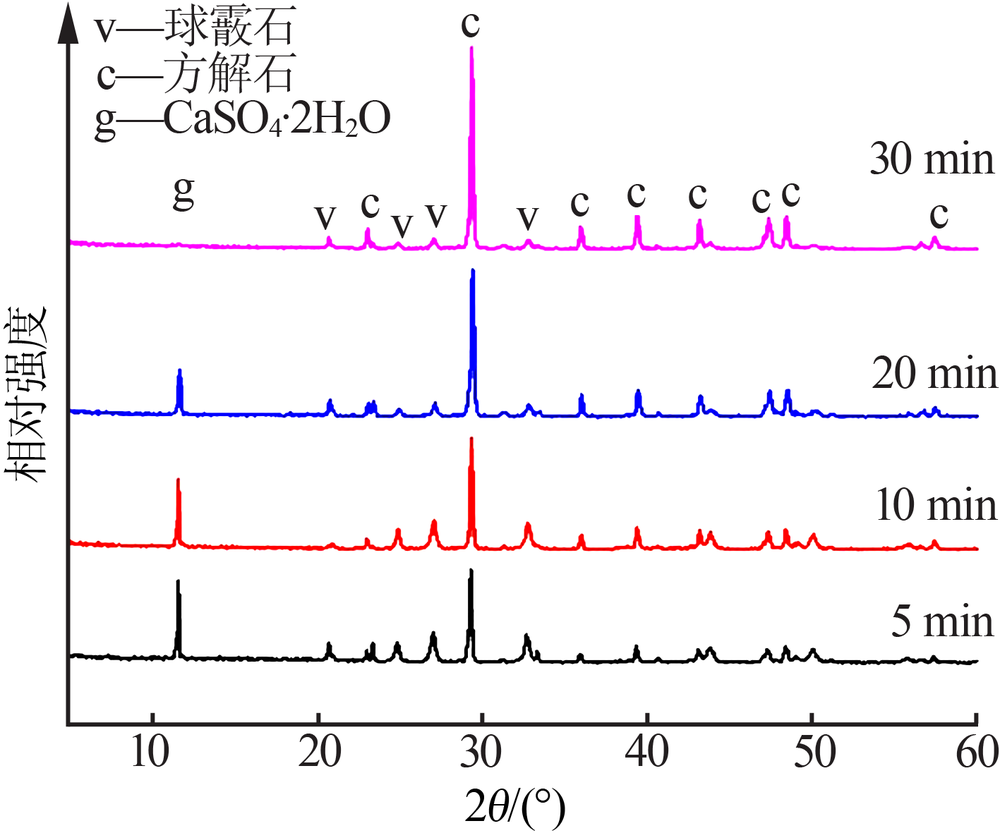
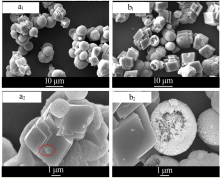
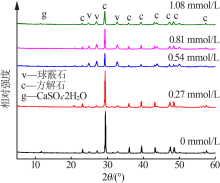
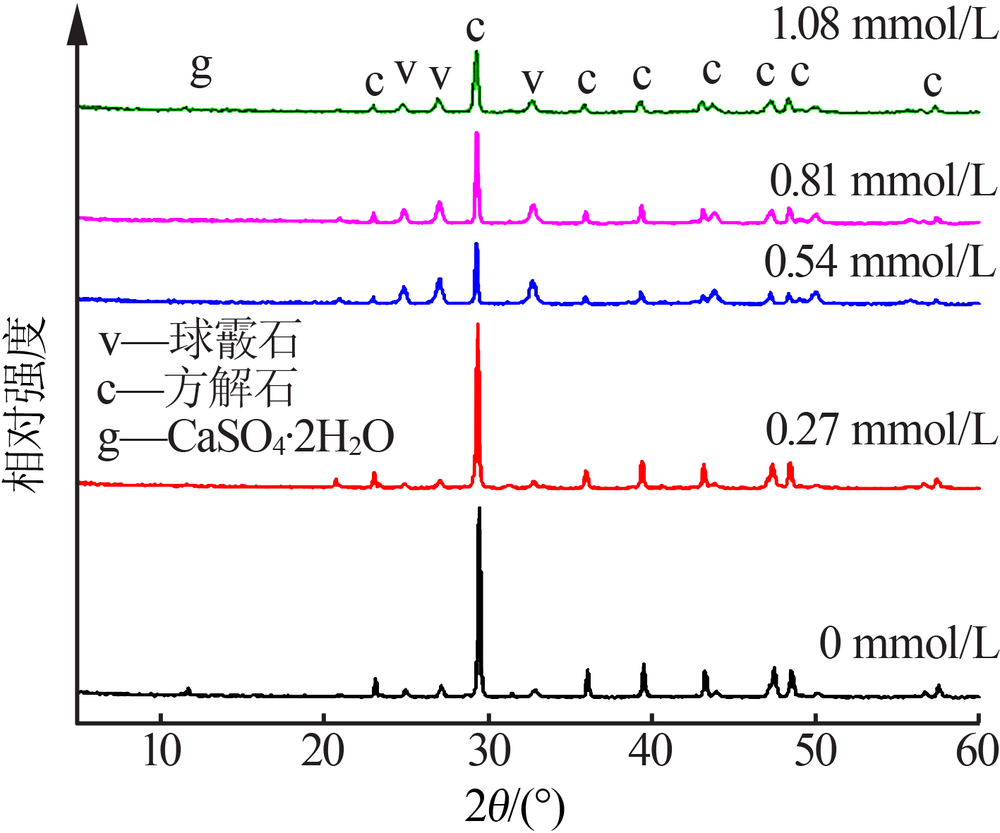
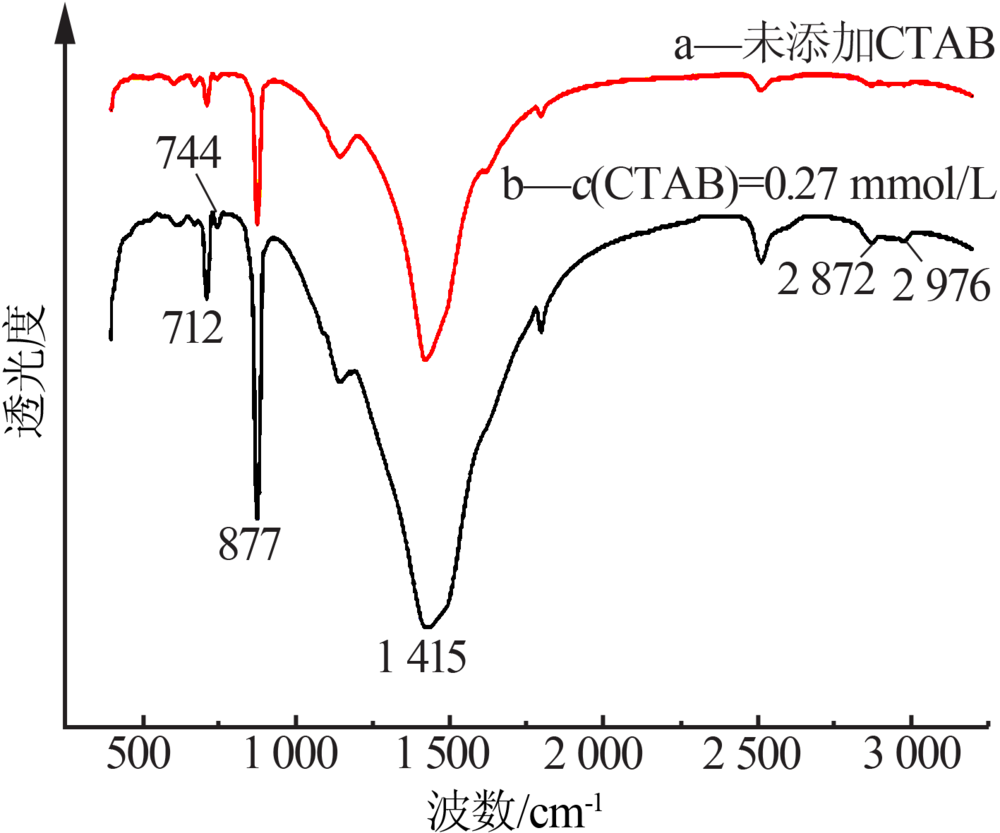
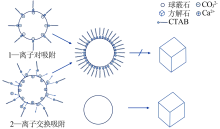
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 75-79.doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2019-0224
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
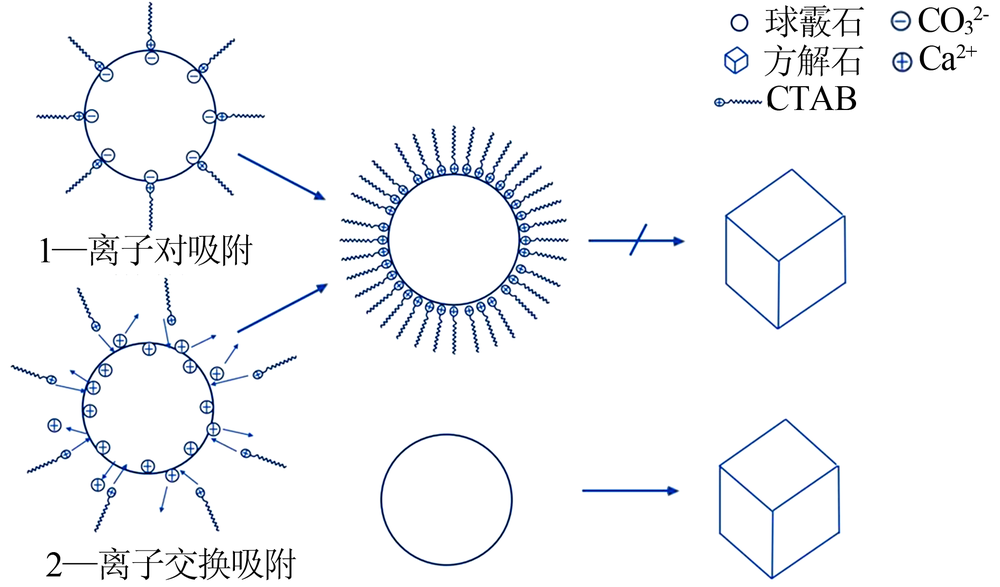
Effect of CTAB on crystal form of CaCO3 in indirect mineralization of CO2 by CaSO4·2H2O
Wang Gang1,2,Tang Shengwei1,2,Chen Yanxiao1,2,Zhang Tao1,2( )
)
- 1. School of Chemical Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,China
2. MOE′s Research Center for Comprehensive Utilization and Clean Processing Engineering of Phosphorus Resources;
-
Received:2019-09-26Online:2020-03-10Published:2020-03-31 -
Contact:Zhang Tao E-mail:zhangtao@scu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Gang,Tang Shengwei,Chen Yanxiao,Zhang Tao. Effect of CTAB on crystal form of CaCO3 in indirect mineralization of CO2 by CaSO4·2H2O[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(3): 75-79.
share this article
| [1] | Falkowski P, Scholes R J, Boyle E , et al. The global carbon cycle:A test of our knowledge of earth as a system[J]. Science, 2000,290(5490):291-296. |
| [2] | Rashidi N A, Yusup S . An overview of activated carbons utilization for the post-combustion carbon dioxide capture[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2016,13:1-16. |
| [3] | 朱家骅, 谢和平, 夏素兰 , 等. 烟气二氧化碳与磷石膏转化一步法节能节水清洁工艺:中国,102836627A[P]. 2012-12-26. |
| [4] | Wang A H, Yang Y, Zhang X M , et al. Gelatin-assisted synjournal of vaterite nanoparticles with higher surface area and porosity as antic-ancer drug containers in vitro[J]. Chempluschem, 2016,81(2):194-201. |
| [5] | Qiu N, Yin H B, Ji B Z , et al. Calcium carbonate microspheres as carriers for the anticancer drug camptothecin[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2012,32(8):2634-2640. |
| [6] | 徐国峰, 王洁欣, 沈志刚 , 等. 单分散纳米碳酸钙的制备和表征[J]. 北京化工大学学报:自然科学版, 2009,36(5):27-30. |
| [7] | Kang S H, Hirasawa I, Kim W S , et al. Morphological control of calci-um carbonate crystallized in reverse micelle system with anionic surfactants SDS and AOT[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Scien-ce, 2005,288(2):496-502. |
| [8] | Walsh D, Lebeau B, Mann S . Morphosynjournal of calcium carbonate (vaterite) microsponges[J]. Advanced Materials, 1999,11(4):324-328. |
| [9] | Li Q, Ding Y, Li F Q , et al. Solvothermal growth of vaterite in the presence of ethylene glycol,1,2-propanediol and glycerin[J]. Jo-urnal of Crystal Growth, 2002,236(1):357-362. |
| [10] | Zhao Y, Li S, Yu L , et al. The preparation of calcium carbonate cry-stals regulated by mixed cationic/cationic surfactants[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011,324(1):278-283. |
| [11] | Zhao L, Wang J . Biomimetic synjournal of hollow microspheres of calcium carbonate crystals in the presence of polymer and surfa-ctant[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineer-ing Aspects, 2012,393:139-143. |
| [12] | Saikia J, Saha B, Das G . Morphosynjournal of framboidal stable vate-rite using a salicylic acid-aniline dye as an additive[J]. RSC Adv-ances, 2012,2(26):10015-10019. |
| [13] | Chen J, Xiang L . Controllable synjournal of calcium carbonate poly-morphs at different temperatures[J]. Powder Technology, 2009,189(1):64-69. |
| [14] | Danielik V, Fellner P, Jurišová J , et al. Kinetics of the conversion reaction of gypsum with ammonium carbonate[J]. Chemical Pa-pers, 2018,72(10):2631-2639. |
| [15] | 郭祥峰, 贾丽华 . 阳离子表面活性剂及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002. |
| [1] | Yan Xin,Wu Jianyi,Lu Yunfeng,Yan Ziteng. Study on new technology of comprehensive utilization of alkali residue in ammonia alkali plant [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(1): 68-71. |
| [2] | Zhang Bin,Xiao Xiao,Han Yunjiao,Zhang Yuanyuan,Yu Hongwei. Study on third-step infrared spectroscopy of calcium carbonate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(1): 97-101. |
| [3] | Yan Xin. Research and production of colorful nano-sized calcium carbonate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(5): 53-55. |
| [4] | Jing Ting. Study on extrudability of silicone sealant by using modified nano-sized calcium carbonate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(4): 57-60. |
| [5] | Wang Qianqian,Bai Chunhua,Ren Hui,Li Guanghui. Crystal structure regulation of calcium carbonate by adding tetradecanoic acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(4): 29-32. |
| [6] | Wang Yubin,Wang Wangbo,Zhu Xinfeng,Xun Jingwen,Dang Weiben. Effect of different magnesium salts on solubility behavior of calcium carbonate under magnetization [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(3): 35-38. |
| [7] | Zhang Wenxian,Liu Liansheng,Cao Hejun,Wu Binke,Cheng Zhenpeng. Effect on kinetics of limestone decomposition under different CO2 atmospheres [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(3): 59-63. |
| [8] | Chang Yuefan,Zhang Huijie,Wang Shanshan,Xue Yongqiang. Controllable preparation of nano-calcium carbonate with different particle sizes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(12): 29-33. |
| [9] | Liu Baoshu,Hao Zhigang,Ma Yongshan,Liu Runjing,Hu Yongqi. Trend analysis and review of calcium carbonate production in China for the past 60 years [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(10): 37-43. |
| [10] | Wang Donghua,Fu Xin. Preparation and properties of iron oxide nanomaterials with different morphologies [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(9): 21-23. |
| [11] | Liu Zaitong,Li Chang′e,Yang Yuling,Li Guoting. Preparation of sub-micron spindle-shaped calcium carbonate and sodium hydroxide co-production by causticizing method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(8): 56-59. |
| [12] | Liu Jianlu,Liu Xia,Yue Maowen. Study on scaling tendency in nanofiltration process by treating underground brine in Laizhou bay,Bohai [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(8): 64-68. |
| [13] | Yan Xin1,Lu Yunfeng2,Ma Yuanyuan3,Xie Long3. Study on composite carbonization mechanism of nano calcium carbonateproduced by calcium chloride-ammonia water system [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(7): 77-80. |
| [14] | Zhang Pinghua,Yan Yunjie,Chen Jianjun,Wang Hongyan,Zhang Chunli,Wu Ning. Preparation of nanometer calcium carbonate from high-Ca-Mg phosphorus tailings by acid leaching [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(3): 63-66. |
| [15] | Tan Tingting1,2,3,Zhong Jianchu1,2,3. Study on controllable synthesis of spherical calcium carbonate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(12): 30-34. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|