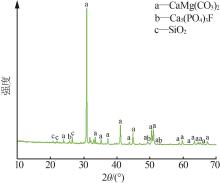
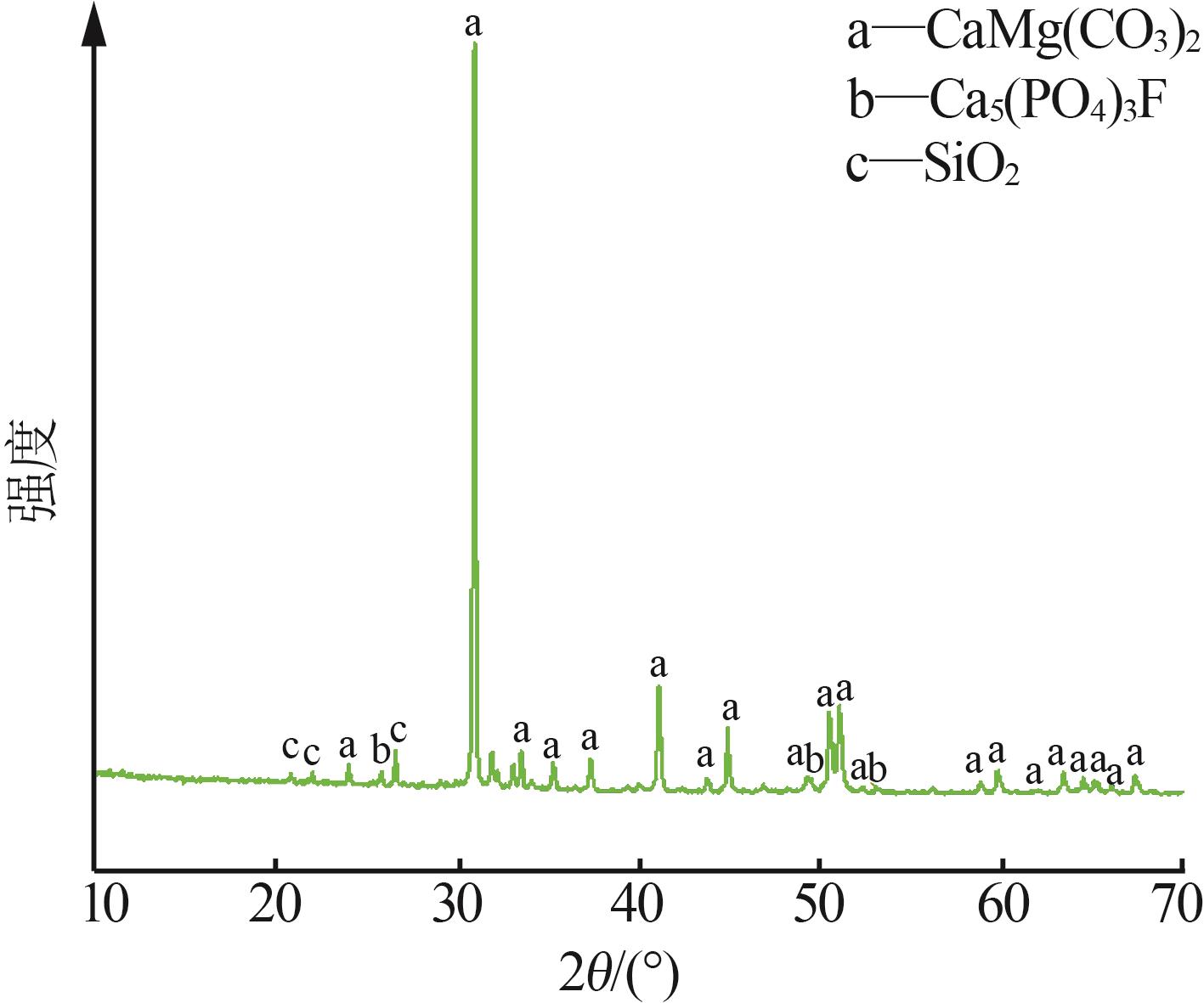
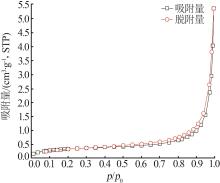
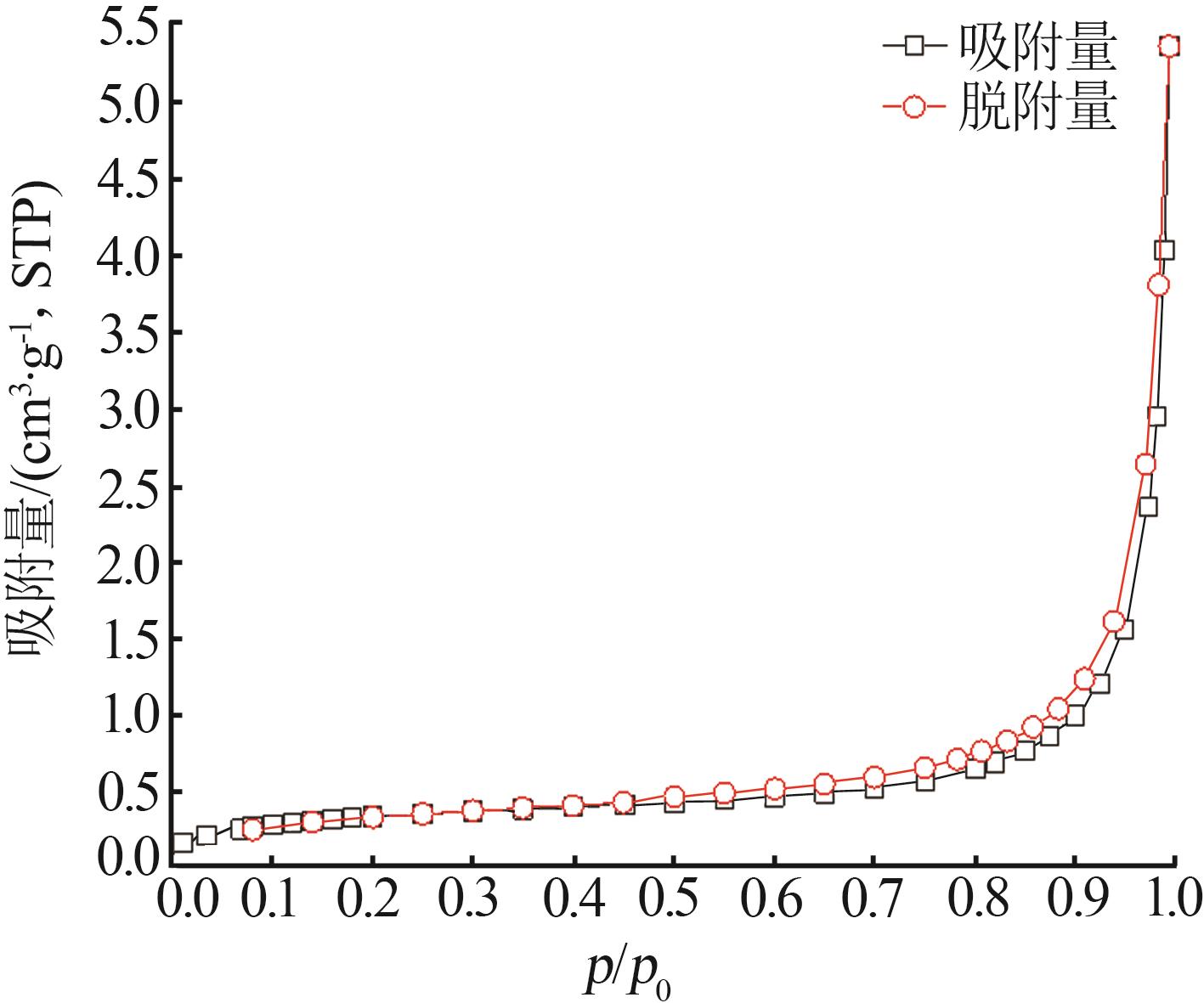
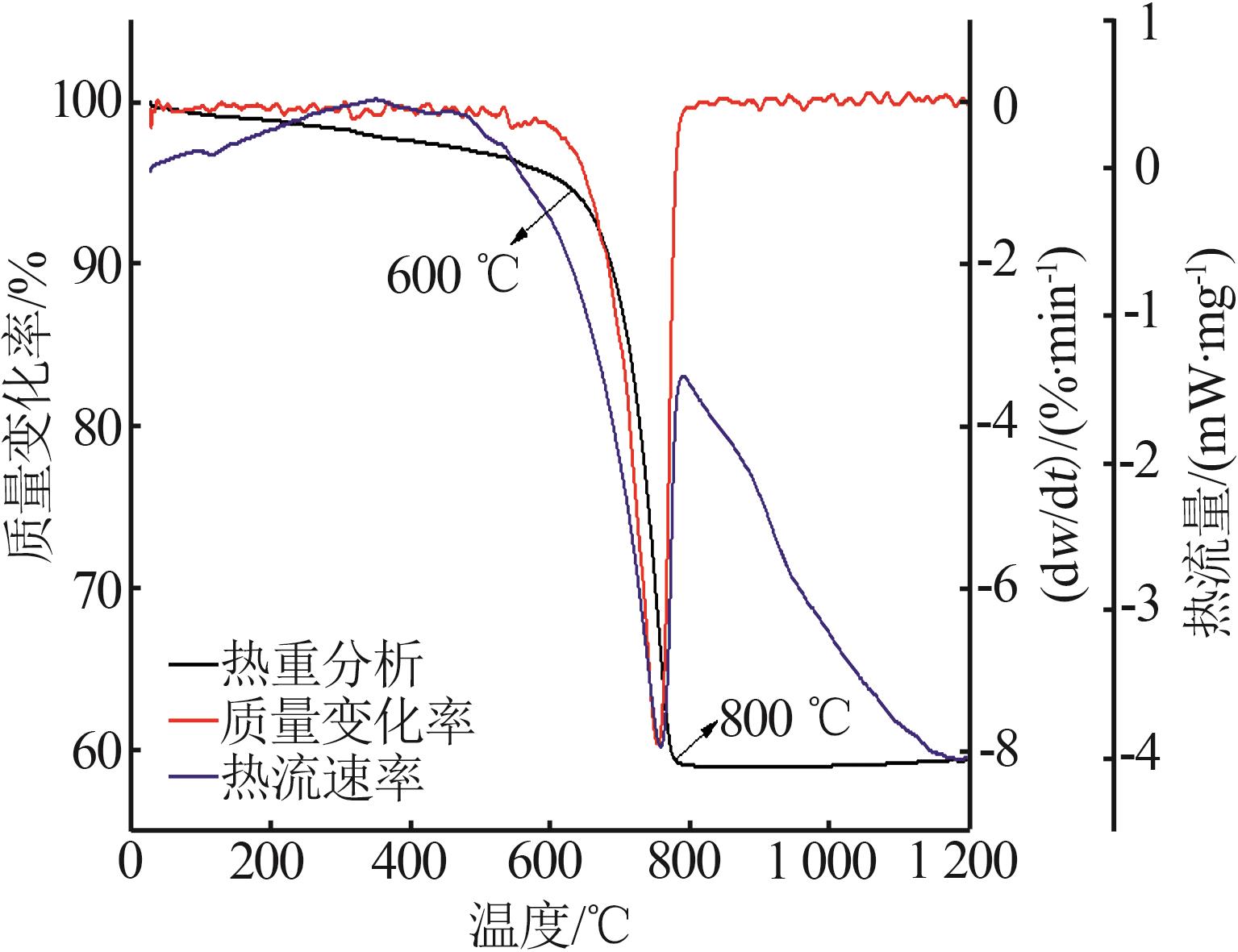
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 94-100.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0202
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on treatment of ammonia nitrogen wastewater by roasted phosphorus tailings
SHI Yunpeng( ), GUO Ze, ZHANG Hanquan, LU Manman(
), GUO Ze, ZHANG Hanquan, LU Manman( )
)
- School of Resources & Safety Engineering,Wuhan Institute of Technology,Wuhan 430073,China
-
Received:2024-04-09Online:2025-03-10Published:2024-06-05 -
Contact:LU Manman E-mail:510695451@qq.com;lummwit@wit.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHI Yunpeng, GUO Ze, ZHANG Hanquan, LU Manman. Study on treatment of ammonia nitrogen wastewater by roasted phosphorus tailings[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 94-100.
share this article
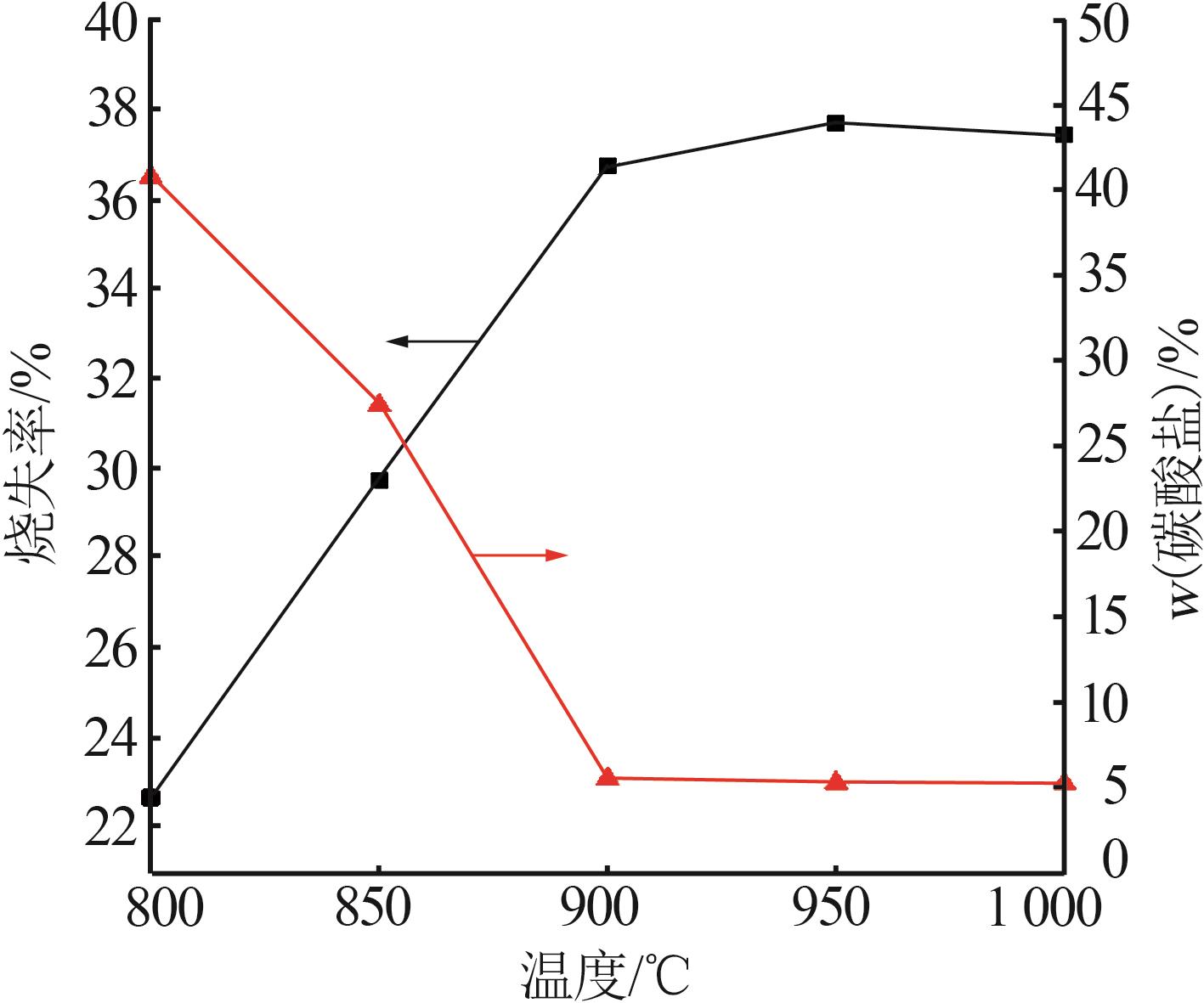
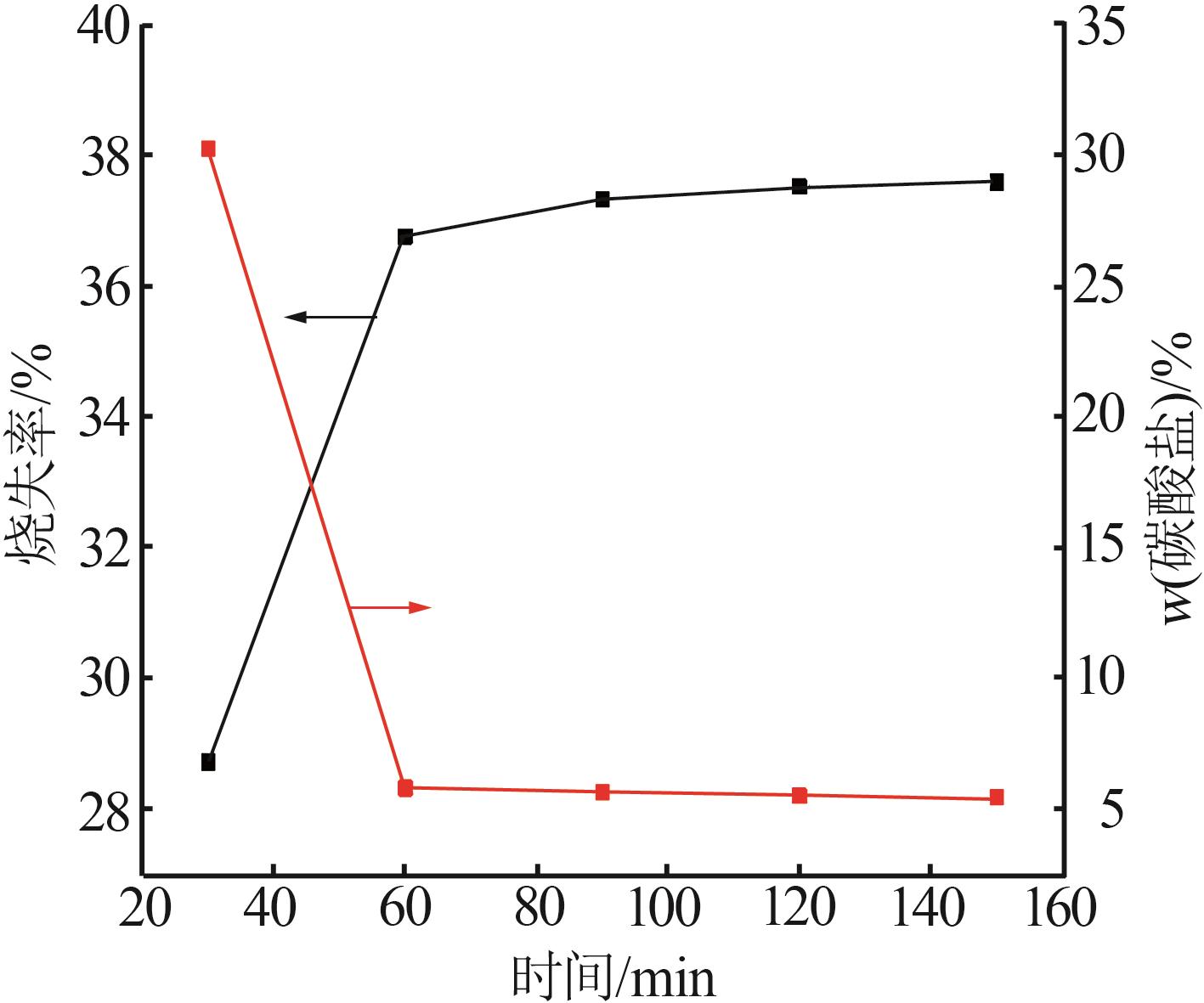
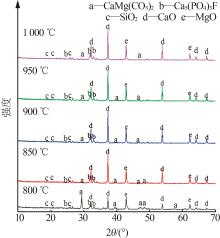
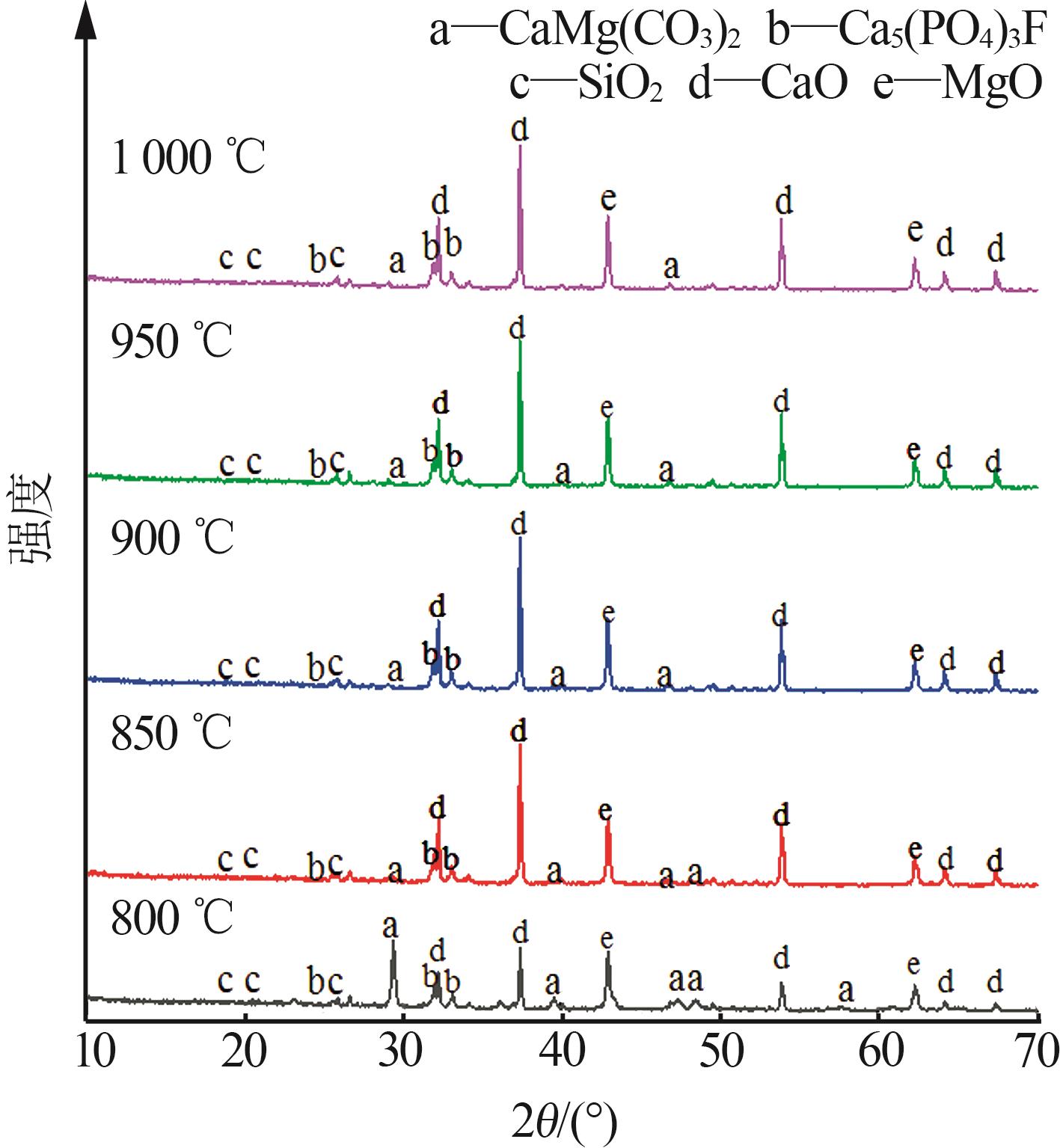
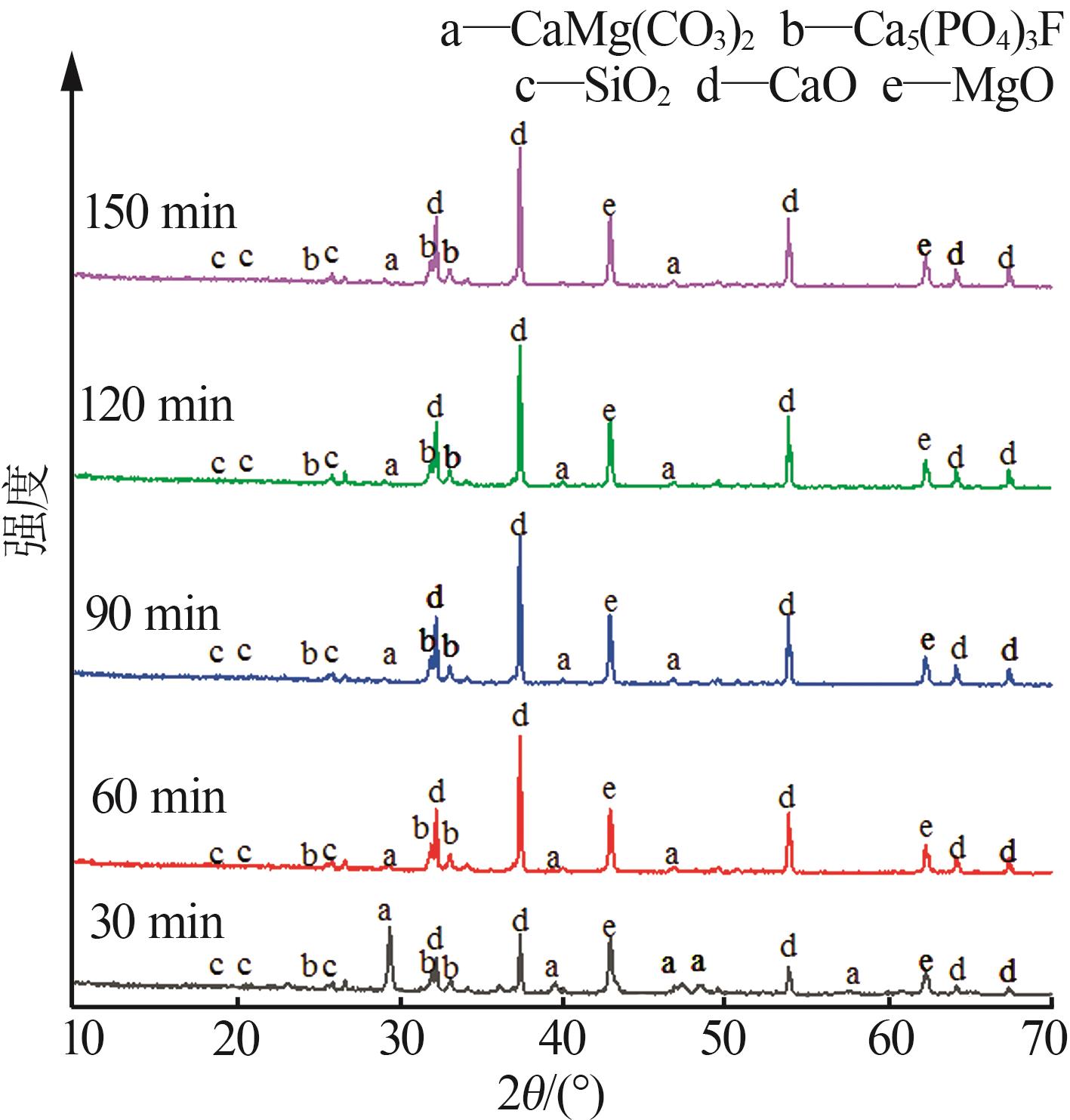
Table 4
Chemical analysis of decomposition products of phosphorus tailings at different roasting temperatures"
| 温度/℃ | w(CaO)/% | w(MgO)/% | w(SiO2)/% | w(P2O5)/% | w(SO3)/% | w(Fe2O3)/% | w(Al2O3)/% | w(F)/% | w(K2O)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | 55.71 | 24.41 | 6.16 | 5.10 | 3.04 | 1.92 | 1.30 | 0.81 | 0.68 |
| 850 | 54.58 | 26.99 | 5.55 | 4.85 | 2.87 | 1.80 | 1.13 | 0.84 | 0.63 |
| 900 | 53.00 | 29.39 | 5.29 | 4.70 | 2.82 | 1.66 | 1.08 | 0.77 | 0.57 |
| 950 | 53.43 | 29.62 | 5.19 | 4.57 | 2.65 | 1.61 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 0.53 |
| 1 000 | 52.86 | 30.25 | 5.07 | 4.74 | 2.63 | 1.64 | 0.98 | 0.72 | 0.47 |
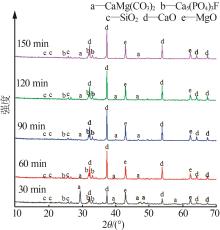
Table 5
Chemical analysis of decomposition products of phosphorus tailings under different roasting time"
| 时间/min | w(CaO)/% | w(MgO)/% | w(SiO2)/% | w(P2O5)/% | w(SO3)/% | w(Fe2O3)/% | w(Al2O3)/% | w(F)/% | w(K2O)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 54.70 | 27.09 | 5.61 | 4.92 | 2.68 | 1.81 | 1.14 | 0.66 | 0.63 |
| 60 | 53.00 | 29.39 | 5.29 | 4.70 | 2.82 | 1.66 | 1.08 | 0.77 | 0.57 |
| 90 | 53.03 | 30.05 | 5.09 | 4.56 | 2.71 | 1.62 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 0.55 |
| 120 | 52.54 | 30.53 | 4.98 | 4.63 | 2.76 | 1.61 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.56 |
| 150 | 52.66 | 30.43 | 5.04 | 4.60 | 2.74 | 1.62 | 0.99 | 0.72 | 0.52 |
| 1 | 张守逊,吴雨瑶,郭永杰,等.磷尾矿综合利用研究现状[J].化工矿物与加工,2024,53(7):27-36. |
| ZHANG Shouxun, WU Yuyao, GUO Yongjie,et al.Research status on comprehensive utilization of phosphorus tailings[J].Industrial Minerals Processing,2024,53(7):27-36. | |
| 2 | 王保明,王兴龙,杨英,等.磷尾矿综合利用现状及研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2024,56(10):1-11. |
| WANG Baoming, WANG Xinglong, YANG Ying,et al.Current status and research progress of comprehensive utilization of phosphorus tailings[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2024,56(10):1-11. | |
| 3 | 杨俊杰,董永刚,张静,等.磷尾矿中物质元素的赋存状态与分布[J].无机盐工业, 2023,55(12):111-118. |
| YANG Junjie, DONG Yonggang, ZHANG Jing,et al.Occurrence and distribution of matter elements in phosphorus tailings[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(12):111-118. | |
| 4 | 林升鉴,饶峰,郑艳金,等.磷尾矿、磷石膏和黄磷渣的地质聚合反应资源化利用研究进展[J].矿产保护与利用,2021,41(4):150-156. |
| LIN Shengjian, RAO Feng, ZHENG Yanjin,et al.Research progress on resource utilization of phosphorus tailings,phosphogypsum and yellow phosphorous slag by geological polymerization[J].Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources,2021,41(4):150-156. | |
| 5 | 张豪.高镁磷尾矿煅烧与应用的研究[D].武汉:武汉工程大学,2022. |
| ZHANG Hao.Study on calcination and application of high magnesium phosphorus tailings[D].Wuhan:Wuhan Institute of Technology,2022. | |
| 6 | 成倩兰,张豪,刘雁,等.焙烧磷尾矿处理含磷废水的研究[J].武汉工程大学学报,2021,43(5):496-499. |
| CHENG Qianlan, ZHANG Hao, LIU Yan,et al.Treatment of phosphorus-containing wastewater by roasted phosphorus tailings[J].Journal of Wuhan Institute of Technology,2021,43(5):496-499. | |
| 7 | 姜立龙,李剑秋,杨林,等.高镁磷尾矿作为矿物掺合料应用于混凝土性能研究[J].无机盐工业,2024,56(1):90-95. |
| JIANG Lilong, LI Jianqiu, YANG Lin,et al.Study on performance of concrete with high-Mg phosphate tailing as mineral admixtu-re[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2024,56(1):90-95. | |
| 8 | 刘族东.磷尾矿路面基层材料应用研究[D].武汉:武汉理工大学,2022. |
| LIU Zudong.Study on application of phosphorus tailings pavement base material[D].Wuhan:Wuhan University of Technology,2022. | |
| 9 | 韦昌桃,王智娟,赵彤.云、贵、川高镁磷尾矿矿石特性对比研究[J].磷肥与复肥,2023,38(7):36-38. |
| WEI Changtao, WANG Zhijuan, ZHAO Tong.Comparative study on characteristics of high Mg-containing phosphate tailings in Yunnan,Guizhou and Sichuan[J].Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer,2023,38(7):36-38. | |
| 10 | 张家鑫,潘益,夏琰,等.磷尾矿制备氢氧化镁阻燃剂的试验研究[J].非金属矿,2020,43(3):64-68. |
| ZHANG Jiaxin, PAN Yi, XIA Yan,et al.Preparation of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant from phosphorus tailings[J].Non-Metallic Mines,2020,43(3):64-68. | |
| 11 | 周佳琦,陈葵,武斌,等.磷尾矿煅烧及酸浸过程动力学研究[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(1):77-82,108. |
| ZHOU Jiaqi, CHEN Kui, WU Bin,et al.Study on kinetics of phosphate tailings calcination and acid leaching process[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(1):77-82,108. | |
| 12 | 秦智峰,王达道,徐志峰,等.磷酸铵镁沉淀-絮凝法处理高浓度氨氮废水[J].化工环保,2021,41(5):595-600. |
| QIN Zhifeng, WANG Dadao, XU Zhifeng,et al.Treatment of high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater by magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation-flocculation[J].Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry,2021,41(5):595-600. | |
| 13 | 卜培彦,张瑞娜,李溪清,等.去除废水中氨氮的吸附材料研究进展[J].应用化工,2023,52(12):3423-3427. |
| BU Peiyan, ZHANG Ruina, LI Xiqing,et al.Research progress of adsorption materials for removing ammonia nitrogen from wastewater[J].Applied Chemical Industry,2023,52(12):3423-3427. | |
| 14 | 蒋晓英,冀云,赵远,等.超声吹脱—吸附工艺处理高浓度氨氮废水[J].化工环保,2020,40(2):142-147. |
| JIANG Xiaoying, JI Yun, ZHAO Yuan,et al.Treatment of high concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater by ultrasonic stripping and adsorption process[J].Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry,2020,40(2):142-147. | |
| 15 | 王芳,徐楠.磷酸铵镁法处理高浓度氨氮废水的应用研究[J].苏州科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,36(3):46-49. |
| WANG Fang, XU Nan.Application of magnesium ammonium phosphate to ammonium removal from wastewater[J].Journal of Suzhou University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition),2019,36(3):46-49. | |
| 16 | 郭涛,卫琦,涂阳辉,等.磷酸铵镁沉淀法处理含高浓度氨氮制药废水的试验[J].南昌大学学报(理科版),2023,47(1):64-68. |
| GUO Tao, WEI Qi, TU Yanghui,et al.Experiment on the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing high ammonia nitrogen by MAP precipitation[J].Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science),2023,47(1):64-68. | |
| 17 | 崔玉格,张豪,郭今锴,等.不同白云石掺量的高镁磷尾矿热处理动力学研究[J].化工矿物与加工,2023,52(6):65-70. |
| CUI Yuge, ZHANG Hao, GUO Jinkai,et al.Study on kinetics of heat treatment on high-magnesium phosphate tailings with different dolomite content[J].Industrial Minerals & Processing,2023,52(6):65-70. | |
| 18 | 周强,武斌,陈葵,等.磷尾矿热分解动力学机理与煅烧工艺研究[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(3):47-54. |
| ZHOU Qiang, WU Bin, CHEN Kui,et al.Study on thermal decomposition kinetic mechanism and calcination process of phosphorus tailings[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(3):47-54. | |
| 19 | 宋智佳,王岁岁,匡勤.空心二氧化钛掺杂铜提升光催化二氧化碳还原性能[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(8):45-50. |
| SONG Zhijia, WANG Suisui, KUANG Qin.Hollow Cu-doped TiO2 for enhancing photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(8):45-50. | |
| 20 | 黄平丹,曹钰嵘.基于化学沉淀法的稀土氨氮废水处理研究[J].山西化工,2023,43(3):189-191,204. |
| HUANG Pingdan, CAO Yurong.Study on the treatment of rare earth ammonia nitrogen wastewater based on chemical precipitation method[J].Shanxi Chemical Industry,2023,43(3):189-191,204. |
| [1] | MAO Shize. Study on microwave roasting-activated coal gangue to improve sulfate corrosion resistance of concrete [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(3): 86-93. |
| [2] | ZENG Yijun, JIANG Ziwen, JIAN Chengzong, QUAN Xuejun. Study on deep extraction of chromium from calcium-free roasting slag of chromite ore [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 90-96. |
| [3] | TANG Dongwu, YE Changwen, DENG Jie, AO Fang. Study on leaching rate of calcium and magnesium from phosphorus tailings based on thermodynamic analysis and response surface method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 98-106. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yaqi, CHEN Xiping, SUN Ningning. Study on preparation process of cryolite from anode carbon slag by catalytic decarburization [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(3): 91-97. |
| [5] | YUAN Xing, DONG Wenyan, WANG Mingshun, CHENG Dilan, AO Xianquan. Effect of metallic ions on dispersion behavior of dolomite mineral particles [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 44-50. |
| [6] | WANG Baoming, WANG Xinglong, YANG Ying, ZHAO Bo, HUA Quanxian, LIU Yong, LIU Pengfei, SHEN Bo, DING Junxiang, TANG Jianwei. Current status and research progress of comprehensive utilization of phosphorus tailings [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(10): 1-11. |
| [7] | QU Xiaoyuan, ZHENG Qiang, FAN Yuanyang, LIU Haili, DENG Xiaoyang, LI Xue. Study on preparation of large cube calcium carbonate by secondary carbonization of dolomite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(7): 58-64. |
| [8] | WANG Benlei, ZHANG Guisheng, JIANG Lingyun, LI Chen, WANG Pengfei, LI Jixia, ZANG Jiazhong. Study on preparation process of rhodium trichloride by roasting recovery technology from waste rhodium solution of carbonyl synthesis [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 104-108. |
| [9] | CHEN Yujue, ZHANG Liangjun, KUANG Huan, JIANG Manwen, XIAO Li. Study on roasting and recovery process of waste lithium iron phosphate powder with sodium bisulfate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 113-117. |
| [10] | YANG Junjie, DONG Yonggang, ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Yu, CAO Jianxin. Occurrence and distribution of matter elements in phosphorus tailings [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(12): 111-118. |
| [11] | GUO Ze, ZHANG Pengfei, YANG Fan, ZHANG Hanquan, LU Manman. Preparation of β-hemihydrate gypsum by phosphogypsum roasting [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 106-113. |
| [12] | DING Yong,FENG Xiaorui,LU Xiangjie,GAO Xiaoqin,FENG Yan,HE Yan. Study on preparation of high purity micron nickel oxide powder by roasting carbonyl nickel powder [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 119-122. |
| [13] | ZENG Yanjie,XU Tongfei,HUANG Ziliang,CHEN Zhipeng,LIU Xudong,YI Meigui. Study on removal of calcium impurities from magnesium waste residue by roasting-hydration complexing [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(11): 118-123. |
| [14] | FAN Tianbo,HU Tingting,HAN Dongxue,JIA Xiaohui,ZHAO Yibo,WANG Xin′an,GUO Hongfan,LI Li,LIU Yunyi. Preparation of micro-nano round flake magnesium hydroxide from calcined dolomite powder [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(1): 29-33. |
| [15] | LI Zheng,HU Meng,DOU Yan,CUI Peng,SHEN Hao,ZHENG Zhiyin,LIU Rong. Effect of sodium oxalate on stability of calcium sulfate hemihydrate crystal [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(1): 62-65. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||