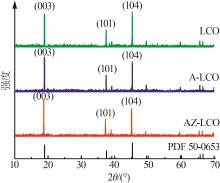
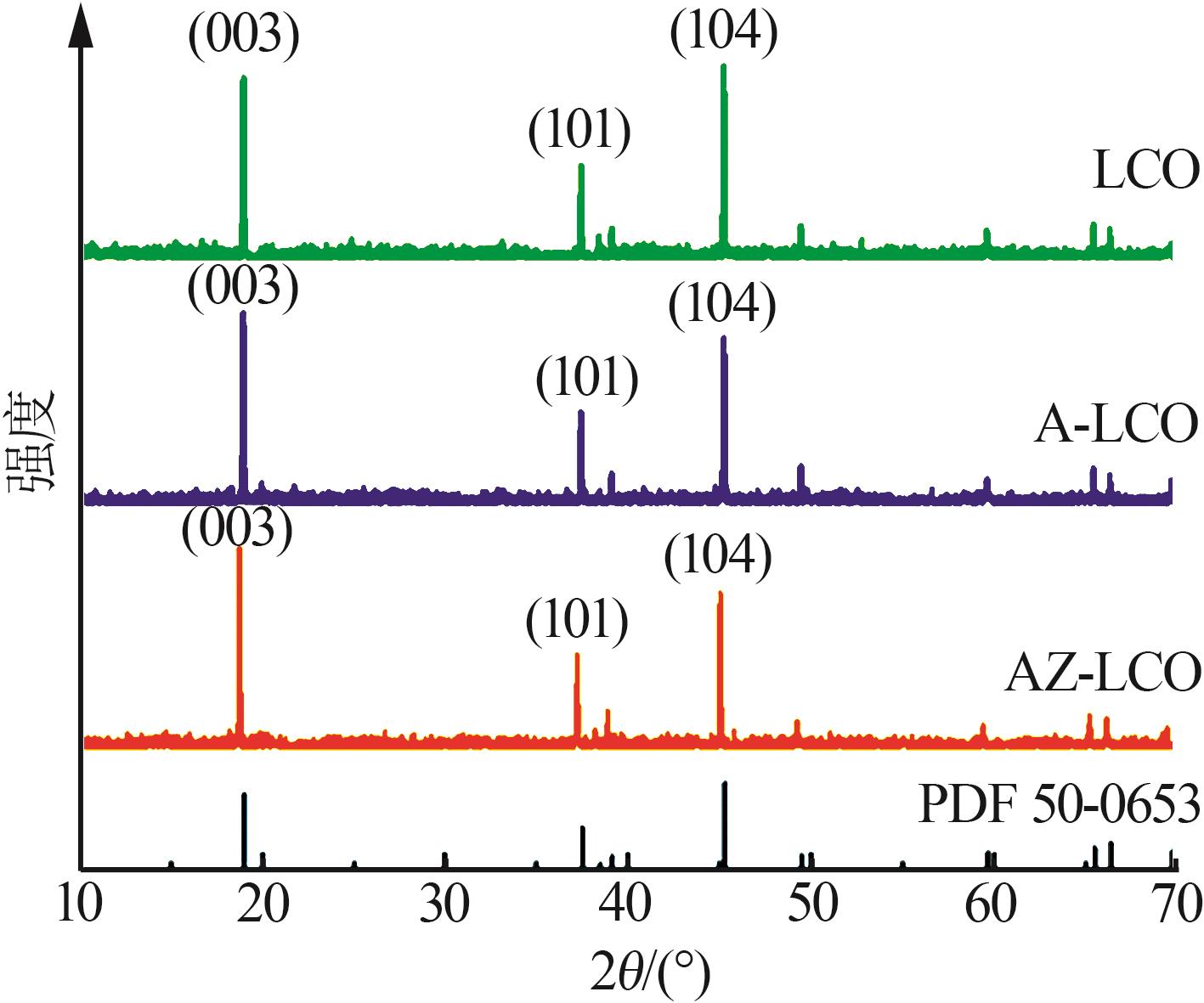
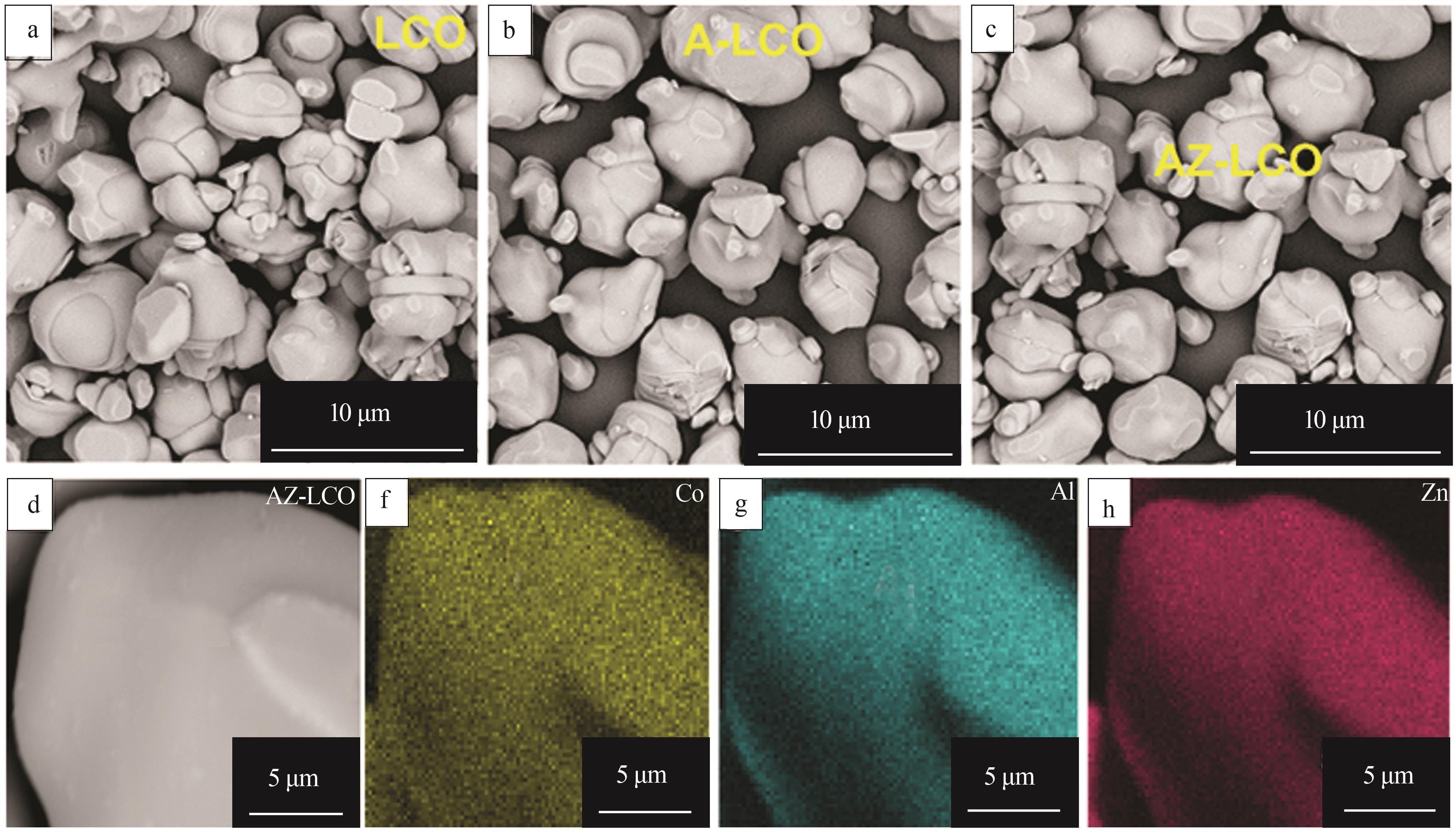
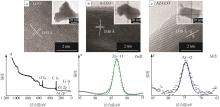
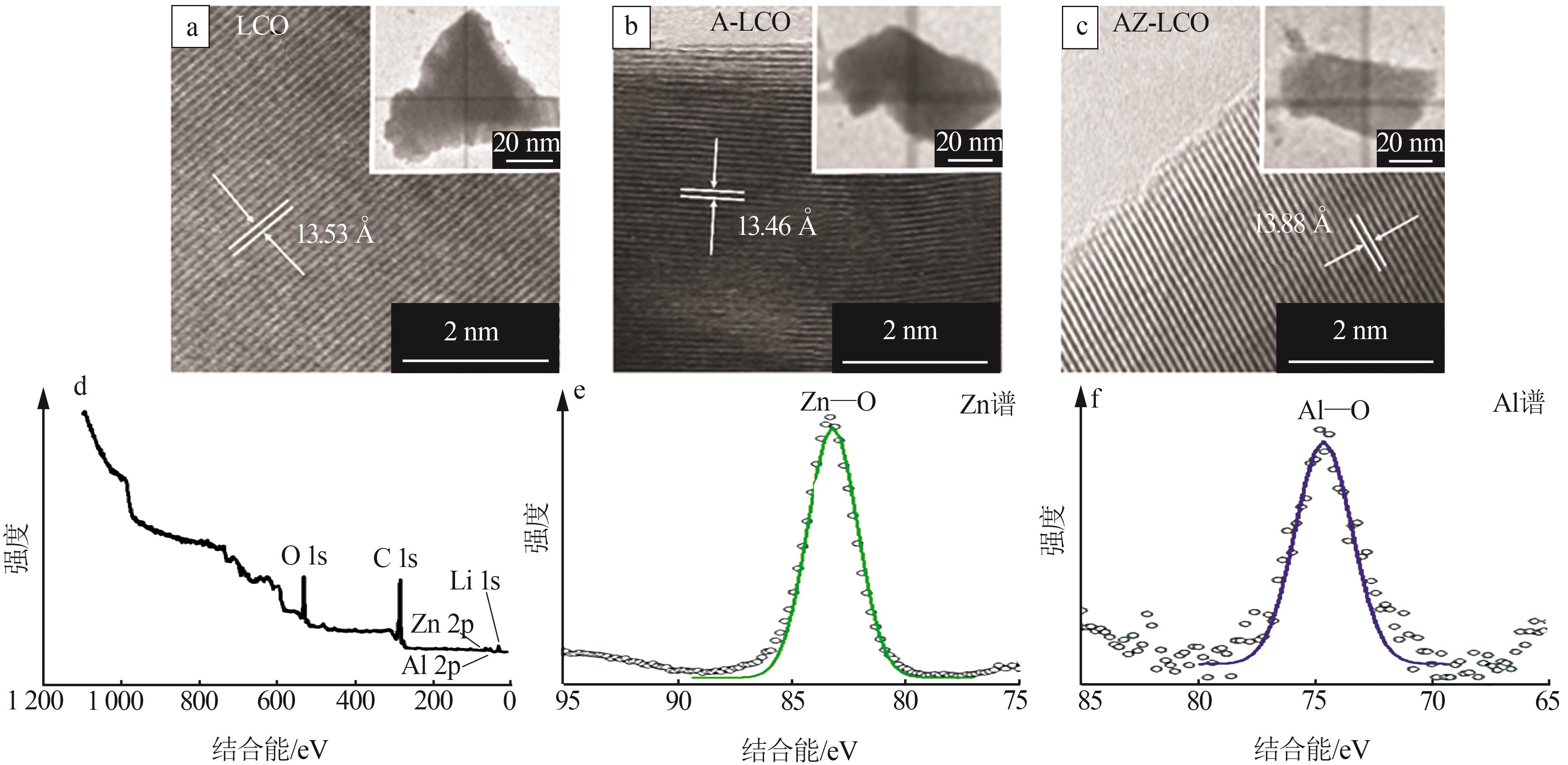
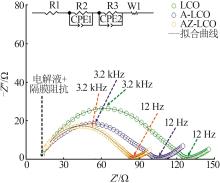
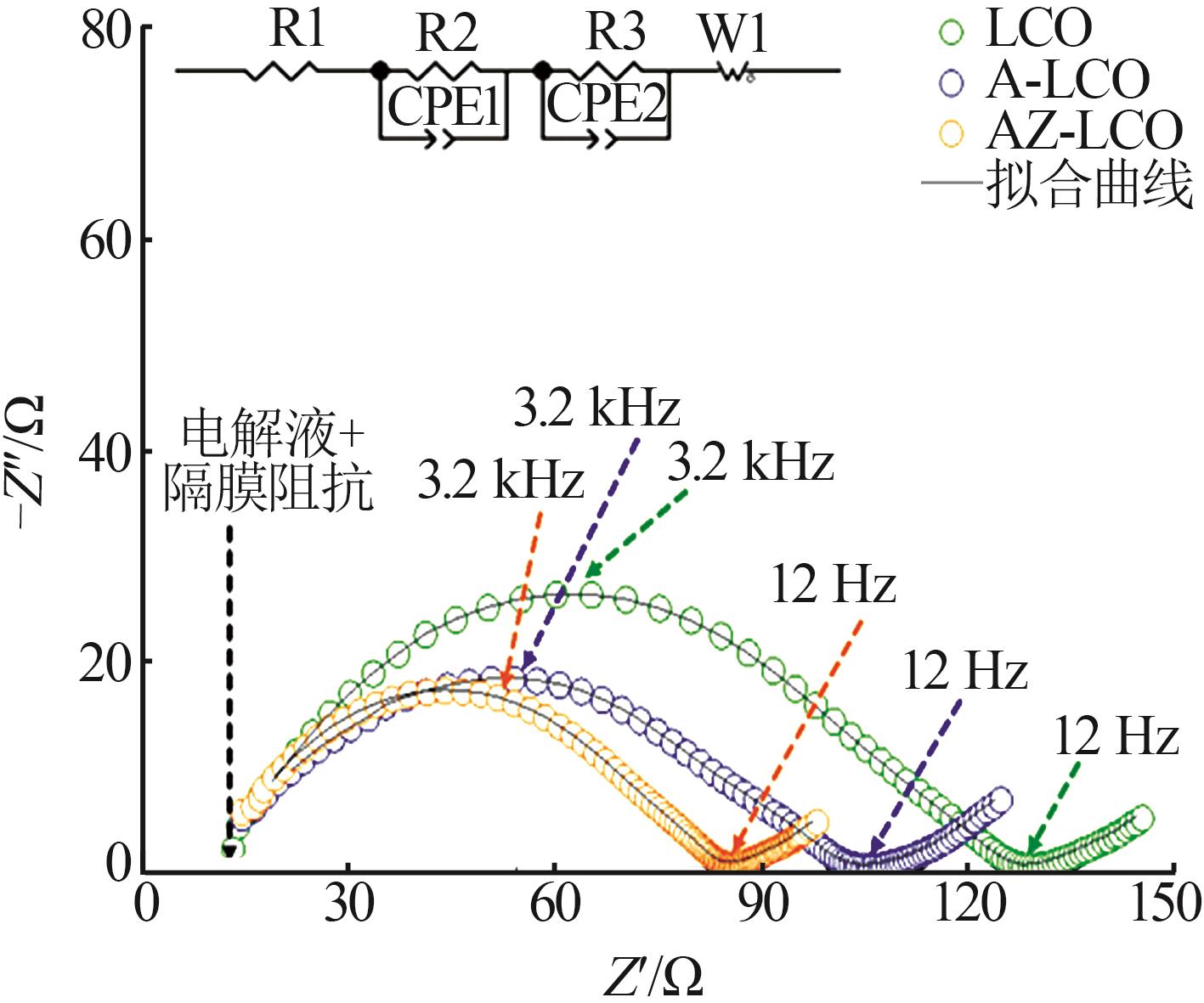
| [1] |
SONG Jiaxi, JI Renfei, CHEN Jun, LIN Sen, YU Jianguo.
Research on characteristics analysis and pretreatment on deeply deactivated power battery ternary cathode materials
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(2): 44-49.
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Shanshan, ZENG Yule, ZHANG Ting, LIN Sen, LIU Chenglin.
Research progress of cathode pre-lithiation technology for lithium-ion batteries
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(1): 1-13.
|
| [3] |
TIAN Peng, ZHANG Haoran, XU Jingang, MOU Chenxi, XU Qianjin, NING Guiling.
Study on aluminum sol modified anode and cathode materials for lithium ion batteries
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 44-53.
|
| [4] |
CHEN Xue, OUYANG Quansheng, SHAO Jiaojing.
Recent research progress of lithium-sulfur batteries based on solid-solid reaction mechanism
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(9): 12-23.
|
| [5] |
LI Yaguang, HAN Dongzhan, QI Lijuan.
Recent research on pretreatment of waste lithium-ion batteries and electrolyte recovery technology
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 1-10.
|
| [6] |
GE Jianhua, XIE Minyan, OUYANG Quansheng, SHAO Jiaojing.
Advances in regeneration processes of cathode materials for spent power batteries
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 79-87.
|
| [7] |
ZHAO Runze, QIAN A′niu.
Research progress of lithium recovery for spent lithium-ion batteries and preparation in battery-grade lithium carbonate
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 70-78.
|
| [8] |
MA Lianren, XIE Hongyan.
Study on preparation of LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/C cathode materials by two-step solid-phase method with surfactant
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 39-44.
|
| [9] |
LU Junhao.
Study on full element recycling process of retired ternary power lithium battery
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 92-103.
|
| [10] |
PENG Chenxi, LIU Jun.
Research progress of layered transition metal oxides cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 1-12.
|
| [11] |
ZHOU Shiyu,HE Ting,FU Tongtong,GUO Zirui,GU Shuai,YU Jianguo.
Life cycle and economic assessment of recycling spent lithium-ion batteries with hydrometallurgical process
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 26-32.
|
| [12] |
QIU Zhixu,ZHU Shaokuan,WEI Yuxiao,LONG Jiaying,HUANG Dongchuang,SHAO Jiaojing.
Study on preparation and electrochemical performance of S/MCNT/Fe3O4 cathode materials
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(6): 73-77.
|
| [13] |
LI Fangkun,WANG Xinyi,XU Xijun,WU Yiwen,YANG Yan,LIU Jun.
Nanoconfined encapsulation of iron-germanium alloy anode and its lithium ion storage performance
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 88-93.
|
| [14] |
YANG Fengyu,DONG Hua,CHEN Botao.
Research progress of reaction mechanism of lithium-rich manganese-based cathode materials
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(12): 19-27.
|
| [15] |
HE Ting,KONG Jiao,CUI Jingzhi,CHEN Zhihao,FU Tongtong,GUO Zirui,GU Shuai,YU Jianguo.
Study on leaching and thermodynamic of spent lithium-ion batteries with electrochemical reduction
[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(12): 34-43.
|
 ), JIANG Qinglai, ZHANG Yueyi
), JIANG Qinglai, ZHANG Yueyi