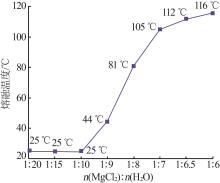
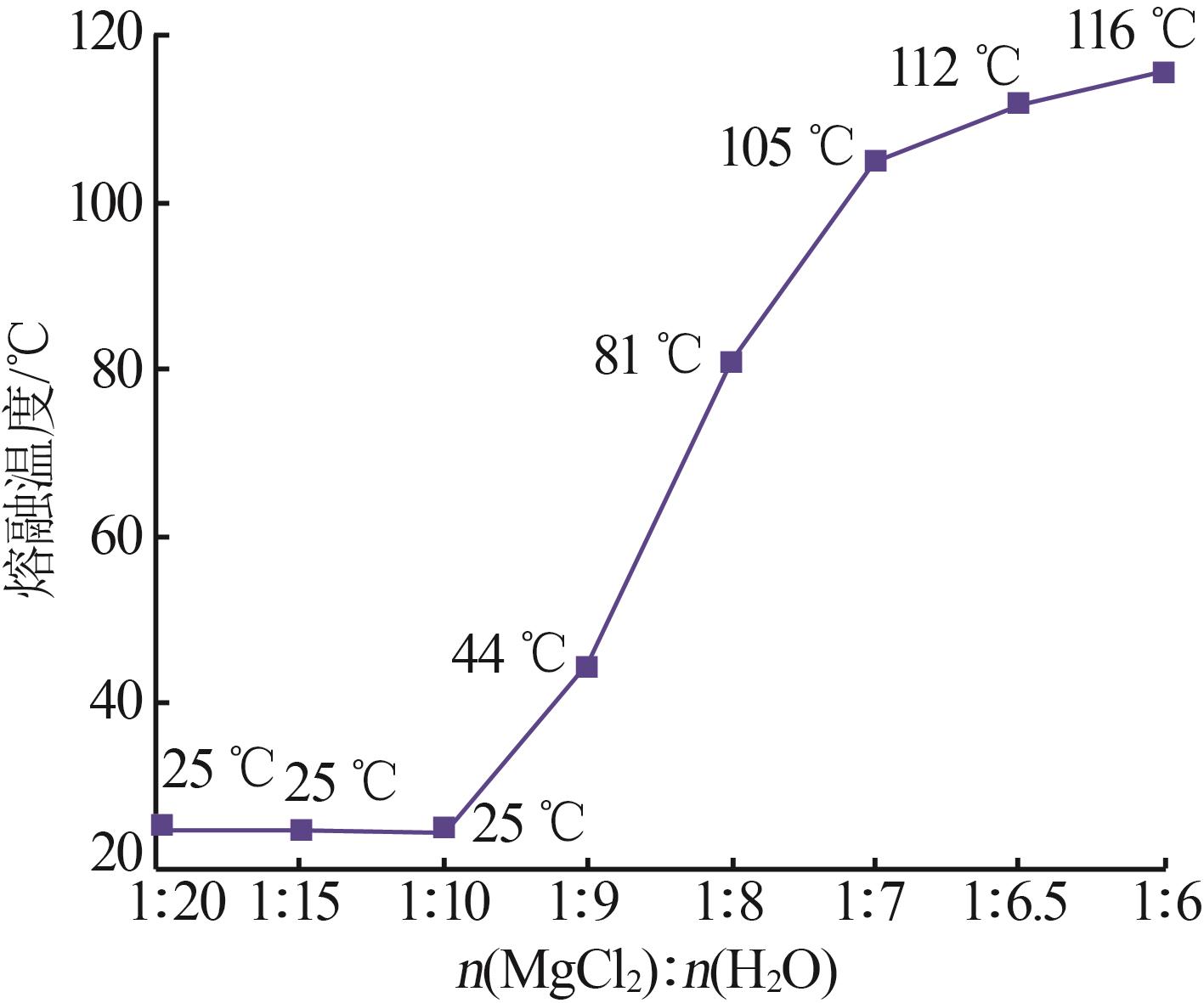
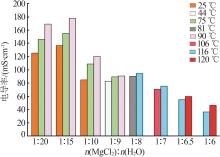
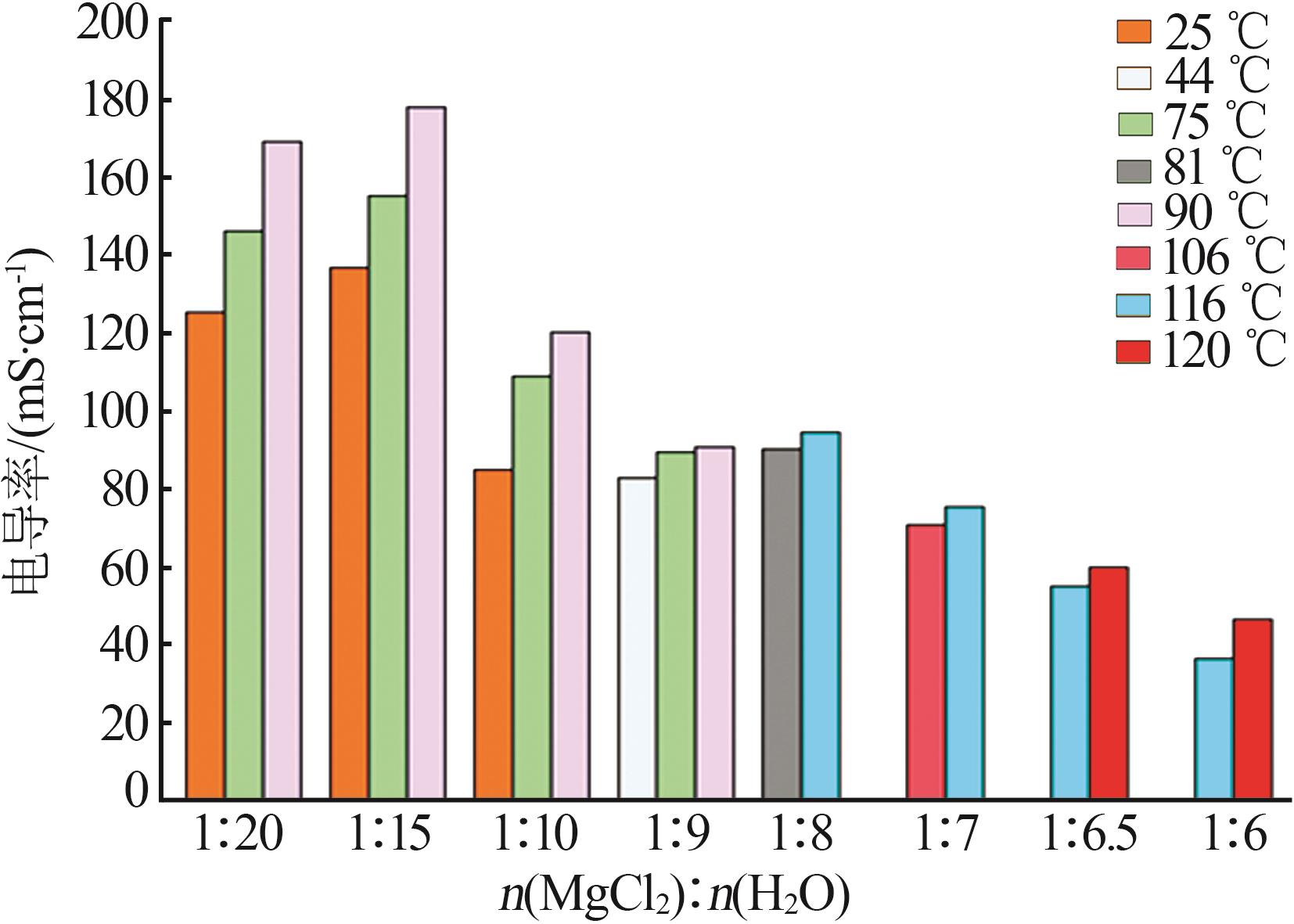
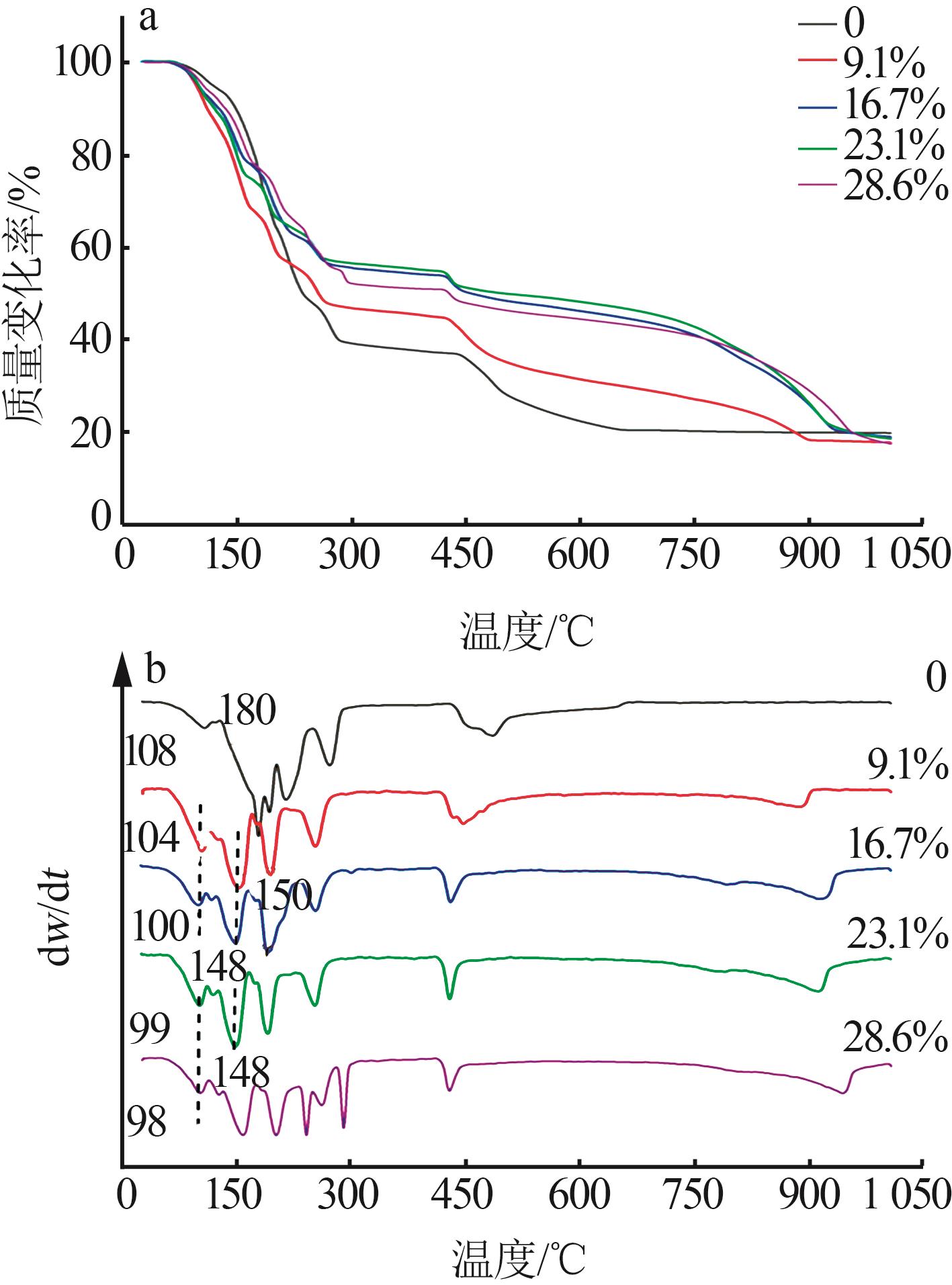
| 1 |
EMONS H H.Structure and properties of molten salt hydrates[J].Electrochimica Acta,1988,33(9):1243-1250.
|
| 2 |
ZHOU Hong, ZHANG Dong.Effect of graphene oxide aerogel on dehydration temperature of graphene oxide aerogel stabilized MgCl2⋅6H2O composites[J].Solar Energy,2019,184:202-208.
|
| 3 |
NARESH G, RAJASEKHAR A, BHARALI J,et al.Homogeneous molten salt formulations as thermal energy storage media and heat transfer fluid[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2022,50:104200.
|
| 4 |
LI Yaxi, LI Chuanchang, LIN Niangzhi,et al.Review on tailored phase change behavior of hydrated salt as phase change materials for energy storage[J].Materials Today Energy,2021,22:100866.
|
| 5 |
刘伟,李振明,刘铭扬,等.高温相变储热材料制备与应用研究进展[J].储能科学与技术,2023,12(2):398-430.
|
|
LIU Wei, LI Zhenming, LIU Mingyang,et al.Review of high-temperature phase change heat storage material preparation and applications[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2023,12(2):398-430.
|
| 6 |
LIU Gang, XIE Yujiao, WEI Chunjie,et al.Synergistic catalysis of species in molten salt hydrate for conversion of cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural[J].Biomass and Bioenergy,2022,158:106363.
|
| 7 |
WANG Jinghua, WANG Jiangang, CUI Hongyou,et al.Promotion effect of molten salt hydrate on co-esterification of biomass-derived levulinic and formic acids[J].Fuel,2022,321:124077.
|
| 8 |
TRAN T Q, ZHENG Weiqing, TSILOMELEKIS G.Molten salt hydrates in the synthesis of TiO2 flakes[J].ACS Omega,2019,4(25):21302-21310.
|
| 9 |
ZHENG Jiaxin, TAN Guoyu, SHAN Peng,et al.Understanding thermodynamic and kinetic contributions in expanding the stability window of aqueous electrolytes[J].Chem,2018,4(12):2872-2882.
|
| 10 |
戴宇成,王增鹏,刘凯豹,等.基于相变材料的储热器及其传热强化研究进展[J].储能科学与技术,2023,12(2):431-458.
|
|
DAI Yucheng, WANG Zengpeng, LIU Kaibao,et al.Research progress of heat storage and heat transfer enhancement based on phase change materials[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2023,12(2):431-458.
|
| 11 |
ZHANG Zhimin, LU Xuchen, WANG Tizhuang,et al.The dehydration of MgCl2·6H2O in MgCl2·6H2O-KCl-NH4Cl system[J].Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2014,110:248-253.
|
| 12 |
王芹,郭亚飞,王士强,等.水氯镁石脱水技术的研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2011,43(4):6-10.
|
|
WANG Qin, GUO Yafei, WANG Shiqiang,et al.Progress in dehydration technique of bischofite[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2011,43(4):6-10.
|
| 13 |
宋丽英,胡庆福,胡晓波.六氨氯化镁制备与应用[J].无机盐工业,2016,48(7):1-3,6.
|
|
SONG Liying, HU Qingfu, HU Xiaobo.Preparation and application of hexammoniated magnesium chloride[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2016,48(7):1-3,6.
|
| 14 |
XU Jiaxing, LI Tingxian, YAN Taisen,et al.Dehydration kinetics and thermodynamics of magnesium chloride hexahydrate for thermal energy storage[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2021,219:110819.
|
| 15 |
张文政,刘正,毛萍莉.镁金属提炼和精炼工艺的研究进展[J].机械工程材料,2013,37(11):12-16.
|
|
ZHANG Wenzheng, LIU Zheng, MAO Pingli.Research progress in magnesium production and refining processes[J].Materials for Mechanical Engineering,2013,37(11):12-16.
|
| 16 |
KARUNADASA K S P, RAJAPAKSE R M G, PITAWALA H M T G A,et al.Microstructural insight into the thermal decomposition of MgCl2·6H2O examined by in situ high-temperature X-ray powder diffraction[J].Journal of Solid State Chemistry,2023,322:123965.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG Zhimin, LU Xuchen, YAN Yan,et al.The dehydration of MgCl2·6H2O by inhibition of hydrolysis and conversion of hydrolysate[J].Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2019,138:114-119.
|
| 18 |
DAI Liu, LONG Xinfeng, LOU Bo,et al.Progress in thermochemical energy storage for concentrated solar power:A review[J].International Journal of Energy Research,2018,42(15):4546-4561.
|
| 19 |
DING Wenjin, YANG Fan, BONK A,et al.Molten chloride salts for high-temperature thermal energy storage:Continuous electrolytic salt purification with two Mg-electrodes and alternating voltage for corrosion control[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2021,223:110979.
|
| 20 |
HUININK H P, ZAHN D.Elucidating water dynamics in MgCl2 hydrates from molecular dynamics simulation[J].Solid State Sciences,2017,69:64-70.
|
| 21 |
CAI Houqin, LI Huiji, WANG Mei,et al.Microscopic insight into the ion aggregation characteristics in aqueous MgCl2 and MgCl2-LiCl solutions:Implications for Mg2+/Li+ separation[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2019,273:374-382.
|
| 22 |
LI Cheng, ZHAO Bin, GUO Hongfei,et al.Stable phase equilibrium of the quaternary system NaCl-MgCl2-NH4Cl-H2O at 348.15 K and its application in industry[J].The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics,2020,146:106102.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG Zhimin, LU Xuchen, YAN Yan.A novel pathway for the preparation of Mg metal from magnesia[J].Journal of Magnesium and Alloys,2022,10(10):2847-2856.
|
 ), LI Kexin1,2,4, YE Xiushen1,2, MA Zhen3, LI Shengting3, LI Quan1,2, WU Zhijian1,2(
), LI Kexin1,2,4, YE Xiushen1,2, MA Zhen3, LI Shengting3, LI Quan1,2, WU Zhijian1,2( )
)