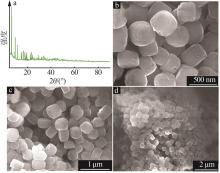
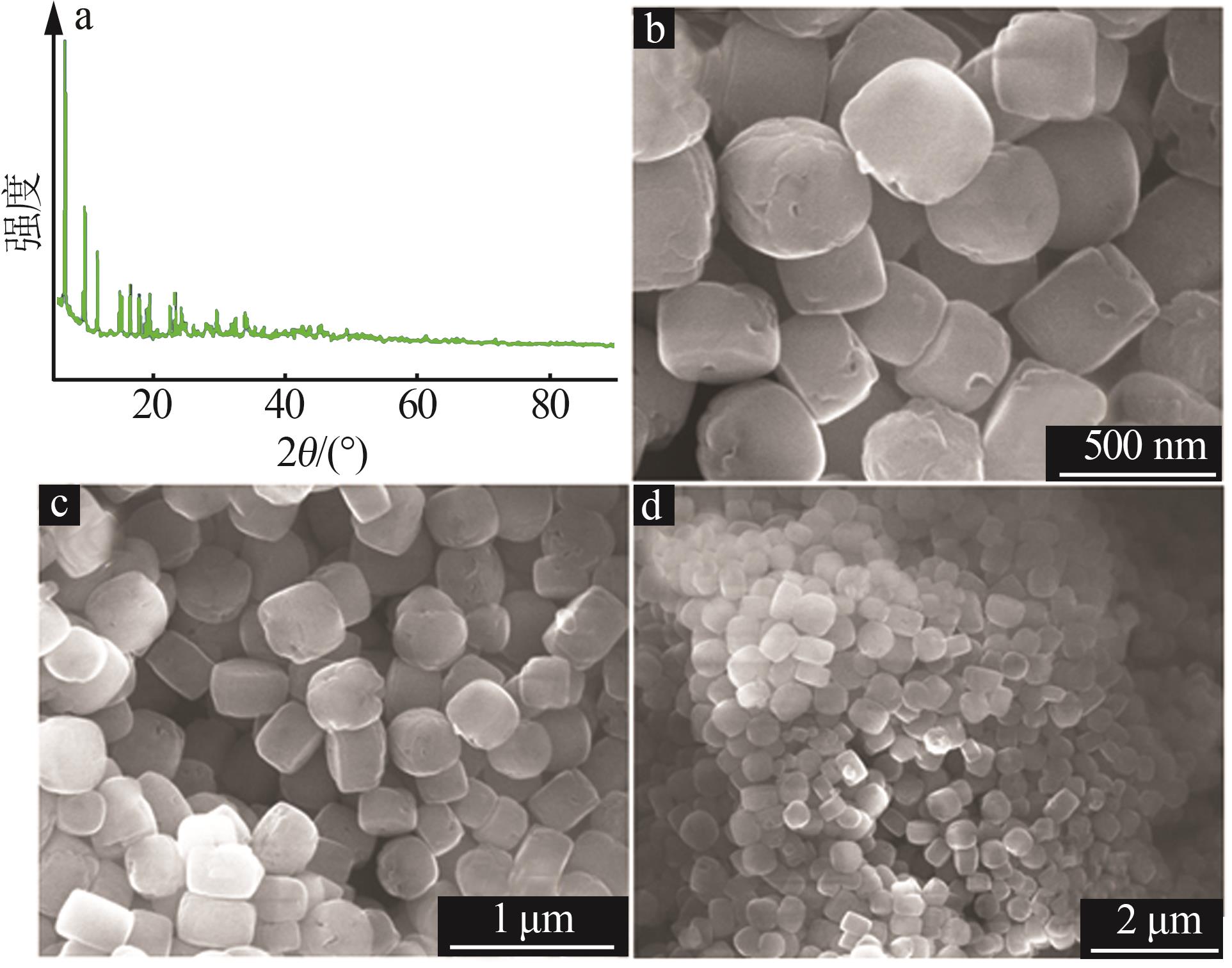
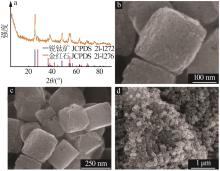
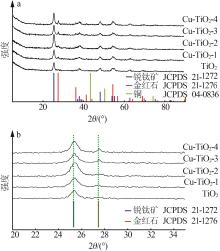
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 45-50.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0295
• Application of novel inorganic materials in photocatalysis and electrocatalysis • Previous Articles Next Articles
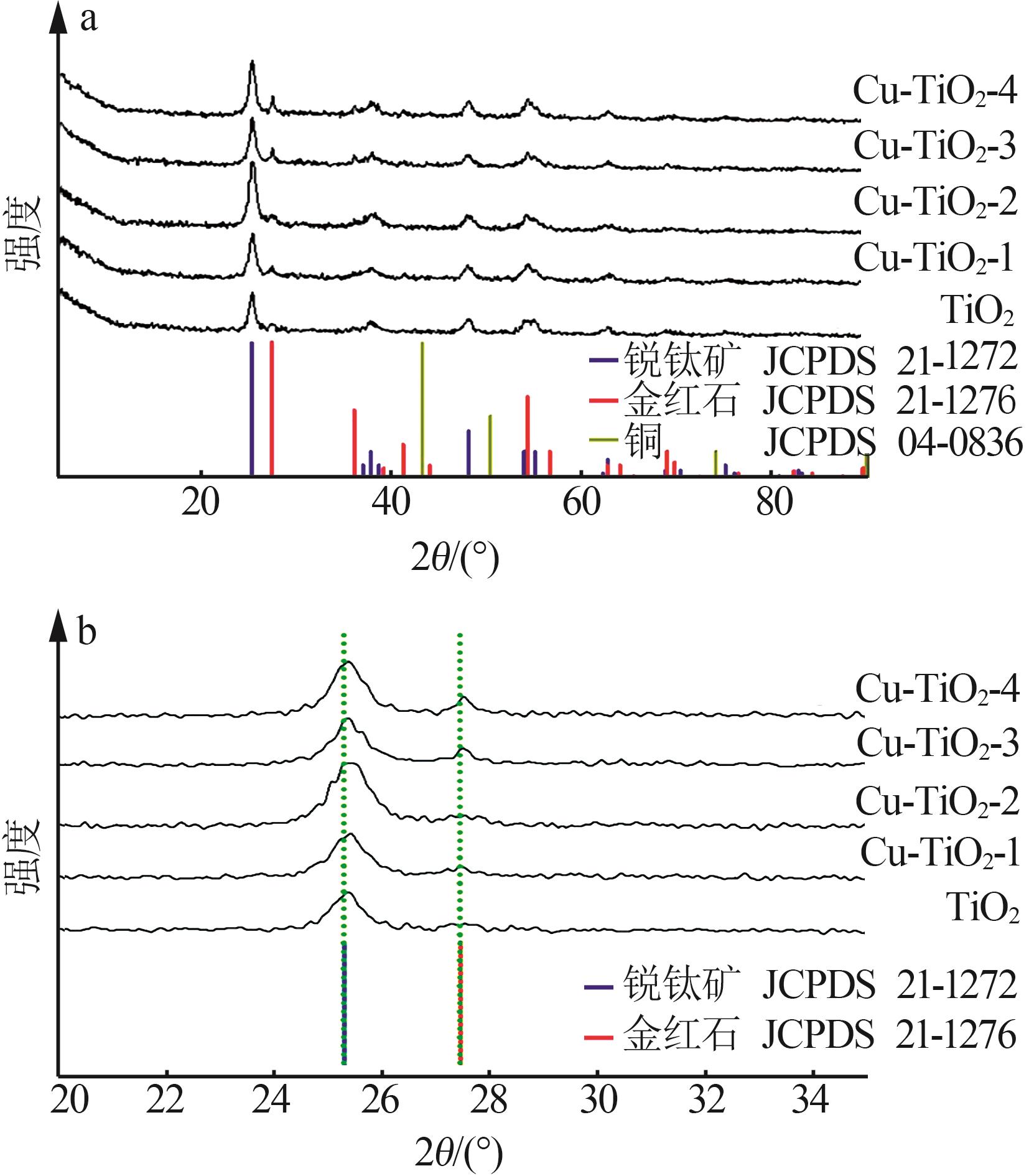
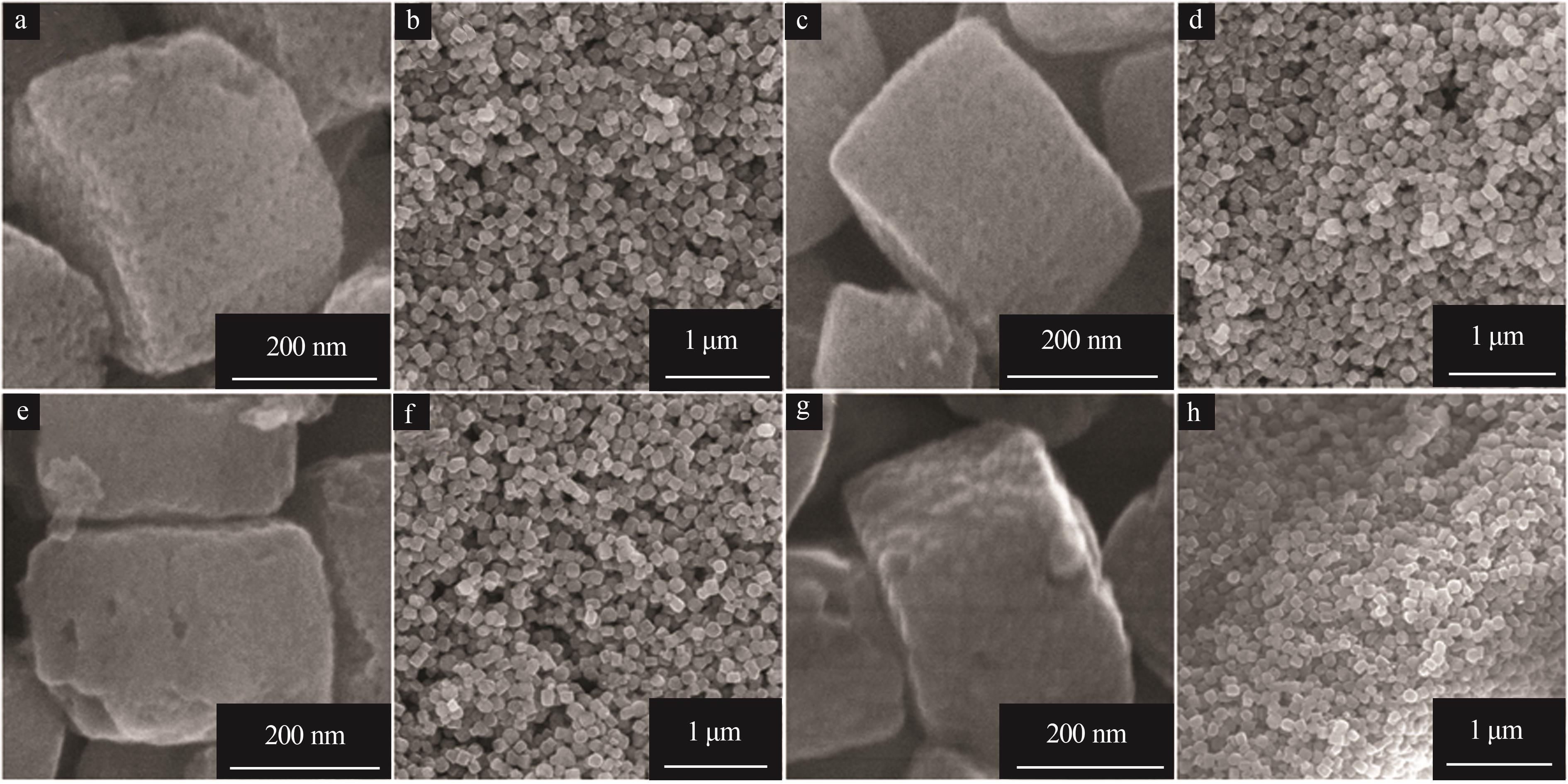
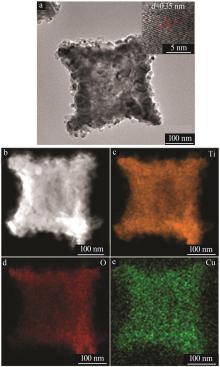
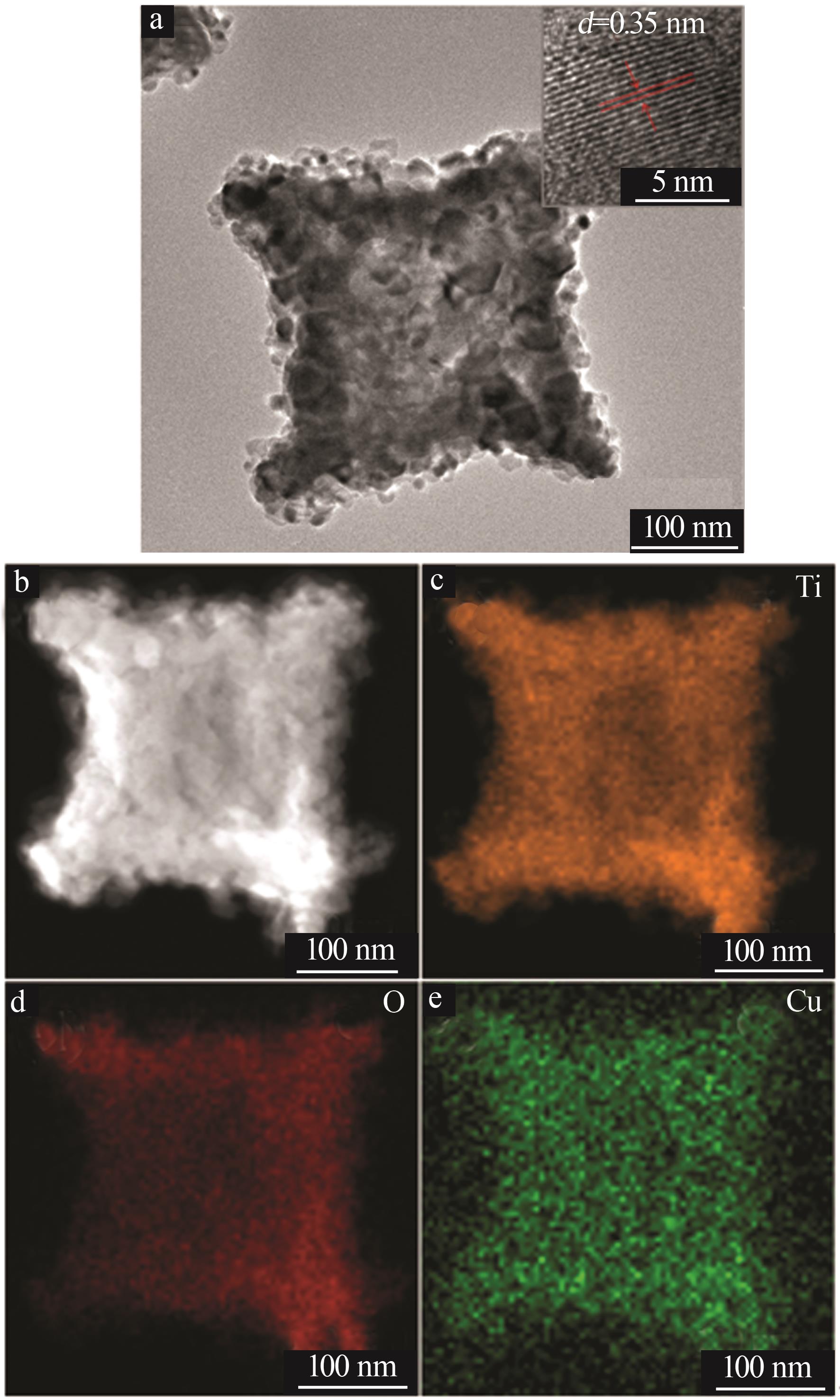
Hollow Cu-doped TiO2 for enhancing photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance
SONG Zhijia( ), WANG Suisui, KUANG Qin(
), WANG Suisui, KUANG Qin( )
)
- Department of Chemistry,College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361005,China
-
Received:2023-05-30Online:2023-08-10Published:2023-08-25 -
Contact:KUANG Qin E-mail:20520200156126@stu.xmu.edu.cn;qkuang@xmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SONG Zhijia, WANG Suisui, KUANG Qin. Hollow Cu-doped TiO2 for enhancing photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 45-50.
share this article
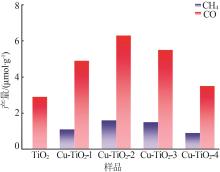
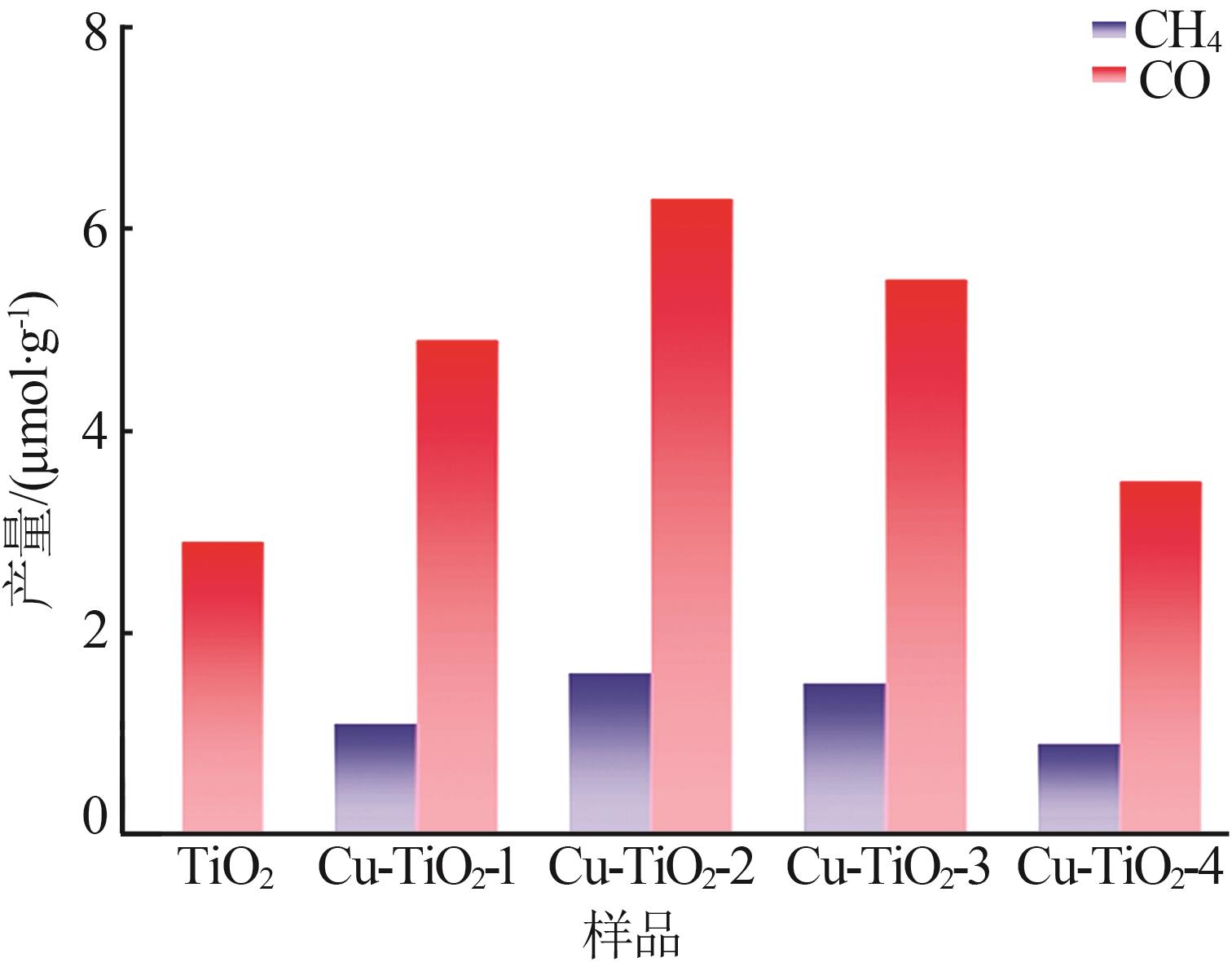
Table 2
Comparison of metal-doped TiO2 catalysts for photocatalytic CO2 reduction"
| 光催化剂 | 实验条件 | 产物/(μmol·g-1·h-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CH4 | ||
| Cu-TiO2-2(本工作) | 300 W Xe Lamp | 1.05 | 0.27 |
| Fe-TiO2-500[ | 300 W Xe Lamp(λ>420 nm) | — | 0.47 |
| 5Bi-TiO2[ | 250 W Hg Lamp(λ=365 nm) | — | 1.16 |
| 0.10Ce-TiO2[ | 300 W Xe Lamp(λ>400 nm) | 2.1 | 0.6 |
| 3%W-TiO2[ | 300 W Xe Lamp(模拟太阳光) | 1.7 | 0.12 |
| Co-TiO2-4[ | 300 W Xe Lamp | 1.94 | 0.09 |
| 1 | HUANG Hengming, SONG Hui, KOU Jiahui,et al.Atomic-level insights into surface engineering of semiconductors for photocatalytic CO2 reduction[J].Journal of Energy Chemistry,2022,67:309-341. |
| 2 | 李佳慧,李克艳,宋春山,等.聚合氮化碳的制备、改性及光催化还原二氧化碳性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(12):21-28. |
| LI Jiahui, LI Keyan, SONG Chunshan,et al.Study on preparation,modification and carbon dioxide photocatalytic reduction performance of polymeric carbon nitride[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(12):21-28. | |
| 3 | WANG Haining, ZOU Yanhong, SUN Hongxu,et al.Recent progress and perspectives in heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 reduction through a solid-gas mode[J].Coordination Chemistry Reviews,2021,438:213906. |
| 4 | WANG Shuobo, HAN Xu, ZHANG Yihe,et al.Inside-and-out semiconductor engineering for CO2 photoreduction:From recent advances to new trends[J].Small Structures,2021,2(1):2000061. |
| 5 | 李书文,周严,汪铁林.BiVO4/rGO复合物的制备及其光催化还原CO2研究[J].无机盐工业,2019,51(11):82-87. |
| LI Shuwen, ZHOU Yan, WANG Tielin.Study on preparation and photocatalysis-reduction for CO2 of BiVO4/rGO composite[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2019,51(11):82-87. | |
| 6 | LI Kai, TENG Chao, WANG Shuang,et al.Recent advances in TiO2-based heterojunctions for photocatalytic CO2 reduction with water oxidation:A review[J].Frontiers in Chemistry,2021,9:637501. |
| 7 | WANG Zhiqiang, ZHU Juncheng, ZU Xiaolong,et al.Selective CO2 photoreduction to CH4 via Pdδ+-assisted hydrodeoxygenation over CeO2 nanosheets[J].Angewandte Chemie,2022,61(30):e202203249. |
| 8 | LIANG Yujie, WU Xi, LIU Xueyan,et al.Recovering solar fuels from photocatalytic CO2 reduction over W6+-incorporated crystalline g-C3N4 nanorods by synergetic modulation of active cente-rs[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2022,304:120978. |
| 9 | XIA Yu, MAN Jianwei, WU Xiaodong,et al.Oxygen-vacancy-assisted construction of Ce-TiO2 aerogel for efficiently boosting photocatalytic CO2 reduction without any sacrifice agent[J].Ceramics International,2023,49(4):6100-6112. |
| 10 | ZHANG Yumin, ZHAO Jianhong, WANG Hui,et al.Single-atom Cu anchored catalysts for photocatalytic renewable H2 production with a quantum efficiency of 56%[J].Nature Communications,2022,13:58. |
| 11 | ZHAO Yunxuan, ZHAO Yufei, SHI Run,et al.Tuning oxygen vacancies in ultrathin TiO2 nanosheets to boost photocatalytic nitrogen fixation up to 700 nm[J].Advanced Materials,2019,31(16):1806482. |
| 12 | JIANG Deli, ZHOU Yimeng, ZHANG Qianxiao,et al.Synergistic integration of AuCu co-catalyst with oxygen vacancies on TiO2 for efficient photocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CH4 [J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(39):46772-46782. |
| 13 | WU Siyao, JI Yangqi, WANG Lei,et al.Selective CO2-to-CH4 photoconversion in aqueous solutions catalyzed by atomically dispersed copper sites anchored on ultrathin graphdiyne oxide nano- sheets[J].Solar RRL,2021,5(7):2100200. |
| 14 | XU Miao, WU Heng, TANG Yawen,et al.One-step in situ synthesis of porous Fe3+-doped TiO2 octahedra toward visible-light photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into solar fuel[J].Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2020,309:110539. |
| 15 | MORADI M, KHORASHEH F, LARIMI A.Pt nanoparticles decorated Bi-doped TiO2 as an efficient photocatalyst for CO2 photo-reduction into CH4 [J].Solar Energy,2020,211:100-110. |
| 16 | XIONG Zhuo, LEI Ze, MA Siming,et al.Photocatalytic CO2 reduction over V and W codoped TiO2 catalyst in an internal-illuminated honeycomb photoreactor under simulated sunlight irradiation[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2017,219:412-424. |
| 17 | WANG Tao, MENG Xianguang, LIU Guigao,et al. In situ synthesis of ordered mesoporous Co-doped TiO2 and its enhanced photocatalytic activity and selectivity for the reduction of CO2 [J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(18):9491-9501. |
| 18 | JI Jixiang, LI Ruru, ZHANG Hao,et al.Highly selective photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to ethane over Au-O-Ce sites at micro-interface[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2023,321:122020. |
| 19 | YU Yangyang, DONG Xingan, CHEN Peng,et al.Synergistic effect of Cu single atoms and Au-Cu alloy nanoparticles on TiO2 for efficient CO2 photoreduction[J].ACS Nano,2021,15(9):14453-14464. |
| 20 | PI Jiacheng, JIA Xiaofang, LONG Zhangwen,et al.Surface and defect engineering coupling of halide double perovskite Cs2NaBiCl6 for efficient CO2 photoreduction[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2022,12(43):2270179. |
| 21 | YIN Haibo, DONG Feng, WANG Dingsheng,et al.Coupling Cu single atoms and phase junction for photocatalytic CO2 reduction with 100% CO selectivity[J].ACS Catalysis,2022,12(22):14096-14105. |
| [1] | TANG Bei. Preparation of ZnO/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalytic material and its degradation of pyridine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 133-142. |
| [2] | HUANG Jianan, LU Xiaoyu, WANG Mitang. Effect of Ba-La co-doping on degradation of methylene blue dye by TaON [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 146-151. |
| [3] | YANG Bo, LIANG Zhiyan, LIU Wenyuan, CAO Jiazhen, LIU Xinyue, XING Mingyang. Research progress of application of molybdenum-based catalytic materials for water pollution control [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 1-12. |
| [4] | YU Hongchao, ZHANG Mengmeng, JIN Tianxiang. Research progress of microstructure and crystal surface effect of Ag3PO4 photocatalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 13-20. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yan, HAO Xuewei, SHI Hainan, LI Jiahui, LI Keyan, GUO Xinwen. Study on photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of Cu-doped TiO2/PCN heterojunction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 21-27. |
| [6] | SUN Haijie, CHENG Yuan, TIAN Yuan, LIU Hongyan, CHEN Zhihao. Preparation of BiOI/g-C3N4 catalyst and its photocatalytic degradation performance of Rhodamine B [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 36-44. |
| [7] | LAN Yinghua, CHEN Yanmei, MA Ruixiao, ZHANG Yanhui. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of Ce-Ti oxide-attapulgite composites [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 133-140. |
| [8] | CHEN Zhangxu, FU Minglian, ZHU Danchen, ZHENG Bingyun. Preparation of carbon/graphite carbon nitride composites and their methylene blue removal performance [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 134-139. |
| [9] | QIU Xiaokui, ZHANG Ruofan, WANG Xiaoyan, WANG Hailong, ZHANG Qixue, WAN Chao, XU Lixin. Research on bamboo shavings carbon supported ruthenium catalysts for hydrogen generation from photocatalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 153-158. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zhe,LIAO Mingyu,CHEN Ming,YU Shanshan,ZHOU Kangdi,LI Jiachun,ZHANG Linfeng,WU Huadong,GUO Jia. Application of CeO2-ZnO/KIT-6 catalyst in photocatalytic adsorption desulfurization [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(9): 143-149. |
| [11] | TONG Haijuan,LI Siqi,FAN Fangfang,ZUO Weiyuan,SHI Bingfang. Facile synthesis of bismuth oxychloride and its photocatalytic degradation performance of p-nitrophenol [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(9): 157-162. |
| [12] | YANG Wenbo,WU Pan,HE Jian,LIU Changjun,JIANG Wei. Study on effect of heating rate on structure-activity of g-C3N4 photocatalyst by pyrolysis of urea [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 169-174. |
| [13] | LIANG Fang,SHI Fanian. Research progress on synthesis of bismuth based bimetallic photocatalyst and degradation of organic pollutants [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 61-68. |
| [14] | BAN Changsheng,LI Jun,JIN Yang,CHEN Ming,ZUO Longtao. Study on preparation of g-C3N4/g-C3N4 homojunction by supramolecular precursor and its photocatalytic property [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 125-131. |
| [15] | CHEN Jianjun,QIAO Yan,LIU Zixian,PENG Huanhuan,SONG Jialin,GAO Yan,LI Yongyu. Preparation of Au-supported porous g-C3N4 nanosheets for photocatalytic H2 evolution performance under visible-light [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 132-136. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||