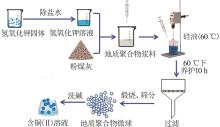
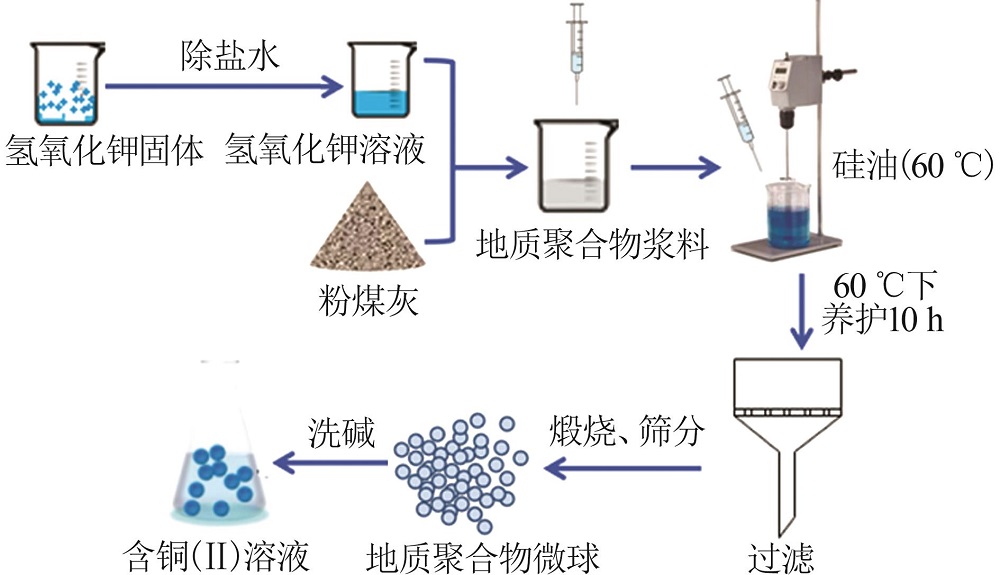
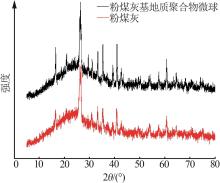
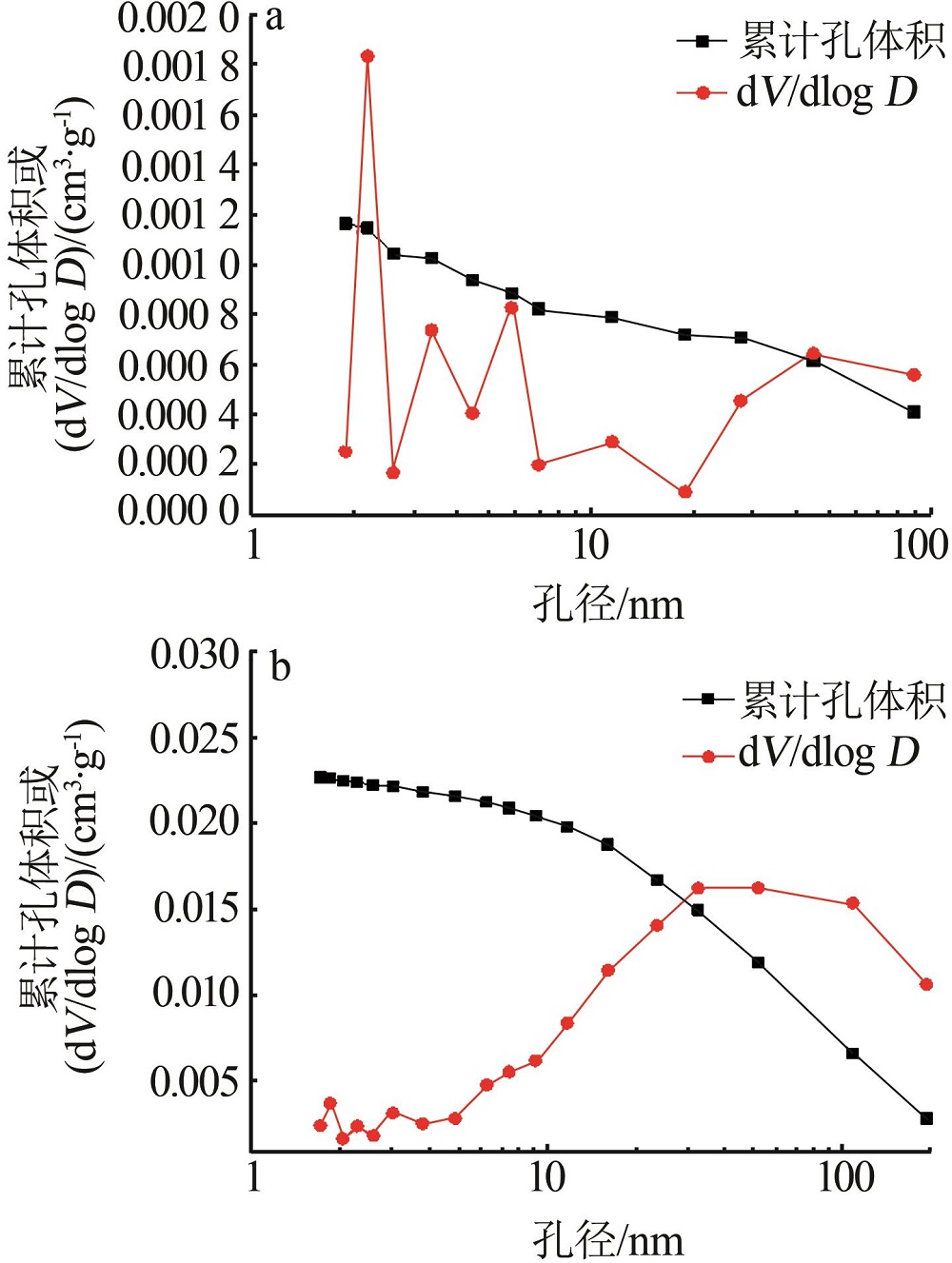
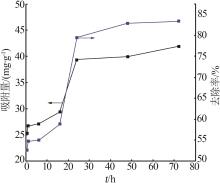
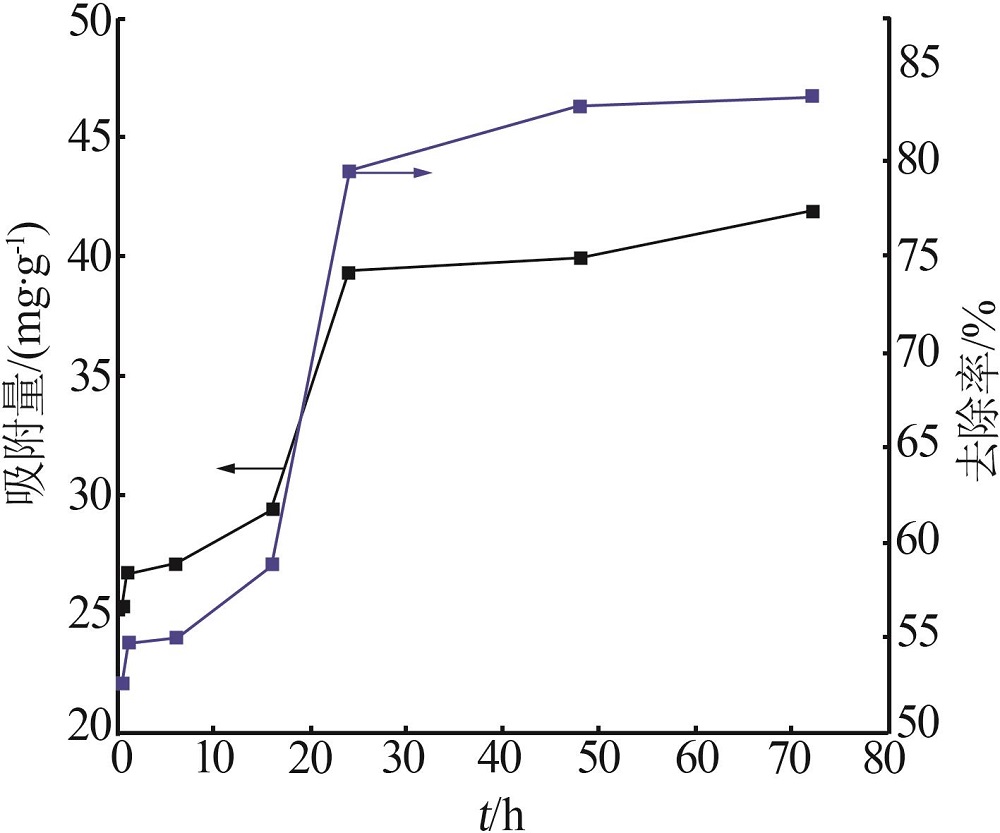
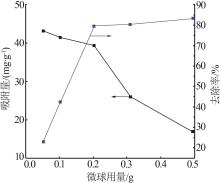
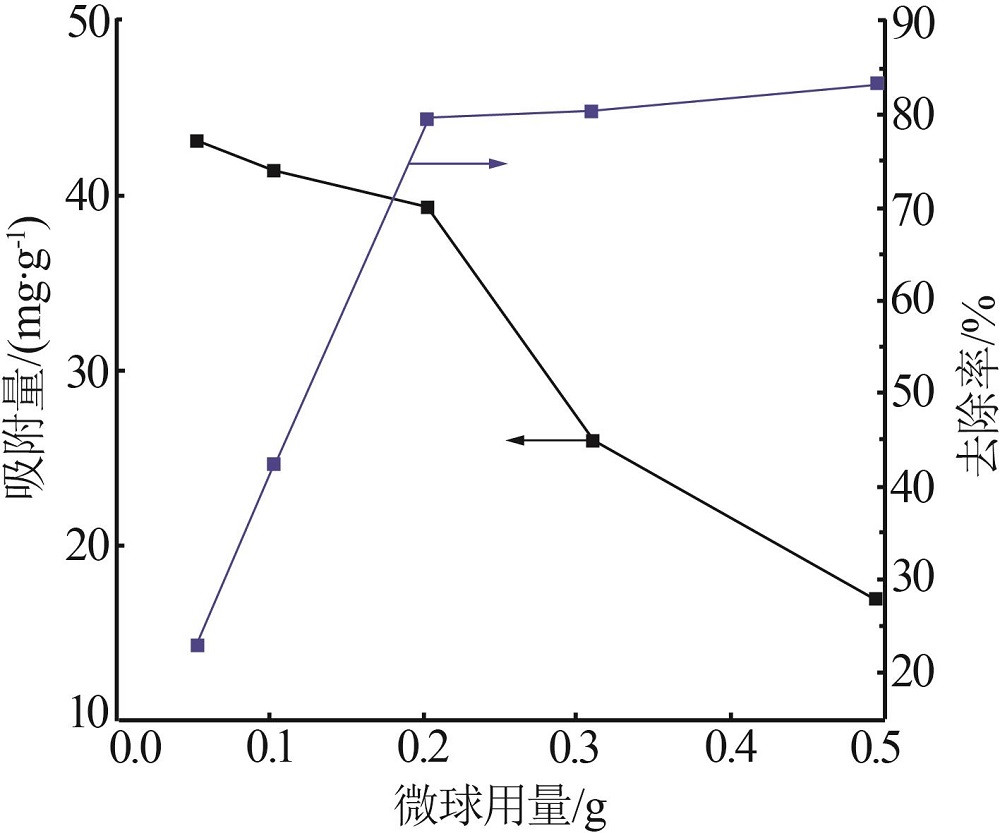
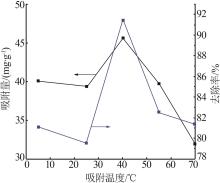
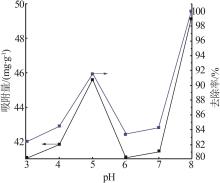
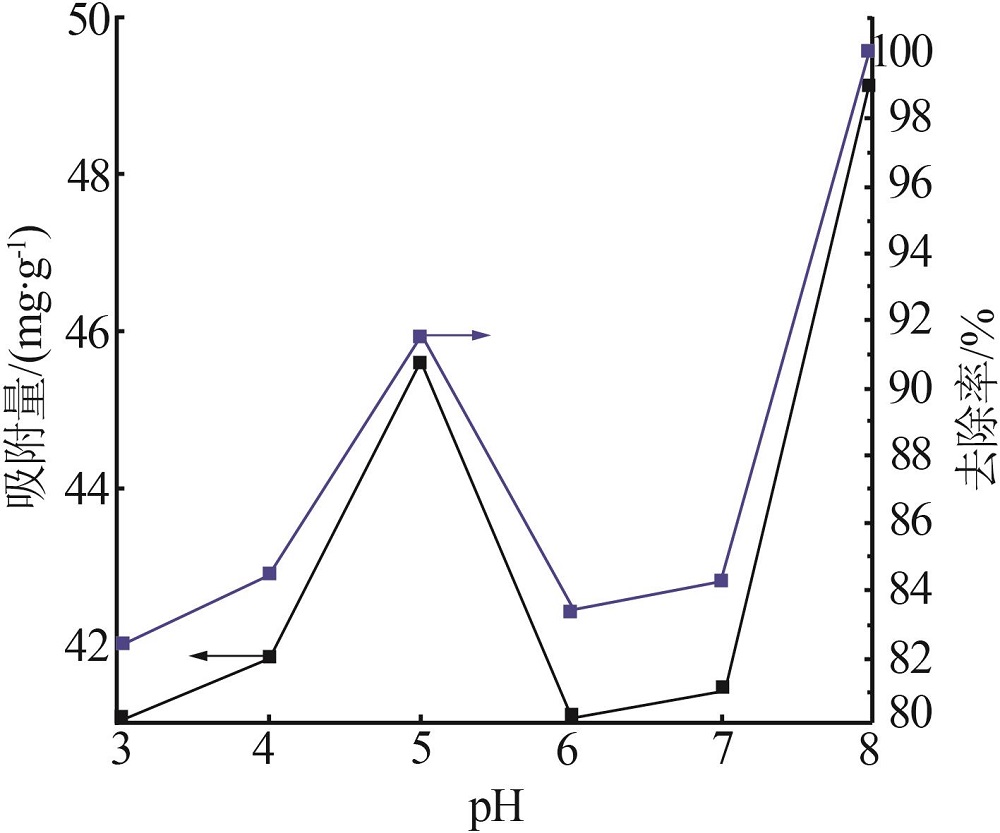
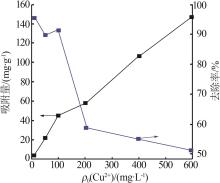
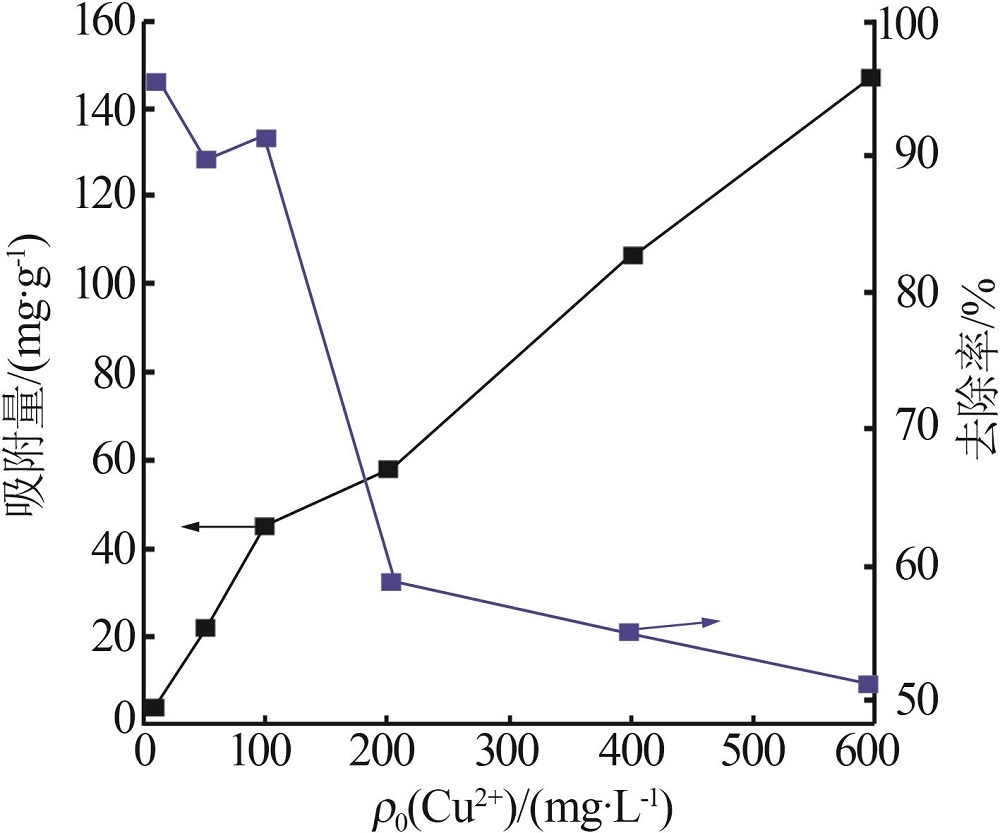
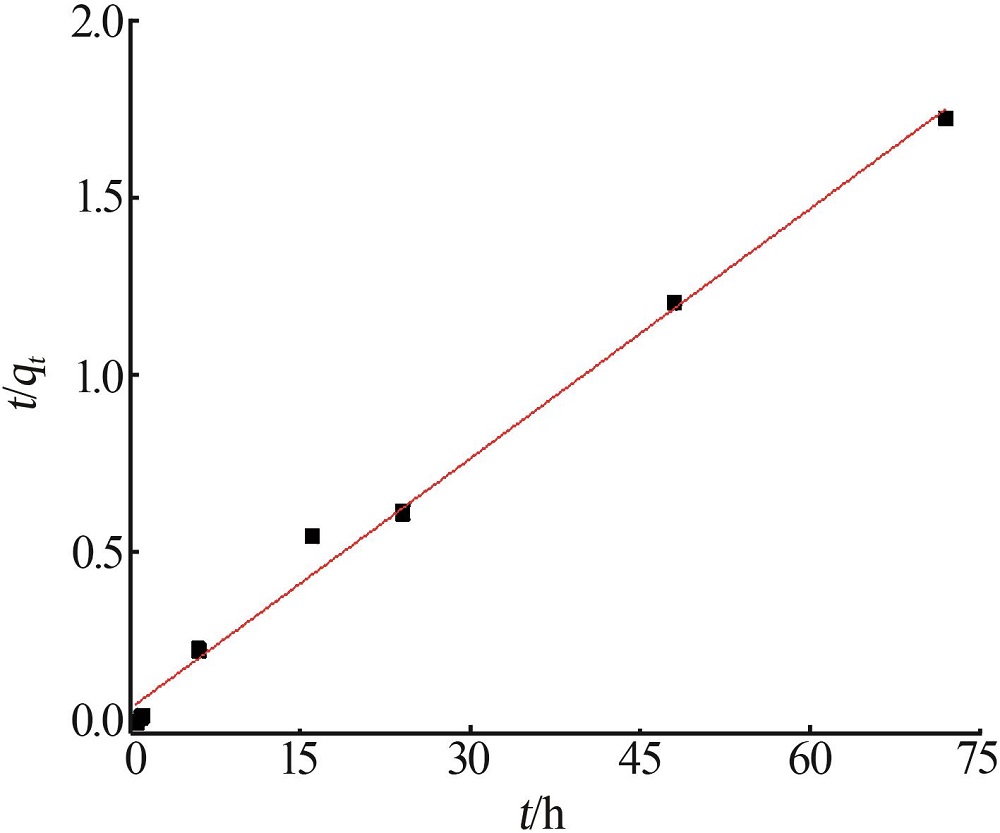
| 1 |
王夏芳. 铜离子对环境危害现状及对策研究[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2015(1):55-57.
|
|
WANG Xiafang. The dangers of copper ions on the environment and research on countermeasure[J]. Territory & Natural Resour-Study ces, 2015(1):55-57.
|
| 2 |
AWUAL M R. Novel ligand functionalized composite material for efficient copper(Ⅱ) capturing from wastewater sample[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 172: 387-396.
|
| 3 |
廖妮. 磁性硅藻土的制备及对铜离子的吸附能力研究[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2019(3):13-15.
|
|
LIAO Ni. Study on preparation of magnetic diatomite and its adsorption capacity for copper ions[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equi-pment, 2019(3):13-15.
|
| 4 |
葛圆圆. 偏高岭土地质聚合物基重金属离子吸附剂的制备及其性能研究[D].南宁:广西大学, 2015.
|
|
GE Yuanyuan. Fabrication of metakaolin geopolymer-based adsorbents and their applied performance for heavy metal retention[D].Nanning:Guangxi University, 2015.
|
| 5 |
KENG P S, LEE S L, HA S T, et al. Removal of hazardous heavy metals from aqueous environment by low-cost adsorption materials[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2014, 12(1):15-25.
|
| 6 |
SUTIRMAN Z A, RAHIM E A, SANAGI M M, et al. New efficient chitosan derivative for Cu(Ⅱ) ions removal:Characterization and adsorption performance[J]. International Journal of Biological Mac- romolecules, 2020, 153: 513-522.
|
| 7 |
李巧云, 贺艳, 徐梦雪, 等. 地质聚合物基无机膜去除水中钙、镁离子的研究[J]. 功能材料, 2017, 48(1):1215-1220.
|
|
LI Qiaoyun, HE Yan, XU Mengxue, et al. Study on the removal of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in water by the geopolymer-based inorganic membrane[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2017, 48(1):1215-1220.
|
| 8 |
唐青. 悬浮固化法制备球形地质聚合物的研究及应用[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2018.
|
|
TANG Qing. Studies on preparation of spherical geopolymer using suspension solidification and its application[D].Nanning:Guan-gxi University, 2018.
|
| 9 |
SU Qiaoqiao, YANG Sijie, HE Yan, et al. Prepared self-growing supported nickel catalyst by recovering Ni(Ⅱ) from metal wastewater using geopolymer microspheres[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389.Doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121919 .
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121919
|
| 10 |
SU Qiaoqiao, YE Quan, DENG Liang, et al. Prepared self-growth supported copper catalyst by recovering Cu(Ⅱ) from wastewater using geopolymer microspheres[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 272.Doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122571 .
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122571
|
| 11 |
唐青, 崔学民, 贺艳, 等. 地质聚合物及其在重金属废水处理中的应用[J]. 现代技术陶瓷, 2016, 37(4):253-269.
|
|
TANG Qing, CUI Xuemin, HE Yan, et al. Geopolymer:research progress and its applications in removing heavy metal from water[J]. Advanced Ceramics, 2016, 37(4):253-269.
|
| 12 |
李巧云. 偏高岭土基地质聚合物无机膜的制备及其对自来水的处理[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2017.
|
|
LI Qiaoyun. Preparation of metakaolin-based geopolymer inorganic membrane and its treatment for tap water[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University, 2017.
|
| 13 |
苏俏俏. 地聚物基吸附剂与催化剂载体微球回收利用重金属的研究[D].南宁:广西大学, 2020.
|
|
SU Qiaoqiao. Study of recovery and utilization of heavy metal by adsorbent and catalyst supports microspheres from geopolymer[D].Nanning:Guangxi University, 2020.
|
| 14 |
WU Qiong, CHEN Jie, CLARK M, et al. Adsorption of copper to different biogenic oyster shell structures[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 311: 264-272.
|
| 15 |
王英明, 姜亮, 董彦博, 等. 粉煤灰基地质聚合物制备及其对Cu2+的吸附性能[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2018, 24(5):120-125, 131.
|
|
WANG Yingming, JIANG Liang, DONG Yanbo, et al. Preparation condition and Cu2+ adsorption properties of fly ash based geopolymer[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2018, 24(5):120-125, 131.
|
| 16 |
于岩. 新型水相吸附材料[M].北京:科学出版社, 2016.
|