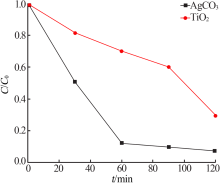
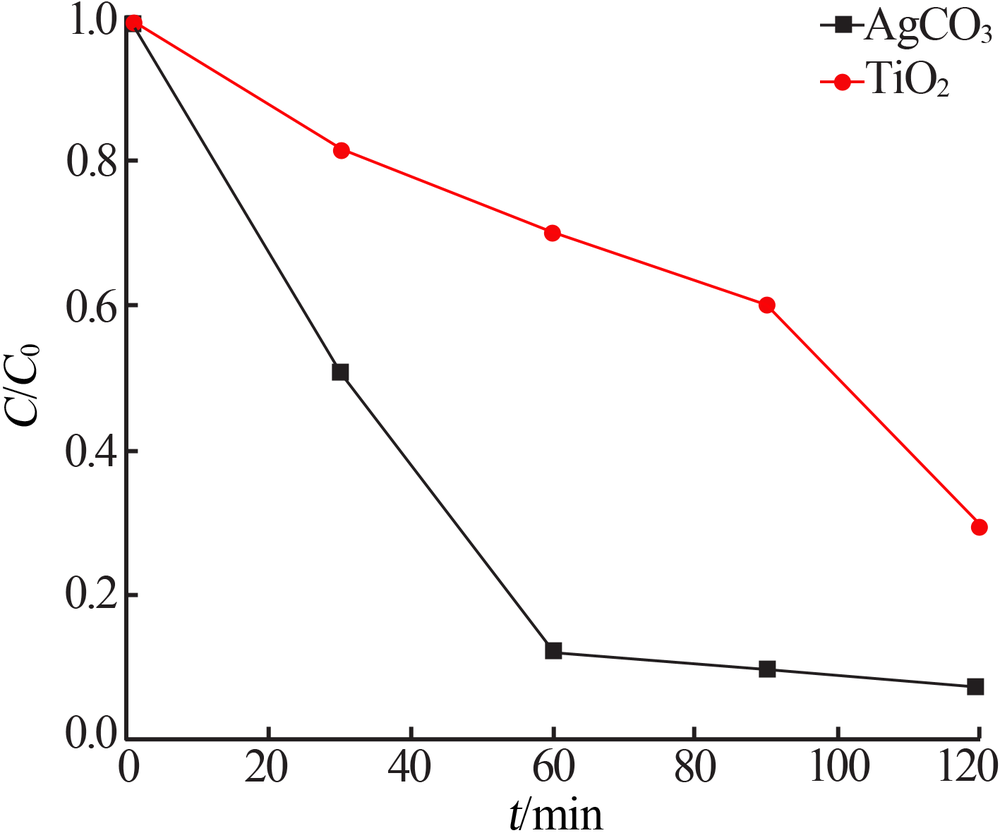
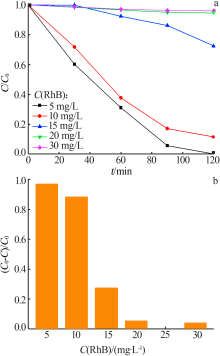
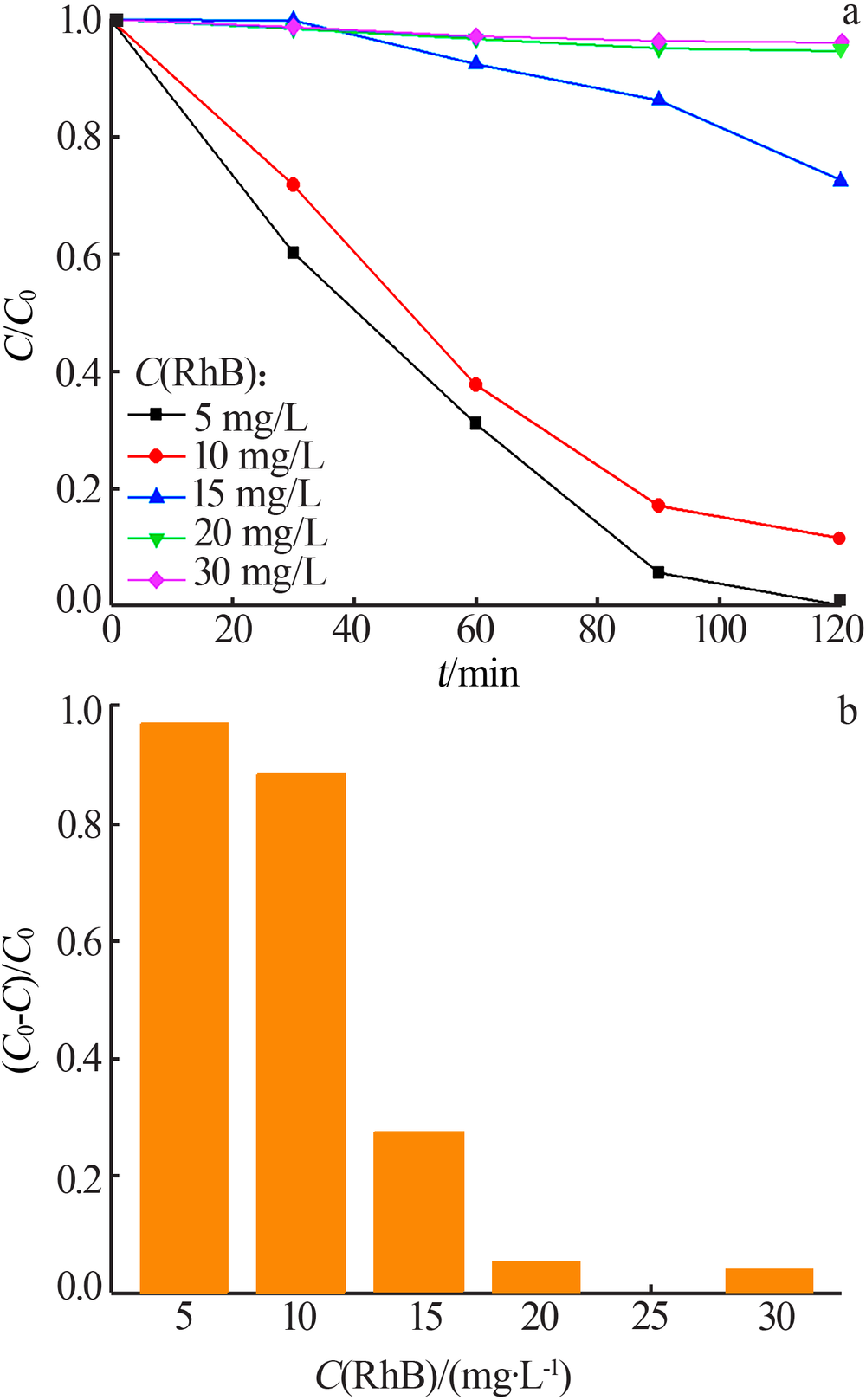
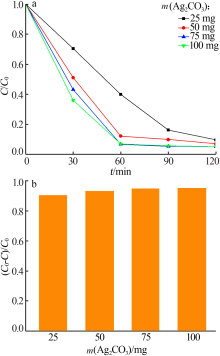
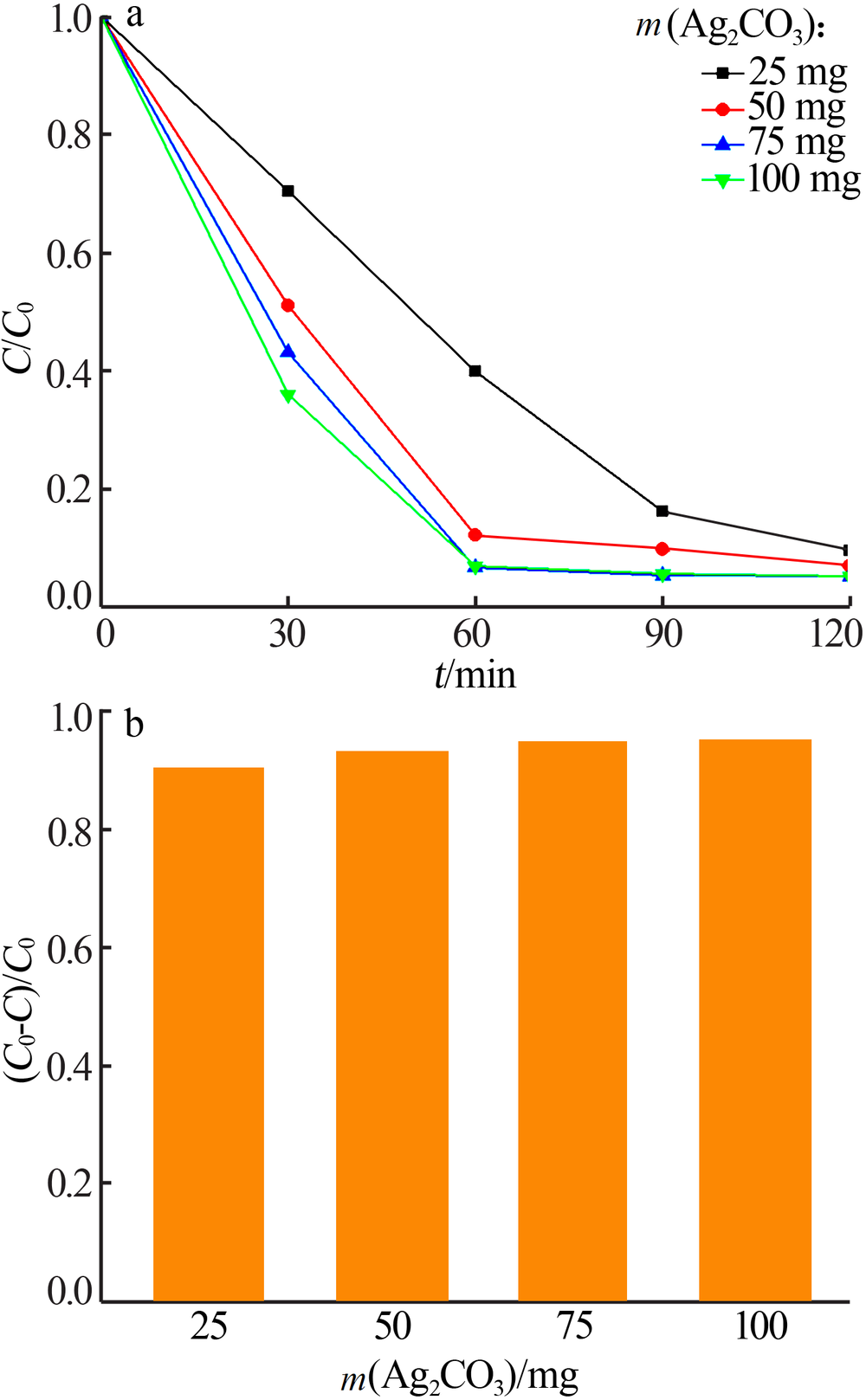
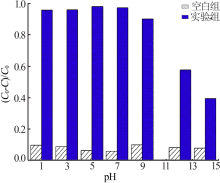
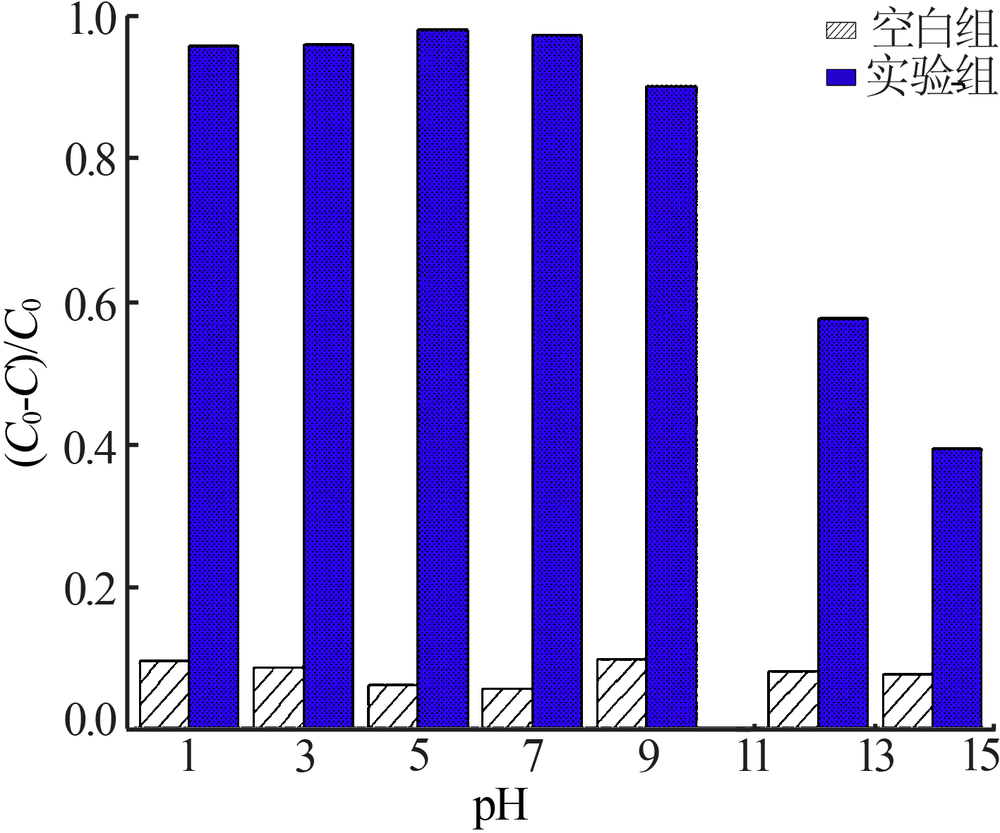
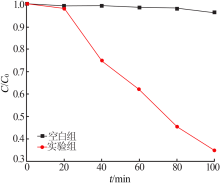
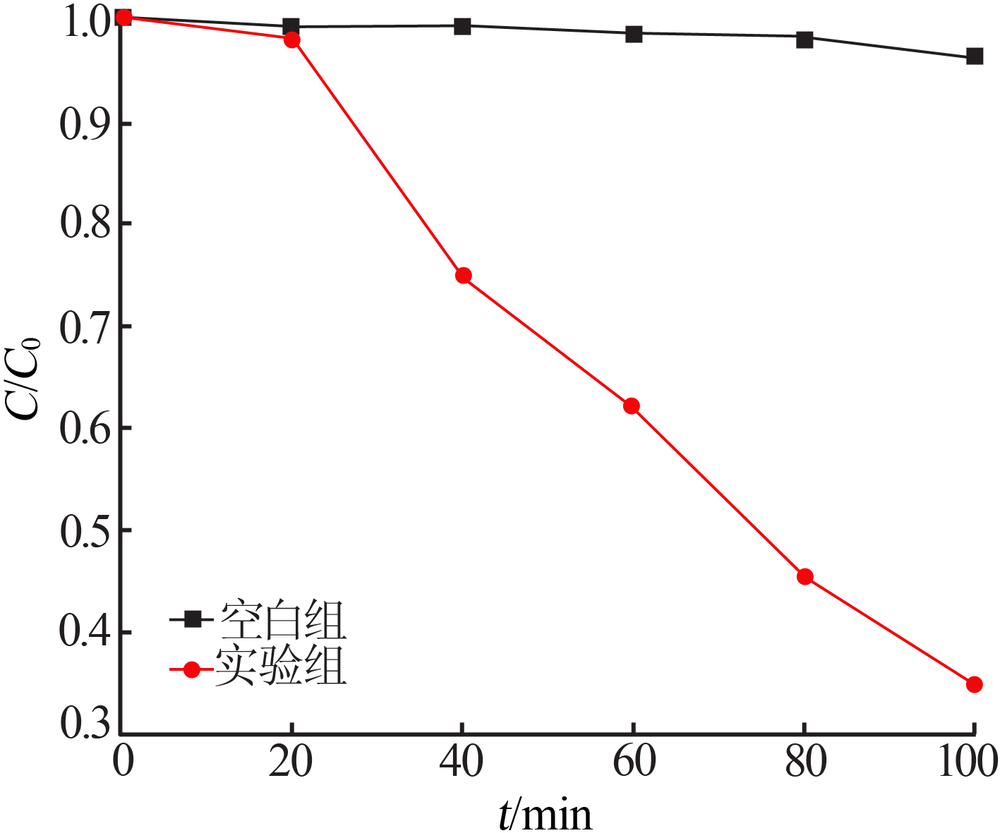
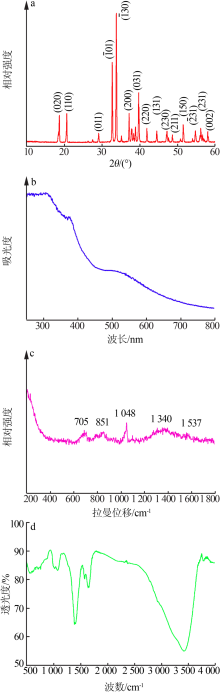
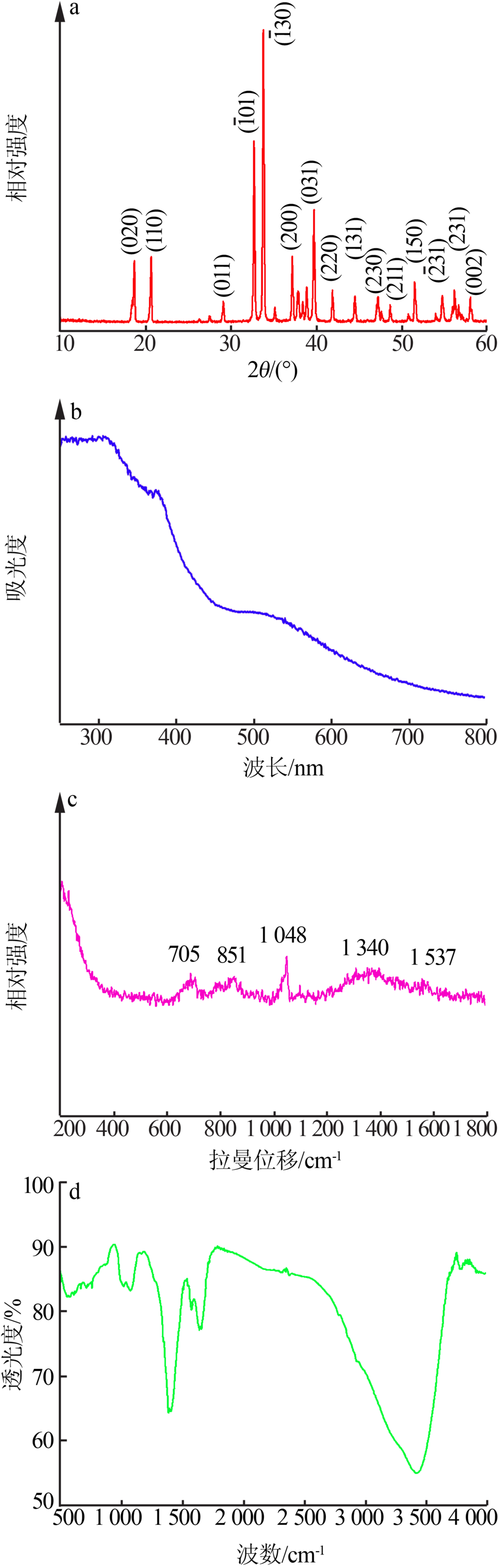
| [1] |
李金环 . 掺杂TiO2光催化剂的制备、表征及降解含聚污水研究[D]. 大庆:大庆石油学院, 2008.
|
| [2] |
曹玉辉 . 具有{101}与{001}晶面异质结TiO2纳米晶的制备及其光催化还原CO2性能研究[D]. 开封:河南大学, 2016.
|
| [3] |
Dai G, Yu J, Liu G . A new approach for photocorrosion inhibition ofAg2CO3 photocatalyst with highly visible-light-responsive reactivi-ty[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012,116(29):15519-15524.
|
| [4] |
Kubacka A, Fernandez-Garcia M, Colon G . Advanced nanoarchitec-tures for solar photocatalytic applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2011,112(3):1555-1614.
|
| [5] |
Tong H, Ouyang S, Bi Y , et al. Nano-photocatalytic materials:possi-bilities and challenges[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012,24(2):229-251.
|
| [6] |
Yi Z, Ye J, Kikugawa N , et al. An orthophosphate semiconductorwith photooxidation properties under visible-light irradiation[J]. Nature Materials, 2010,9(7):559-564.
|
| [7] |
Li J, Wei L, Yu C , et al. Preparation and characterization of grapheneoxide/Ag2CO3 photocatalyst and its visible light photocatalytic acti-vity[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015,358:168-174.
|
| [8] |
王瑜琦 . 碳酸银基半导体复合材料的制备及其光催化性能研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2016.
|
| [9] |
Varma R, Yadav M, Tiwari K , et al. Roles of vanadium and nitrogenin photocatalytic activity of VN-codoped TiO2 photocatalyst[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2018,94(5):955-964.
|
| [10] |
王震 . 新型可见光催化剂的制备及其性能研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2014.
|
| [11] |
邱毅伟 . 基于Ag3PO4纳米复合材料的设计、制备和光催化性能研究[D]. 杭州:浙江理工大学, 2016.
|
| [12] |
闫世成, 罗文俊, 李朝升 , 等. 新型光催化材料探索和研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010,29(1):1-9,53.
|
| [13] |
Ng Y H, Iwase A, Kudo A , et al. Reducing graphene oxide on a visi-ble-light BiVO4 photocatalyst for an enhanced photoelectrochemi-cal water splitting[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010,1(17):2607-2612.
|
| [14] |
Wu L, Bi J, Li Z , et al. Rapid preparation of Bi2WO6 photocatalystwith nanosheet morphology via microwave-assisted solvothermal synjournal[J]. Catalysis Today, 2008,131(1/2/3/4):15-20.
|
| [15] |
Wen J, Xie J, Chen X , et al. A review on g-C3N4-based photocata-lysts[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017,391:72-123.
|
| [16] |
Li Q, Li X, Wageh S , et al. CdS/graphene nanocomposite photocat-alysts[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015,5(14):1500010.
|
| [17] |
Ha E, Lee L Y S, Wang J , et al. Significant enhancement in photo-catalytic reduction of water to hydrogen by Au/Cu2ZnSnS4 nanos-tructure[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014,26(21):3496-3500.
|
| [18] |
林婵 . TiO2纳米材料的制备、改性及其光催化性能研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2014.
|
| [19] |
Wen X J, Niu C G, Guo H , et al. Photocatalytic degradation of levo-floxacin by ternary Ag2CO3/CeO2/AgBr photocatalyst under visible-light irradiation:Degradation pathways,mineralization ability,and an accelerated interfacial charge transfer process study[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2018,358:211-223.
|
| [20] |
Hu W, Zhao L, Zhang Y , et al. Preparation and photocatalytic acti-vity of graphene-modified Ag2S composite[J]. Journal of Experi-mental Nanoscience, 2016,11(6):433-444.
|
| [21] |
Frontistis Z, Antonopoulou M, Petala A , et al. Photodegradation ofethyl paraben using simulated solar radiation and Ag3PO4 photo-catalyst[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017,323:478-488.
|
| [22] |
Zhu T, Song Y, Ji H , et al. Synjournal of g-C3N4/Ag3VO4 compositeswith enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015,271:96-105.
|
| [23] |
周丽, 邓慧萍, 张为 . 可见光响应的银系光催化材料[J]. 化学进展, 2015,27(4):349-360.
|
| [24] |
任南琪, 周显娇, 郭婉茜 , 等. 染料废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2013,64(1):84-94.
|
| [25] |
Xu C, Liu Y, Huang B , et al. Preparation,characterization,and pho-tocatalytic properties of silver carbonate[J]. Applied Surface Sci-ence, 2011,257(20):8732-8736.
|
| [26] |
张嘉慧 . β-Ag2CO3纳米粒子的制备及催化端炔氢叠氮化反应研究[D]. 长春:东北师范大学, 2018.
|
| [27] |
魏龙福, 余长林, 陈建钗 , 等. 水热法合成Ag2CO3/ZnO异质结复合光催化剂及其光催化性能[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2014,5(1):47-53.
|
| [28] |
Dong H, Chen G, Sun J , et al. A novel high-efficiency visible-lightsensitive Ag2CO3 photocatalyst with universal photodegradationperformances:simple synjournal,reaction mechanism and first-pr-inciples study[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013,134:46-54.
|
| [29] |
余忠雄, 向垒, 钟方龙 , 等. pH对低温燃烧法合成钨酸铋光催化降解罗丹明B的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015,30(5):535-541.
|
| [30] |
郝辰春, 贾莹, 王文忠 . Ag2CO3/Ag2O异质p-n结光催化剂的制备及其可见光光催化性能[J]. 中央民族大学学报:自然科学版, 2015,24(2):76-81.
|
| [31] |
Song Y, Zhu J, Xu H , et al. Synjournal,characterization and visible-light photocatalytic performance of Ag2CO3 modified by graphene-oxide[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014,592:258-265.
|
| [32] |
Yu C, Wei L, Zhou W , et al. A visible-light-driven core-shell likeAg2S@Ag2CO3 composite photocatalyst with high performance inpollutants degradation[J]. Chemosphere, 2016,157:250-261.
|