Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (7): 73-79.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0371
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on phase structure and properties of hydrogen storage alloy for automotive battery anode
CHEN Chengchun1( ), LI Yunqin2, ZHAO Meiqin3
), LI Yunqin2, ZHAO Meiqin3
- 1. Fujian Chuanzheng Communications College,Fuzhou 350007,China
2. Fuzhou University,Fuzhou 350108,China
3. Xiamen University,Xiamen 361005,China
-
Received:2024-07-01Online:2025-07-10Published:2025-07-22
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Chengchun, LI Yunqin, ZHAO Meiqin. Study on phase structure and properties of hydrogen storage alloy for automotive battery anode[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(7): 73-79.
share this article
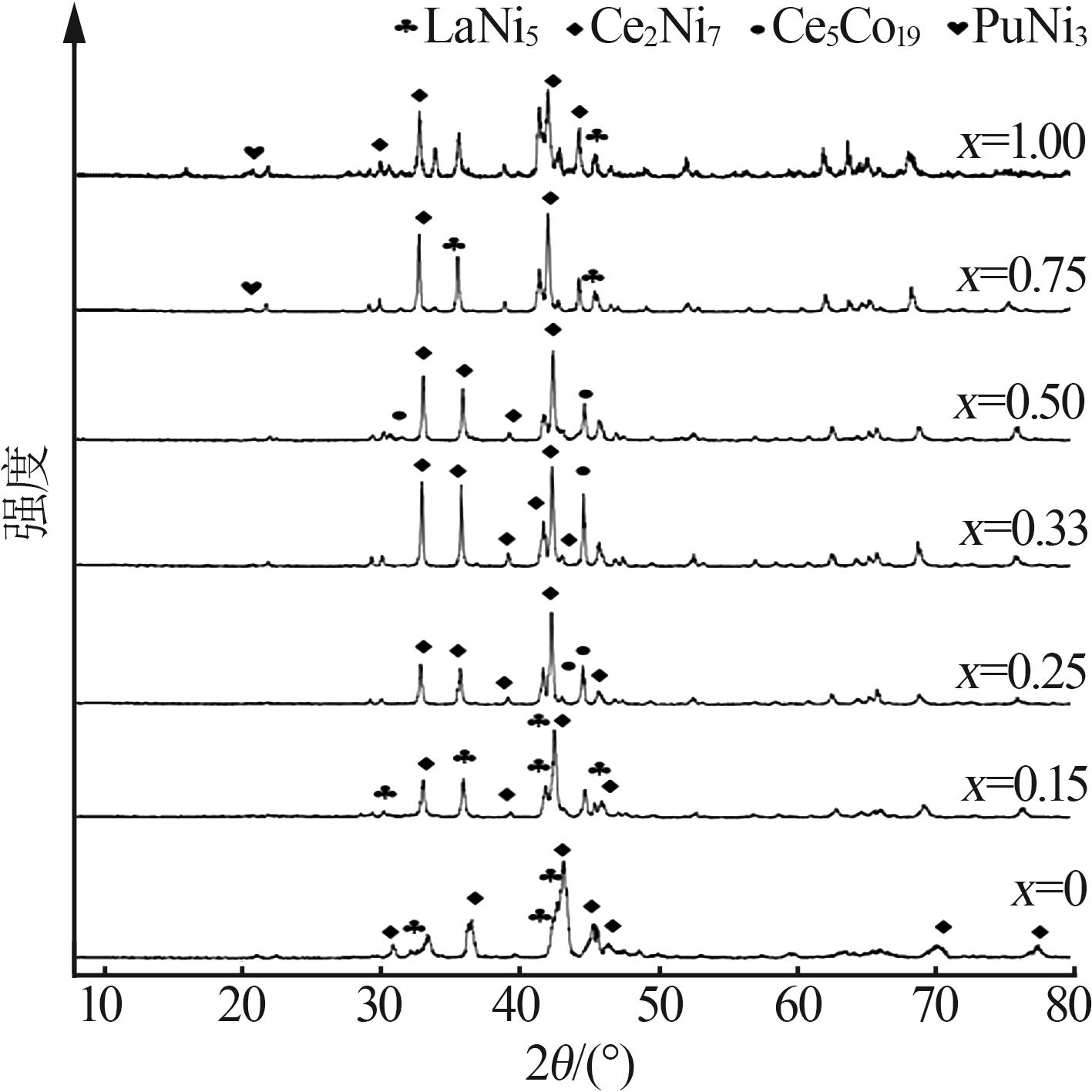
Table 1
Phase structure and phase abundance test results of RENi3.2Mn0.2Al0.15 hydrogen storage alloy"
| x值 | 相结构 | 晶格常数 | 相丰度/ % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | |||
| 0 | LaNi5 | 0.502 3 | 0.398 3 | 0.086 4 | 47.47 |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.499 3 | 2.441 6 | 0.524 7 | 52.53 | |
| 0.15 | LaNi5 | 0.501 5 | 0.400 6 | 0.086 7 | 38.84 |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.500 3 | 2.432 5 | 0.524 9 | 61.16 | |
| 0.25 | Ce5Co19 | 0.494 5 | 4.878 5 | 1.029 4 | 21.20 |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.502 2 | 2.439 7 | 0.530 3 | 78.80 | |
| 0.33 | Ce5Co19 | 0.498 7 | 4.861 2 | 1.043 4 | 6.93 |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.502 6 | 2.435 8 | 0.533 4 | 93.07 | |
| 0.50 | Ce5Co19 | 0.491 4 | 4.868 0 | 1.025 3 | 37.98 |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.502 1 | 2.432 9 | 0.529 6 | 62.02 | |
| 0.75 | PuNi3 | 0.502 7 | 2.432 1 | 0.530 7 | 28.09 |
| LaNi5 | 0.502 7 | 0.406 5 | 0.089 4 | 11.60 | |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.499 2 | 2.458 0 | 0.528 9 | 60.31 | |
| 1.00 | PuNi3 | 0.499 9 | 2.436 5 | 0.525 8 | 17.59 |
| LaNi5 | 0.506 9 | 0.402 5 | 0.089 0 | 33.64 | |
| Ce2Ni7 | 0.499 8 | 2.458 9 | 0.530 3 | 48.77 | |
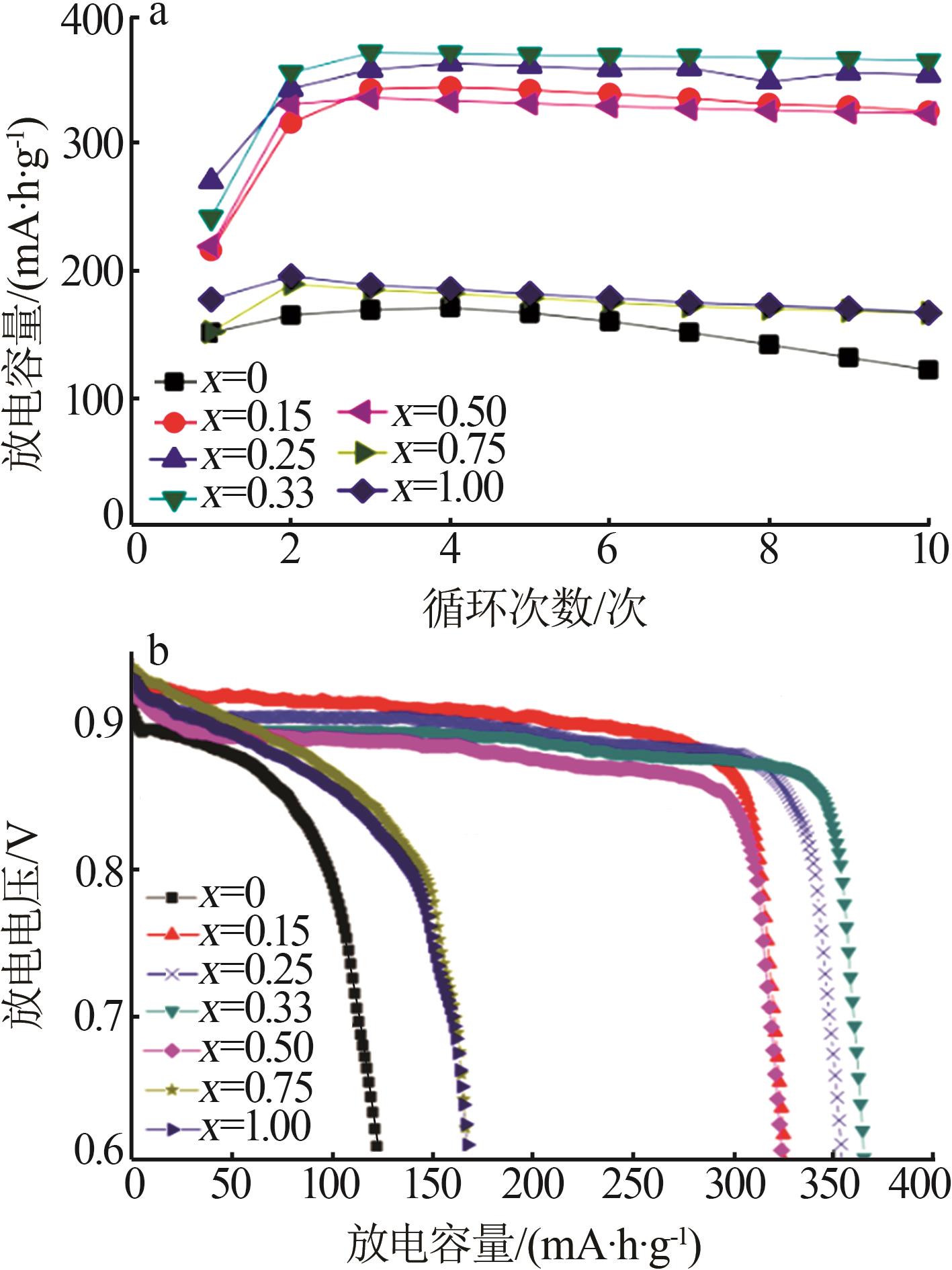
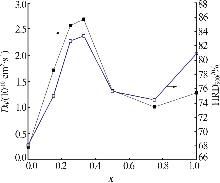
Table 2
Electrochemical property of RENi3.2Mn0.2Al0.15 hydrogen storage alloy at different x values"
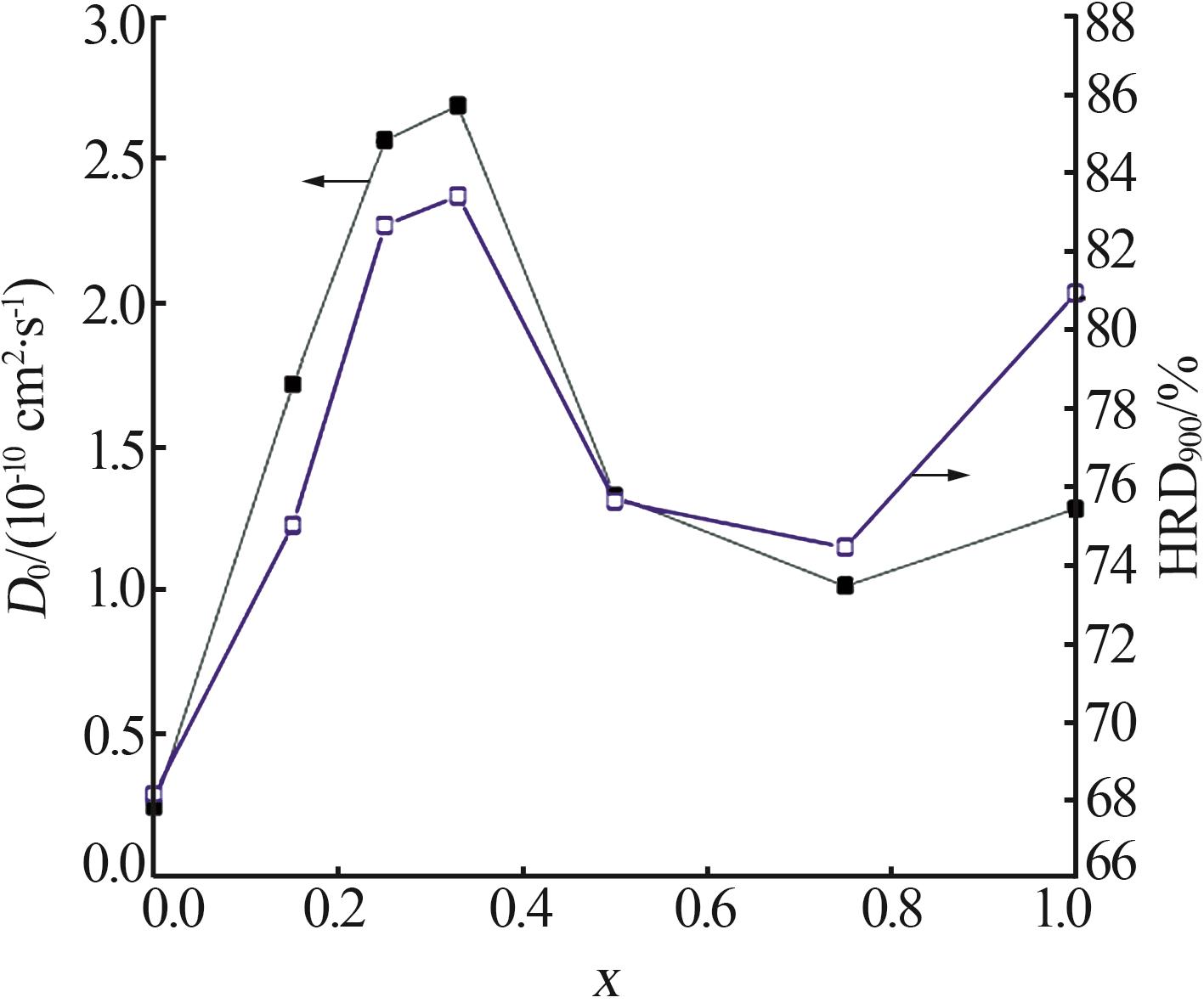
| x值 | 循环100次时的容量保持率(S100)/% | 腐蚀电 位(E)/V | 腐蚀电流 密度(i)/ (mA·cm-2) | 高倍率放 电性能(HRD900)/% | 氢扩散 系数(D0)/ (10-10cm2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 14.34 | -0.924 | 8.85 | 68.23 | 0.95 |
| 0.15 | 33.70 | -0.916 | 8.84 | 75.11 | 1.82 |
| 0.25 | 74.02 | -0.901 | 6.68 | 82.77 | 2.67 |
| 0.33 | 89.01 | -0.900 | 5.92 | 83.53 | 2.80 |
| 0.50 | 77.98 | -0.904 | 6.90 | 75.73 | 1.43 |
| 0.75 | 78.36 | -0.908 | 6.80 | 74.55 | 1.12 |
| 1.00 | 79.06 | -0.905 | 6.84 | 81.03 | 1.39 |
| [1] | 臧金环,李春玲.《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035年)》调整解读[J].汽车工艺师,2021(S1):32-34. |
| ZANG Jinhuan, LI Chunling.Interpretation of the adjustment of the development plan for the new energy vehicle industry(2021-2035)[J].Auto Manufacturing Engineer,2021(S1):32-34. | |
| [2] | 李瑾瑜.稀土储氢合金产业现状及发展趋势[J].稀土信息,2023(6):30-34. |
| LI Jinyu.The current situation and development trend of rare earth hydrogen storage alloy industry[J].Rare Earth Information,2023(6):30-34. | |
| [3] | LI Jinyu.Current situation and development trends of rare earth hydrogen storage alloy industry[J].China Rare Earth Information,2023,29(2):12-20. |
| [4] | 熊玮,周淑娟,赵玉园,等.超晶格稀土储氢合金材料的研究进展[J].稀土,2023,44(4):40-57. |
| XIONG Wei, ZHOU Shujuan, ZHAO Yuyuan,et al.Review of rare earth hydrogen storage alloy materials with superlattice structures[J].Chinese Rare Earths,2023,44(4):40-57. | |
| [5] | 李媛,张璐,韩树民.稀土-镁-镍系超晶格合金结构与储氢性能研究及进展[J].燕山大学学报,2020,44(3):323-330. |
| LI Yuan, ZHANG Lu, HAN Shumin.Development in structure and hydrogen storage properties of rare earth-magnesium-nickel-based super-lattice alloys[J].Journal of Yanshan University,2020,44(3):323-330. | |
| [6] | TANG Rui, LIU Liqin, LIU Yongning,et al.Study on the microstructure and the electrochemical properties of Ml0.7Mg0.2Ni2.8Co0.6 hydrogen storage alloy[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2003,28(8):815-819. |
| [7] | JIANG Zhaojun, WANG Jun, CAO Dongmei.Research progress of rare earth-based hydrogen storage alloys[J].Key Engineering Materials,2020,861:354-362. |
| [8] | 杨天辉,刘力,周曦,等.汽车电池用无镁储氢合金的合金化与电化学性能[J].实验室研究与探索,2022,41(12):57-62. |
| YANG Tianhui, LIU Li, ZHOU Xi,et al.Alloying and electrochemical properties of magnesium free hydrogen storage alloys for automotive batteries[J].Research and Exploration in Laboratory,2022,41(12):57-62. | |
| [9] | LI Jiaxuan, HE Xiangyang, XIONG Wei,et al.Phase forming law and electrochemical properties of A2B7-type La-Y-Ni-based hydrogen storage alloys with different La/Y ratios[J].Journal of Rare Earths,2023,41(2):268-276. |
| [10] | 鲁航,王文凤,陶旭杰,等.AB4相对A5B19型稀土镁镍系合金储氢性能的影响研究[J].稀土,2023,44(1):157-164. |
| LU Hang, WANG Wenfeng, TAO Xujie,et al.Effect of AB4 phase on hydrogen storage properties of A5B19-type RE-Mg-Ni-based alloy[J].Chinese Rare Earths,2023,44(1):157-164. | |
| [11] | 熊玮,张旭,周淑娟,等.不同化学计量比La-Y-Ni系储氢合金的研究Ⅰ:表面状态与组织结构[J].稀土,2020,41(6):9-17. |
| XIONG Wei, ZHANG Xu, ZHOU Shujuan,et al.Study on La-Y-Ni hydrogen storage alloys with different stoichiometric ratiosⅠ:Surface state and structure[J].Chinese Rare Earths,2020, 41(6):9-17. | |
| [12] | 同艳维,李娜丽,张雪峰.稀土Ce添加量对钒基储氢合金显微组织和电化学性能的影响[J].稀有金属与硬质合金,2021,49(6):42-46. |
| TONG Yanwei, LI Nali, ZHANG Xuefeng.Effect of addition amount of rare earth Ce on microstructure and electrochemical properties of vanadium-based hydrogen storage alloys[J].Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides,2021,49(6):42-46. | |
| [13] | WU Ran, YUAN Huiping, LIU Yuru,et al.Effect of carbon coating on electrochemical properties of AB3.5-type La-Y-Ni-based hydrogen storage alloys[J].Journal of Rare Earths,2022,40(8):1264-1271. |
| [14] | 范庆科,孟庆华.汽车用La0.79Mg0.21Ni3.95储氢合金的制备与电化学性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(3):71-76. |
| FAN Qingke, MENG Qinghua.Study on preparation and electrochemical properties of La0.79Mg0.21Ni3.95 hydrogen storage alloy for vehicles[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54 (3):71-76. | |
| [15] | ZHOU Na, DU Wenbo, ZHANG Peilong,et al.Microstructure and electrochemical properties of La0.8– x MM x Mg0.2Ni3.1Co0.3Al0.1 (x=0,0.1,0.2,0.3) alloys[J].Rare Metals,2017,36(8):645- 650. |
| [16] | 邵光俭,王克乐.成分对汽车用(La0.7Mg0.3)Nix合金储氢特性的影响[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(9):51-56. |
| SHAO Guangjian, WANG Kele.Effect of composition on hydrogen storage characteristics of (La0.7Mg0.3)Ni x alloy for vehicle[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(9):51-56. | |
| [17] | LIN Shuangping, NIE Zuoren, HUANG Hui,et al.Annealing behavior of a modified 5083 aluminum alloy[J].Materials & Design,2010,31(3):1607-1612. |
| [18] | 徐津,李宝犬,王利,等.A2B7型La-Y-Ni与La-Mg-Ni储氢合金电化学性能研究[J].有色金属工程,2020,10(12):9-15, 37. |
| XU Jin, LI Baoquan, WANG Li,et al.Study on the electrochemical properties of La-Y-Ni and La-Mg-Ni hydrogen storage alloys with A2B7 type[J].Nonferrous Metals Engineering,2020,10(12):9-15,37. | |
| [19] | 李英杰,姚继伟,雍辉,等.稀土掺杂对稀土-镁基合金储氢性能的影响[J].材料导报,2022,36(20):187-194. |
| LI Yingjie, YAO Jiwei, YONG Hui,et al.Effect of rare earth doping on hydrogen storage properties of RE-Mg based hydrogen storage alloys[J].Materials Reports,2022,36(20):187-194. | |
| [20] | 李通,罗新宇,陈子然.退火温度对汽车镍氢电池用储氢合金电化学性能的影响[J].稀土,2022,43(5):93-101. |
| LI Tong, LUO Xinyu, CHEN Ziran.Effect of annealing temperature on electrochemical properties of hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH battery[J].Chinese Rare Earths,2022,43(5):93- 101. | |
| [21] | GUO Jin, LI Chonghe, LIU Honglin,et al.Effect of rare earth compositions on the hydrogen storage properties of AB5-type alloys and pattern recognition analysis[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2019,144(7):2276-2278. |
| [1] | YU Panpan, WU Zongjin, WU Lang, YANG Yi, LIN Qian, PAN Hongyan. Study on synergistic preparation of wood chip based carbon materials with phosphoric acid-sulfuric acid and their electrochemical properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 79-88. |
| [2] | CAO Shengliang, ZHENG Biaodi, ZHOU Xi, MENG Ranhao. Effect of Nd replacing Y on electrochemical performance of hydrogen storage alloys for automotive battery anodes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 45-51. |
| [3] | WANG Peng, PU Zhihua, WANG Tianxiang, LIN Jingyi, WAN Yuanxin. Investigation on effecte of different carbon source on processing performance of LiFePO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 60-66. |
| [4] | SU Baocai, ZHANG Qin, XIE Yuanjian, CAI Pingxiong, PAN Yuanfeng. Advances in synthesis methods and structural modification of LiMnFePO4 materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 28-36. |
| [5] | HU Wenjuan, SHEN Xiaozhong, WANG Rujia, LU Lu, ZOU Lianli. Effect of annealing temperature on phase structure and electrochemical performance of hydrogen storage alloys for automotive batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 51-58. |
| [6] | LIU Jiasheng, LUO Xiaoqiang, HOU Cuihong, XUE Lingwei. Effects of fluorine doping on electrochemical behavior of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 45-50. |
| [7] | WAN Feng, YAN Yingchun, FAN Zhuangjun. Research progress and prospect of halide solid electrolytes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 15-29. |
| [8] | PENG Weifeng, SHI Wei. Effect of Co replacing Ni on electrochemical performance of La0.8Mg0.2Ni3.8-x Co x hydrogen storage alloy for automotive batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 65-71. |
| [9] | CHEN Tiandong, ZHAO Guangzhao, HAI Chunxi, DONG Shengde, HE Xin, XU Qi, FENG Hang, YUAN Shaoxiong, MA Luxiang, ZHOU Yuan. Research and industrialization progress on coating and doping modification of lithium-rich manganese-based materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 1-8. |
| [10] | LI Zhiqiang, GUO Zhenghua, HE Yuru. Effect of Zr/Mn element substitution and annealing treatment on electrochemical properties of hydrogen storage alloys for automotive batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 78-84. |
| [11] | QU Lian, LI Yuezhu, LI Mingya, WANG Zhaopei, CHEN Yanyu, LI Yineng. Study on effect of Fe2P on electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(12): 88-94. |
| [12] | HOU Shunli,ZHAO Duan,ZHOU Geng,WEI Shishi,LI Jian,WANG Jiatai. Research progress on doping modification of high nickel ternary nickel-cobalt-aluminum cathode material [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(8): 40-46. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xinyi,DI Yuli,DONG Qi,CHEN Xingyu,ZHANG Zhengdong. Research progress on preparation of Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 38-44. |
| [14] | LU Zheng,CHEN Kunfeng,XUE Dongfeng. Study on large-scale preparation and electrochemical properties of high thermal stabilized α-Fe2O3 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 45-50. |
| [15] | FAN Qingke,MENG Qinghua. Study on preparation and electrochemical properties of La0.79Mg0.21Ni3.95 hydrogen storage alloy for vehicles [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 71-76. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||