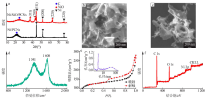
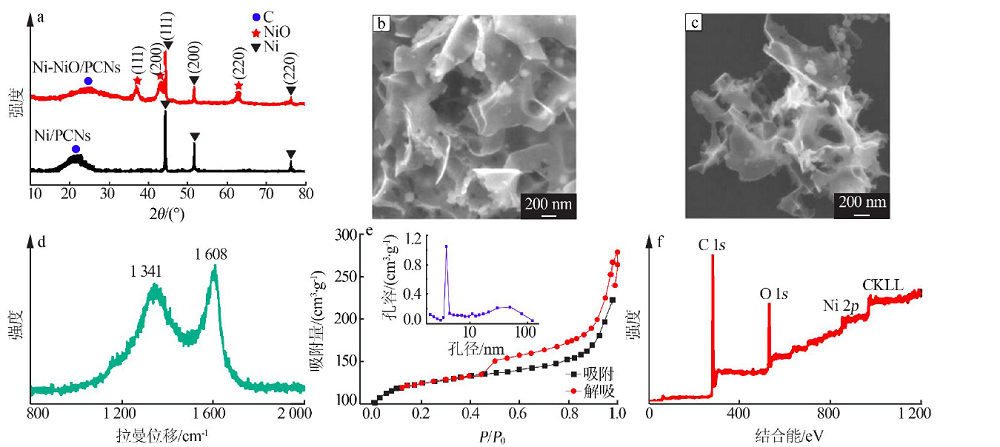
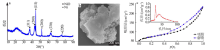
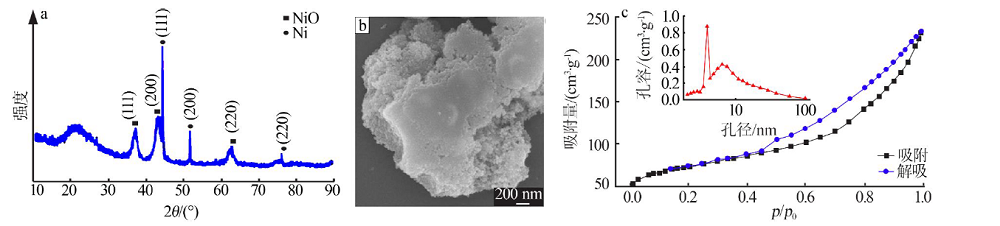
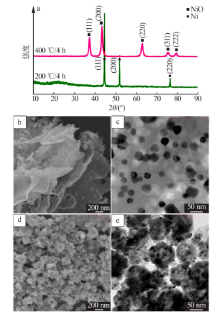
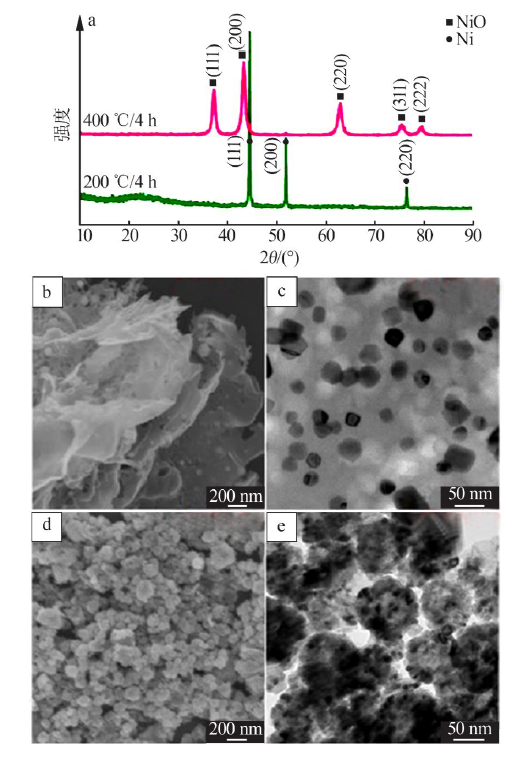
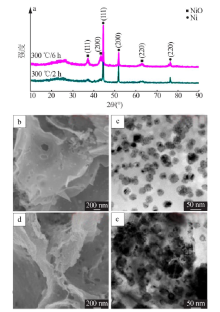
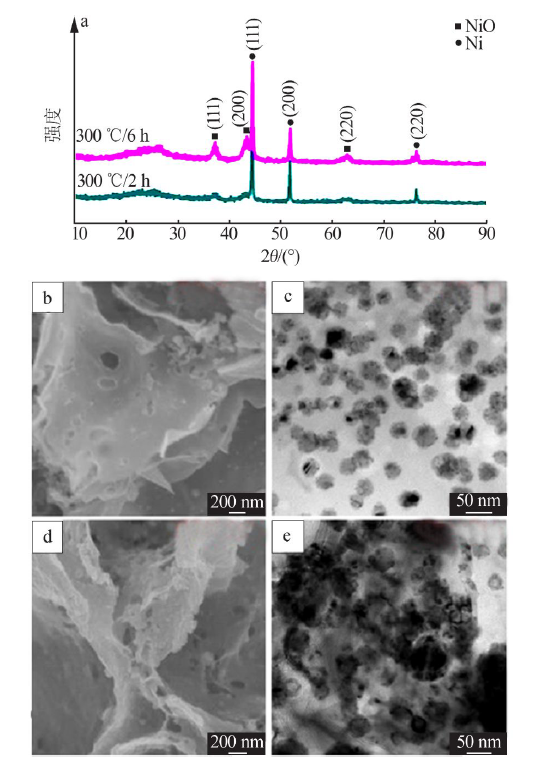
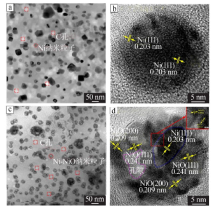
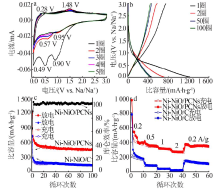
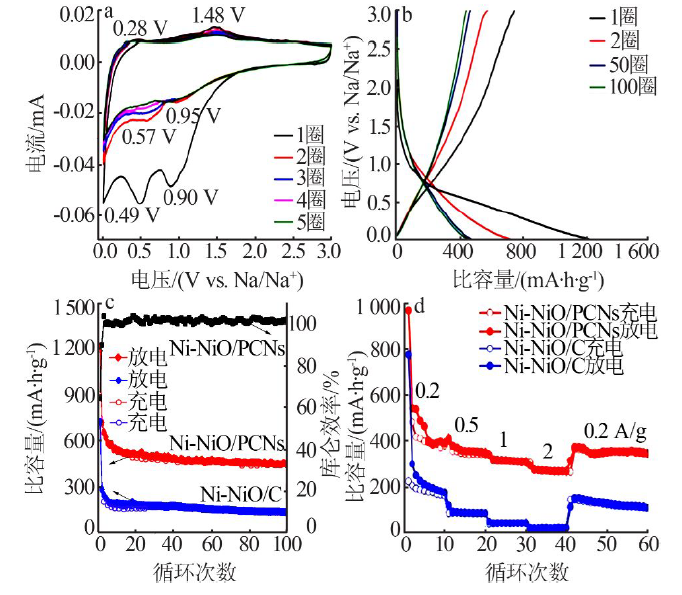
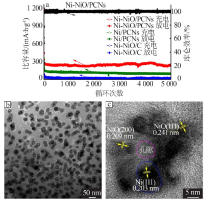
| [1] |
赵立敏, 王惠亚, 解启飞, 等. 车用动力锂离子电池纳米硅/碳负极材料的制备技术与发展[J]. 材料导报, 2020,34(7):7026-7035.
|
| [2] |
申晨, 王怀国. 我国锂离子电池产业技术发展概况[J]. 新材料产业, 2019(9):15-21.
|
| [3] |
张惠泽. 新能源汽车动力电池研究现状[J]. 通信电源技术, 2018,35(7):273-274.
|
| [4] |
朱子翼, 董鹏, 张举峰, 等. 新一代储能钠离子电池正极材料的改性研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020,39(3):1043-1056.
|
| [5] |
梁丽萍. 基于高温煅烧法的新能源汽车电池负极材料的制备与性能优化研究[J]. 冶金管理, 2019(17):45-46.
|
| [6] |
张雨薇, 刘成龙, 徐志江. 新能源汽车钠离子电池富锂锰基正极材料掺杂改性[J]. 电源技术, 2019,43(10):1596-1600.
|
| [7] |
郑世界, 陈翀, 陆琴. 新能源汽车电池负极材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2018,39(11):2473-2476.
|
| [8] |
陈跃, 郑成博. 循环后负极材料对汽车动力电池性能的影响[J]. 电源技术, 2018,42(9):1278-1280.
|
| [9] |
Zhang D M, Jia J H, Yang C C, et al. Fe7Se8 nanoparticles anchored on N-doped carbon nanofibers as high-rate anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020,24:439-449.
|
| [10] |
李通, 史云斌, 刘庆彬, 等. 硒掺杂改性新能源汽车钠离子电池正极材料的结构与电化学性能[J]. 无机盐工业, 2020,52(2):17-22.
|
| [11] |
Liang D, Gang S, Kokswee G, et al. Facile one-step carbothermal reduction synjournal of Na3V2(PO4)2F3/C serving as cathode for so-dium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019,298:459-467.
|
| [12] |
Liang J, Yuan C, Li H, et al. Growth of SnO2 nanoflowers on N-do-ped carbon nanofibers as anode for Li- and Na-ion batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2018,10(2):21-23.
doi: 10.1007/s40820-017-0172-2
pmid: 30393670
|
| [13] |
孙硕, 谢天欢, 张敬远, 等. 磷化铜/石墨烯锂离子负极材料的制备及其电化学性能研究[J]. 常熟理工学院学报, 2020,34(2):11-14.
|
| [14] |
Zhang L, Hu X, Chen C, et al. In operando mechanism analysis on nanocrystalline silicon anode material for reversible and ultrafast sodium storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017,29(5):1-8.
|
| [15] |
黄艳婷, 镇顺英, 李爱菊. Kapton基多微孔碳作为钠离子电池负极材料[J]. 电源技术, 2019,43(11):1825-1827.
|
| [16] |
吴瑞峰, 王宏伟, 皮晓媛. 二硫化钼复合导电碳作为高性能钠离子电池负极材料的研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019,51(7):28-32.
|
| [17] |
Khan M A, Han D W, Gihyeok L, et al. P2/O3 phase-integrated Na0.7MnO2 cathode materials for sodium-ion rechargeable batteri-es[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,771:987-993.
|
| [18] |
Chakraborti H. Assessment of amine functionalized graphene nano-flakes for anode materials in Li-ion batteries:an ab initio study[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2014,600(4):118-122.
|
| [19] |
Xiao Y, Zhu Y F, Yao H R, et al. A stable layered oxide cathode material for high-performance sodium-ion battery[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019,9(19):1-8.
|
| [20] |
Hsieh A G, Bhadra S, Hertzberg B J, et al. Electrochemical-acoustic time of flight:in operando correlation of physical dynamics with battery charge and health[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015,8(5):1569-1577.
|
| [21] |
Gao H, Ma W, Yang W, et al. Sodium storage mechanisms of bismuth in sodium ion batteries:An operando X-ray diffraction study[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018,379:1-9.
|