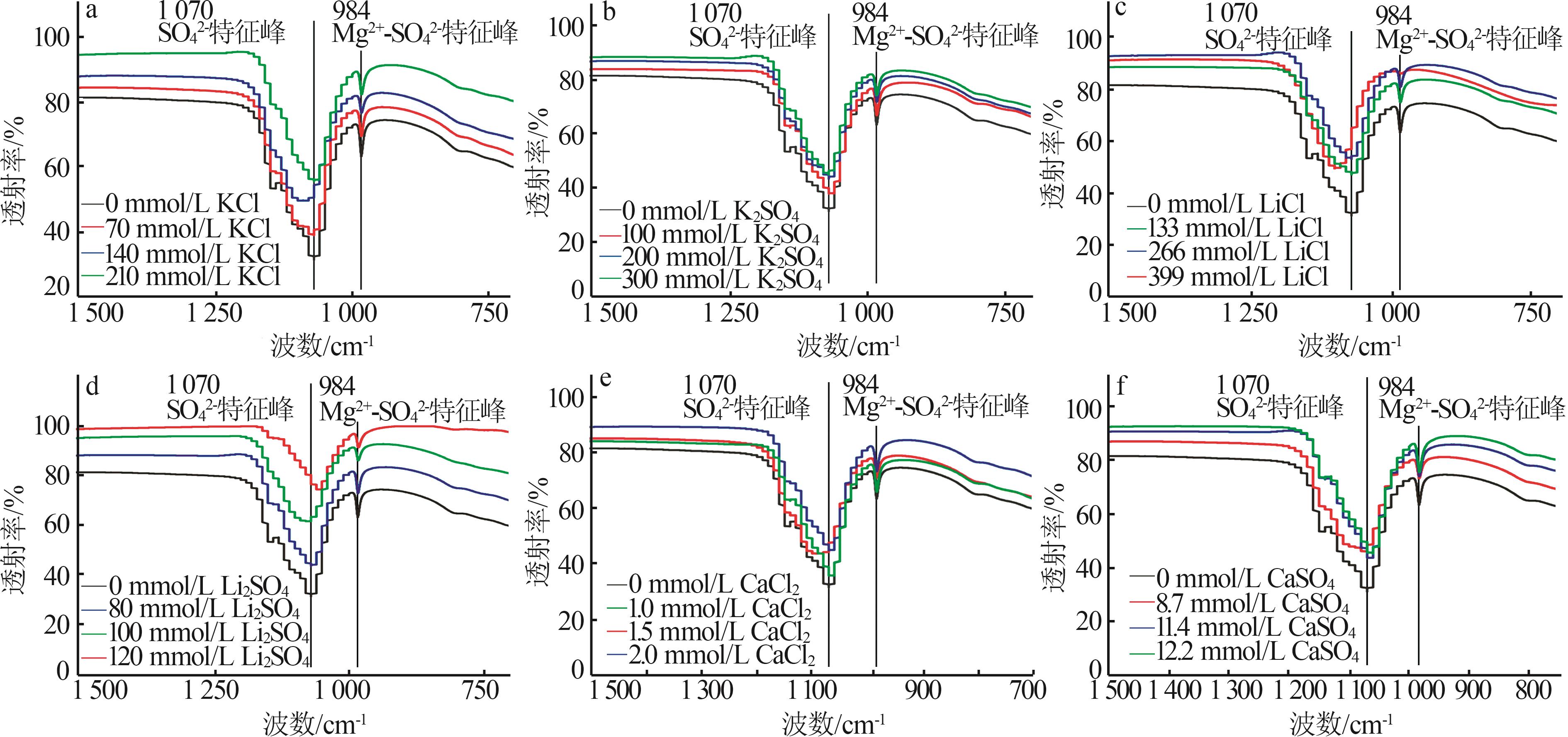
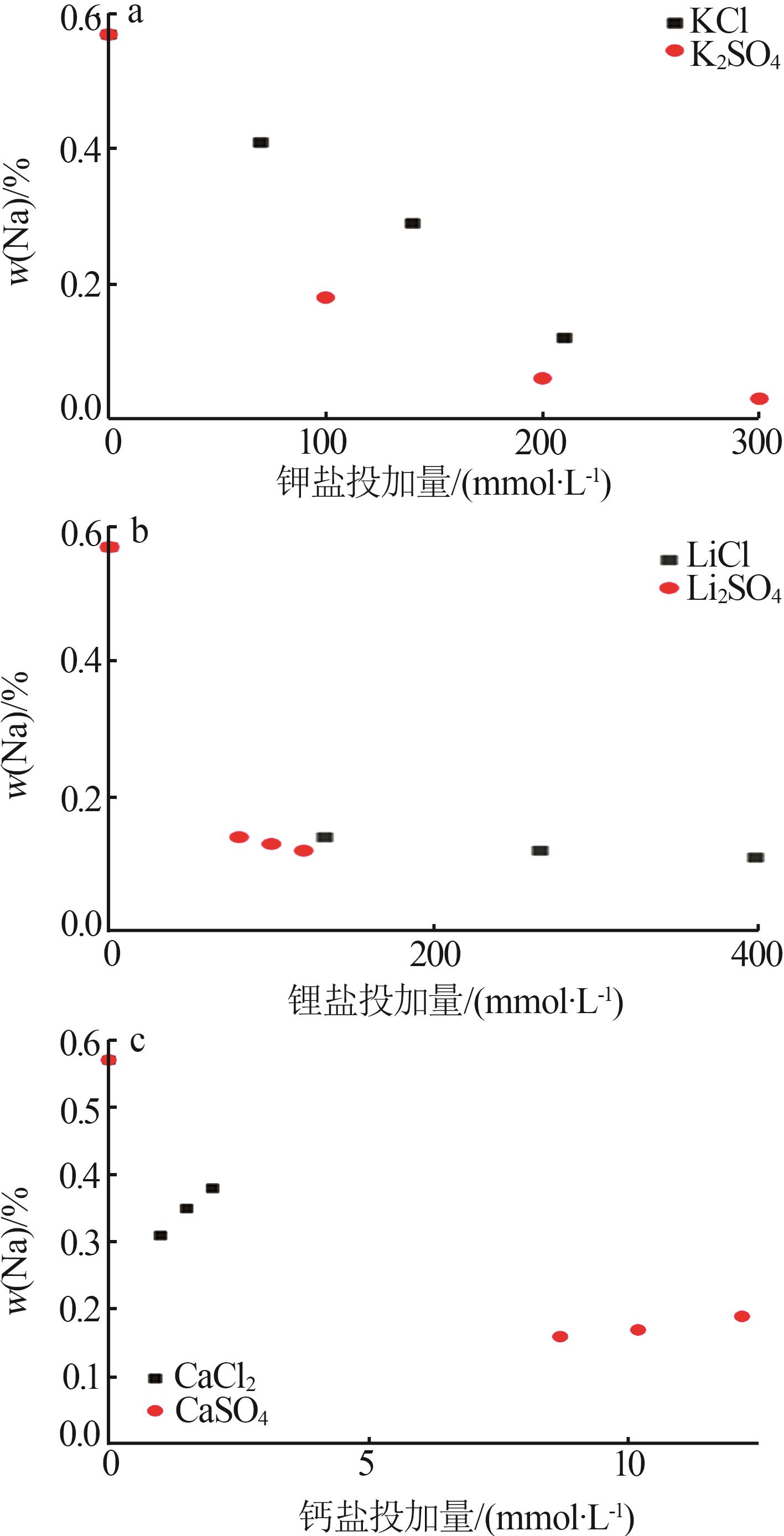
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 22-30.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0303
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
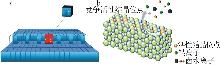
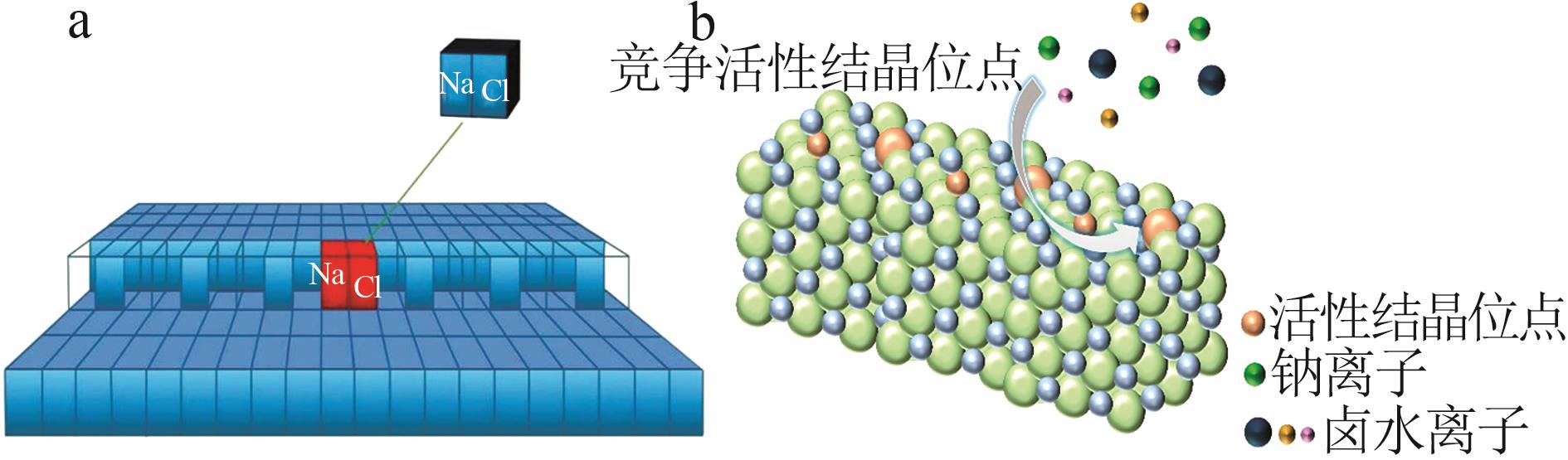
Regular study on effect of impurity ions in brine on morphology of magnesium sulfate crystallized by halogenation-cold precipitation
YANG Minhang1( ), XU Kai1, CHENG Huaigang1,2(
), XU Kai1, CHENG Huaigang1,2( ), CHENG Wenting1,3, SONG Huiping1,3
), CHENG Wenting1,3, SONG Huiping1,3
- 1. Institute of Resources and Environmental Eneineering,Engineering Research Center of Resource Efficiency Enhancing and Carbon Emission Reduction in Yellow River Basin,Ministry of Education of the People′s Republic of China,Taiyuan 030032,China
2. Qinghai university school of chemical engineering,Xining 810016,China
3. Shanxi yellow river laboratory,Taiyuan 030032,China
-
Received:2024-05-29Online:2025-04-10Published:2025-04-21 -
Contact:CHENG Huaigang E-mail:18346185592@163.com;chenghg@sxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Minhang, XU Kai, CHENG Huaigang, CHENG Wenting, SONG Huiping. Regular study on effect of impurity ions in brine on morphology of magnesium sulfate crystallized by halogenation-cold precipitation[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 22-30.
share this article
| [1] | 凌奇,王琪,魏玉玉,等.硫酸镁的制备方法及研究进展[J].盐科学与化工,2023,52(5):18-23. |
| LING Qi, WANG Qi, WEI Yuyu,et al.Preparation method and research progress of magnesium sulfate[J].Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry,2023,52(5):18-23. | |
| [2] | 朱亮,邵朔朔,赵京鑫.含钙硫酸镁溶液闪冷结晶过程颗粒粒度控制研究[J].盐科学与化工,2021,50(9):28-32,36. |
| ZHU Liang, SHAO Shuoshuo, ZHAO Jingxin.Study on particle size control in flash crystallization process of magnesium sulfate solution containing calcium[J].Journal of Salt Science and Chemical Industry,2021,50(9):28-32,36. | |
| [3] | 高姣丽.基于低锂损耗的盐湖老卤非平衡动态变温脱镁研究[D].太原:山西大学,2022. |
| GAO Jiaoli.Nonequilibrium dynamic temperature-varying removal of magnesium from salt lake brine with low lithium loss[D].Taiyuan:Shanxi University,2022. | |
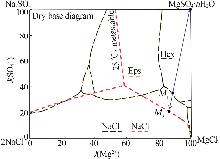
| [4] | CHENG Huaigang, HE Yueyue, ZHAO Jing,et al.Pilot test and cost-based feasibility study of solar-assisted evaporation for direct preparation of high-purity magnesium sulfate hydrates from metastable Na+,Mg2+//Cl-,SO4 2--H2O salt-water system[J].Hydrometallurgy,2019,189:105140. |
| [5] | 李琳琳.Na+,Mg2+//Cl-,SO4 2--H2O体系卤水变温分离提取结晶硫酸镁[D].山西:山西大学,2022. |
| LI Linlin.Extraction of crystalline magnesium sulfate from brine by variable temperature separation of Na+,Mg2+//Cl-,SO4 2--H2O system[D].Shanxi:Shanxi University,2022. | |
| [6] | 高姣丽,李恩泽,康锦,等.盐湖老卤动态变温分离高纯结晶硫酸镁[J].化工学报,2021,72(6):3022-3030. |
| GAO Jiaoli, LI Enze, KANG Jin,et al.Separation of high purity magnesium sulfate hydrates from salt lake tail brine in a dynamic temperature-changing process[J].CIESC Journal,2021,72(6):3022-3030. | |
| [7] | 宋谦益,游俊杰,杨成,等.玄武岩纤维-木纤维复合碱式硫酸镁水泥性能的改性机理[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2023,45(5):202-211. |
| SONG Qianyi, YOU Junjie, YANG Cheng,et al.Modification mechanism of basalt and wood fiber composite basic magnesium sulfate cement performance[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2023,45(5):202-211. | |
| [8] | POJNAR K, PILCH-PITERA B.Correlation between the chemical structure of(meth)acrylic monomers and the properties of powder clear coatings based on the polyacrylate resins[J].Materials,2024,17(7):1655. |
| [9] | RACHTANAPUN P, SAWANGRAT C, KANTHIYA T,et al.Effect of plasma treatment on bamboo fiber-reinforced epoxy composites[J].Polymers,2024,16(7):938. |
| [10] | XU Feng, SHANG Jin, ABDUREXIT A,et al.Effect of chemical treatment of cotton stalk fibers on the mechanical and thermal properties of PLA/PP blended composites[J].Polymers,2024,16(12):1641. |
| [11] | YANAGISAWA R, UEDA T, NAKAMOTO K I,et al.The interface between ice and alcohols analyzed by atomic force microscopy[J].The Journal of chemical physics,2024,161(2):024702. |
| [12] | FERNÁNDEZ M, MARÍN R, PROVERBIO F,et al.Effect of magnesium sulfate in oxidized lipid bilayers properties by using molecular dynamics[J].Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports,2021,26:100998. |
| [13] | CUI Xinjiao, YANG Chao, SUN Qiangqiang,et al.Investigating shear stress of ice accumulated on surfaces with various roughnesses:Effects of a quasi-water layer[J].Langmuir,2024,40(28):14214-14223. |
| [14] | 韦茹涵,崔振昌,闫玉东.医用镁合金表面改性技术的研究现状[J].广东化工,2023,50(14):104-106. |
| WEI Ruhan, CUI Zhenchang, YAN Yudong.Research status of surface modification technology for medical magnesium alloy[J].Guangdong Chemical Industry,2023,50(14):104-106. | |
| [15] | 明星星,秦舒浩,龙雪彬,等.硅烷偶联剂对低含量碱式硫酸镁晶须/聚丙烯复合材料的结晶行为及力学性能的影响[J].塑料工业,2024,52(3):160-167. |
| MING Xingxing, QIN Shuhao, LONG Xuebin,et al.Effect of silane coupling agents on crystallization behaviors and mechanical properties of low-content basic magnesium sulfate whisker/polypropylene composites[J].China Plastics Industry,2024,52(3):160-167. | |
| [16] | 蒋德敏,李顺梅,李青青,等.氢氧化镁与七水硫酸镁水热法合成碱式硫酸镁晶须[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(12):74-81. |
| JIANG Demin, LI Shunmei, LI Qingqing,et al.Hydrothermal synthesis of basic magnesium sulfate whiskers from magnesium hydroxide and magnesium sulfate heptahydrate[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(12):74-81. | |
| [17] | YANG Jun, HAN Zhiqiang, WANG Zhiqiang,et al.Enabling stable Zn anodes by molecularly engineering the inner Helmholtz plane with amphiphilic dibenzenesulfonimide additive[J].Advanced Science,2023,10(22):2301785. |
| [18] | SEYDIOGLU T, KURNAZ S, TOKEŞER E A,et al.Effect of foreign impurity and growth temperatures on hexagonal structure and fundamental properties of ZnO nanorods[J].Microscopy Research and Technique,2024,87(11):2687-2700. |
| [19] | JIA Haolin, YANG Wenxian, ZHANG Xue,et al.Effects and mechanisms of in surfactant on high Al-content AlGaN grown by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy[J].Optics Express,2022,30(2):1782. |
| [20] | WU Peng, LIU Jianping, LI Fangzhi,et al.Effects of miscut on step instabilities in homo-epitaxially grown GaN[J].Nanomaterials,2024,14(9):748. |
| [21] | WIDJAJA T, ALTWAY A, NURKHAMIDAH S,et al.Effectiveness study of recrystallisation method in pharmaceutical salt production from processed salt with zero waste concept[J].Heliyon,2024,10(10):e30472. |
| [22] | KESHAVARZ L, STEENDAM R R, BLIJLEVENS M A,et al.Influence of impurities on the solubility,nucleation,crystallization,and compressibility of paracetamol[J].Crystal Growth and Design,2019,19(7):4193-4201. |
| [23] | MIELNICZEK-BRZÓSKA E, SANGWAL K, CHOCYK D,et al.Effect of Al(Ⅲ) impurity on the crystallization of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate(ADP) from aqueous solutions by cooling method[J].Journal of Crystal Growth,2022,595:126816. |
| [24] | ZHANG Na, YU Hongfa, MA Haiyan,et al.The phase composition of the MgO-MgSO4-H2O system and mechanisms of chemical additives[J].Composites Part B:Engineering,2022,247:110328. |
| [25] | SUN C Q.Water electrification:Principles and applications[J].Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2020,282:102188. |
| [26] | VERMA L, VEKILOV P G, PALMER J C.Solvent structure and dynamics near the surfaces of β-hematin crystals[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2021,125(40):11264-11274. |
| [27] | TAMILSELVAN S, SONIYA R M, VASANTHARAJA R,et al.Silver nanoparticles based spectroscopic sensing of eight metal ions in aqueous solutions[J].Environmental Research,2022,212:113585. |
| [28] | FENG Jiangtao, WANG Zhenyu, ZHANG Wenlong,et al.Insight into the ion exchange in the adsorptive removal of fluoride by doped polypyrrole from water[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(47):67267-67279. |
| [29] | HABIBI M, SADEGHI M, ARMAN A,et al.Corrosion resistance and surface microstructure of Mg3N2/SS thin films by plasma focus instrument[J].Microscopy Research and Technique,2022,85(8):2880-2893. |
| [30] | KıRBOĞA S, MUALLA Ö.The role of vinyl sulfonic acid homopolymer in calcium oxalate crystallization[J].Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2010,78(2):357-362. |
| [31] | 程丹续,成怀刚,高姣丽,等.基于盐湖尾卤溶液结构变化的镁锂分离研究[J].盐湖研究,2022,30(4):146-153. |
| CHENG Danxu, CHENG Huaigang, GAO Jiaoli,et al.Separation of magnesium and lithium based on the structure change of tail brine[J].Journal of Salt Lake Research,2022,30(4):146-153. | |
| [32] | 阎波,周桓,李文轩.拉曼光谱法研究Na+,Mg2+//Cl-,SO4 2--H2O四元体系中SO4 2-离子缔合结构特征及其变化规律[J].物理化学学报,2016,32(2):405-414. |
| YAN Bo, ZHOU Huan, LI Wenxuan.Studies on the characteristics and behaviors of the ion association structures of SO4 2- in Na+,Mg2+//Cl-,SO4 2--H2O system by Raman spectroscopy[J].Acta Physico Chimica Sinica,2016,32(2):405-414. | |
| [33] | SUI Yiming, SCIDA A M, LI Bo,et al.The influence of ions on the electrochemical stability of aqueous electrolytes[J].Angewan-dte Chemie International Edition,2024,63(19):e202401555. |
| [34] | 代云.盐溶液体系的光谱分析和指认[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2012. |
| DAI Yun.Analysis and assignment of the spectra of a salt/solution system [D].Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2012. | |
| [35] | 乔梦丹,李非,王美玲,等.应用分子动力学模拟和拉曼光谱对钙、镁、氯离子水化现象的研究[J].原子与分子物理学报,2023,40(1):21-30. |
| QIAO Mengdan, LI Fei, WANG Meiling,et al.Application of molecular dynamics simulation and Raman spectroscopy to study the hydration phenomena of calcium,magnesium and chloride ions[J].Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics,2023,40(1):21-30. | |
| [36] | MITIĆ Ž, NIKOLIĆ G S, CAKIĆ M,et al.FTIR spectroscopic characterization of Cu(Ⅱ) coordination compounds with exopolysaccharide pullulan and its derivatives[J].Journal of Molecular Structure,2009,924:264-273. |
| [37] | TANG Weijian, ZHOU Guojun, HU Chengzhi,et al.Regulating the anion redox and suppressing the structural distortion of cation-disordered rock-salt cathode materials to improve cycling durability through chlorine substitution[J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2023,15(14):17938-17946. |
| [38] | 华彤文,陈景祖.普通化学原理[M].3版.北京:北京大学出版社,2005. |
| [39] | FELDMANN T, DEMOPOULOS G P.Influence of impurities on crystallization kinetics of calcium sulfate dihydrate and hemihydrate in strong HCl-CaCl2 solutions[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2013,52(19):6540-6549. |
| [40] | CHEN Siqi, ZHAO Wei, WU Biao.Separation of sulfate anion from aqueous solution governed by recognition chemistry:A minireview[J].Frontiers in Chemistry,2022,10:905563. |
| [41] | JIA Shengzhe, GAO Zhenguo, YAO Tuo,et al.Fractal model-based crystal pillar structure simulation and mechanism analysis of impurity migration process in layer melt crystallization[J].Chemical Engineering Science,2023,275:118722. |
| [42] | KIRBOGA S, ONER M.Inhibition of calcium oxalate crystallization by graft copolymers[J].Crystal Growth & Design,2009,9(5):2159-2167. |
| [43] | XU Yong, JIA Hongbing, PIAO Jinnv,et al.Crystallization behavior of poly(trimethylene terephthalate)/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites[J].Journal of Materials Science,2008,43(1):417-421. |
| [44] | 陈园园.不动杆菌YT-02环己胺氧化酶的晶体结构解析及活性位点研究[D].武汉:武汉轻工大学,2020. |
| CHEN Yuanyuan.Crystal structure and active site analysis of cyclohexylamine oxidase from Acinetobacter sp.YT-02 [D].Wuhan:Wuhan Polytechnic University,2020. | |
| [45] | DOBBERSCHÜTZ S, NIELSEN M R, SAND K K,et al.The mechanisms of crystal growth inhibition by organic and inorganic inhibitors[J].Nature Communications,2018,9(1):1578. |
| [46] | BORSOS A, NAGY Z K.Adsorption based competitive purity control in crystallization[J].Computer-Aided Chemical Engineering,2015,37:1679-1684. |
| [1] | TANG Kaijing, LIU Chuanbei, LI Yingding, JIANG Yong, WU Junnan, ZHANG Tao. Research on preparation and mechanism of superhydrophobic phosphogypsum products [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 97-102. |
| [2] | LUO Tong, YE Jianzhou, CHEN Shangwei, YANG Houwen, CHEN Fuping. Study on effect of ash calcium on properties of phosphorus building gypsum doped with PCE [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 116-122. |
| [3] | HU Jingrong, LI Xincong. Research on modified carbon aerogel/paraffin composite phase change thermal storage materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 58-63. |
| [4] | BI Chao, ZHANG Xiaokang, WANG Xiugui. Study on hydration characteristics and durability of high-strength concrete modified by mechanically activated waste incineration slag [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 142-149. |
| [5] | YU Hongchao, ZHANG Mengmeng, JIN Tianxiang. Research progress of microstructure and crystal surface effect of Ag3PO4 photocatalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 13-20. |
| [6] | XU Li, ZHANG Qiang. Experimental study on properties of iron tailings powder cement-based materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 116-123. |
| [7] | LI Peng, WANG Likun, MENG Qiuyan. Study on effect of α-hemihydrate gypsum on performance of cement mortar and its hydration mechanism [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 98-103. |
| [8] | JIANG Demin, LI Shunmei, Li Qingqing, Chen Yuxin, LIU Daijun. Hydrothermal synthesis of basic magnesium sulfate whiskers from magnesium hydroxide and magnesium sulfate heptahydrate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(12): 74-81. |
| [9] | LAI Xianrong, CHEN Zhouqin, SUN Hao, YANG Chao. Pilot study on lithium extraction by adsorption from raw brine of magnesium sulfate subtype salt lakes in Tibet [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 86-92. |
| [10] | WANG Bingjian,QI Daozheng,CHEN Deng. Degradation processes and mechanism of tricalcium aluminate in different sulfate environment [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(8): 119-124. |
| [11] | FAN Qingke,MENG Qinghua. Study on preparation and electrochemical properties of La0.79Mg0.21Ni3.95 hydrogen storage alloy for vehicles [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 71-76. |
| [12] | MA Caifu,YUAN Chuanlai,ZHAO Xueqi. Effect of ball milling time on electrochemical properties of graphene composites [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(12): 68-73. |
| [13] | Li Xuelian,Wu Dongen,Shao Xuelan,Huang Deyou,Kuai Xianfen. Preparation and electro-catalytic activity analysis of GRQD-NiCo2O4complexes for DMFC anode catalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(7): 109-112. |
| [14] | Bao Kejie,Lu lingran. Study on preparation and performance of negative electrode materials for batteries of new energy vehicles [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(3): 54-59. |
| [15] | YANG Zhuoying,YANG Fan,YI Meigui,XIANG Lan. Rule of hydrothermal hydrolysis of Mg/Al-bearing TiOSO4 solution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12): 113-116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||