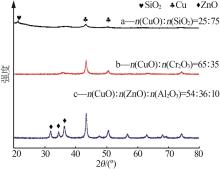
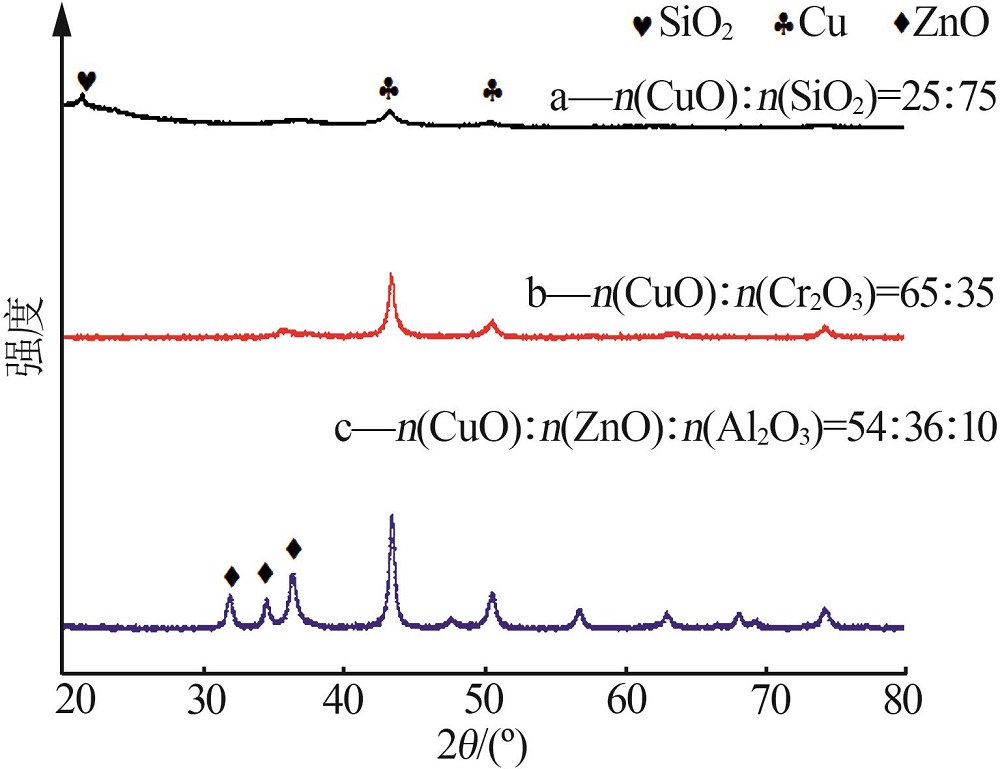
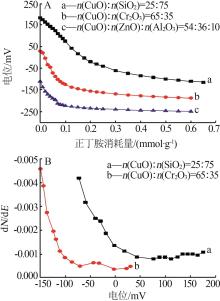
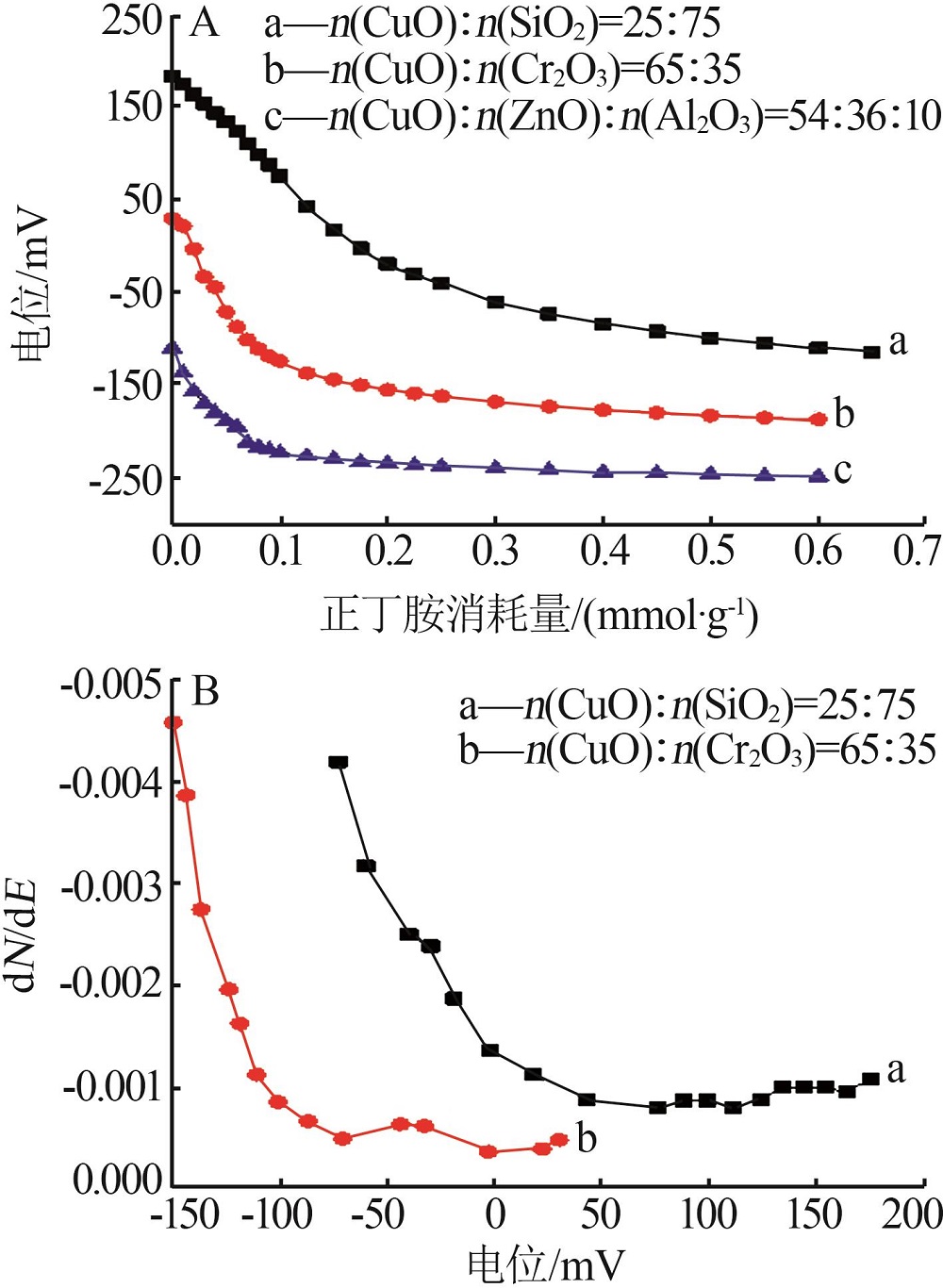
| 1 |
ZHAO Lili, AN Hualiang, ZHAO Xinqiang, et al. Effect of Ni/Co mass ratio and NiO-Co3O4 loading on catalytic performance of NiO-Co3O4/Nb2O5-TiO2 for direct synthesis of 2-propylheptanol from n-valeraldehyde[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(3):1736-1742.
|
| 2 |
王雪峰, 夏伟, 许红云, 等. 2-丙基-2-庚烯醛加氢制2-丙基庚醇催化剂制备工艺研究[J]. 天然气化工:C1化学与化工 2021, 46(2):44-46, 70.
|
|
WANG Xuefeng, XIA Wei, XU Hongyun, et al. Study on preparation process of catalysts for hydrogenation of 2-propyl-2-heptaneal to 2-propyl heptanol[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2021, 46(2):44-46, 70.
|
| 3 |
张卉, 陈和. C10烯醛液相加氢催化剂的性能评价[J]. 石化技术与应用, 2022, 40(1):17-19.
|
|
ZHANG Hui, CHEN He. Performance evaluation of C10 olefin aldehyde liquid phase hydrogenation catalyst[J]. Petrochemical Technology & Application, 2022, 40(1):17-19.
|
| 4 |
李选志, 曹晓玲. CuO-ZnO/Al2O3催化剂上异丁醛加氢制异丁醇的性能研究[C]//安阳:第十四届全国工业催化技术及应用年会.西安:中国化工学会全国工业催化信息站, 2017:97-103.
|
| 5 |
倪术荣, 吴显军, 徐伟池, 等. 气相醛加氢催化剂及其制备方法:中国,114054033A[P]. 2022-02-18.
|
| 6 |
赵修波. 改性铜铬加氢催化剂的开发[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2005.
|
|
ZHAO Xiubo. Development of copper chromite catalyst for furfural hydrogenation[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2005.
|
| 7 |
孙中华, 殷玉圣, 殷惠琴. 一种用于癸烯醛液相加氢制异癸醇的催化剂及其制备方法:中国,106179373A[P]. 2016-12-07.
|
| 8 |
LI Zengxin, KUANG Tangbin, ZHOU Xuyi, et al. The ammonia leaching method of recycling the spent copper-chromium oxide catalysts[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 1015: 430-433.
|
| 9 |
王淇锋, 赵雨, 宋冰洁, 等. 制备方法对CuO-Cr2O3催化剂结构及其催化2-丙基-2-庚烯醛加氢性能的影响[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2020, 36(5):421-427.
|
|
WANG Qifeng, ZHAO Yu, SONG Bingjie, et al. The effect of preparation methods on the structure of CuO-Cr2O3 catalysts and the catalytic performances in the hydrogenation of 2-propyl-2-heptenal[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2020, 36(5):421-427.
|
| 10 |
孙中华. 异癸醛气相加氢制异癸醇催化剂的研究[J]. 化学工业与工程技术, 2007, 28(4):8-11.
|
|
SUN Zhonghua. Research on the catalyst for preparing isodecyl alcohol by gas hydrogenation of isodecyl aldehyde[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry & Engineering, 2007, 28(4):8-11.
|
| 11 |
吴显军, 王刚, 张志华, 等. 气相醛加氢催化剂(VAH-1/VAH-2)[J]. 石油科技论坛, 2015, 34(S1):213-215.
|
|
WU Xianjun, WANG Gang, ZHANG Zhihua, et al. Aldehyde hydrogenation catalyst of vapor phase(VAH-1/VAH-2)[J]. Oil Forum, 2015, 34(S1):213-215.
|
| 12 |
荀彤, 张文成, 于宏伟. 新型辛烯醛加氢催化剂的研制[J]. 炼油与化工, 2002, 13(3):18-22.
|
|
XUN Tong, ZHANG Wencheng, YU Hongwei. Development of new type octenal hydrogenation catalyst[J]. Refining and Chemicals, 2002, 13(3):18-22.
|
| 13 |
王珂, 鄢冬茂, 龚党生, 等. 连续化加氢工艺和设备研究进展[J]. 染料与染色, 2019, 56(3):51-59.
|
|
WANG Ke, YAN Dongmao, GONG Dangsheng, et al. Progress in continuous hydrogenation process and equipment[J]. Dyestuffs and Coloration, 2019, 56(3):51-59.
|
| 14 |
WANG J X, SPENCER J E, CAI Yeping. Promoted copper/zinc catalyst for hydrogenating aldehydes to alcohols:US, 8399718[P]. 2013-03-19.
|
| 15 |
于海斌, 常俊石, 成宏, 等. 辛烯醛气相加氢制辛醇催化剂工业侧线试验[J]. 无机盐工业, 2005, 37(12):22-24.
|
|
YU Haibin, CHANG Junshi, CHENG Hong, et al. Industrial experiment of TCAH catalyst for the preparation of octanal from octene aldehyde by vapor phase hydrogenation[J]. Inorganic Che-Industry micals, 2005, 37(12):22-24.
|
| 16 |
张豫. 醋酸甲酯加氢制乙醇催化材料的研究[D].天津:天津大学, 2018.
|
|
ZHANG Yu. Study on catalytic materials of hydrogenation of methyl acetate to ethanol[D].Tianjin:Tianjin University, 2018.
|
| 17 |
尚城城, 郭湾, 姚志龙, 等. 异丁烯与醋酸酯化合成醋酸叔丁酯[J]. 精细化工, 2019, 36(8):1604-1609.
|
|
SHANG Chengcheng, GUO Wan, YAO Zhilong, et al. Esterification of acetic acid with isobutene to tert-butyl acetate[J]. Fine Che micals, 2019, 36(8):1604-1609.
|
 ),CHEN He3,SUN Peiyong1,2,CHAI Wenzheng3,ZHANG Shenghong1,2,FU Songbao3,YAO Zhilong1,2(
),CHEN He3,SUN Peiyong1,2,CHAI Wenzheng3,ZHANG Shenghong1,2,FU Songbao3,YAO Zhilong1,2( )
)