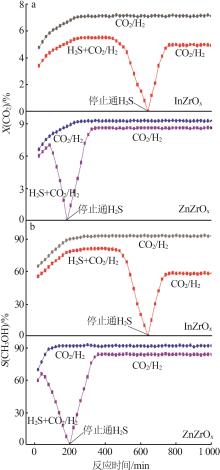
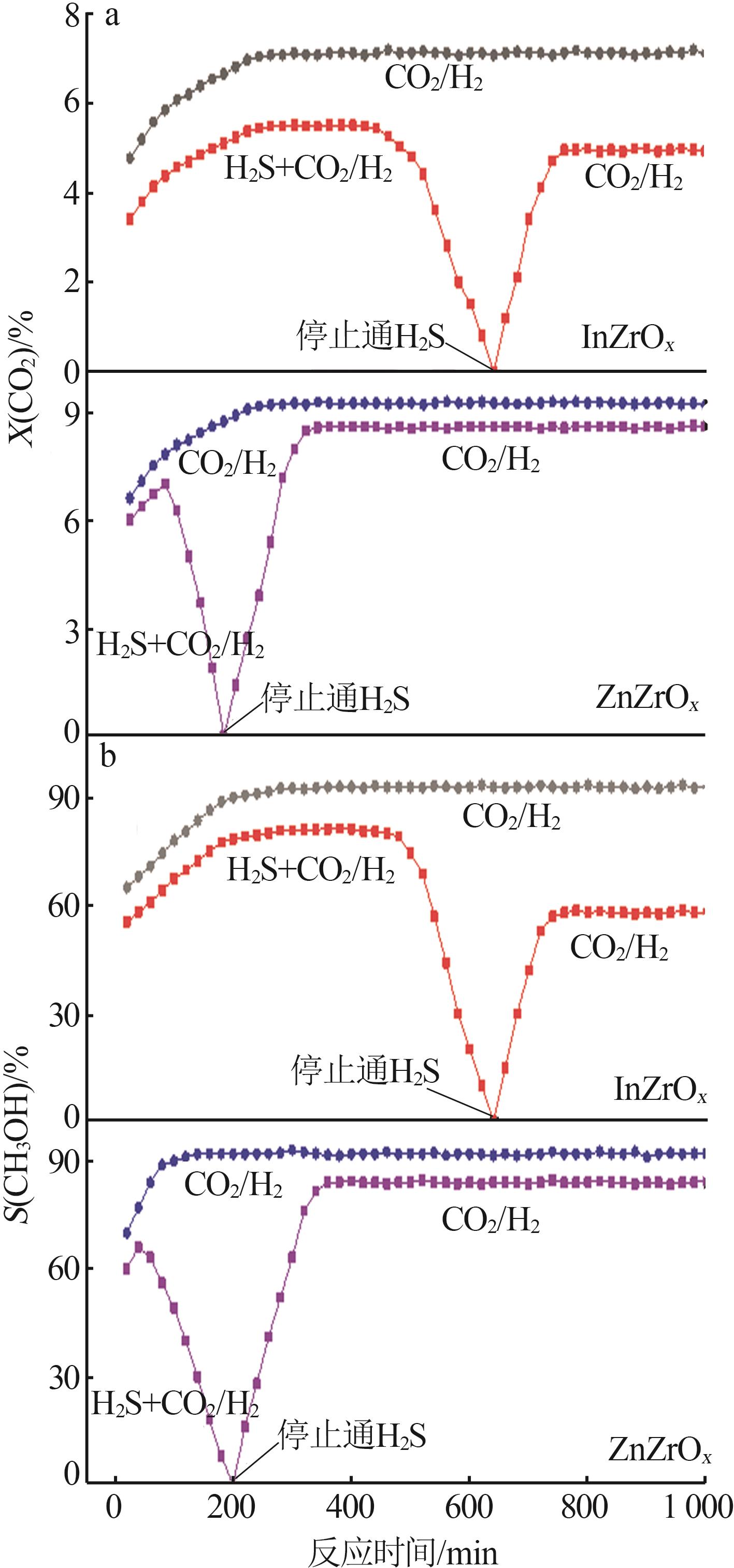
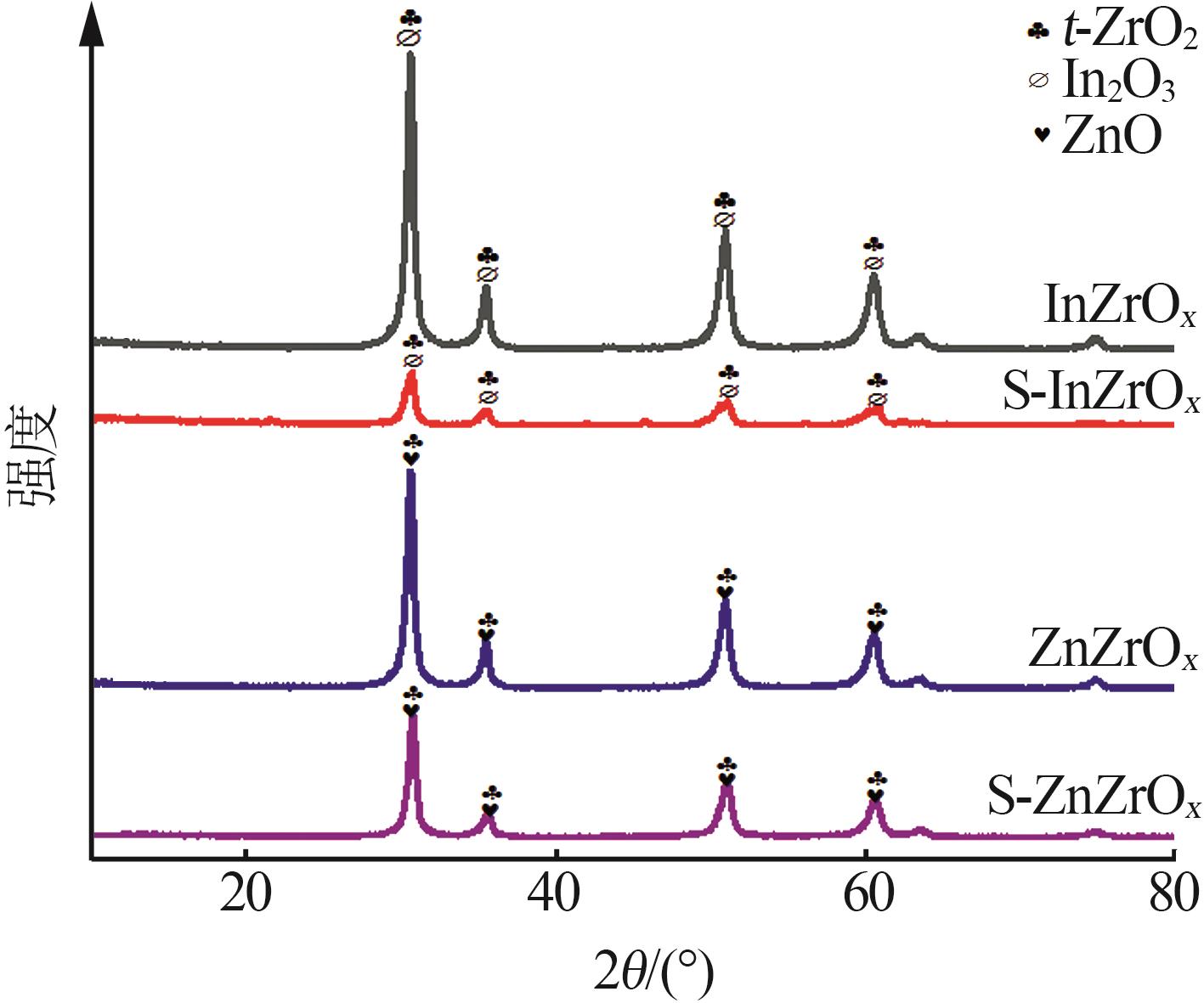
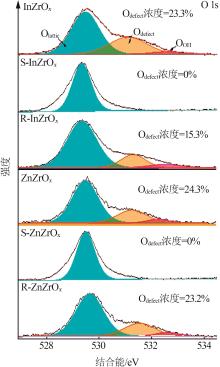
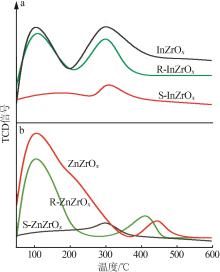
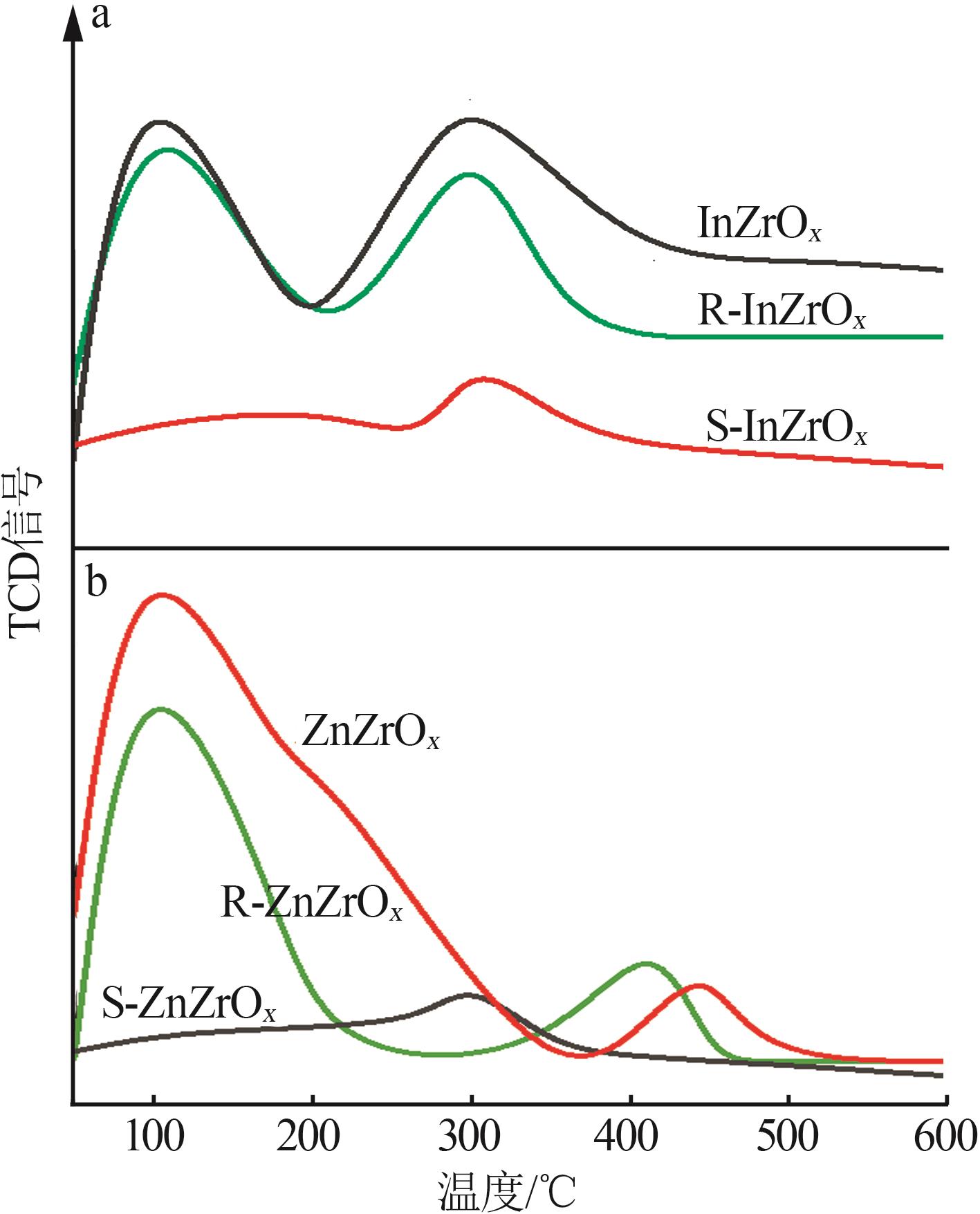
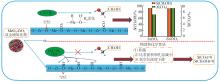
| 1 |
GRACIANI J, MUDIYANSELAGE K, XU Fang, et al. Highly active copper-ceria and copper-ceria-titania catalysts for methanol synthesis from CO₂[J].Science, 2014, 345(6196):546-550.
|
| 2 |
YANG Haiyan, ZHANG Chen, GAO Peng, et al. A review of the catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide into value-added hydrocarbons[J].Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7(20):4580-4598.
|
| 3 |
ZOU Qizhuang, LONG Guangcai, ZHAO Tianxiang, et al. Catalyst-free selective N-formylation and N-methylation of amines using CO2 as a sustainable C1 source[J].Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(4):1134-1138.
|
| 4 |
GARCÍA-TRENCO A, REGOUTZ A, WHITE E R, et al. PdIn intermetallic nanoparticles for the hydrogenation of CO2 to metha-nol[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 220:9-18.
|
| 5 |
LI Zhenhua, LIU Jinjia, ZHAO Yufei, et al. Co-based catalysts derived from layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets for the photothermal production of light olefins[J].Advanced Materials:Deerfield Beach, Fla.,2018, 30(31).Doi:10.1002/adma.201800527.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201800527
|
| 6 |
WANG L, WANG L, ZHANG J, et al. Selective hydrogenation of CO2 to ethanol over cobalt catalysts[J].Angewandte Chemie:International Ed.in English, 2018, 57(21):6104-6108.
|
| 7 |
SHIH C F, ZHANG Tao, LI Jinghai, et al. Powering the future with liquid sunshine[J].Joule, 2018, 2(10):1925-1949.
|
| 8 |
BAVYKINA A, YARULINA I, ABDULGHANI A J AL, et al. Turning a methanation co catalyst into an in-co methanol producer[J].ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(8):6910-6918.
|
| 9 |
DOSTAGIR N H M, THOMPSON C, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Rh promoted In2O3 as a highly active catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J].Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(24):8196-8202.
|
| 10 |
AN Bing, ZHANG Jingzheng, CHENG Kang, et al. Confinement of ultrasmall Cu/ZnO x nanoparticles in metal-organic frameworks for selective methanol synthesis from catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 [J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(10):3834-3840.
|
| 11 |
KATTEL S, RAMÍREZ P J, CHEN J G, et al. Active sites for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol on Cu/ZnO catalysts[J].Science, 2017, 355(6331):1296-1299.
|
| 12 |
FIORDALISO E M, SHARAFUTDINOV I, CARVALHO H W P, et al. Intermetallic GaPd2 nanoparticles on SiO2 for low-pressure CO2 hydrogenation to methanol:Catalytic performance and in situ characterization[J].ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(10):5827-5836.
|
| 13 |
KATTEL S, YU Weiting, YANG Xiaofang, et al. CO2 hydrogenation over oxide-supported PtCo catalysts:The role of the oxide support in determining the product selectivity[J].Angewandte Chemie:International Ed.in English, 2016, 55(28):7968-7973.
|
| 14 |
WANG Jijie, LI Guanna, LI Zelong, et al. A highly selective and stable ZnO-ZrO2 solid solution catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J].Science Advances, 2017, 3(10).Doi:10.1126/sciadv.1701290.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701290
|
| 15 |
WANG Jijie, TANG Chizhou, LI Guanna, et al. High-performance MaZrO x (Ma=Cd,Ga) solid-solution catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J].ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(11):10253-10259.
|
| 16 |
LIU Xiaoliang, WANG Mengheng, ZHOU Cheng, et al. Selective transformation of carbon dioxide into lower olefins with a bifunctional catalyst composed of ZnGa2O4 and SAPO-34[J].Chemical Communications:Cambridge, England,2018, 54(2):140-143.
|
| 17 |
STANGELAND K, KALAI D Y, DING Yi, et al. Mesoporous manganese-cobalt oxide spinel catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2019, 32:146-154.
|
| 18 |
LIU Xiaoliang, WANG Mengheng, YIN Haoren, et al. Tandem catalysis for hydrogenation of CO and CO2 to lower olefins with bifunctional catalysts composed of spinel oxide and SAPO-34[J].ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(15):8303-8314.
|
| 19 |
肖亦寒, 曹建新, 刘飞, 等. 焙烧温度对MnZnO x 物化性质及催化性能的影响[J].无机盐工业, 2021, 53(4):95-100.
|
|
XIAO Yihan, CAO Jianxin, LIU Fei, et al. Effect of calcination temperature on physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of MnZnO x [J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(4):95-100.
|
| 20 |
MARTIN O, MARTÍN A J, MONDELLI C, et al. Indium oxide as a superior catalyst for methanol synthesis by CO2 hydrogenati-on[J].Angewandte Chemie:International Ed.in English, 2016, 55(21):6261-6265.
|
| 21 |
DANG Shanshan, GAO Peng, LIU Ziyu, et al. Role of zirconium in direct CO2 hydrogenation to lower olefins on oxide/zeolite bifunctional catalysts[J].Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 364:382-393.
|
| 22 |
WANG Xiuxiu, WANG Yizhou, YANG Chunliang, et al. A novel microreaction strategy to fabricate superior hybrid zirconium and zinc oxides for methanol synthesis from CO2 [J].Applied Catalysis A:General, 2020, 595.Doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117507.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117507
|
| 23 |
PAN Y X, LIU C J, MEI D, et al. Effects of hydration and oxygen vacancy on CO2 adsorption and activation on beta-Ga2O3(100)[J].Langmuir, 2010, 26(8):5551-5558.
|
| 24 |
GRABOWSKI R, SŁOCZYŃSKI J, ŚLIWA M, et al. Influence of polymorphic ZrO2 phases and the silver electronic state on the activity of Ag/ZrO2 catalysts in the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol[J].ACS Catalysis, 2011, 1(4):266-278.
|
| 25 |
YE Jingyun, LIU Changjun, GE Qingfeng. DFT study of CO2 adsorption and hydrogenation on the In2O3 surface[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(14):7817-7825.
|
| 26 |
YE Jingyun, LIU Changjun, MEI Donghai, et al. Active oxygen vacancy site for methanol synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation on In2O3(110):A DFT study[J].ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(6):1296-1306.
|
| 27 |
SUN Kaihang, FAN Zhigang, YE Jingyun, et al. Hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol over In2O3 catalyst[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2015, 12:1-6.
|
| 28 |
KUMARI N, HAIDER M A, AGARWAL M, et al. Role of reduced CeO2(110) surface for CO2 reduction to CO and metha-
|
|
nol[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(30):16626-16635.
|
| 29 |
RUNGTAWEEVORANIT B, BAEK J, ARAUJO J R, et al. Copper nanocrystals encapsulated in Zr-based metal-organic frameworks for highly selective CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J].Nano Letters, 2016, 16(12):7645-7649.
|
| 30 |
LARMIER K, LIAO W C, TADA S, et al. CO2-to-methanol hydrogenation on zirconia-supported copper nanoparticles:Reaction intermediates and the role of the metal-support interface[J].Angewandte Chemie:International Ed.in English, 2017, 56(9):2318-2323.
|
| 31 |
LIU Piao, CAO Jianxin, XU Zheng, et al. Thiolation of methanol with H2S using core-shell structured ZSM-5@t-ZrO2 catalyst[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 211.Doi:10.1016/j.ces.2019.115273.
doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2019.115273
|
| 32 |
WANG Ying, YANG Tinglong, LIU Fei, et al. High selectivity in methanethiol synthesis over a coated composite comprising ZSM-5 with t-ZrO2 [J].Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 305.Doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110358.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110358
|
 ),WANG Fuzhong,LIU Fei(
),WANG Fuzhong,LIU Fei( )
)