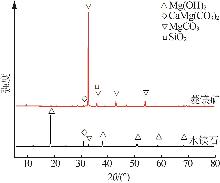
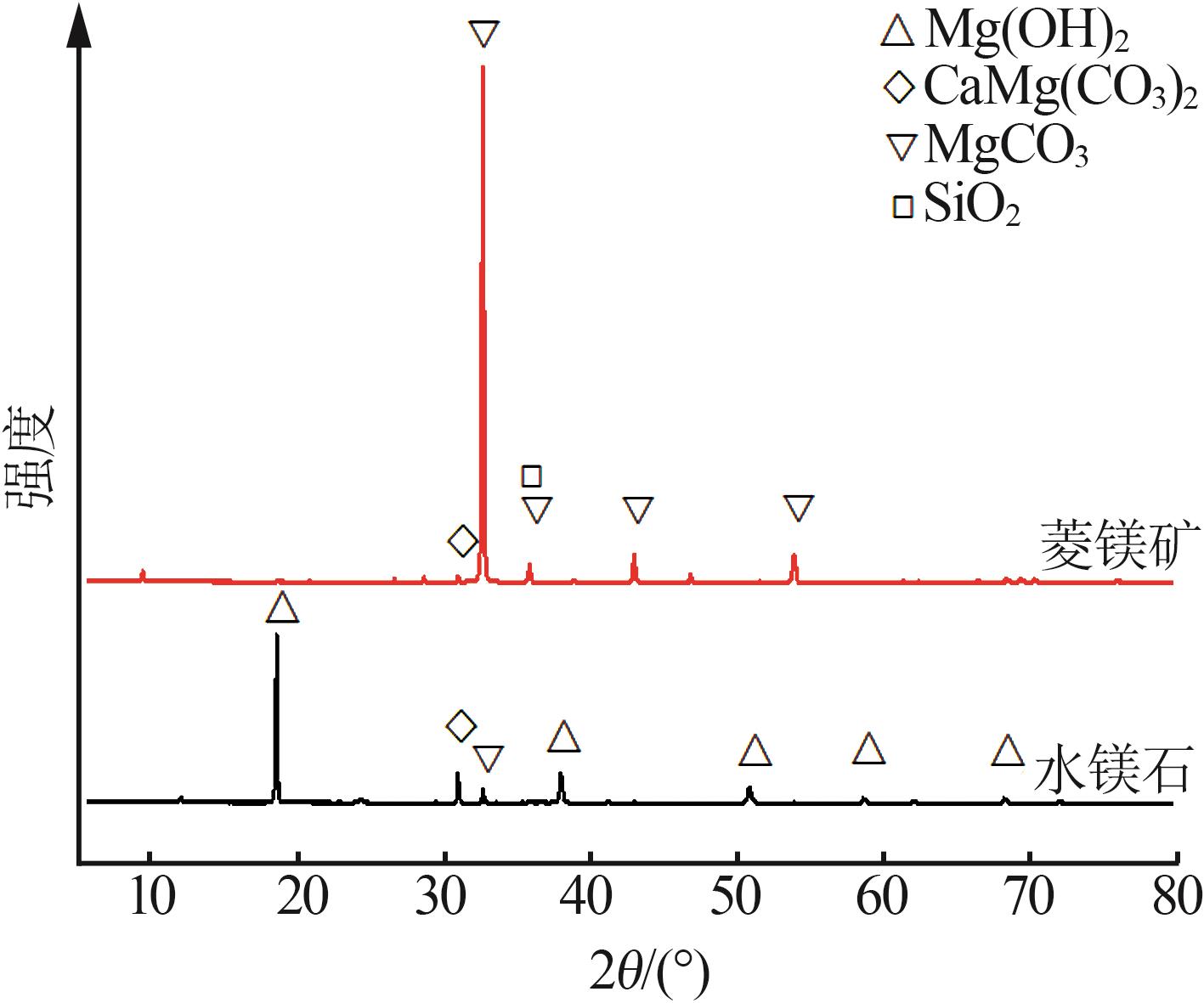
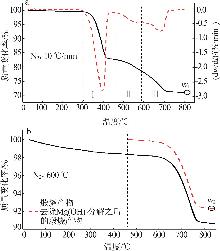
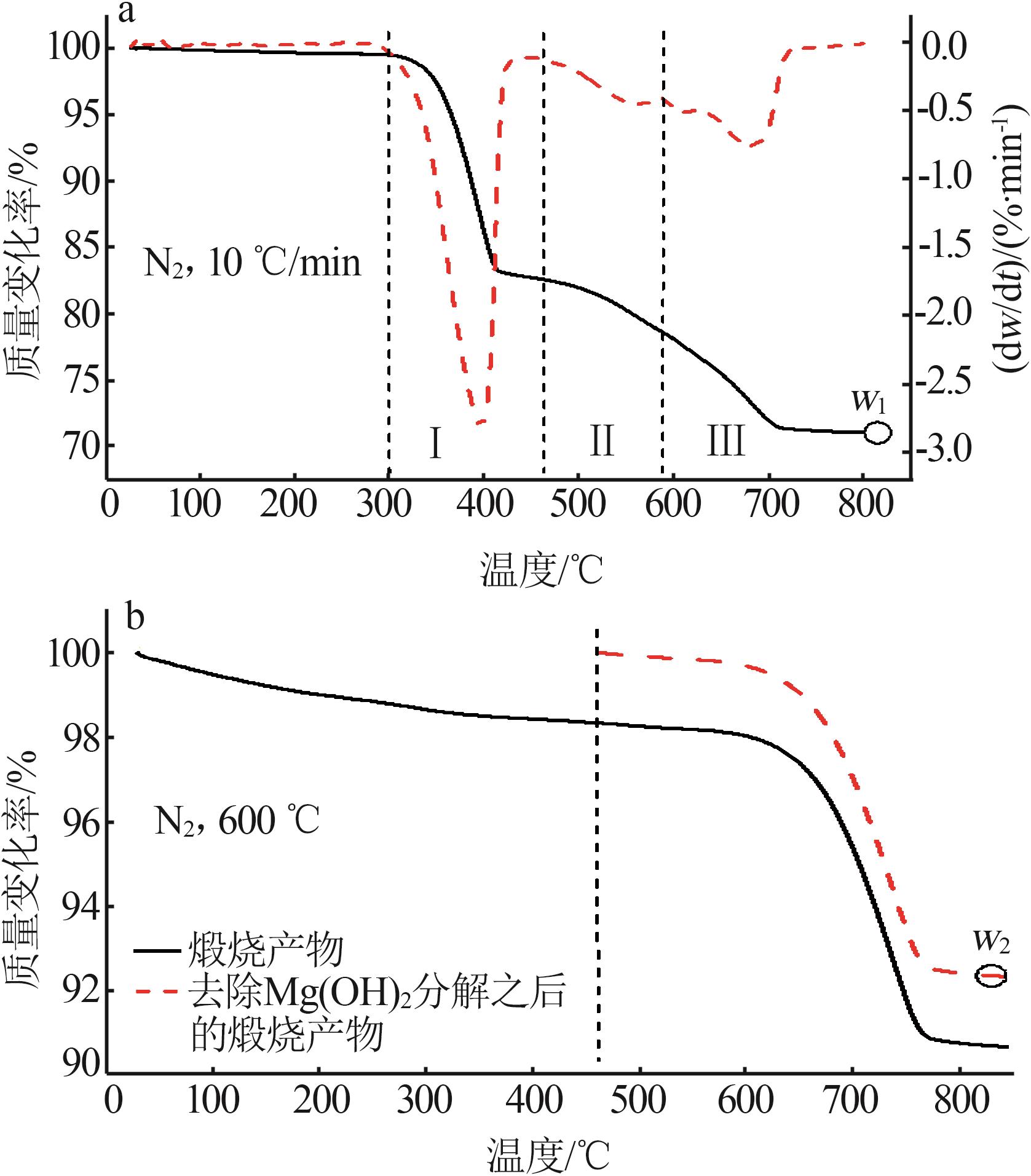
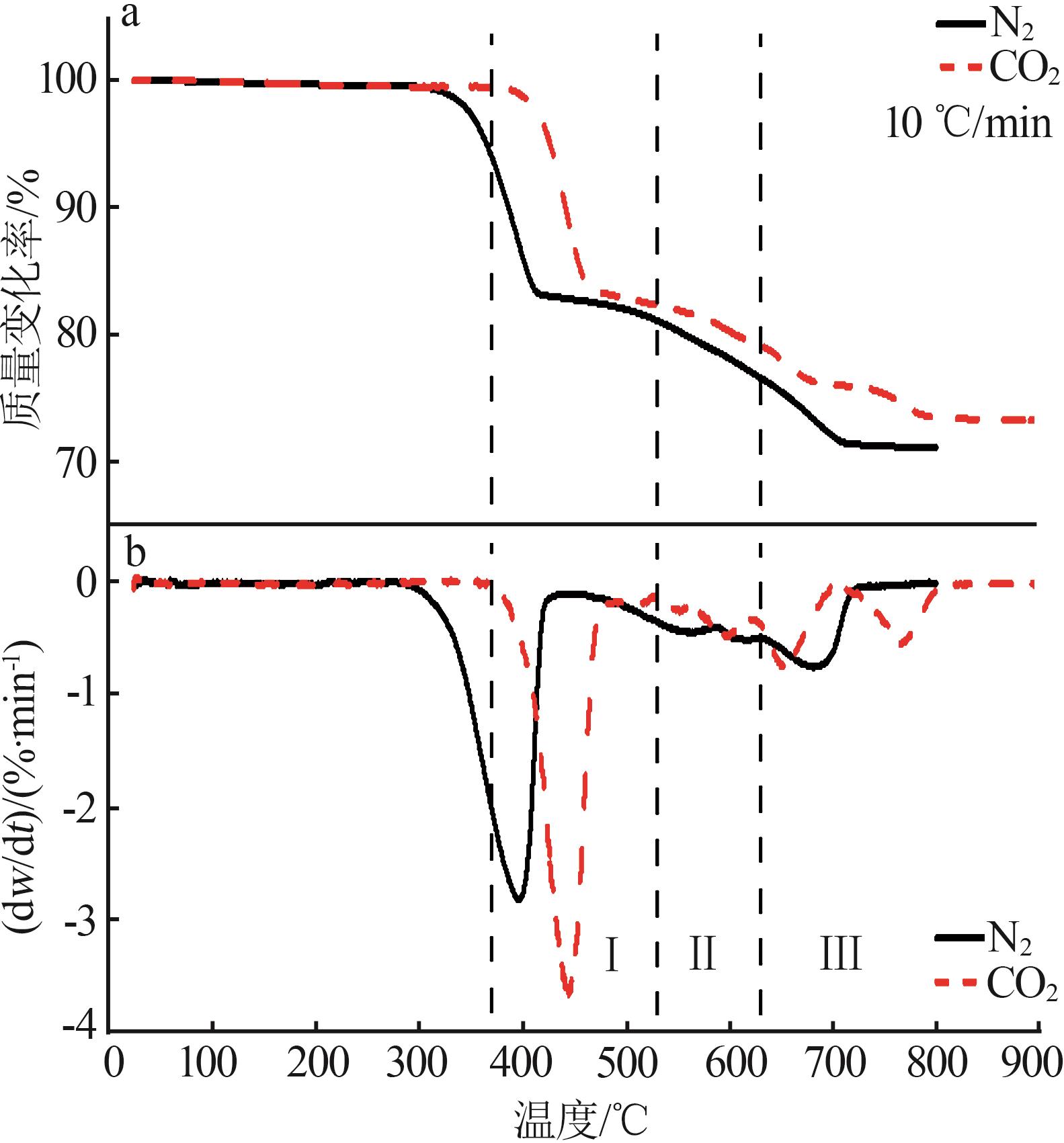
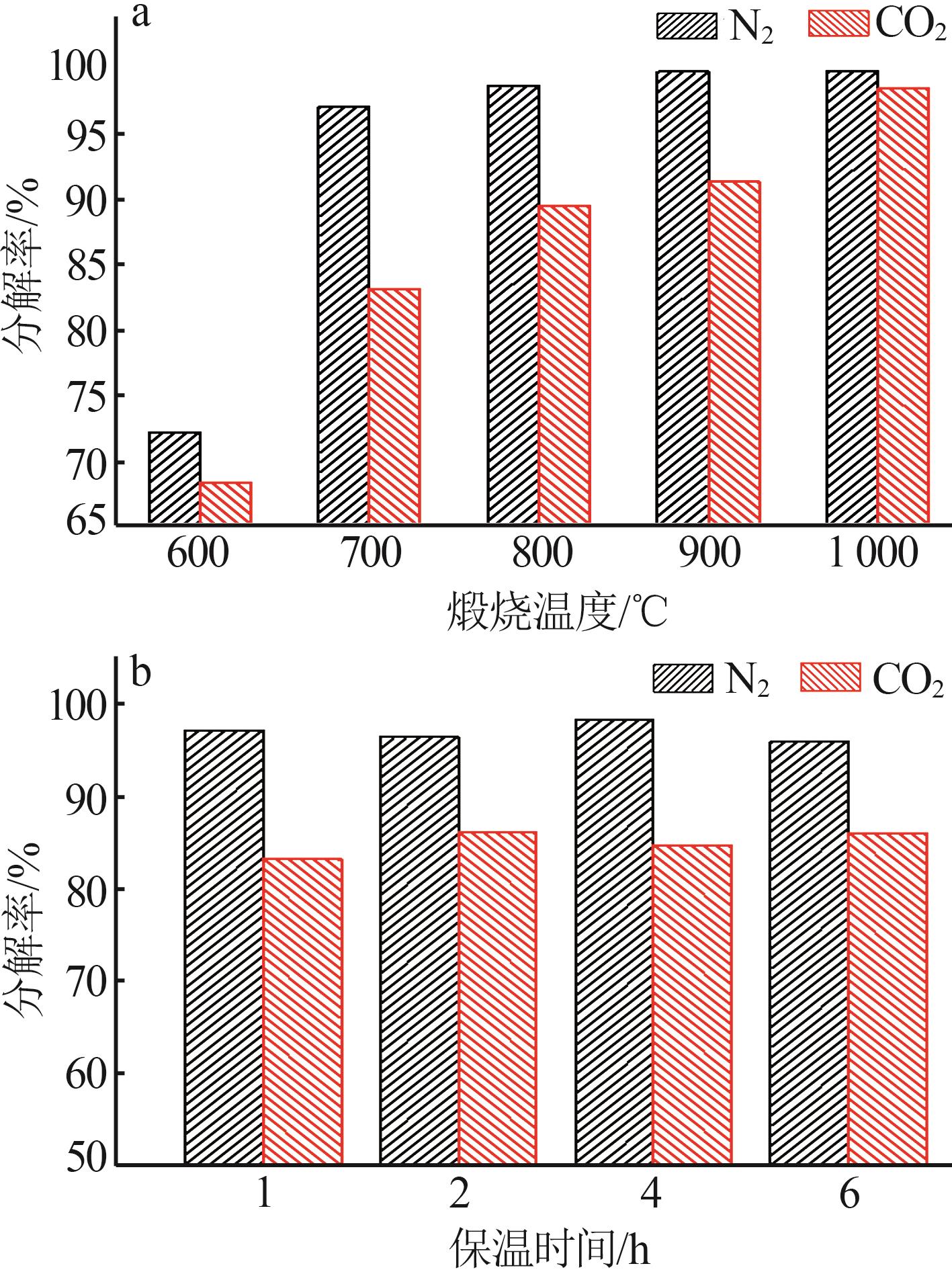
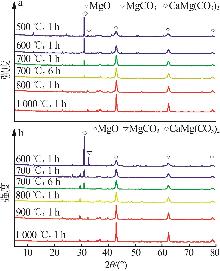
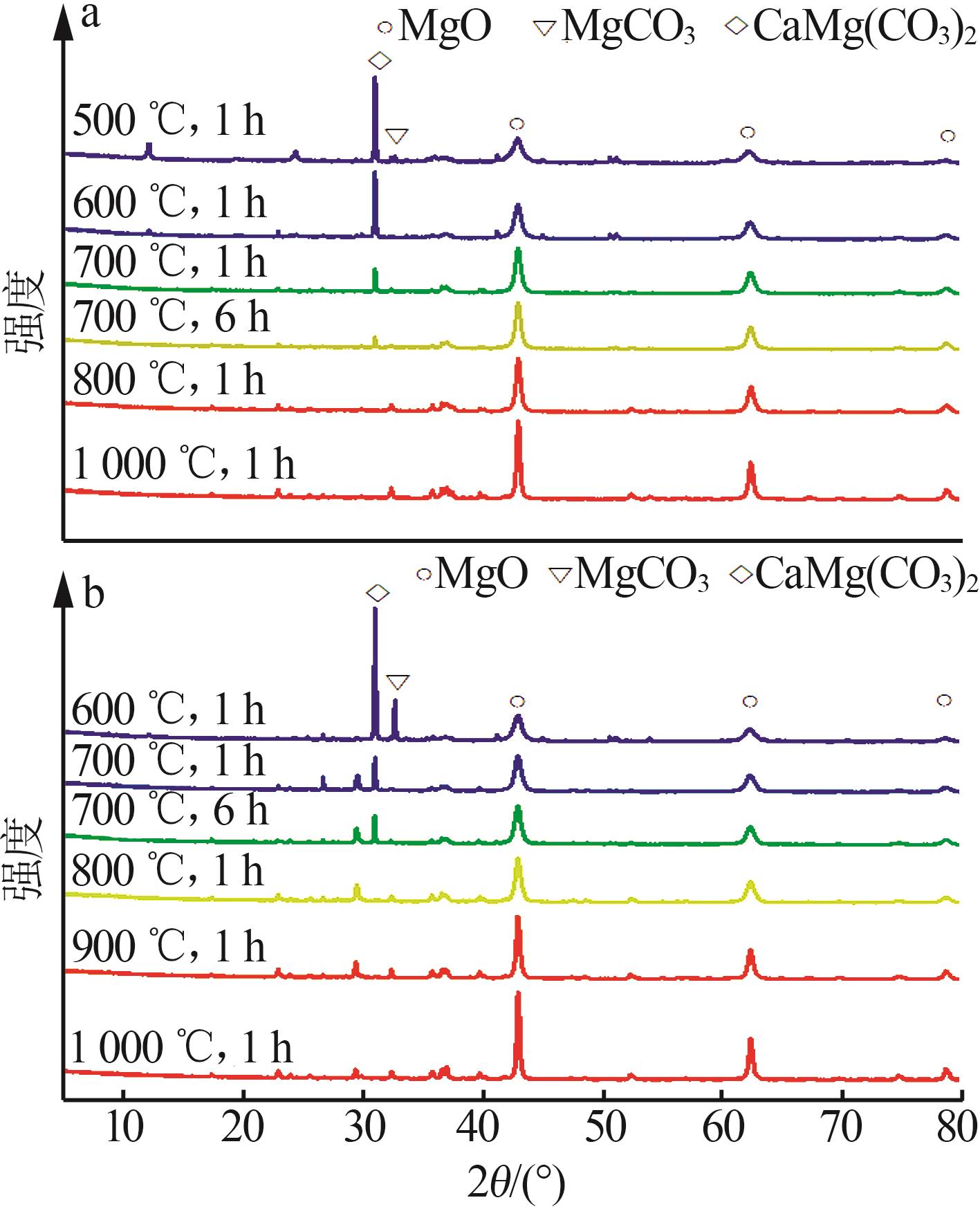
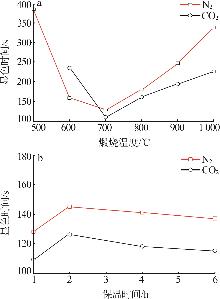
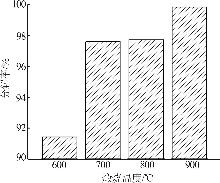
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 39-45.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0194
• High-value utilization of magnesium resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
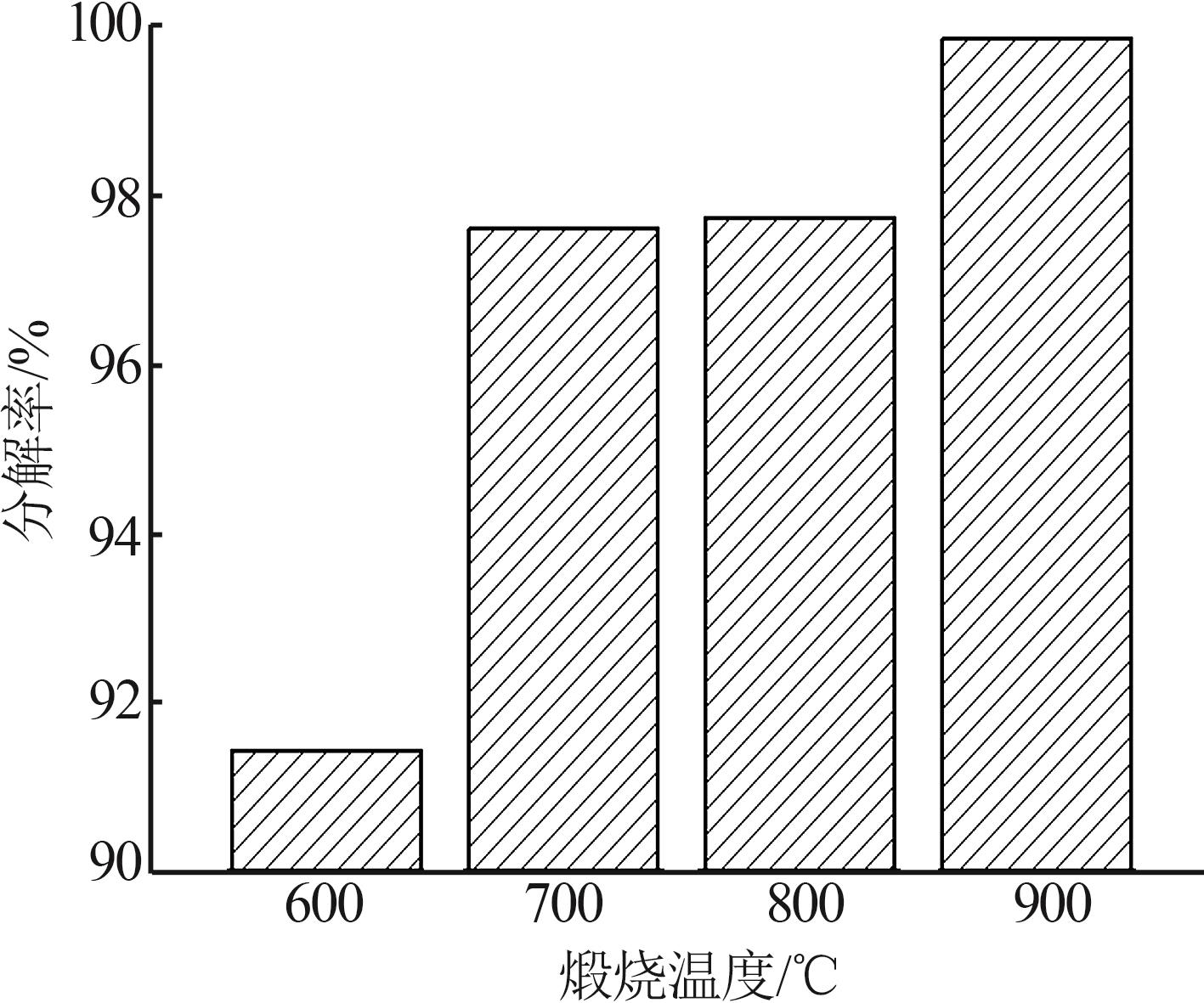
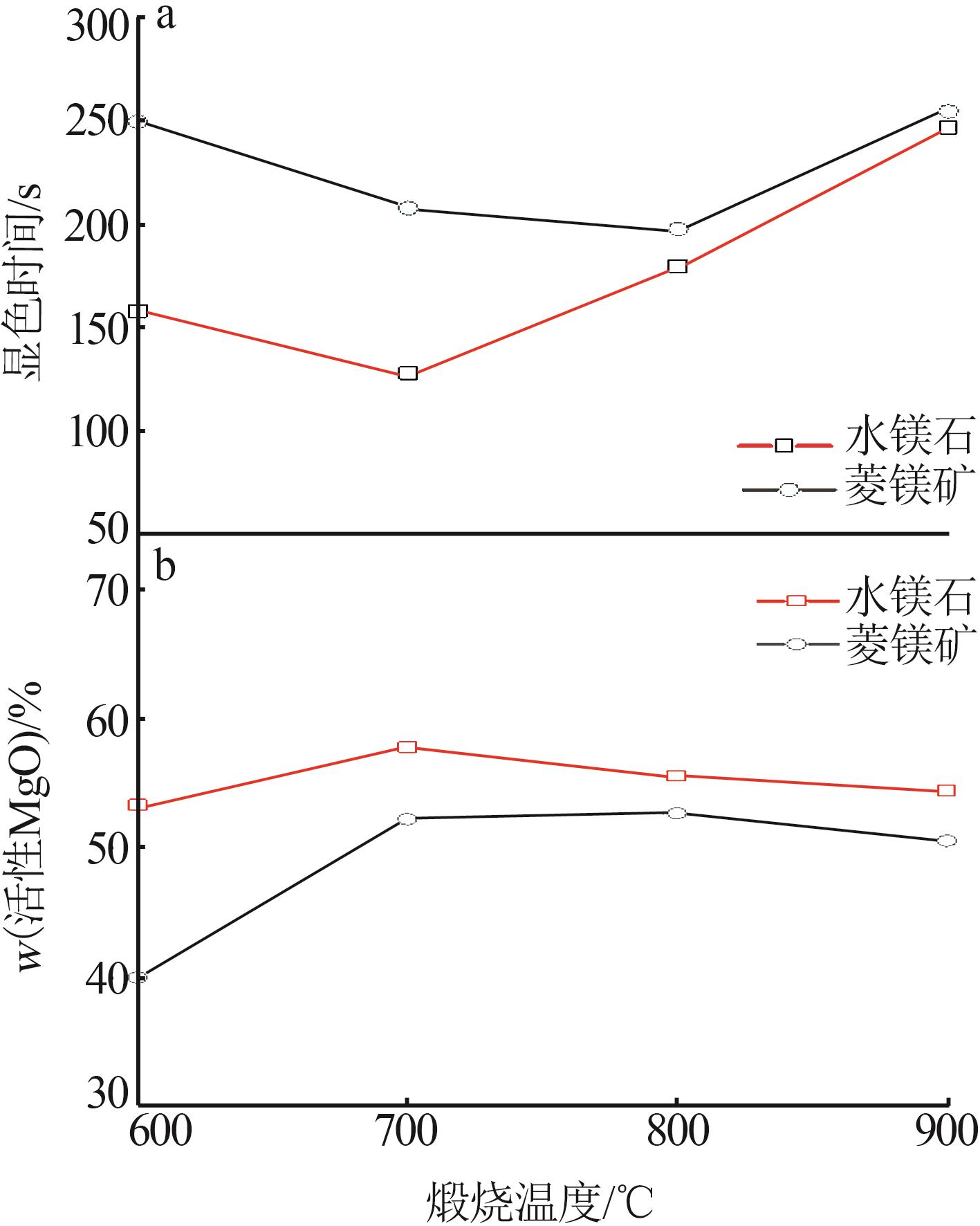
Study on characteristics of brucite calcination product
LI Jiaxin1( ), ZHANG Hong1,2, XIE Jiaqi1, BI Haoran1, LIU Xuejing1(
), ZHANG Hong1,2, XIE Jiaqi1, BI Haoran1, LIU Xuejing1( )
)
- 1. Institute of Industrial Chemistry and Energy Technology,Key Laboratory on Resources Chemicals and Materials of Ministry of Education,Shenyang University of Chemical Technology,Shenyang 110142,China
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering,Shenyang University of Technology,Shenyang 110870,China
-
Received:2024-04-07Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-05 -
Contact:LIU Xuejing E-mail:15163645662@163.com;liuxuejing6@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Jiaxin, ZHANG Hong, XIE Jiaqi, BI Haoran, LIU Xuejing. Study on characteristics of brucite calcination product[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(5): 39-45.
share this article
| 1 | FERNANDES M, SINGH KR, SARKAR T,et al.Recent applications of magnesium oxide(MgO) nanoparticles in various domai⁃ns[J].Advanced Materials Letters,2020,11(8):1-10. |
| 2 | 丁宁,张健,平清伟,等.镁改性硅藻土对苦参碱的吸附释放性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(11):37-46. |
| DING Ning, ZHANG Jian, PING Qingwei,et al.Study on adsorption and release properties of matrine by magnesium⁃modified diatomite[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(11):37-46. | |
| 3 | 高云琴,王嘉玮,田晓利,等.轻烧氧化镁的微观特征及其活性[J].硅酸盐学报,2023,51(6):1572-1582. |
| GAO Yunqin, WANG Jiawei, TIAN Xiaoli,et al.Microscopic characteristics and activity of light⁃burned magnesia[J].Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2023,51(6):1572-1582. | |
| 4 | SUPIN K K, SAJI A, CHANDA A,et al.Effects of calcinations temperatures on structural,optical and magnetic properties of MgO nanoflakes and its photocatalytic applications[J].Optical Materials,2022,132:112777. |
| 5 | 任伟康,刘百宽,田晓利.新疆和静菱镁矿热分解特性及轻烧工艺研究[J].硅酸盐通报,2016,35(11):3556-3561,3568. |
| REN Weikang, LIU Baikuan, TIAN Xiaoli.Thermal decomposition and light burning process of Xinjiang Hejing magnesite[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2016,35(11):3556-3561,3568. | |
| 6 | GUO Z, MA Y, RIGAUD M.Sinterability of macrocrystalline and cryptocrystalline magnesite to refractory magnesia[J].International Journal of Ceramic Engineering & Science,2020,2(6):271-341. |
| 7 | 彭强,郭玉香,曲殿利,等.悬浮态煅烧菱镁矿制备高活性轻烧氧化镁[J].耐火材料,2017,51(4):264-267. |
| PENG Qiang, GUO Yuxiang, QU Dianli,et al.Preparation of high activity light calcined magnesia by calcining suspended state magnesite[J].Refractories,2017,51(4):264-267. | |
| 8 | HUANG L, YANG Z, WANG S.Influence of calcination temperature on the structure and hydration of MgO[J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,262:120776. |
| 9 | 曹连山,张继宇,王作敏,等.低品位菱镁矿闪速旋流动态煅烧生产高活性氧化镁关键技术及示范推广[J].环境保护与循环经济,2023,43(7):38-42,51. |
| CAO Lianshan, ZHANG Jiyu, WANG Zuomin,et al.Key technology and demonstration of producing high active magnesium oxide by flash cyclone dynamic calcination of lowgrade magnesite[J].Environmental Protection and Circular Economy,2023,43(7):38-42,51. | |
| 10 | 彭强,郭玉香,曲殿利,等.菱镁矿悬浮态与堆积态煅烧对产物特性的影响[J].人工晶体学报,2017,46(6):1088-1091. |
| PENG Qiang, GUO Yuxiang, QU Dianli,et al.Influence of calcined magnesite with suspension state and accumulation state on properties of product[J].Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2017,46(6):1088-1091. | |
| 11 | 翟俊,黄春晖,张琴,等.水镁石-碱法制备重质氧化镁的研究[J].无机盐工业,2016,48(9):33-35,44. |
| ZHAI Jun, HUANG Chunhui, ZHANG Qin,et al.Research on preparation of heavy MgO by brucite⁃alkali method[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2016,48(9):33-35,44. | |
| 12 | 王刚,夏志豪,李希艳,等.不同气氛下流化床菱镁矿轻烧产物特性研究[J].化工学报,2022,73(8):3699-3707. |
| WANG Gang, XIA Zhihao, LI Xiyan,et al.Effect of atmosphere on active performance of light⁃burned magnesium oxides from calcined magnesite in fluidized bed[J].CIESC Journal,2022,73(8):3699-3707. | |
| 13 | 孙聪,闫博威,蔡长庸,等.菱镁矿输送床轻烧过程反应与产物微观结构特性[J].化工学报,2020,71(12):5735-5744. |
| SUN Cong, YAN Bowei, CAI Changyong,et al.Characteristics of reaction and product microstructure during light calcination of magnesite in transport bed[J].CIESC Journal,2020,71(12):5735-5744. | |
| 14 | 高陟,马北越,任鑫明,等.利用菱镁矿制备先进镁质材料的研究进展[J].耐火材料,2020,54(1):88-92. |
| GAO Zhi, MA Beiyue, REN Xinming,et al.Research progress of preparing advanced magnesia materials from magnesite[J].Refractories,2020,54(1):88-92. | |
| 15 | PAPALAS T, ANTZARAS A N, LEMONIDOU A A.Magnesite⁃derived MgO promoted with molten salts and limestone as highly⁃efficient CO2 sorbent[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2021,53:101725. |
| 16 | MA Beiyue, ZAN Wenyu, LIU Kun,et al.Preparation and properties of porous MgO based ceramics from magnesite tailings and fused magnesia[J].Ceramics International,2023,49(11):19072- 19082. |
| 17 | 白炳华,刘百宽,田晓利,等.微晶菱镁矿所制轻烧氧化镁提纯及水化动力学[J].材料科学与工程学报,2023,41(1):93-97. |
| BAI Binghua, LIU Baikuan, TIAN Xiaoli,et al.Purification and hydration kinetics of caustic calcined magnesia prepared from microcrystalline magnesite[J].Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2023,41(1):93-97. | |
| 18 | 杨俊峰,余跃,王曦.我国菱镁矿业绿色高质量发展对策研究[J].中国矿山工程,2022,51(4):25-28. |
| YANG Junfeng, YU Yue, WANG Xi.Research on green and high quality development strategy of magnesite mining industry in China[J].China Mine Engineering,2022,51(4):25-28. | |
| 19 | 凌观爽,宗俊.影响微晶质菱镁矿制备纳米氢氧化镁的工艺研究[J].盐科学与化工,2021,50(9):11-16,20. |
| LING Guanshuang, ZONG Jun.Study on the effect of different process methods on the preparation of nanometer magnesium hydroxide from microcrystalline magnesite[J].Journal of Salt Science and Chemical Industry,2021,50(9):11-16,20. | |
| 20 | 秦雅静,朱德山.中国水镁石矿资源利用现状及展望[J].中国非金属矿工业导刊,2014(6):1-3. |
| QIN Yajing, ZHU Deshan.Mineral processing status and prospect of China′s brucite[J].China Non⁃Metallic Minerals Industry,2014(6):1-3. | |
| 21 | 马安博.煅烧温度对氧化镁微观结构和性能的影响[J].化学与粘合,2020,42(3):197-199. |
| MA Anbo.The effect of calcination temperature on the microstructure and properties of magnesium oxide[J].Chemistry and Adhesion,2020,42(3):197-199. | |
| 22 | 桂昌青,王雅静,凌长见,等.氧化镁基二氧化碳吸附剂的制备及改性研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(8):77-83. |
| GUI Changqing, WANG Yajing, LING Changjian,et al.Research progress of preparation and modification of MgO-based CO2 adsorbents[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(8):77- 83. |
| [1] | SUN Mengyuan, HE Wei, WANG Chen. Research progress of preparation and adsorption of magnesium oxide fibers and their composite fibers [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(5): 1-10. |
| [2] | MAO Shize. Study on microwave roasting-activated coal gangue to improve sulfate corrosion resistance of concrete [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 86-93. |
| [3] | SONG Jiaxi, JI Renfei, CHEN Jun, LIN Sen, YU Jianguo. Research on characteristics analysis and pretreatment on deeply deactivated power battery ternary cathode materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 44-49. |
| [4] | TANG Dongwu, YE Changwen, DENG Jie, AO Fang. Study on leaching rate of calcium and magnesium from phosphorus tailings based on thermodynamic analysis and response surface method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 98-106. |
| [5] | TANG Xuemei, WANG Meibo, XU Li, ZHANG Xujie, TAI Shijun, YI Xianmei, LIU Hongjuan, PAN Linyi. Study on whitening of phosphogypsum by low⁃temperature calcination [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 110-115. |
| [6] | WANG Wei, GUO Lihui, REN Siqian, HUA Chunfeng, WU Yuanting, LIU Hulin, WANG Zhao. Study on modification of inorganic activators and their active excitation on sulfur fixing ash [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 135-142. |
| [7] | LIU Hui, WANG Hongliang, YU Kun, GAO Shengnan. Effect of calcination on porous structure and electrochemical properties of air electrode [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 80-86. |
| [8] | FANG Xiaoning, KUANG Fei, LIU Chenglin. Study on extraction of potassium from K-feldspar by roasting-leaching of mixed salts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 53-57. |
| [9] | WANG Shengchang, HAO Jianying, CHEN Jianing, TIAN Bo. Effect of calcination on properties of calcined gypsum prepared from desulphurization gypsum with potassium aluminum sulfate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 105-111. |
| [10] | QIAN Zhihui, ZHU Qin, MA Jiao, GUO Yujiao, XIANG Mingwu, GUO Junming. Study on preparation and electrochemical properties of nano-sized LiNi0.05Mn1.95O4 cathode materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 50-56. |
| [11] | YANG Kun, REN Qixia, DONG Yonggang, LIU Fei, YAO Mengqin, CAO Jianxin. Effect of calcination temperature on catalytic performance of ZnGaZrO x /SAPO-34 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 136-145. |
| [12] | WANG Chen, HE Wei, SUN Mengyuan. Research on preparation of nano-bismuth oxide-enhanced chloride/magnesium oxide composites and their thermophysical properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 120-126. |
| [13] | CHEN Qi, LIAO Dankui, ZHANG Qingnian, YAN Jinsheng, HUANG Yu, CHEN Xiaopeng, TONG Zhangfa. Fast and efficient determination of quicklime activity by conductivity method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 114-120. |
| [14] | LI Qiang, YOU Xiaomin, SHE Xuefeng, JIANG Zeyi, XUE Qingguo, WANG Jingsong. Effect of calcination temperature and carbon structure on compressive strength of CaO-containing carbon pellets [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 43-49. |
| [15] | LI Heng, ZHANG Hui, ZI Xuemin. Analysis on calcination process progress of phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 27-35. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||