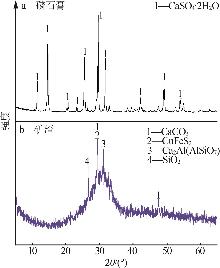
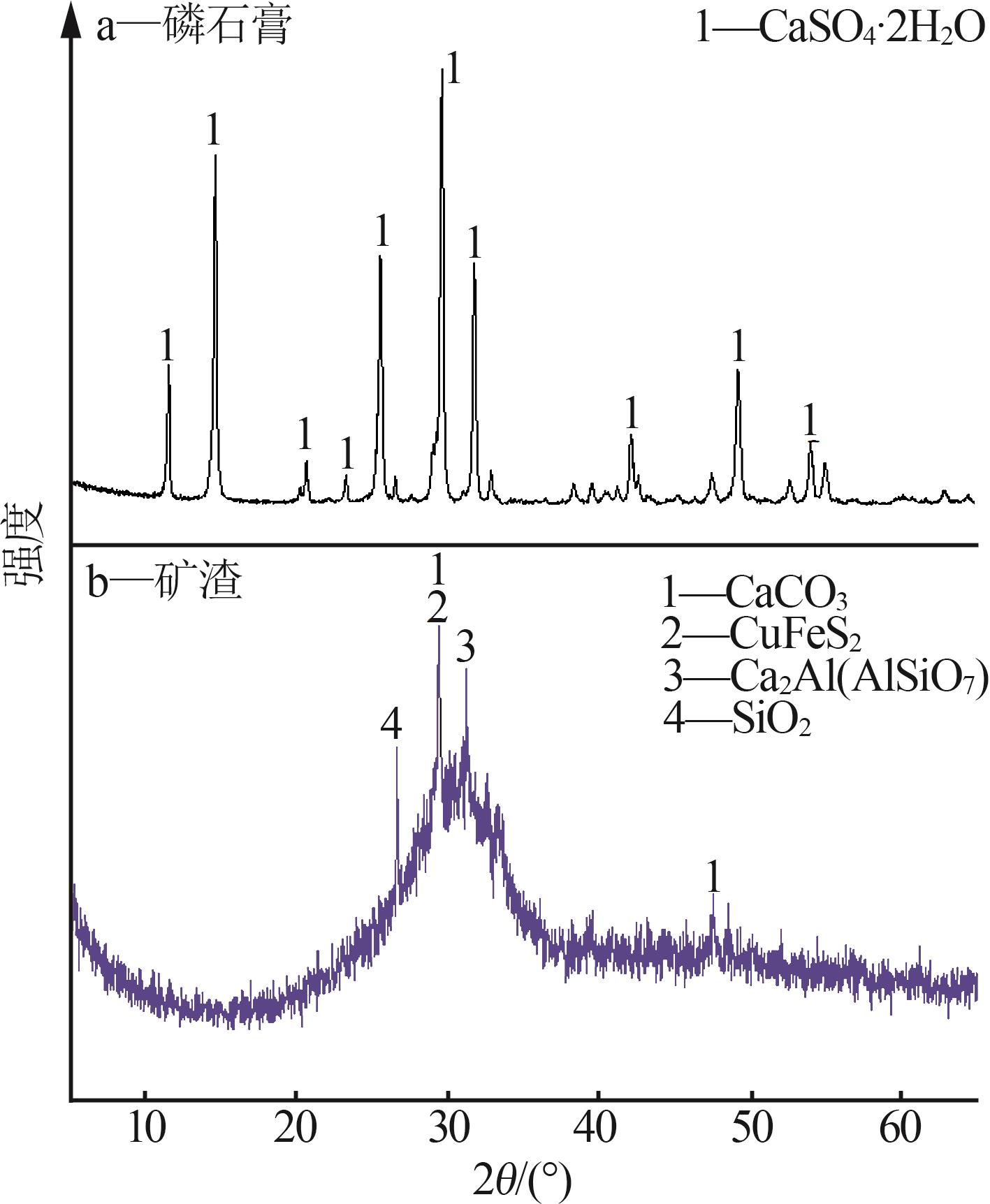
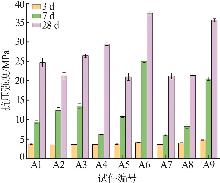
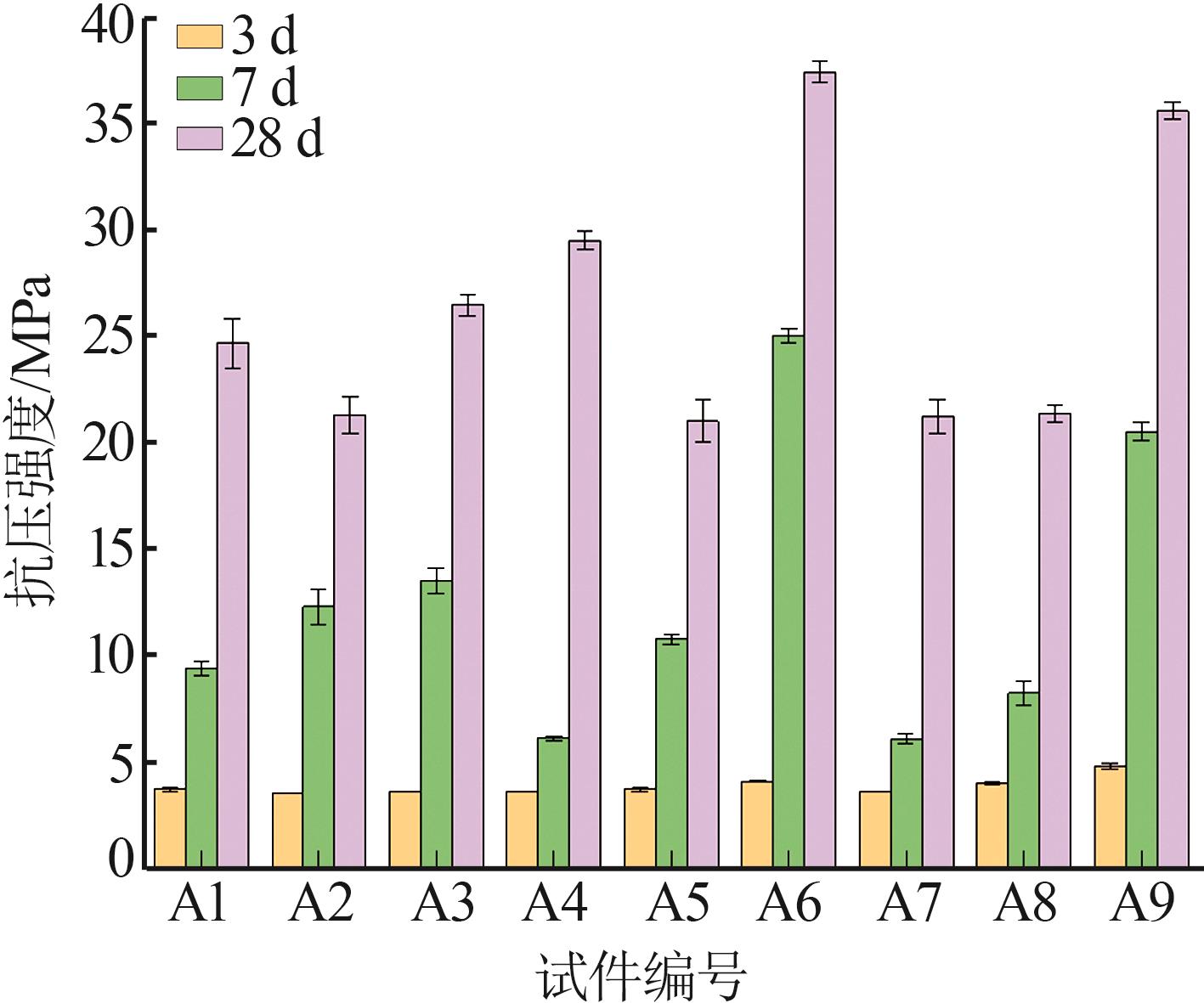
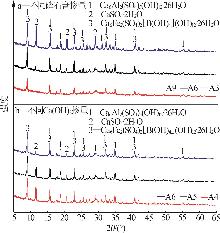
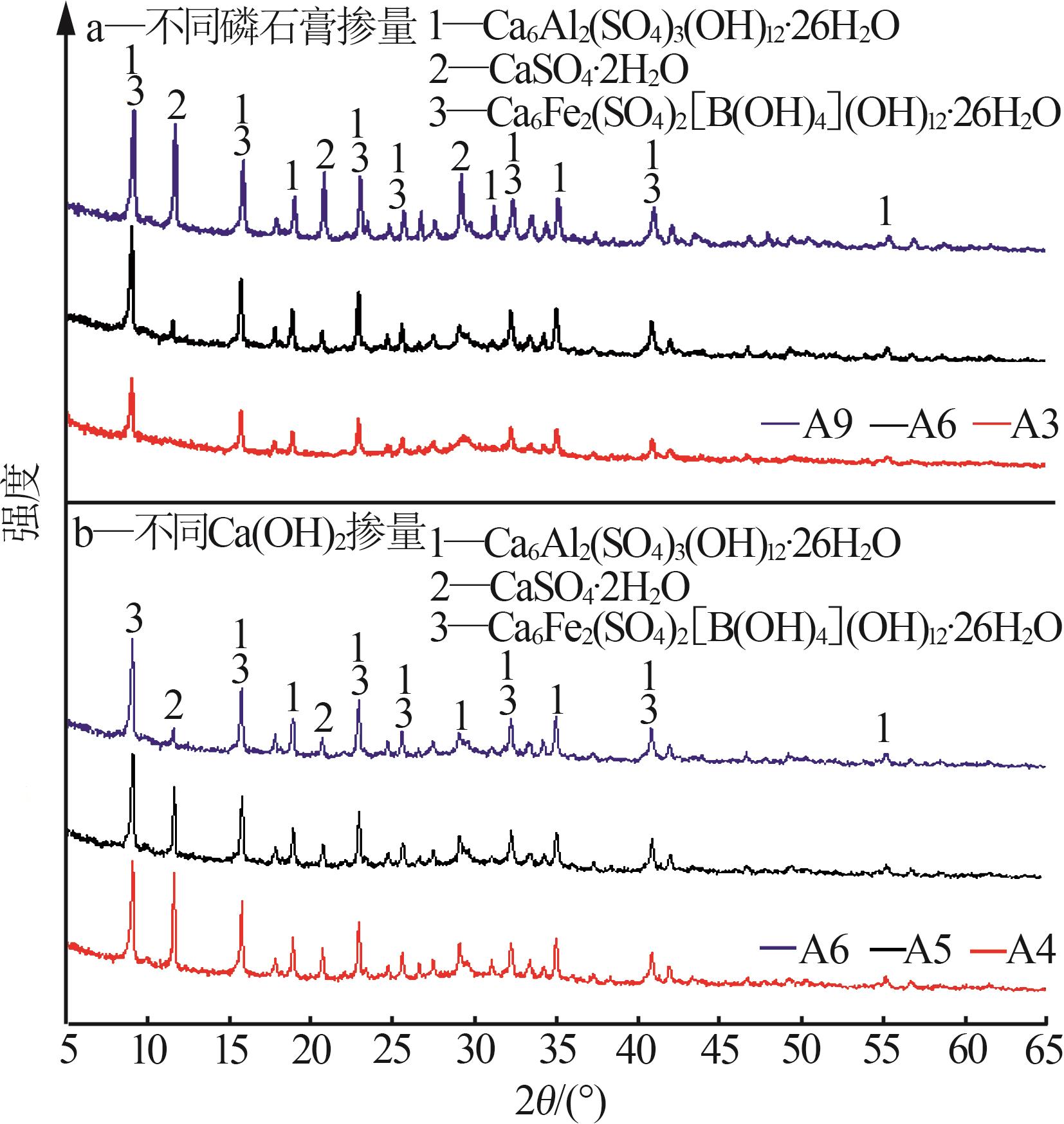
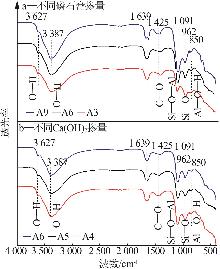
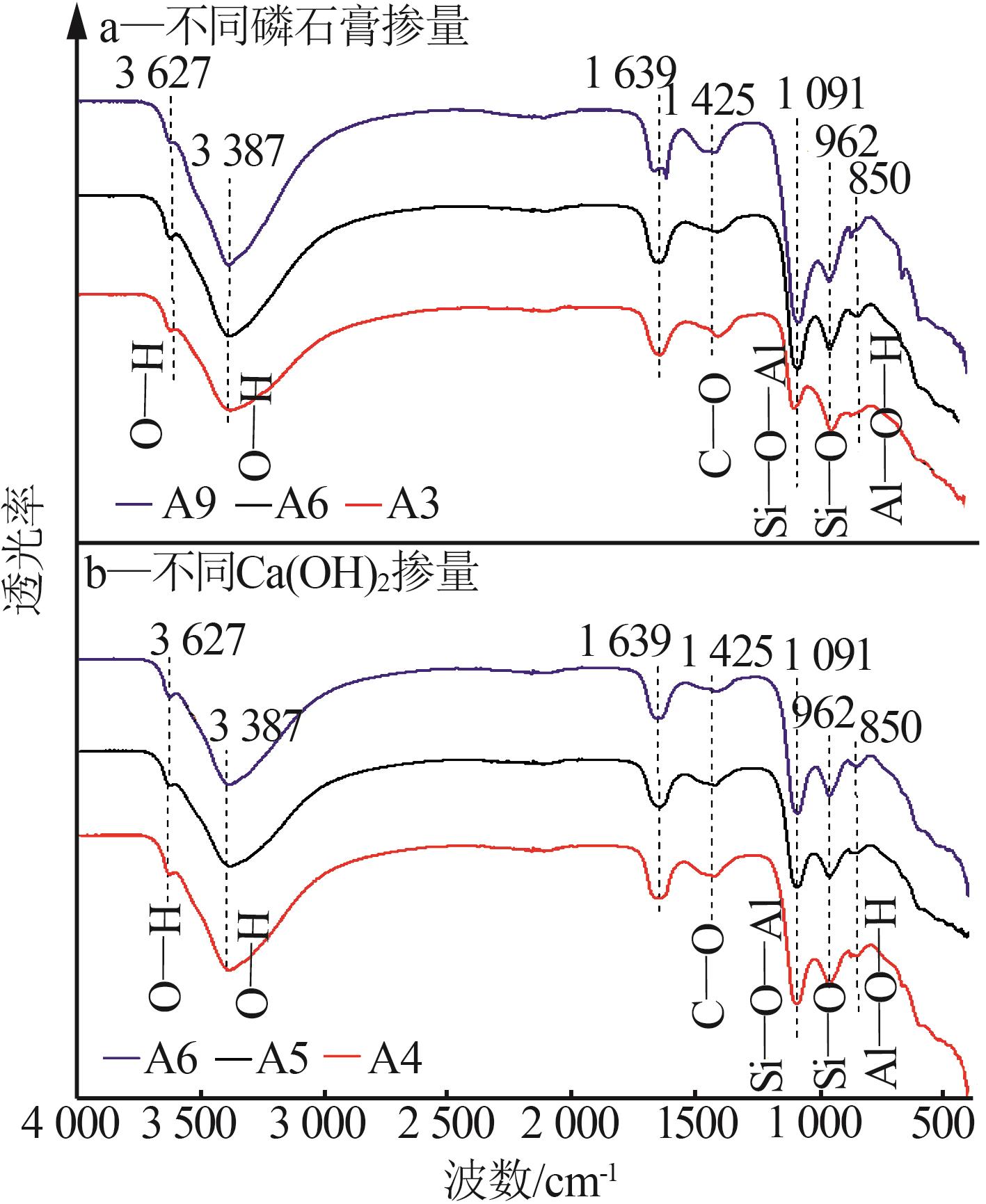
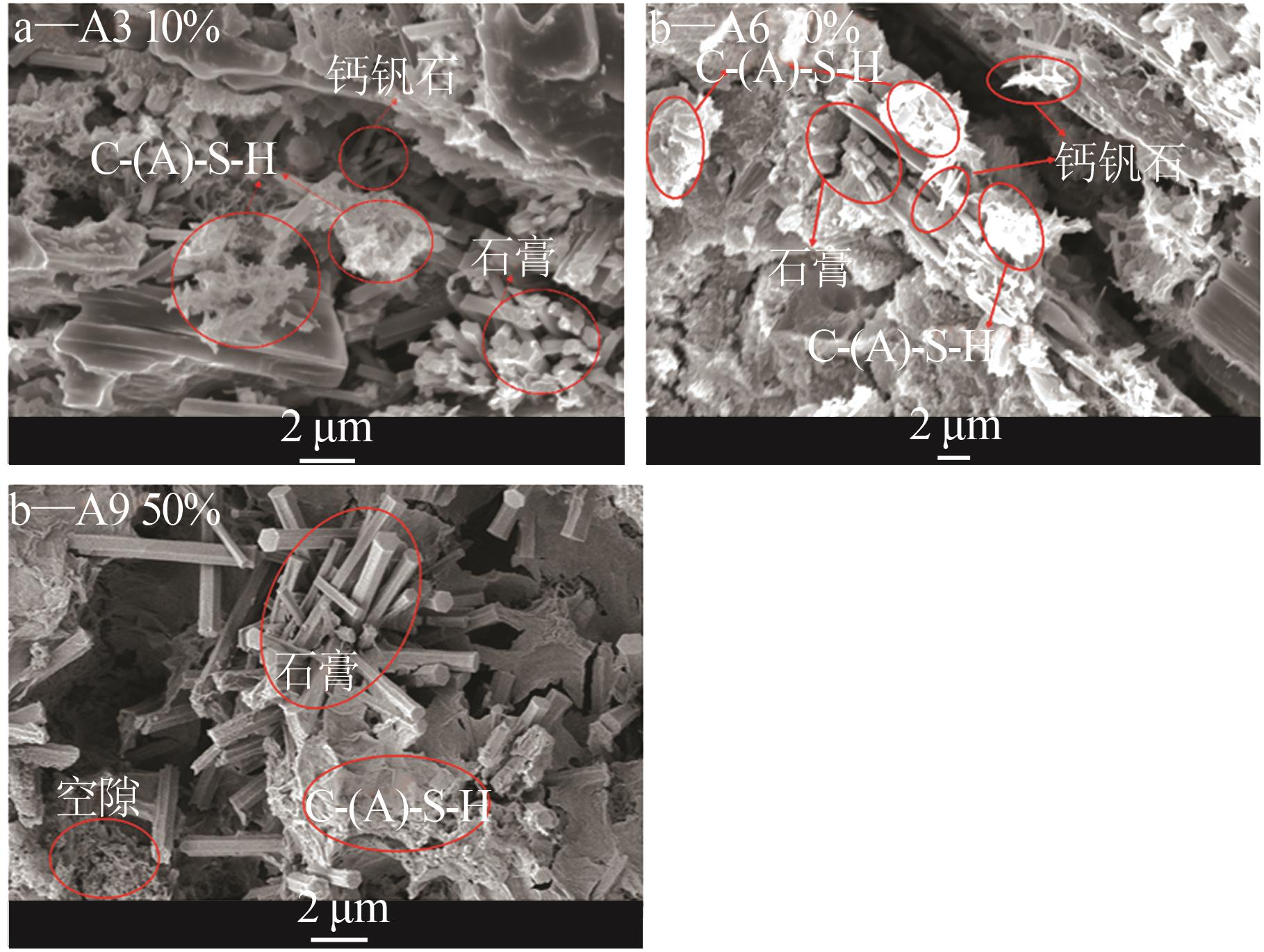
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 93-99.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0413
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on mechanical properties and microscopic characterization of phosphogypsum composite cementitious materials
WANG Feng1( ), SONG Yu1, HE Zhaoyi2, XIA Yuhua3(
), SONG Yu1, HE Zhaoyi2, XIA Yuhua3( ), BI Yanli1, FENG Hao1, CAO Dongwei4
), BI Yanli1, FENG Hao1, CAO Dongwei4
- 1. MCC Construction Engineering Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Chongqing 400037,China
2. School of Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
3. School of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
4. Highway Science Research Institute of the Ministry of Transport,Beijing 100088,China
-
Received:2024-07-19Online:2025-05-10Published:2024-08-12 -
Contact:XIA Yuhua E-mail:156993217@qq.com;2022467498@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Feng, SONG Yu, HE Zhaoyi, XIA Yuhua, BI Yanli, FENG Hao, CAO Dongwei. Study on mechanical properties and microscopic characterization of phosphogypsum composite cementitious materials[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(5): 93-99.
share this article
Table 3
Leaching toxicity test results of phosphogypsum and phosphogypsum composite cementitious materials"
| 组别 | 浸出质量浓度/(mg·L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F- | PO43- | Hg2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Cu2+ | |
| 原始磷石膏 | 148.23 | 298.24 | 0.015 00 | 0.013 0 | 0.006 0 | 0.586 |
| A7 | 4.32 | 0.18 | 0.000 15 | 0.004 5 | 0.001 0 | 0.025 |
| A8 | 3.12 | 0.06 | 0.000 08 | 0.004 1 | 0.001 1 | 0.024 |
| A9 | 2.34 | 0.05 | 0.000 08 | 0.001 2 | 0.001 2 | 0.022 |
| GB 8978—1996限值 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 周武,李杨,冯伟光,等.磷石膏的综合利用及其在建筑材料领域的应用研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报,2024,43(2):534-542. |
| ZHOU Wu, LI Yang, FENG Weiguang,et al.Research progress on comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum and its application in the field of building materials[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2024,43(2):534-542. | |
| 2 | 赵静,段晓牧,刘佳佳,等.磷石膏复合胶凝材料配比优化及浸出机制[J].矿业研究与开发,2023,43(4):30-36. |
| ZHAO Jing, DUAN Xiaomu, LIU Jiajia,et al.Ratio optimization and leaching mechanism of phosphogypsum composite cementitious material[J].Mining Research and Development,2023,43(4):30-36. | |
| 3 | 陈明胜,刘鹏,孔德文,等.外掺料对磷石膏基胶凝材料力学及导热性能的影响[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(9):113-118. |
| CHEN Mingsheng, LIU Peng, KONG Dewen,et al.Effect of external admixtures on mechanical and thermal conductivity of phosphogypsum composite cementitious materials[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(9):113-118. | |
| 4 | 徐坤,王玲玲,孔德文,等.磷石膏基胶凝材料抗压性能研究[J].中国水运(下半月),2021(22):157-158. |
| XU Kun, WANG Lingling, KONG Dewen,et al.Study on compressive properties of phosphogypsum based cementitious materials[J].China Water Transport,2021(22):157-158. | |
| 5 | 杨晨,贾永祥,杨啸,等.磷石膏基充填胶凝材料配方优选及水化机理[J/OL].华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2024(5):100-108. |
| YANG Chen, JIA Yongxiang, YANG Xiao,et al.Optimization of formula and hydration mechanism of phosphogypsum based filling cementitious materials[J].Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power(Natural Science Edition),2024(5):100-108. | |
| 6 | ZHENG Tao, LU Yuexian, LUO Shuang,et al.Effect of the phosphogypsum calcination time on the compressive mechanical properties of phosphogypsum⁃based composite cementitious materi⁃als[J].Materials Research Express,2022,9(3):035506. |
| 7 | 罗晓洪,张世俊,郭荣鑫,等.电石渣替代水泥作碱激发剂对过硫磷石膏胶凝材料性能和微观结构的影响[J].材料导报,2023,37(S2):298-304. |
| LUO Xiaohong, ZHANG Shijun, GUO Rongxin,et al.Effects of using carbide slag as an alkali activator instead of cement on the properties and microstructure of peroxyphosphogypsum cementitious materials[J].Materials Reports,2023,37(S2):298-304. | |
| 8 | 张太玥,谢凡,郭君渊.磷石膏基复合胶凝材料的性能优化及机理研究[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(9):136-142. |
| ZHANG Taiyue, XIE Fan, GUO Junyuan.Study on performance optimization and mechanism of phosphogypsum based composite cementitious materials[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(9):136-142. | |
| 9 | 王维,许向群,李杰,等.磷石膏与铜尾渣的高效耦合固定/稳定化处理[J].硅酸盐通报,2021,40(5):1601-1609. |
| WANG Wei, XU Xiangqun, LI Jie,et al.Efficient synergistic stabilization/solidification of phosphogypsum and copper smelterslag[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(5):1601-1609. | |
| 10 | 姜关照,吴爱祥,王贻明,等.生石灰对半水磷石膏充填胶凝材料性能影响[J].硅酸盐学报,2020,48(1):86-93. |
| JIANG Guanzhao, WU Aixiang, WANG Yiming,et al.Effect of lime on properties of filling cementitious material prepared by hemihydrate phosphogypsum[J].Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(1):86-93. | |
| 11 | 麻鹏飞,杨文,程宝军,等.碱激发磷石膏复合胶凝材料力学性能研究[J].混凝土与水泥制品,2021(8):83-87. |
| MA Pengfei, YANG Wen, CHENG Baojun,et al.Study on mechanical properties of alkali activated phosphogypsum composite cementitious materials[J].China Concrete and Cement Products,2021(8):83-87. | |
| 12 | 肖力光,李正鹏.复合矿物掺合料对高性能混凝土强度的研究[J].应用化工,2023,52(8):2284-2287. |
| XIAO Liguang, LI Zhengpeng.A study of the potency of composite mineral amalgamated with high⁃performance concrete[J].Applied Chemical Industry,2023,52(8):2284-2287. | |
| 13 | 余舟,何兆益,唐亮,等.典型硫酸盐固废复合胶凝材料制备与微观特性研究[J].无机盐工业,2024,56(4):90-97. |
| YU Zhou, HE Zhaoyi, TANG Liang,et al.Study on preparation and microscopic properties of typical sulfate solid waste composite cementitious materials[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2024,56(4):90-97. | |
| 14 | 刘树龙.基于矿渣基胶凝材料的充填体早期力学行为宏细观响应机制[D].淄博:山东理工大学,2021. |
| LIU Shulong.Macroscopic and microscopic response mechanisms of early mechanical behavior of filling materials based on slag based cementitious materials[D].Zibo:Shandong University of Technology,2021. | |
| 15 | TANG Liang, HE Zhaoyi, PEI Shanshan,et al.Hydration characteristics and pollutant solidification mechanism of full solid waste electrolytic manganese residue super sulfate cement[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2024,84:108563. |
| 16 | 张歆,刘方,朱健,等.基于电解锰渣-磷石膏复合胶凝材料的制备与表征[J].硅酸盐通报,2021,40(5):1610-1619. |
| ZHANG Xin, LIU Fang, ZHU Jian,et al.Preparation and characterization of composite cementitious material based on electrolytic manganese residue⁃phosphogypsum[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(5):1610-1619. | |
| 17 | 闫蔚,曾柏淋,孟江,等.石膏红外图谱鉴定研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2016,36(7):2098-2103. |
| YAN Wei, ZENG Bolin, MENG Jiang,et al.Study on the identification of gypsum fibrosum with FTIR[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2016,36(7):2098-2103. | |
| 18 | 马飞越.含磷石膏的复合胶凝材料的制备及其关键性能研究[D].昆明:昆明理工大学,2023. |
| MA Feiyue.The horse flew over preparation and key performance study of composite cementitious materials containing phosphorus gypsum[D].Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology,2023. | |
| 19 | HAN Yi, LIN Runsheng, WANG Xiaoyong.Performance and sustainability of quaternary composite paste comprising limestone,calcined Hwangtoh clay,and granulated blast furnace slag[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2021,43:102655. |
| 20 | JIN Mantong, ZHENG Zidan, SUN Ye,et al.Resistance of metakaolin-MSWI fly ash based geopolymer to acid and alkaline environments[J].Journal of Non⁃Crystalline Solids,2016,450:116-122. |
| 21 | ZHANG Zuhua, WANG Hao, PROVIS J L,et al.Quantitative kinetic and structural analysis of geopolymers.Part 1.The activation of metakaolin with sodium hydroxide[J].Thermochimica Acta,2012,539:23-33. |
| 22 | YLMÉN R, JÄGLID U, STEENARI B M,et al.Early hydration and setting of Portland cement monitored by IR,SEM and Vicat techniques[J].Cement and Concrete Research,2009,39(5):433-439. |
| [1] | LONG Qijun, WU Qin, TAO Jia, CHEN Chuanxiang, WANG Jianxiang, YU Fang. Study on mechanical properties of high content modified hemihydrate phosphogypsum wall materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 89-96. |
| [2] | ZHAO Mengyan, CHEN Junwu, WANG Xun, WEI Na, WENG Xiaoqing, CHEN Yingxin. Study on purification of phosphogypsum by reverse flotation of octadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride and its removal mechanism of quartz [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 111-117. |
| [3] | HAN Yingming, SUN Ruize, SUN Yining, SONG Xingfei. Study on properties of modified magnesia sulfide cement by calcined coal gangue powder [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 97-104. |
| [4] | LENG Manxi, ZHU Yu, YAN Jikang, XIE Ke, ZOU Yongjie. Study on crystallization characteristics and mineral flotation performance of industrial waste phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 108-115. |
| [5] | TAN Shanyi, WEN Huizi, HE Shuyu, ZHANG Liwen, CHEN Shaohua, XI Benjun. Study on leaching behavior and kinetics of phosphorus from phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 105-112. |
| [6] | TANG Kaijing, LIU Chuanbei, LI Yingding, JIANG Yong, WU Junnan, ZHANG Tao. Research on preparation and mechanism of superhydrophobic phosphogypsum products [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 97-102. |
| [7] | LIU Cijun, WU Ziyang, CHENG Shukai, CHEN Xuyong. Effect of recycled fine aggregate on mechanical properties and autogenous shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 75-81. |
| [8] | TANG Xuemei, WANG Meibo, XU Li, ZHANG Xujie, TAI Shijun, YI Xianmei, LIU Hongjuan, PAN Linyi. Study on whitening of phosphogypsum by low⁃temperature calcination [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 110-115. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ruijun, CHEN Guoliang, SONG Chuncao, ZHU Yafei. Effects of graphene oxide on mechanical properties and chloride penetration resistance of ultra⁃high performance concrete incorporating recycled sand [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 54-59. |
| [10] | SUN Lan, CHEN Shiying, YANG Liuxu, NIU Yiming, ZHAO Aonan. Basic study on fixing soluble phosphorus in phosphogypsum with magnesium slag [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 92-98. |
| [11] | HU Cheng, LIU Meng, XIANG Weiheng, CHEN Ping, WANG Neng, LU Guanju, ZHOU Jinlan. Preparation of α-hemihydrous gypsum from CaCl2 and MgCl2 and their composite solution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 112-117. |
| [12] | HU Dian, GUO Ze, ZHANG Hanquan, LU Manman. Research on effects of roasting process and typical impurities on reduction and decomposition process of phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 88-95. |
| [13] | HU Cheng, LIU Meng, XIANG Weiheng, DUAN Pengxuan, LI Shunkai, MING Yang, WANG Neng, LU Guanju. Effect of NaCl solution concentration on transcrystallization behavior of α-hemihydrate gypsum from phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 87-93. |
| [14] | TU Yanping, BAI Dengxian, CHENG Shukai, XIE Junjie, HUANG Zhiliang, CHEN Guofu. Effect of high temperature modification of mineral powder and quicklime on properties of phosphogypsum cement based materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 94-101. |
| [15] | WANG Mingshun, AO Xianquan, YUAN Xing, DONG Wenyan, CHEN Qianlin. Study on effect of crystallizer on preparation of anhydrous calcium sulfate from phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 101-107. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||