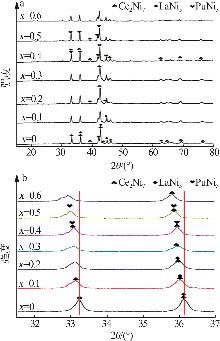
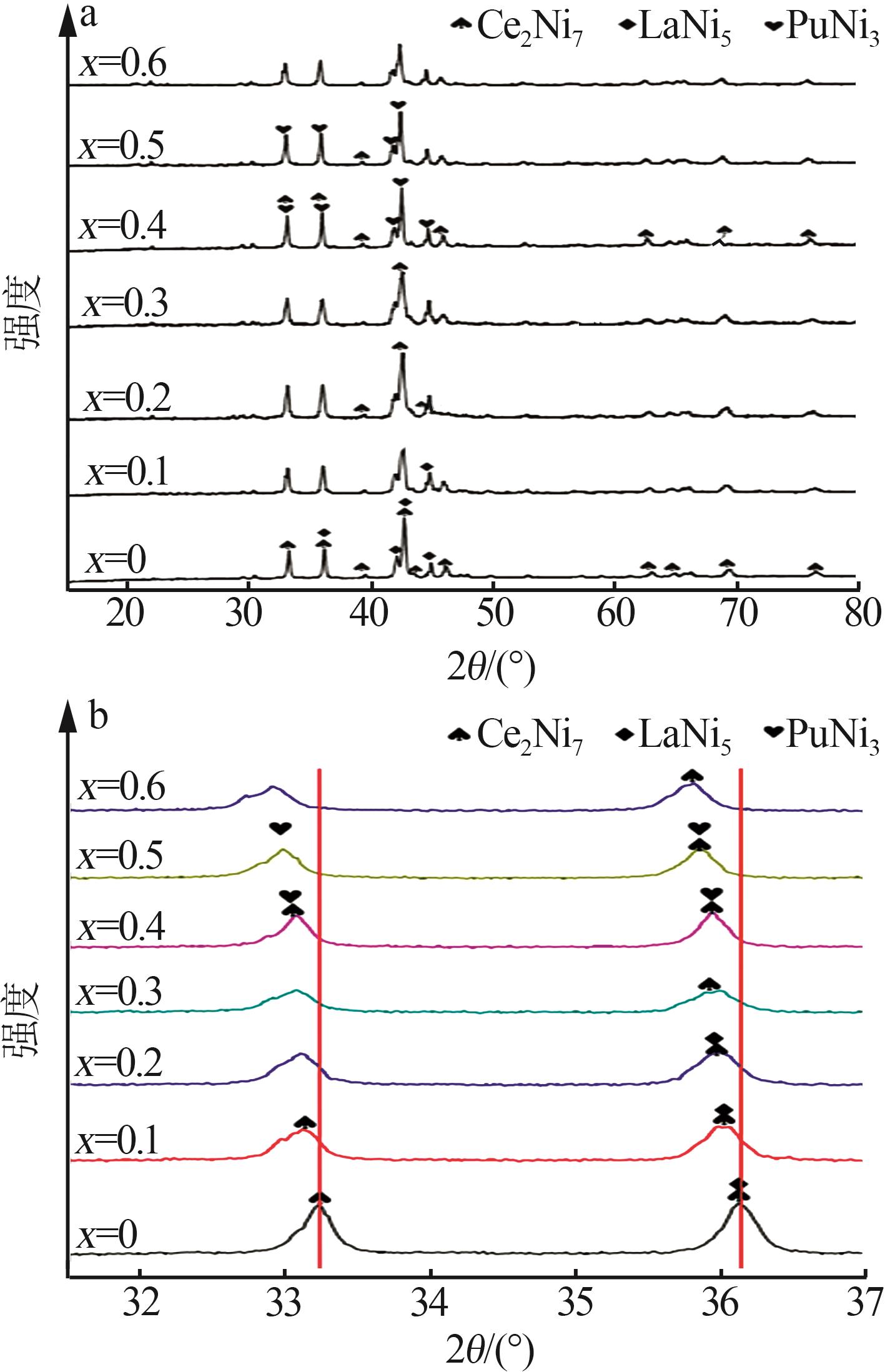
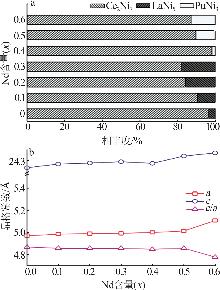
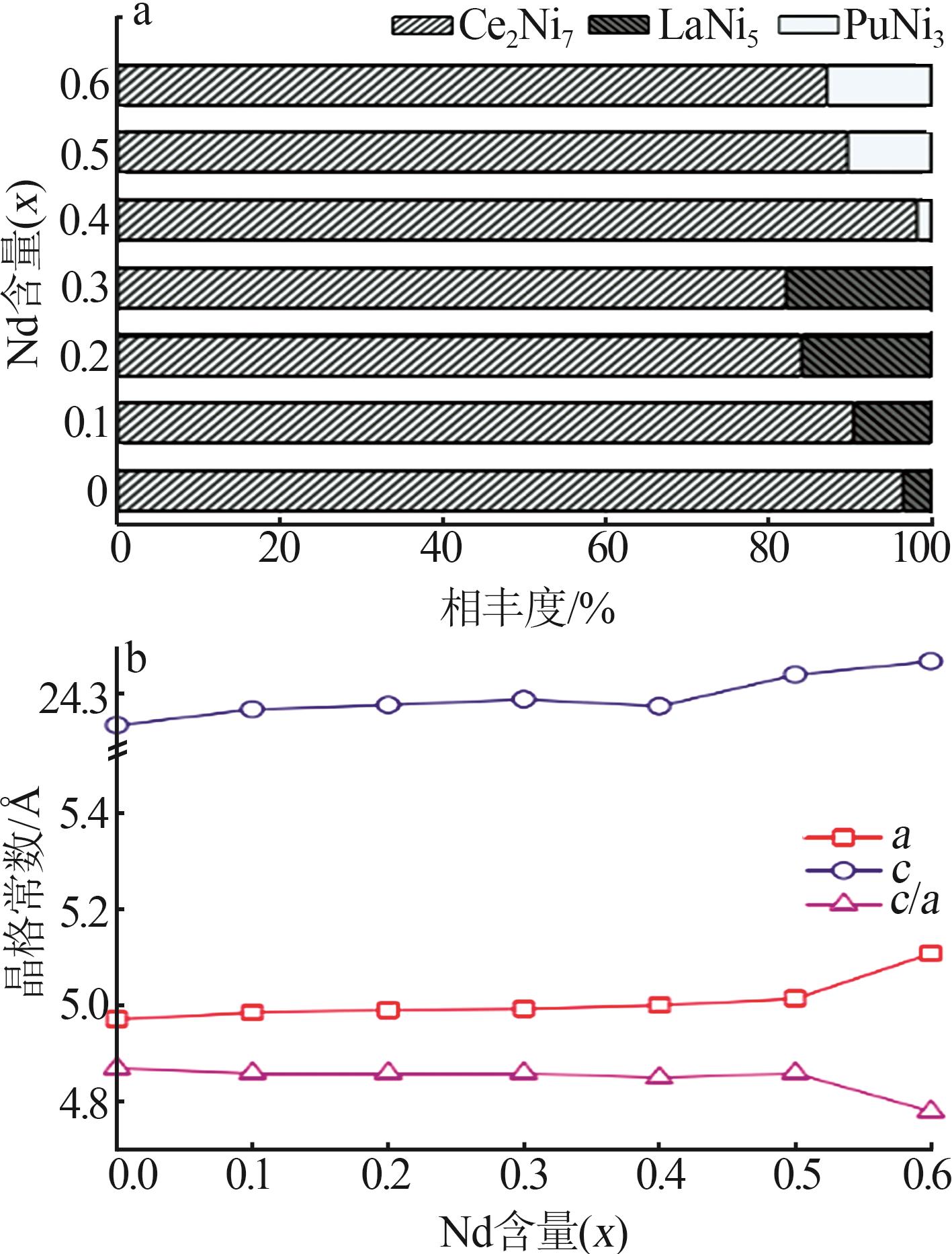
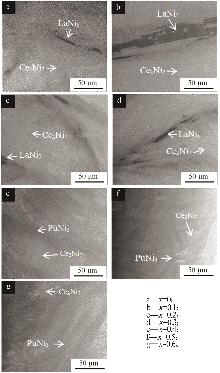
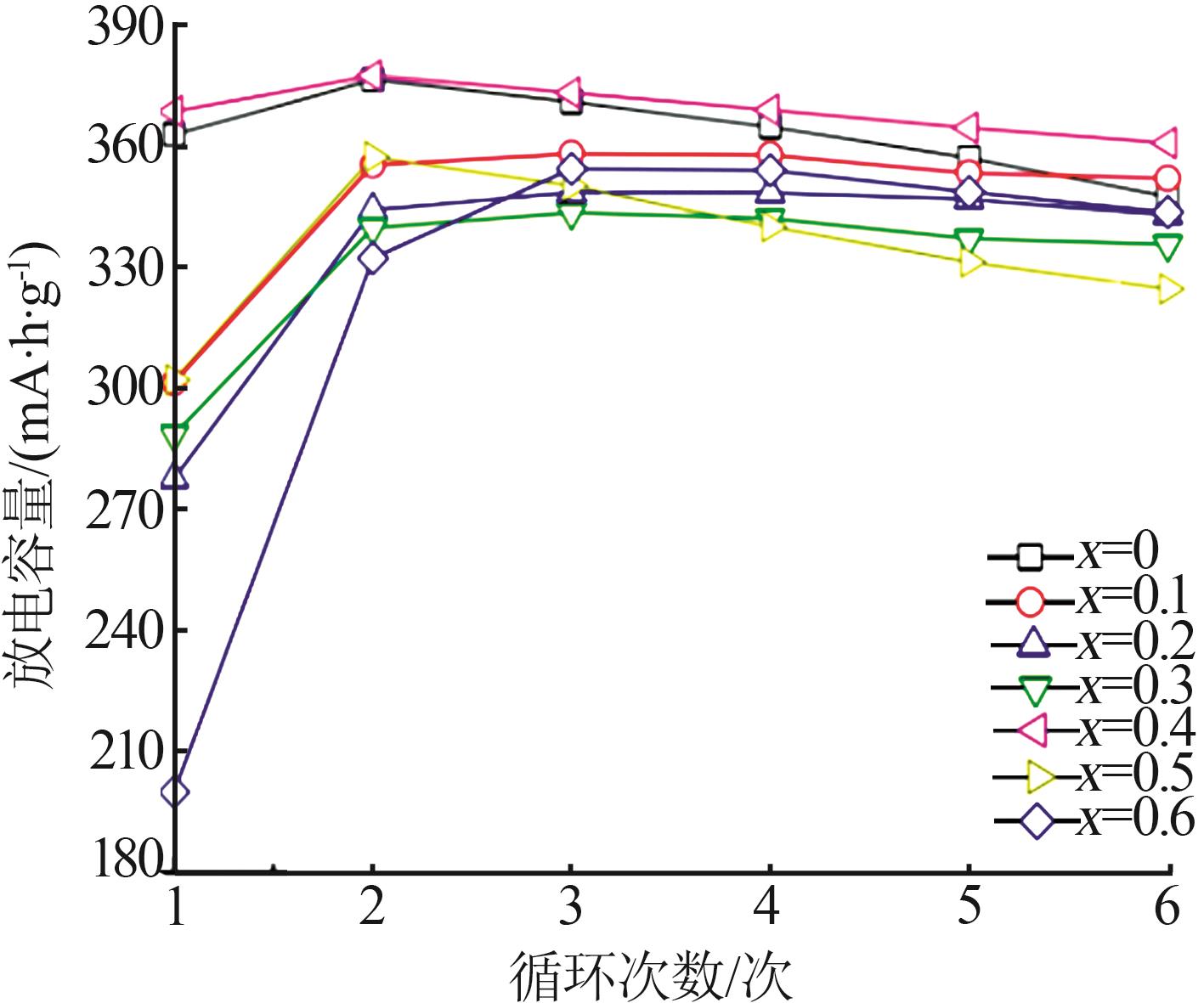
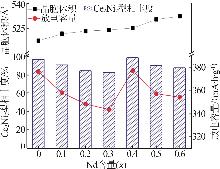
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 45-51.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0251
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Nd replacing Y on electrochemical performance of hydrogen storage alloys for automotive battery anodes
CAO Shengliang1( ), ZHENG Biaodi1, ZHOU Xi2, MENG Ranhao2
), ZHENG Biaodi1, ZHOU Xi2, MENG Ranhao2
- 1. Jiyuan vocational and technical college,Jiyuan 459000,China
2. Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450001,China
-
Received:2024-05-07Online:2025-04-10Published:2025-04-21
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CAO Shengliang, ZHENG Biaodi, ZHOU Xi, MENG Ranhao. Effect of Nd replacing Y on electrochemical performance of hydrogen storage alloys for automotive battery anodes[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 45-51.
share this article
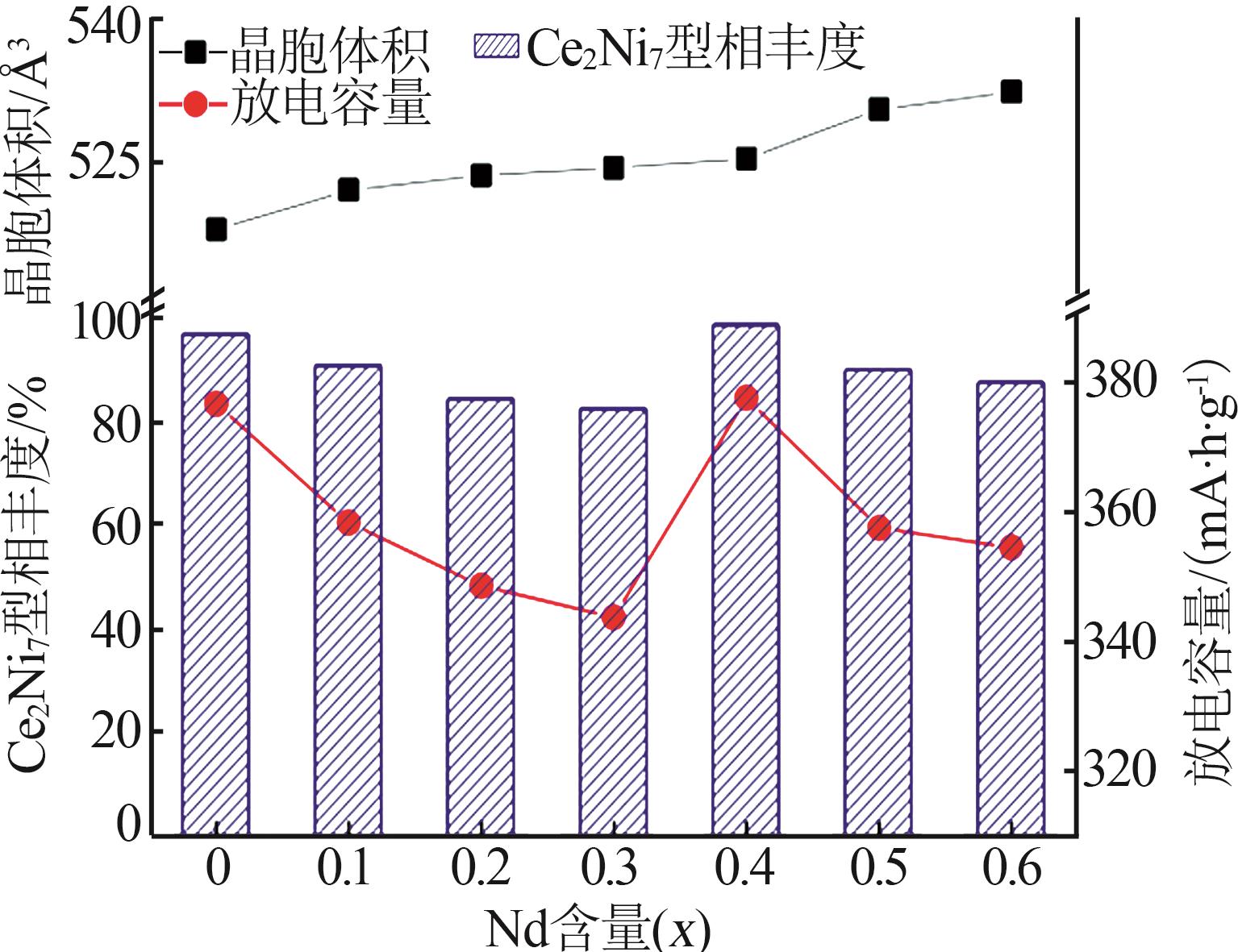
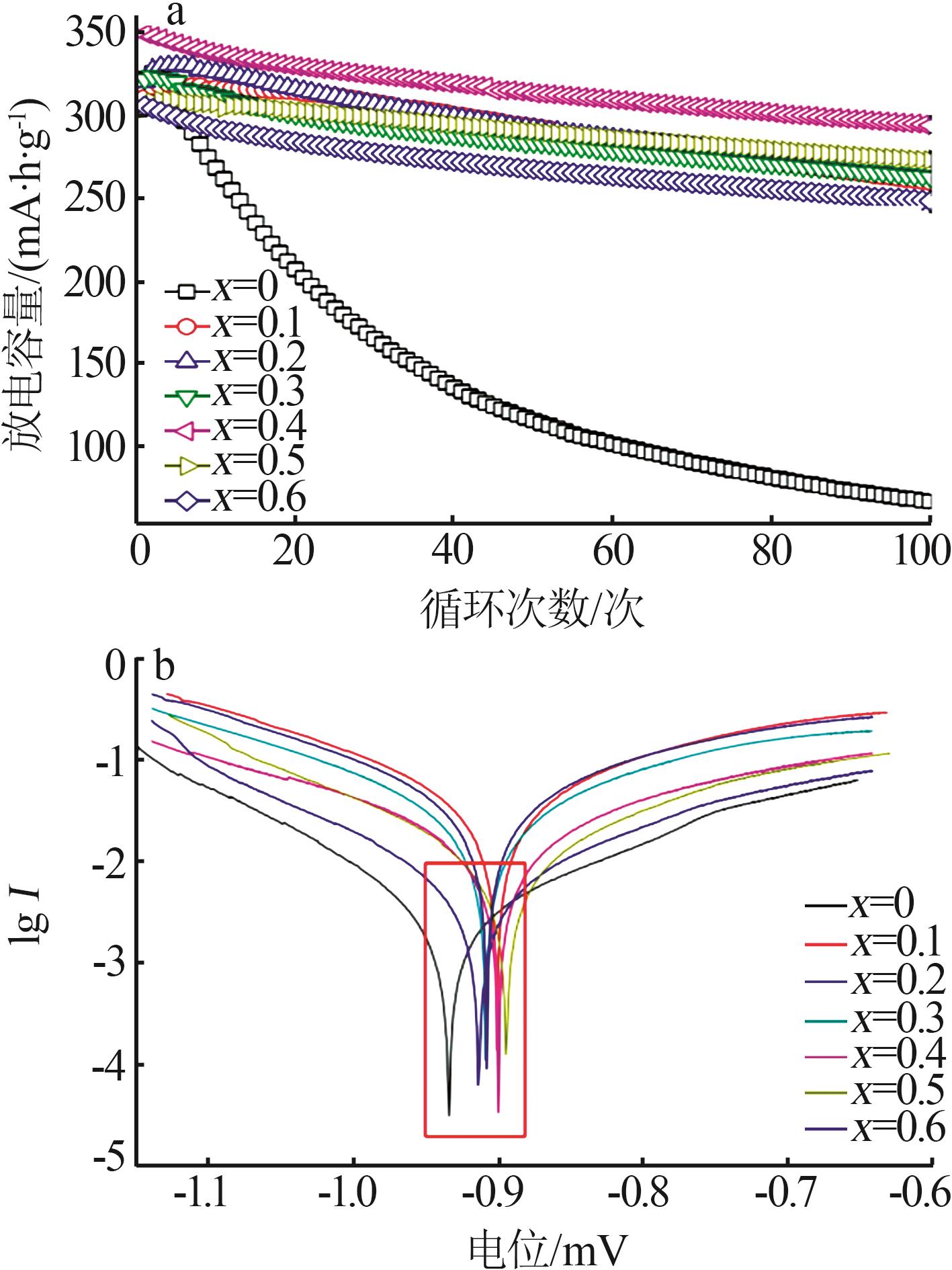
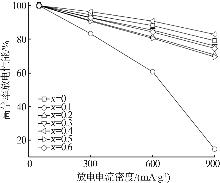
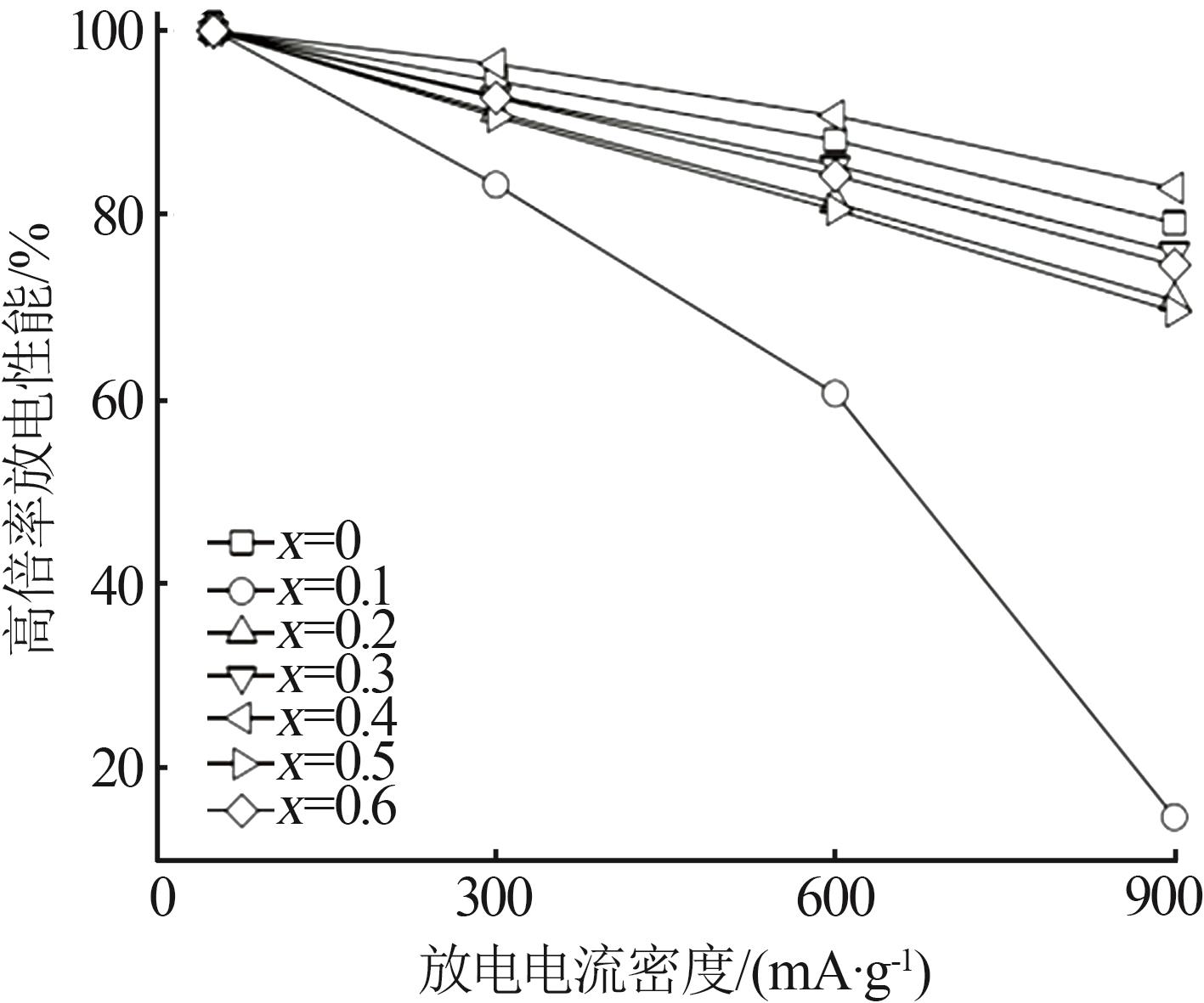
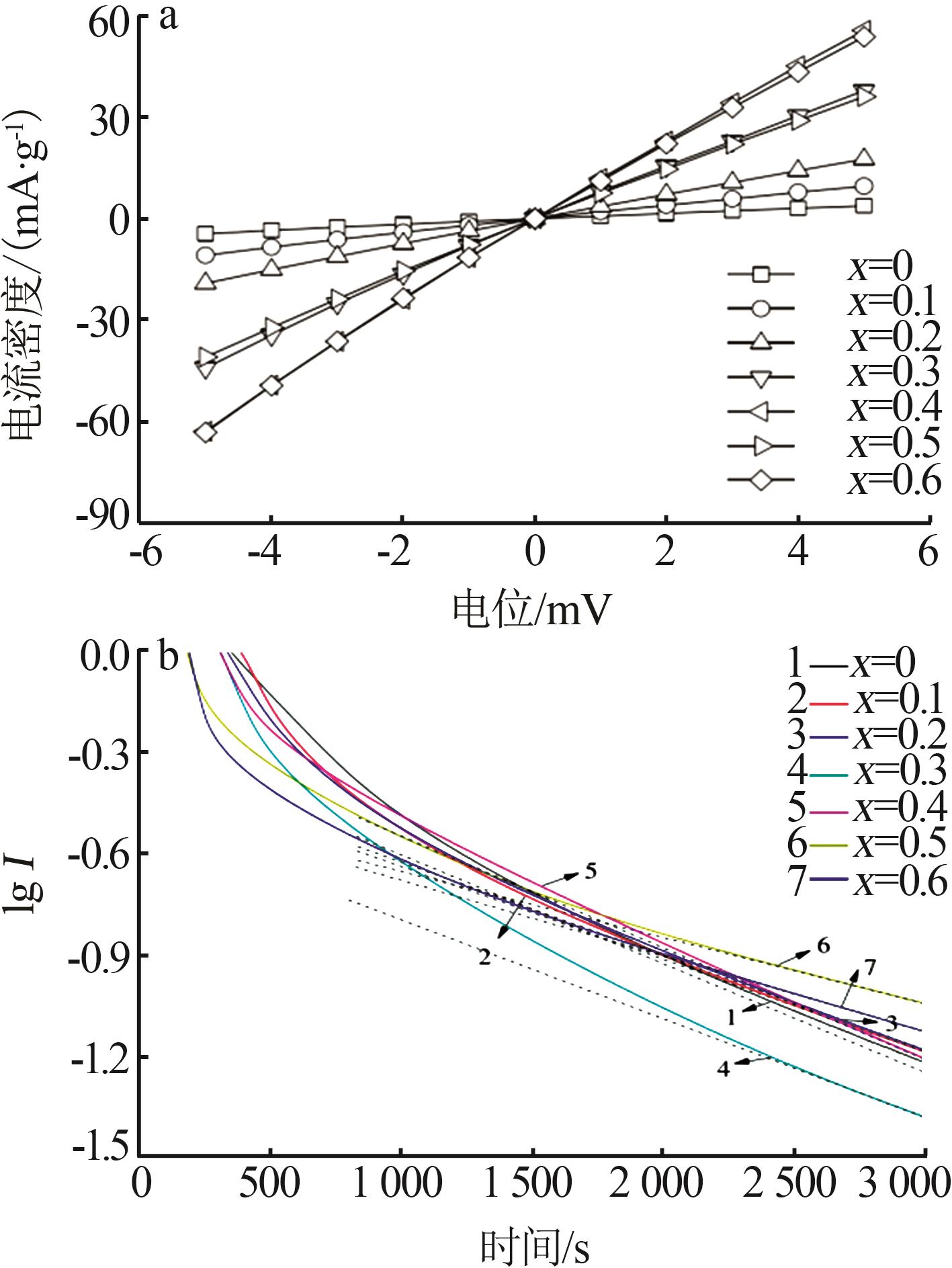
Table 1
Electrochemical parameters of hydrogen storage alloys with different contents of Nd element replacing Y"
| x | 最大放电容量 Cmax/(mA∙h∙g-1) | 容量保持率S100/% | 高倍率放电性能HRD900/% | 腐蚀电位/ V | 腐蚀电流密度/ (mA·cm-2) | 交换电流密度/ (mA·g-1) | 氢扩散系数/ (10-10 cm2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 377.8 | 20.33 | 79.23 | -0.945 | 6.330 | 22.82 | 1.70 |
| 0.1 | 359.5 | 81.50 | 14.75 | -0.912 | 5.253 | 54.54 | 1.54 |
| 0.2 | 349.8 | 80.75 | 70.82 | -0.925 | 6.054 | 96.36 | 1.59 |
| 0.3 | 344.9 | 81.32 | 76.09 | -0.920 | 5.745 | 214.72 | 1.65 |
| 0.4 | 378.8 | 84.27 | 82.99 | -0.911 | 5.067 | 310.07 | 1.86 |
| 0.5 | 358.7 | 88.28 | 69.64 | -0.906 | 4.698 | 201.42 | 1.14 |
| 0.6 | 355.7 | 81.33 | 74.66 | -0.919 | 5.321 | 305.91 | 1.29 |
| [1] | 张凤霞,谈诚.先进镍氢电池负极材料的研究进展[J].材料导报,2023,37(S2):10-18. |
| ZHANG Fengxia, TAN Cheng.Research progress of advanced cathode electrode materials for nickel-metal hydride battery[J].Materials Reports,2023,37(S2):10-18. | |
| [2] | 熊玮,周淑娟,赵玉园,等.超晶格稀土储氢合金材料的研究进展[J].稀土,2023,44(4):40-57. |
| XIONG Wei, ZHOU Shujuan, ZHAO Yuyuan,et al.Review of rare earth hydrogen storage alloy materials with superlattice structur-es[J].Chinese Rare Earths,2023,44(4):40-57. | |
| [3] | XIE Yichao, WU Guanjiu, LI Yuan,et al.High-performance La-Mg-Ni-based alloys prepared with low cost raw materials[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(79):30832-30843. |
| [4] | 李通,罗新宇,陈子然.退火温度对汽车镍氢电池用储氢合金电化学性能的影响[J].稀土,2022,43(5):93-101. |
| LI Tong, LUO Xinyu, CHEN Ziran.Effect of annealing temperature on electrochemical properties of hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH battery[J].Chinese Rare Earths,2022,43(5):93-101. | |
| [5] | 郗玉平,罗志欢,田可欣.快淬速度对汽车用储氢合金电化学性能的影响[J].实验室研究与探索,2022,41(2):8-12,83. |
| XI Yuping, LUO Zhihuan, TIAN Kexin.Effect of rapid quenching speed on electrochemical properties of hydrogen storage alloy for automobile[J].Research and Exploration in Laboratory,2022,41(2):8-12,83. | |
| [6] | LIU Yuru, YUAN Huiping, JIANG Lijun,et al.Microstructure and gas-solid hydrogen storage properties of La1- x Ce x Y2Ni10.95Mn0.45(x=0-0.75) alloys[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2024,976:173069. |
| [7] | 刘雯雯,赖华生,王玉香,等.La/Y比对A2B7型La-Y-Ni储氢合金性能的影响[J].矿冶工程,2023,43(2):149-153. |
| LIU Wenwen, LAI Huasheng, WANG Yuxiang,et al.Effect of La/Y ratio on properties of A2B7-type La-Y-Ni hydrogen storage alloy[J].Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2023,43(2):149- 153. | |
| [8] | 宋云波,赵欣.新能源汽车用Mg2Ni基储氢合金的制备与性能[J].电源技术,2020,44(2):186-191. |
| SONG Yunbo, ZHAO Xin.Preparation and properties of Mg2Ni-based hydrogen storage alloy for new energy vehicle[J].Chinese Journal of Power Sources,2020,44(2):186-191. | |
| [9] | 范庆科,孟庆华.汽车用La0.79Mg0.21Ni3.95储氢合金的制备与电化学性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(3):71-76. |
| FAN Qingke, MENG Qinghua.Study on preparation and electrochemical properties of La0.79Mg0.21Ni3.95 hydrogen storage alloy for vehicles[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(3):71-76. | |
| [10] | 郑波,刘雯雯,任权兵,等.不同Mn含量对A2B7型La-Y-Ni储氢合金性能的影响[J].有色金属(冶炼部分),2023(8):82-88. |
| ZHENG Bo, LIU Wenwen, REN Quanbing,et al.Effect of different Mn contents on properties of A2B7-type La-Y-Ni hydrogen storage alloy[J].Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy),2023(8):82-88. | |
| [11] | 梁丽萍,曾志伟.电动汽车电池用储氢合金的制备与性能[J].电池,2021,51(3):233-237. |
| LIANG Liping, ZENG Zhiwei.Preparation and performance of hydrogen storage alloys of battery for electric vehicle[J].Battery Bimonthly,2021,51(3):233-237. | |
| [12] | 李志强,郭正华,何玉汝.Zr/Mn元素替代及退火处理对汽车电池用储氢合金电化学性能的影响[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(6):78-84. |
| LI Zhiqiang, GUO Zhenghua, HE Yuru.Effect of Zr/Mn element substitution and annealing treatment on electrochemical properties of hydrogen storage alloys for automotive batteries[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(6):78-84. | |
| [13] | LI Ruyue, LU Hang, PAN Xiangyu,et al.Improvement on cyclic stability of AB4-type La-Mg-Ni-based hydrogen storage alloys via merging Y element for nickel-metal hydride batteries[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(84):32849-32859. |
| [14] | 苏张磊,李玮,罗志敏.汽车电池负极材料的制备与电化学性能研究[J].现代化工,2022,42(7):141-146. |
| SU Zhanglei, LI Wei, LUO Zhimin.Preparation of anode materials for automotive batteries and research on their electrochemical properties[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2022,42(7):141-146. | |
| [15] | 陶炳全,张华,杨星焕,等.汽车氢镍电池负极材料的热处理与性能研究[J].电源技术,2020,44(11):1642-1646. |
| TAO Bingquan, ZHANG Hua, YANG Xinghuan,et al.Study on heat treatment and performance of negative electrode material for vehicle NiMH battery[J].Chinese Journal of Power Sources,2020,44(11):1642-1646. | |
| [16] | 宋捷,李琦峰.添加剂对汽车电池用Mg2Ni合金性能的影响[J].电池,2022,52(5):559-563. |
| SONG Jie, LI Qifeng.Effect of additives on performance of Mg2Ni alloy for automotive battery[J].Battery Bimonthly,2022,52(5):559-563. | |
| [17] | 杨天辉,刘力,周曦,等.汽车电池用无镁储氢合金的合金化与电化学性能[J].实验室研究与探索,2022,41(12):57- 62. |
| YANG Tianhui, LIU Li, ZHOU Xi,et al.Alloying and electrochemical properties of magnesium free hydrogen storage alloys for automotive batteries[J].Research and Exploration in Laboratory,2022,41(12):57-62. | |
| [18] | 刘冬梅,肖润谋,佘翔.新能源汽车用储氢合金的制备与电化学性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2021,49(6):131-136. |
| LIU Dongmei, XIAO Runmou, SHE Xiang.Preparation and electrochemical property of hydrogen storage alloy for new energy vehicle[J].New Chemical Materials,2021,49(6):131-136. | |
| [19] | 王姗姗,裴婷,张新庄,等.La0.7Mg0.3Ni2.5- x Co0.6Mn0.4Cu x (x=0~0.20)储氢合金的制备及电化学性能研究[J].石油化工应用,2023,42(9):96-98,102. |
| WANG Shanshan, PEI Ting, ZHANG Xinzhuang,et al.Preparation and electrochemical properties of La0.7Mg0.3Ni2.5- x Co0.6Mn0.4Cu x (x=0~0.20)hydrogen storage alloy[J].Petrochemical Industry Application,2023,42(9):96-98,102. | |
| [20] | LI Jiaxuan, HE Xiangyang, XIONG Wei,et al.Phase forming law and electrochemical properties of A2B7-type La-Y-Ni-based hydrogen storage alloys with different La/Y ratios[J].Journal of Rare Earths,2023,41(2):268-276. |
| [1] | YU Panpan, WU Zongjin, WU Lang, YANG Yi, LIN Qian, PAN Hongyan. Study on synergistic preparation of wood chip based carbon materials with phosphoric acid-sulfuric acid and their electrochemical properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 79-88. |
| [2] | ZHANG Dian. Degradation performance analysis of S-scheme activated carbon supported g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalytic concrete [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 118-127. |
| [3] | ZHAO Mengyan, CHEN Junwu, WANG Xun, WEI Na, WENG Xiaoqing, CHEN Yingxin. Study on purification of phosphogypsum by reverse flotation of octadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride and its removal mechanism of quartz [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 111-117. |
| [4] | WANG Peng, PU Zhihua, WANG Tianxiang, LIN Jingyi, WAN Yuanxin. Investigation on effecte of different carbon source on processing performance of LiFePO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 60-66. |
| [5] | HAN Yingming, SUN Ruize, SUN Yining, SONG Xingfei. Study on properties of modified magnesia sulfide cement by calcined coal gangue powder [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(4): 97-104. |
| [6] | ZHU Jicheng, YANG Qixin, LIANG Haoquan, WANG Zengkun, OUYANG Fugui, DI Jing, GAI Xikun. Effect of confined catalyst Ni@S2 on performance of methane dry reforming reaction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 138-146. |
| [7] | KONG Lingjie, LI Guangbi, XIE Jiahao, YANG Xinhui, BAI Xiaoqin. Research progress on lithium extraction technology from salt lake brine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 14-26. |
| [8] | LIU Jintong, ZHANG Jie, ZHOU Junliang, WU Bingdang, HUANG Tianyin, YANG Jingjing. Summary of antimony residues and status in antimony recovery technology [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 1-11. |
| [9] | TANG Dongwu, YE Changwen, DENG Jie, AO Fang. Study on leaching rate of calcium and magnesium from phosphorus tailings based on thermodynamic analysis and response surface method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 98-106. |
| [10] | WANG Yong, LI Jixia, ZHANG Guisheng, WANG Pengfei, WANG Benlei. Determination of rhodium for catalyst solution of 2-Propylheptanol [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 142-146. |
| [11] | ZOU Yang, LU Zhiyan, HU Zhilin, SUN Ze. Study on metastable zone width and primary nucleation kinetics for cooling crystallization of KNO3 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 67-74. |
| [12] | WANG Jianjie, SHU Xiaolong, XIAO Xia, WANG Peng, FAN Xiaoqiang, KONG Lian, XIE Zean, ZHAO Zhen. Study on synthesis of hierarchical flower⁃like ZSM-5 zeolite and its catalytic performance for n-octane cracking [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 139-146. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ruijun, CHEN Guoliang, SONG Chuncao, ZHU Yafei. Effects of graphene oxide on mechanical properties and chloride penetration resistance of ultra⁃high performance concrete incorporating recycled sand [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 54-59. |
| [14] | ZHAO Leilei, SHU Yizhou, QI Zenglian, LIU Dandan, KUANG Jialing, HUANG Chengdong, WU Jiaxiang, PU Zhengxian. Effect of different addition amount of ammonium polyphosphate on granulation performance of compound fertilizer [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 74-82. |
| [15] | GUO Kaihua, FAN Yuxin, YANG Jing, ZHAO Wenli, JIA Yuanyuan, WANG Yanfei. Analysis of effect of carnallite raw ore grade on its cold decomposition and crystallization of potassium chloride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 9-18. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||