Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 132-138.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0013
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on conductivity of electrolyte in aqueous Zn-Mn battery
QIN Ye( ), LIU Chang, HAN Song, WANG Shuo
), LIU Chang, HAN Song, WANG Shuo
- Shenyang University of Chemical Technology,Shenyang 110142,China
-
Received:2024-01-08Online:2024-11-10Published:2024-02-05
CLC Number:
Cite this article
QIN Ye, LIU Chang, HAN Song, WANG Shuo. Study on conductivity of electrolyte in aqueous Zn-Mn battery[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 132-138.
share this article
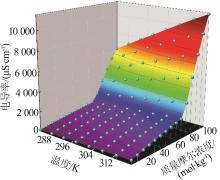
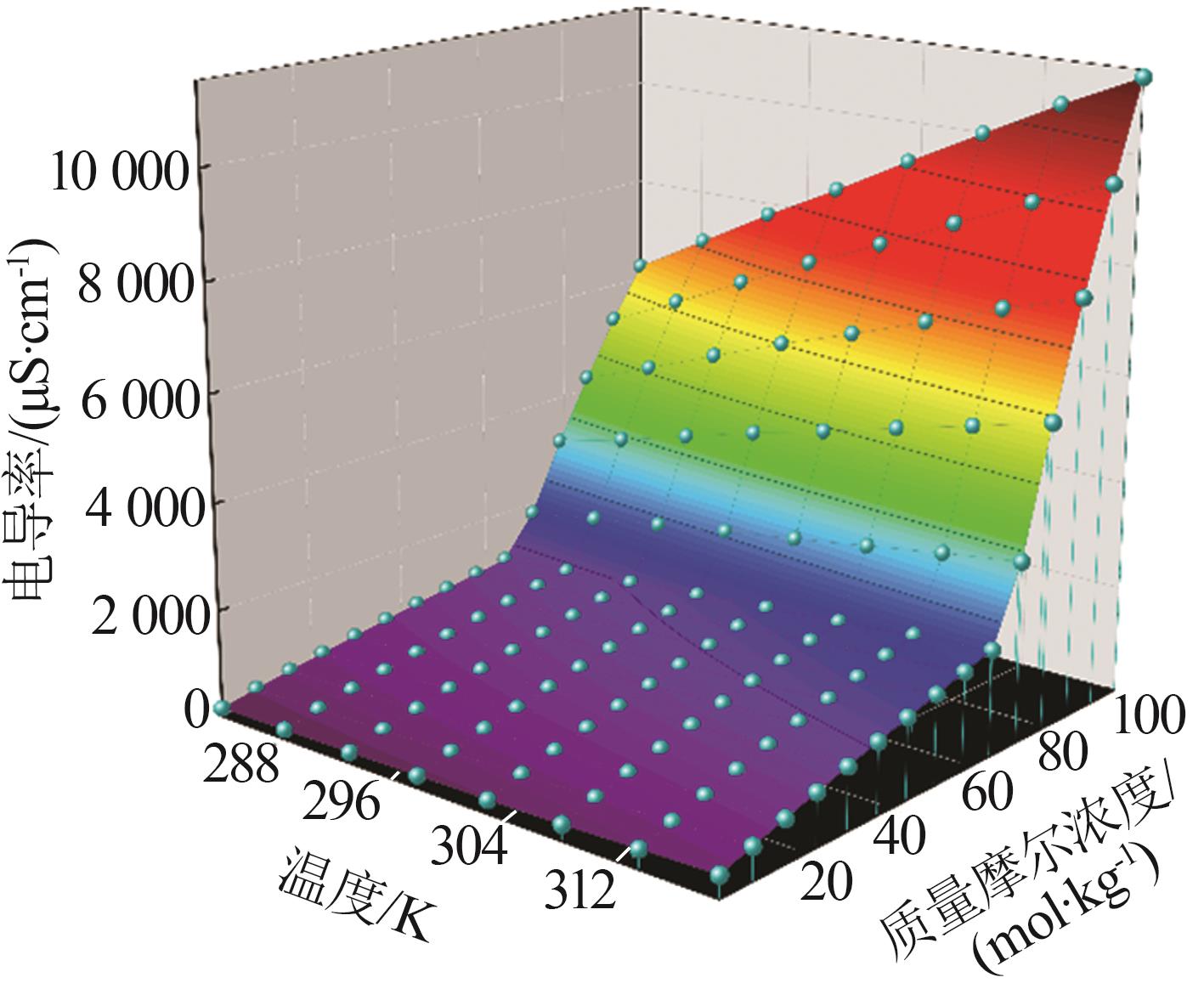
Table 1
Conductivity of MnSO4 aqueous solution at different molalities and temperatures"
质量摩尔浓度/ (10-3 mol·kg-1) | 电导率/(μS·cm-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 K | 288.15 K | 293.15 K | 298.15 K | 303.15 K | 308.15 K | 313.15 K | 318.15 K | |
| 1.009 | 153.4 | 175.9 | 198.8 | 225.8 | 249.8 | 290.0 | 351.4 | 406.8 |
| 2.002 | 279.0 | 313.8 | 351.8 | 391.4 | 432.4 | 479.4 | 530.2 | 595.6 |
| 2.998 | 387.0 | 436.0 | 487.0 | 544.0 | 594.6 | 652.4 | 714.2 | 787.6 |
| 4.007 | 493.0 | 554.8 | 621.8 | 687.8 | 751.4 | 819.0 | 891.8 | 967.4 |
| 4.999 | 590.0 | 664.0 | 743.6 | 822.2 | 897.8 | 980.0 | 1 065 | 1 145 |
| 6.003 | 687.0 | 775.4 | 865.0 | 953.8 | 1 041 | 1 130 | 1 222 | 1 318 |
| 7.001 | 779.4 | 873.8 | 975.8 | 1 078 | 1 177 | 1 278 | 1 385 | 1 487 |
| 7.995 | 867.4 | 972.8 | 1 086 | 1 199 | 1 307 | 1 416 | 1 535 | 1 649 |
| 9.004 | 954.8 | 1 074 | 1 194 | 1 315 | 1 435 | 1 560 | 1 688 | 1 814 |
| 10.08 | 1 037 | 1 163 | 1 306 | 1 439 | 1 571 | 1 700 | 1 839 | 1 970 |
| 20.12 | 1 802 | 2 028 | 2 258 | 2 484 | 2 698 | 2 922 | 3 152 | 3 358 |
| 39.96 | 3 100 | 3 450 | 3 840 | 4 224 | 4 572 | 4 946 | 5 306 | 5 676 |
| 60.01 | 4 238 | 4 740 | 5 272 | 5 792 | 6 266 | 6 764 | 7 278 | 7 738 |
| 80.01 | 5 290 | 5 916 | 6 572 | 7 212 | 7 814 | 8 444 | 9 060 | 9 612 |
| 100.0 | 6 248 | 7 012 | 7 776 | 8 492 | 9 250 | 9 980 | 10 702 | 11 368 |
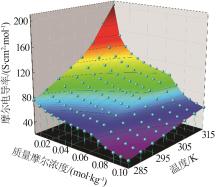
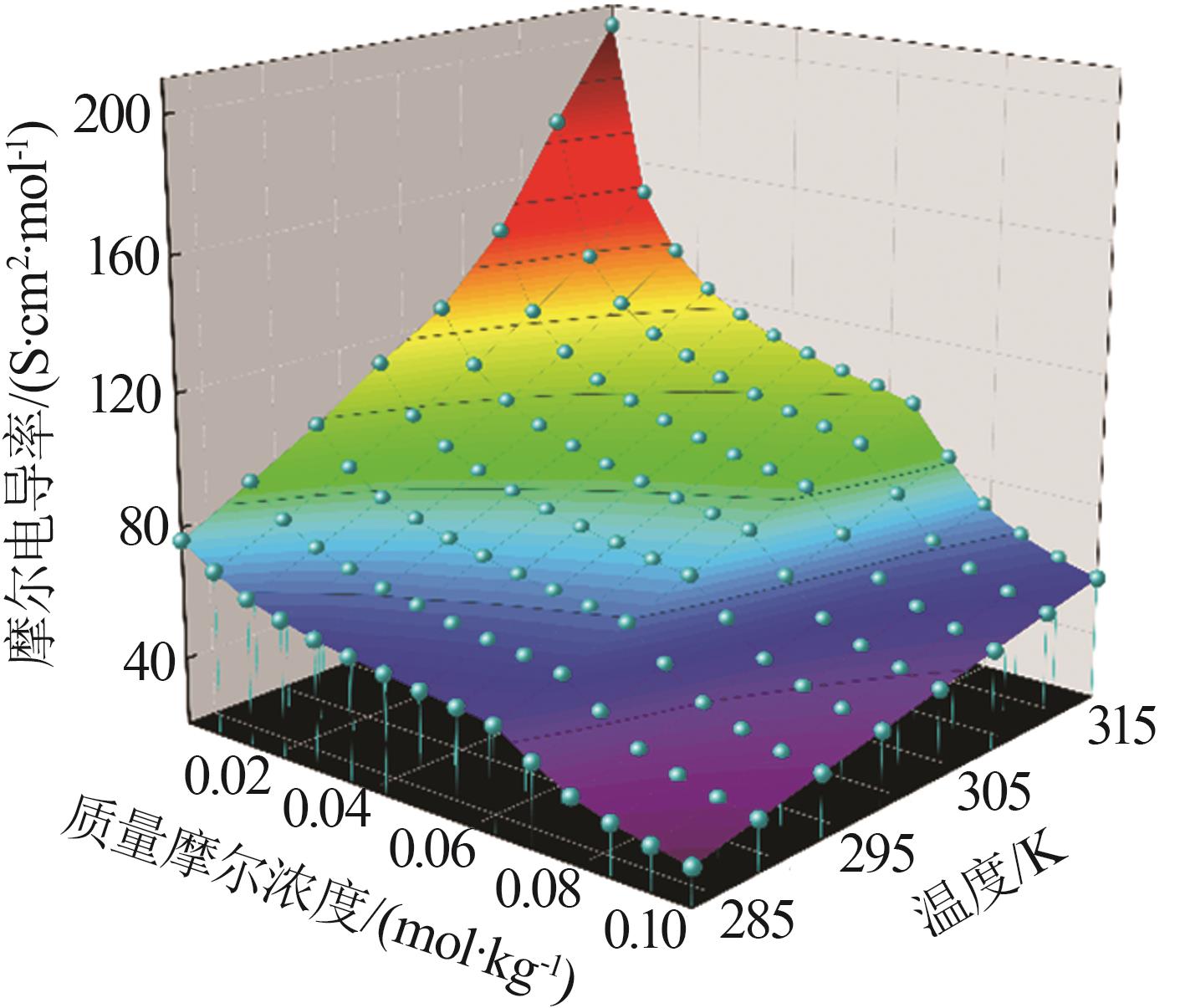
Table 2
Molar conductivity of MnSO4 aqueous solution at different molalities and temperatures"
质量摩尔浓度/ (10-3 mol·kg-1) | 摩尔电导率/(S·cm2·mol-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 K | 288.15 K | 293.15 K | 298.15 K | 303.15 K | 308.15 K | 313.15 K | 318.15 K | |
| 1.009 | 76.03 | 87.24 | 98.71 | 112.22 | 124.32 | 144.56 | 175.49 | 203.56 |
| 2.002 | 69.70 | 78.43 | 88.01 | 98.03 | 108.45 | 120.43 | 133.44 | 150.20 |
| 2.998 | 64.56 | 72.77 | 81.35 | 90.98 | 99.58 | 109.44 | 120.02 | 132.63 |
| 4.007 | 61.53 | 69.28 | 77.72 | 86.07 | 94.15 | 102.79 | 112.13 | 121.88 |
| 4.999 | 59.03 | 66.47 | 74.50 | 82.47 | 90.18 | 98.60 | 107.37 | 115.68 |
| 6.003 | 57.24 | 64.64 | 72.18 | 79.68 | 87.07 | 94.72 | 102.60 | 110.87 |
| 7.001 | 55.68 | 62.46 | 69.81 | 77.18 | 84.39 | 91.84 | 99.70 | 107.26 |
| 7.995 | 54.26 | 60.89 | 68.02 | 75.22 | 82.07 | 89.11 | 96.72 | 104.14 |
| 9.004 | 53.04 | 59.68 | 66.41 | 73.22 | 80.06 | 87.17 | 94.48 | 101.71 |
| 10.08 | 51.47 | 57.76 | 64.91 | 71.58 | 78.28 | 84.85 | 91.93 | 98.70 |
| 20.12 | 44.79 | 50.43 | 56.20 | 61.90 | 67.33 | 73.04 | 78.93 | 84.26 |
| 39.96 | 38.79 | 43.20 | 48.13 | 53.00 | 57.45 | 62.25 | 66.90 | 71.71 |
| 60.01 | 35.33 | 39.53 | 44.01 | 48.41 | 52.45 | 56.71 | 61.13 | 65.12 |
| 80.01 | 33.08 | 37.01 | 41.16 | 45.22 | 49.06 | 53.10 | 57.10 | 60.68 |
| 100.0 | 31.26 | 35.10 | 38.96 | 42.60 | 46.47 | 50.22 | 53.95 | 57.43 |
Table 3
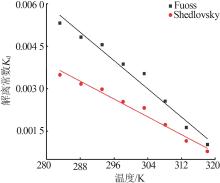
Dissociation constants of Fuoss method and Shedlovsky method"
温度/ K | Fuoss | Shedlovsky | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Λ0/(S·cm2·mol-1) | Kd | r | 104 s | Λ0/(S·cm2·mol-1) | Kd | r | 104 s | ||
| 283.15 | 87.8 | 0.005 32 | 0.985 | 4.46 | 91.9 | 0.003 49 | 0.997 | 2.33 | |
| 288.15 | 100.7 | 0.004 83 | 0.979 | 4.86 | 105.7 | 0.003 17 | 0.995 | 2.79 | |
| 293.15 | 114.0 | 0.004 56 | 0.976 | 4.81 | 120.0 | 0.002 98 | 0.994 | 2.78 | |
| 298.15 | 130.7 | 0.003 87 | 0.970 | 5.26 | 138.3 | 0.002 54 | 0.991 | 3.27 | |
| 303.15 | 146.0 | 0.003 53 | 0.965 | 5.38 | 155.0 | 0.002 32 | 0.989 | 3.47 | |
| 308.15 | 172.1 | 0.002 56 | 0.943 | 7.39 | 184.5 | 0.001 72 | 0.972 | 5.72 | |
| 313.15 | 212.8 | 0.001 63 | 0.896 | 11.10 | 230.4 | 0.001 15 | 0.931 | 10.00 | |
| 318.15 | 267.4 | 0.001 02 | 0.899 | 11.70 | 289.0 | 0.000 78 | 0.927 | 10.80 | |
Table 4
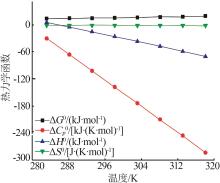
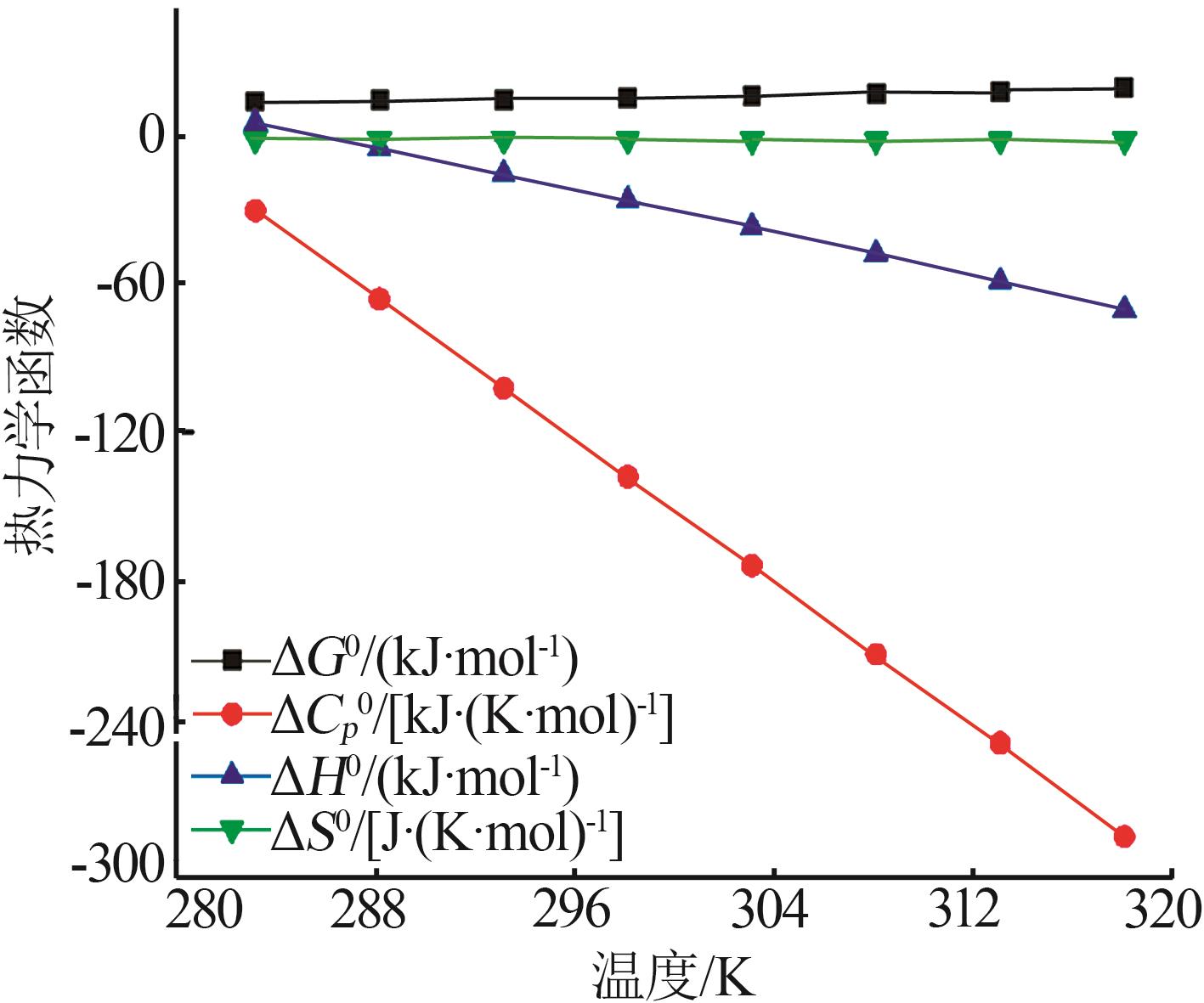
Values of [MnSO4]0 thermodynamic functions"
| 温度/K | ΔG0/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔS0/ [J·(K·mol)-1] | ΔH0/ (kJ·mol-1) | [kJ·(K·mol)-1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 | 13.43 | -30.67 | 4.74 | -2.026 |
| 288.15 | 13.68 | -66.45 | -5.47 | -2.062 |
| 293.15 | 14.10 | -102.23 | -15.87 | -2.098 |
| 298.15 | 14.70 | -138.01 | -26.45 | -2.134 |
| 303.15 | 15.48 | -173.79 | -37.21 | -2.169 |
| 308.15 | 16.44 | -209.57 | -48.14 | -2.205 |
| 313.15 | 17.57 | -245.35 | -59.26 | -2.241 |
| 318.15 | 18.89 | -283.13 | -70.55 | -2.277 |
Table 5
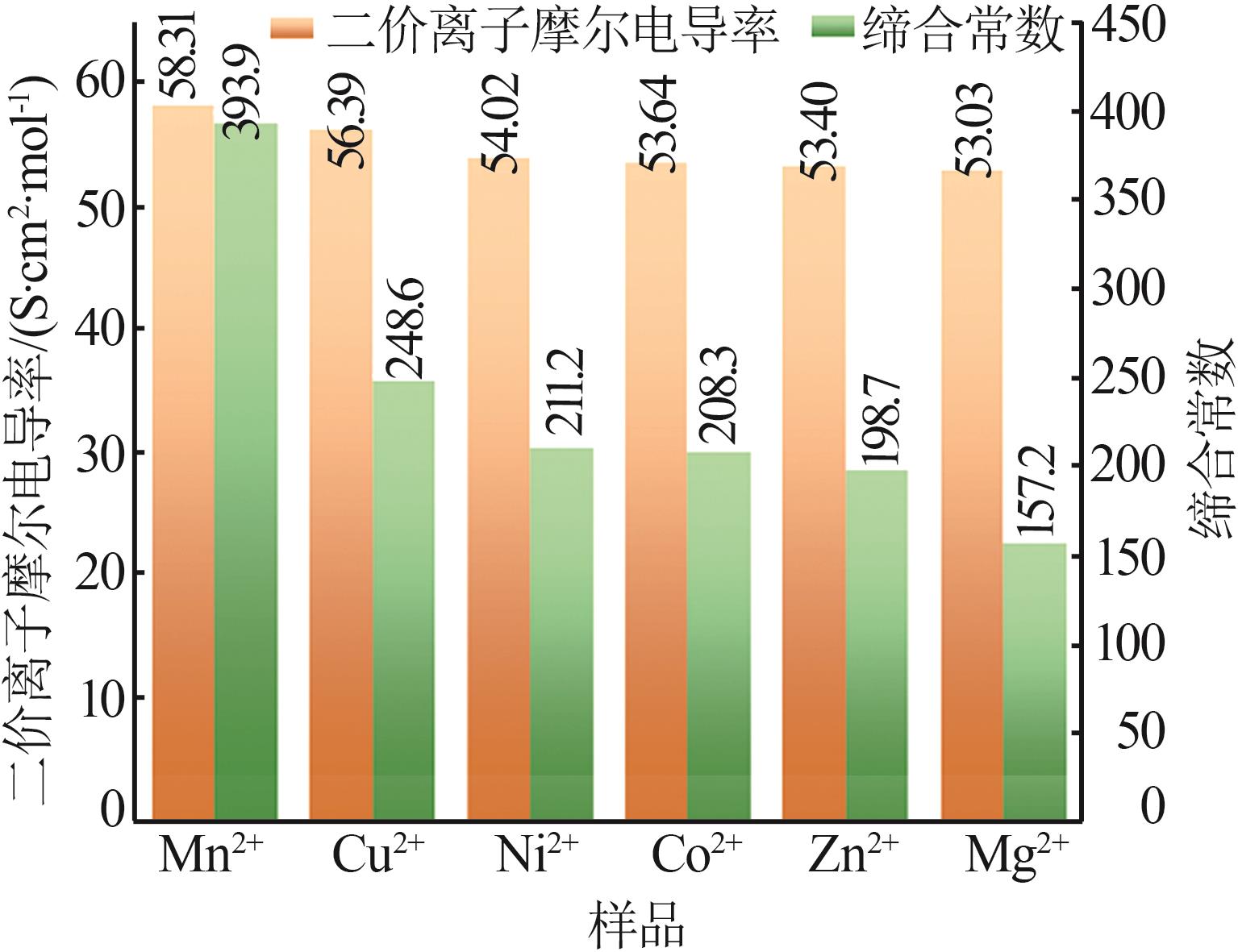
Limiting molar conductivity,ion radius,transference number and diffusion coefficient of Mn2+ and SO42-"
| 温度/K | D0 /(10-6 m2·s-1) | rst/Å | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 | 38.23 | 53.68 | 4.83 | 6.79 | 5.65 | 0.416 | 0.584 | 3.28 |
| 288.15 | 43.90 | 61.81 | 5.65 | 7.95 | 6.61 | 0.415 | 0.585 | 3.28 |
| 293.15 | 49.58 | 70.47 | 6.49 | 9.23 | 7.62 | 0.413 | 0.587 | 3.30 |
| 298.15 | 58.31 | 80.00 | 7.76 | 10.65 | 8.98 | 0.422 | 0.578 | 3.16 |
| 303.15 | 65.57 | 89.47 | 8.88 | 12.11 | 10.24 | 0.423 | 0.577 | 3.13 |
| 308.15 | 84.60 | 99.90 | 11.64 | 13.75 | 12.61 | 0.459 | 0.541 | 2.69 |
| 313.15 | 119.40 | 111.00 | 16.70 | 15.53 | 16.09 | 0.518 | 0.482 | 2.10 |
| 318.15 | 166.20 | 122.90 | 23.61 | 17.46 | 20.07 | 0.575 | 0.425 | 1.65 |
| 1 | DING Mei, FU Hu, LOU Xuechun,et al.A stable and energy-dense polysulfide/permanganate flow battery[J].ACS Nano,2023,17(16):16252-16263. |
| 2 | CHAO Dongliang, YE Chao, XIE Fangxi,et al.Atomic engineering catalyzed MnO2 electrolysis kinetics for a hybrid aqueous battery with high power and energy density[J].Advanced Materials,2020,32(25):e2001894. |
| 3 | FAN Weijia, LIU Fei, LIU Yu,et al.A high voltage aqueous zinc-manganese battery using a hybrid alkaline-mild electrolyte[J].Chemical Communications,2020,56(13):2039-2042. |
| 4 | LIU Chang, CHI Xiaowei, HAN Qi,et al.A high energy density aqueous battery achieved by dual dissolution/deposition reactions separated in acid-alkaline electrolyte[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2020,10(12):1903589. |
| 5 | ZHONG Cheng, LIU Bin, DING Jia,et al.Decoupling electrolytes towards stable and high-energy rechargeable aqueous zinc-manganese dioxide batteries[J].Nature Energy,2020,5:440-449. |
| 6 | XIE Congxin, LI Tianyu, DENG Congzhi,et al.A highly reversible neutral zinc/manganese battery for stationary energy storage[J].Energy & Environmental Science,2020,13(1):135-143. |
| 7 | 闫芳宁,郭锦春,黄雪莉,等.258.15 K下五元体系Li+,Na+,Mg2+//SO4 2-,Cl--H2O相平衡研究[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(2):61- 66. |
| YAN Fangning, GUO Jinchun, HUANG Xueli,et al.Study on phase equilibrium of quinary system of Li+,Na+,Mg2+//SO4 2-,Cl--H2O at 258.15 K[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(2):61-66. | |
| 8 | WANG Mingming, ZHENG Xinhua, ZHANG Xiang,et al.Opportunities of aqueous manganese-based batteries with deposition and stripping chemistry[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2021,11(5):2002904. |
| 9 | QIN Ye, QI Peixia, ZHAO Jinling,et al.Measurement and accurate prediction of surface tension for VOSO4-H2SO4-H2O ternary electrolyte system at high-concentration in vanadium redox flow batteries[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2022,365:120079. |
| 10 | 陈帅,杨博,陈念粗,等.三元体系NH4Cl+MgCl2+H2O 323.2 K相平衡研究[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(4):100-103. |
| CHEN Shuai, YANG Bo, CHEN Niancu,et al.Study on phase equilibria of ternary system NH4Cl+MgCl2+H2O at 323.2 K[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(4):100-103. | |
| 11 | 周宁宁,殷天翔.胆碱氨基酸离子液体水溶液在288.15~323.15 K的传输性质[J].华东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,48(1):8-18. |
| ZHOU Ningning, YIN Tianxiang.Transport properties of aqueous solution of choline-amino acid based ionic liquid at 288.15~323.15 K[J].Journal of East China University of Science and Technology,2022,48(1):8-18. | |
| 12 | LI Xiangrong, QIN Ye, XU Weiguo,et al.Thermodynamic investigation of electrolytes of the vanadium redox flow battery(V):Conductivity and ionic dissociation of vanadyl sulfate in aqueous solution in the 278.15~318.15 K temperature range[J].Journal of Solution Chemistry,2016,45(12):1879-1889. |
| 13 | 金宏静.四价/五价钒溶液的物理化学性质的研究[D].沈阳:辽宁大学,2013. |
| JIN Hongjing.Study on physical and chemical properties of tetravalent/pentavalent vanadium solution[D].Shenyang:Liaoning Uni- | |
| versity,2013. | |
| 14 | ZHANG Shudi, MA Peihua, ZHAI Yuchun,et al.Determination of vanadyl sulfate ion-pair dissociation constant at 298.15 K by Fuoss method[J].Rare Metals,2015,34(12):873-876. |
| 15 | 黄子卿.电解质溶液理论导论[M].北京:科学出版社,1983. |
| 16 | SIMONIN J P, BERNARD O, BLUM L.Real ionic solutions in the mean spherical approximation.3.Osmotic and activity coefficients for associating electrolytes in the primitive model[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,1998,102(22):4411-4417. |
| 17 | PITZER K S.Activity coefficients in electrolyte solutions[M].CRC Press,2018. |
| 18 | ARCIS H, CONRAD J K, FERGUSON J P,et al.First ionization constant of phosphoric acid and of acetic acid in H2O and D2O from T=373 K to 573 K at P=11.5 and 20 MPa by AC conductivity methods[J].Journal of Solution Chemistry,2024,53(1):91-125. |
| 19 | YANG Jiazhen, SUN Bai, SONG Pengsheng.Thermodynamics of ionic association 1:The standard association constant of the ion pair Li+B(OH)4 - [J].Thermochimica acta,2000,352:69-74. |
| 20 | 李享容.全钒液流电池正极电解液物理化学性质研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2017. |
| LI Xiangrong.Study on physical and chemical properties of cathode electrolyte for vanadium flow battery[D].Shenyang:Northeastern University,2017. | |
| 21 | HANNA K, DANIEL L, INGMAR P.Solvation and coordination chemistry of manganese(Ⅱ) in some solvents.A transfer thermodynamic,complex formation,EXAFS spectroscopic and crystallographic study[J].Polyhedron,2021,195.Doi:10.1016/j.poly.2020.114961. |
| 22 | BOCKRIS J O, REDDY A K N.Modern electrochemistry 1:Ionics[M].Boston:MAS pringer US,1998. |
| 23 | BESTER ROGAC M, BABIC V, PERGER T M,et al.Conductometric study of ion association of divalent symmetric electrolytes:I.CoSO4,NiSO4,CuSO4 and ZnSO4 in water[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2005,118(1/2/3):111-118. |
| [1] | MA Jingyuan, LI Yan, ZHOU Hanjie, LI Jiangang. Research progress of PEO based organic/inorganic composite solid electrolyte [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 1-8. |
| [2] | CHEN Xue, JIANG Guanghui, OUYANG Quansheng, SHAO Jiaojing. Recent research progress of lithium sulfur batteries under lean electrolyte based on sulfur electrode design [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 1-13. |
| [3] | CHEN Xue, OUYANG Quansheng, SHAO Jiaojing. Recent research progress of lithium-sulfur batteries based on solid-solid reaction mechanism [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 12-23. |
| [4] | ZHU Zongjiang, WANG Gang, WEI Yuanfeng, TANG Yanhong, KAKUTA Cheng, LIU Chengbin. Research progress and prospect of resourceful recycling technology of electrolyte from decommissioned lithium⁃ion battery [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 11-17. |
| [5] | LIU Jie, SHI Xueru, WEI Shubing, CAO Xinxin. Artificial interface layer construction and sodium storage performance of P2-type layered oxide cathode [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 39-44. |
| [6] | LI Yaguang, HAN Dongzhan, QI Lijuan. Recent research on pretreatment of waste lithium-ion batteries and electrolyte recovery technology [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 1-10. |
| [7] | DONG Mingzhe, LI Kexin, YE Xiushen, MA Zhen, LI Shengting, LI Quan, WU Zhijian. Study on electrochemical properties of magnesium chloride molten salt hydrates [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 51-56. |
| [8] | WANG Chen, HE Wei, SUN Mengyuan. Research on preparation of nano-bismuth oxide-enhanced chloride/magnesium oxide composites and their thermophysical properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 120-126. |
| [9] | WAN Feng, YAN Yingchun, FAN Zhuangjun. Research progress and prospect of halide solid electrolytes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 15-29. |
| [10] | XU Xijun, LIN Jianfeng, LUO Xiongwei, ZHAO Jingwei, HUO Yanping. Recent progress of NASICON-type Na1+x Zr2Si x P3-x O12 solid electrolyte for sodium metal batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 1-14. |
| [11] | CHEN Qi, LIAO Dankui, ZHANG Qingnian, YAN Jinsheng, HUANG Yu, CHEN Xiaopeng, TONG Zhangfa. Fast and efficient determination of quicklime activity by conductivity method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 114-120. |
| [12] | KANG Le, JING Maoxiang, LI Donghong, HU Xinyu, JIA Chunyan. Study on preparation and electrochemical performance of lithium aluminate nanorods modified solid electrolyte [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(8): 65-70. |
| [13] | WANG Song, WANG Jiawei, GOU Bibo, YANG Pan, HE Yue, YANG Chunyuan, WANG Haifeng. Study on distribution law of magnesium in leaching solution of rhodochrosite by complex salt crystallization method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 65-71. |
| [14] | GUO Jianye, WANG Dong, SU Lijun, LI Wenjing. Effect of aerogel doping on thermal insulation performance of glass fiber felt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 53-57. |
| [15] | ZHOU Min. Preparation of PANI/TIO composites and their application in polyurethane coatings [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 112-117. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||