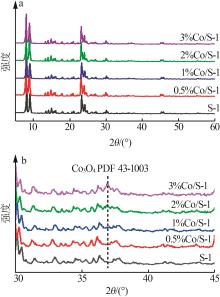
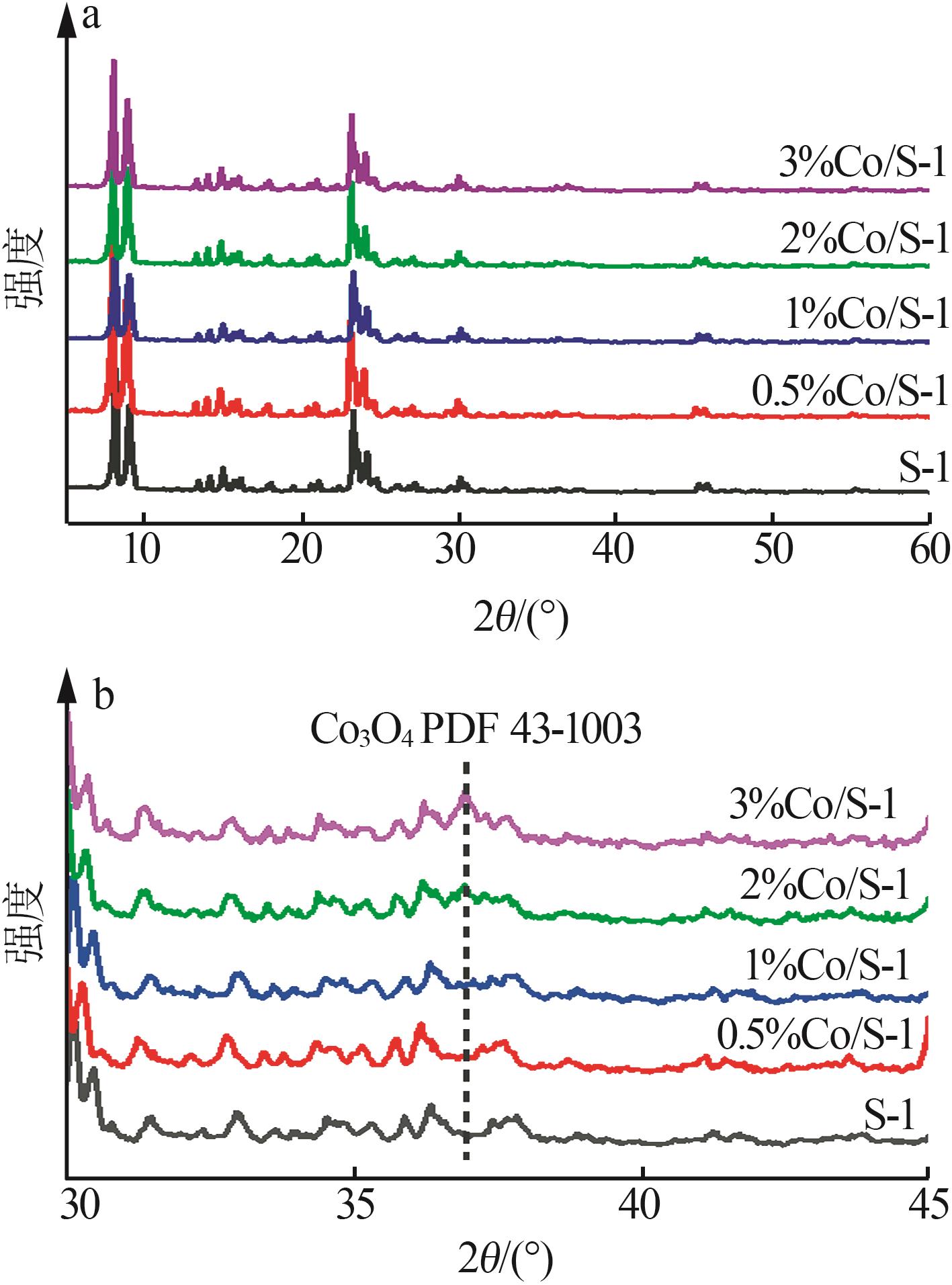
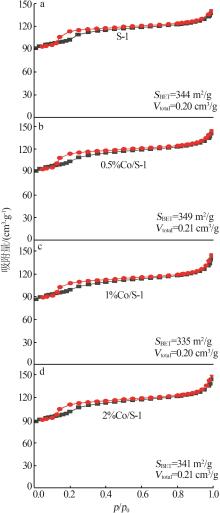
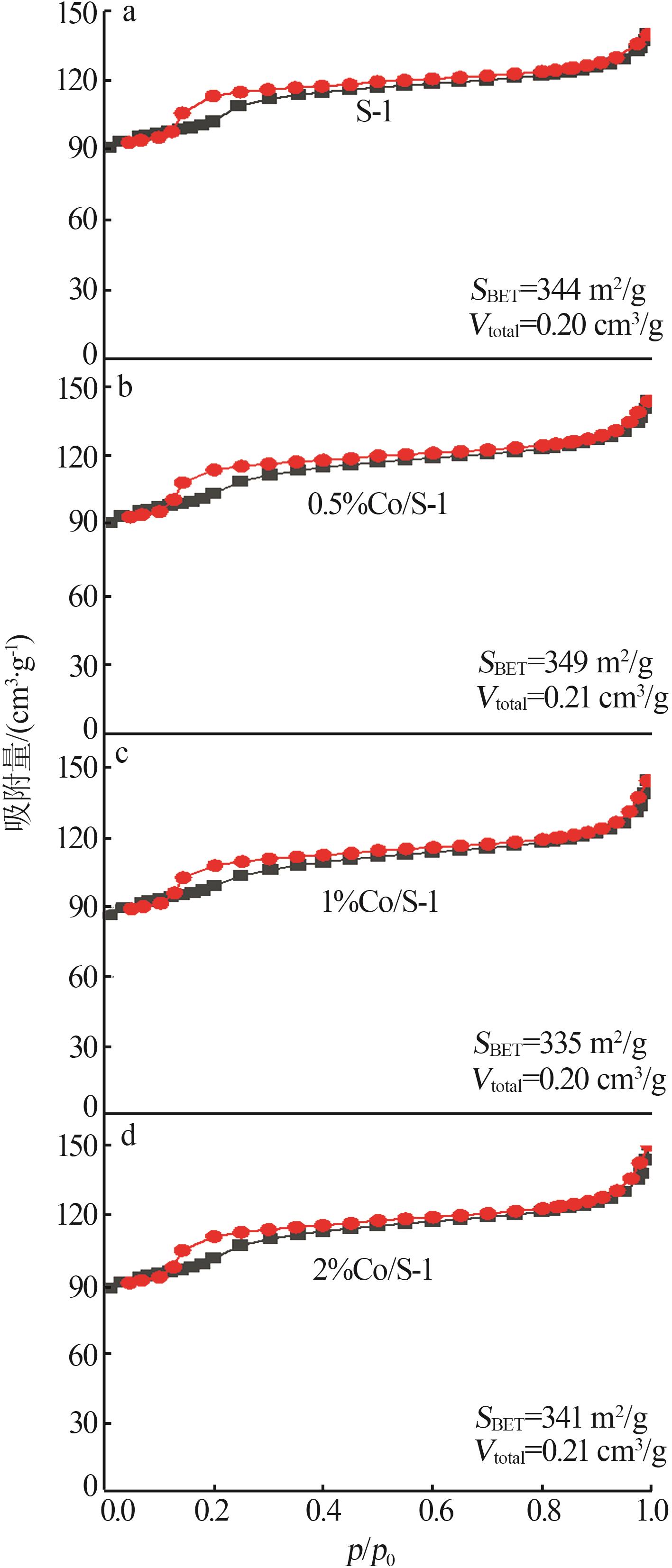
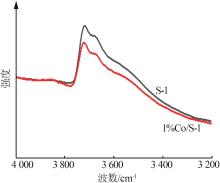
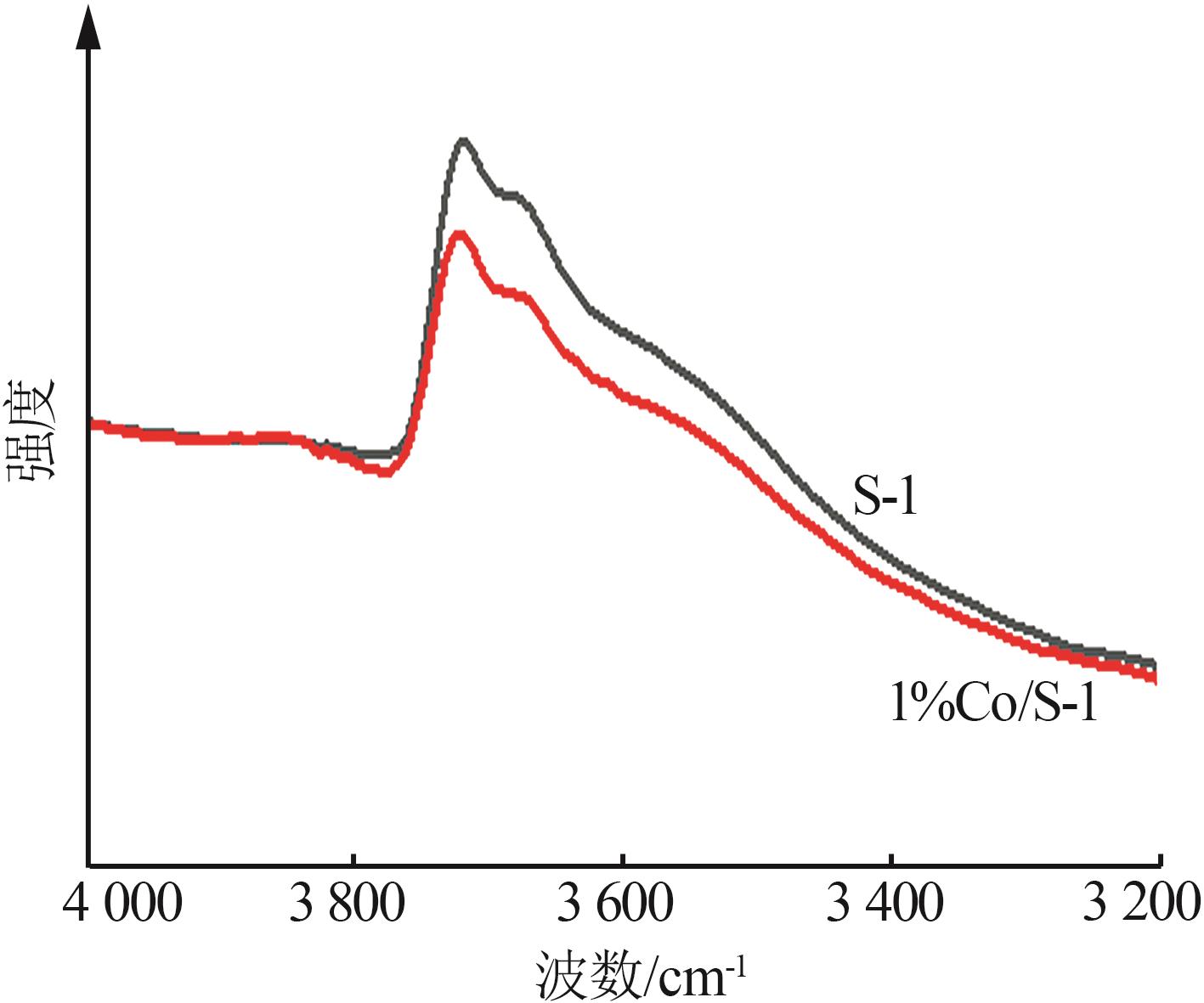
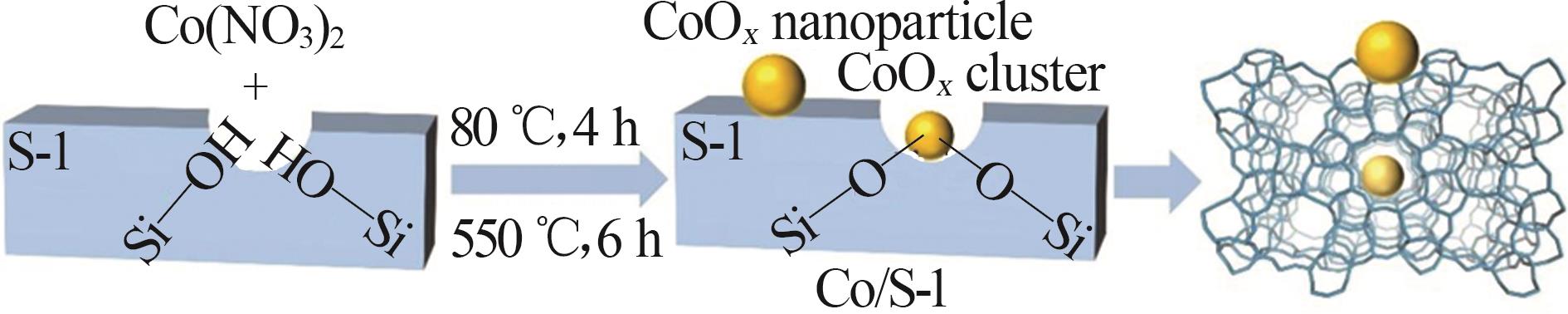
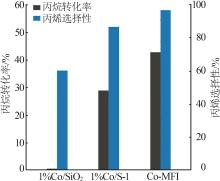
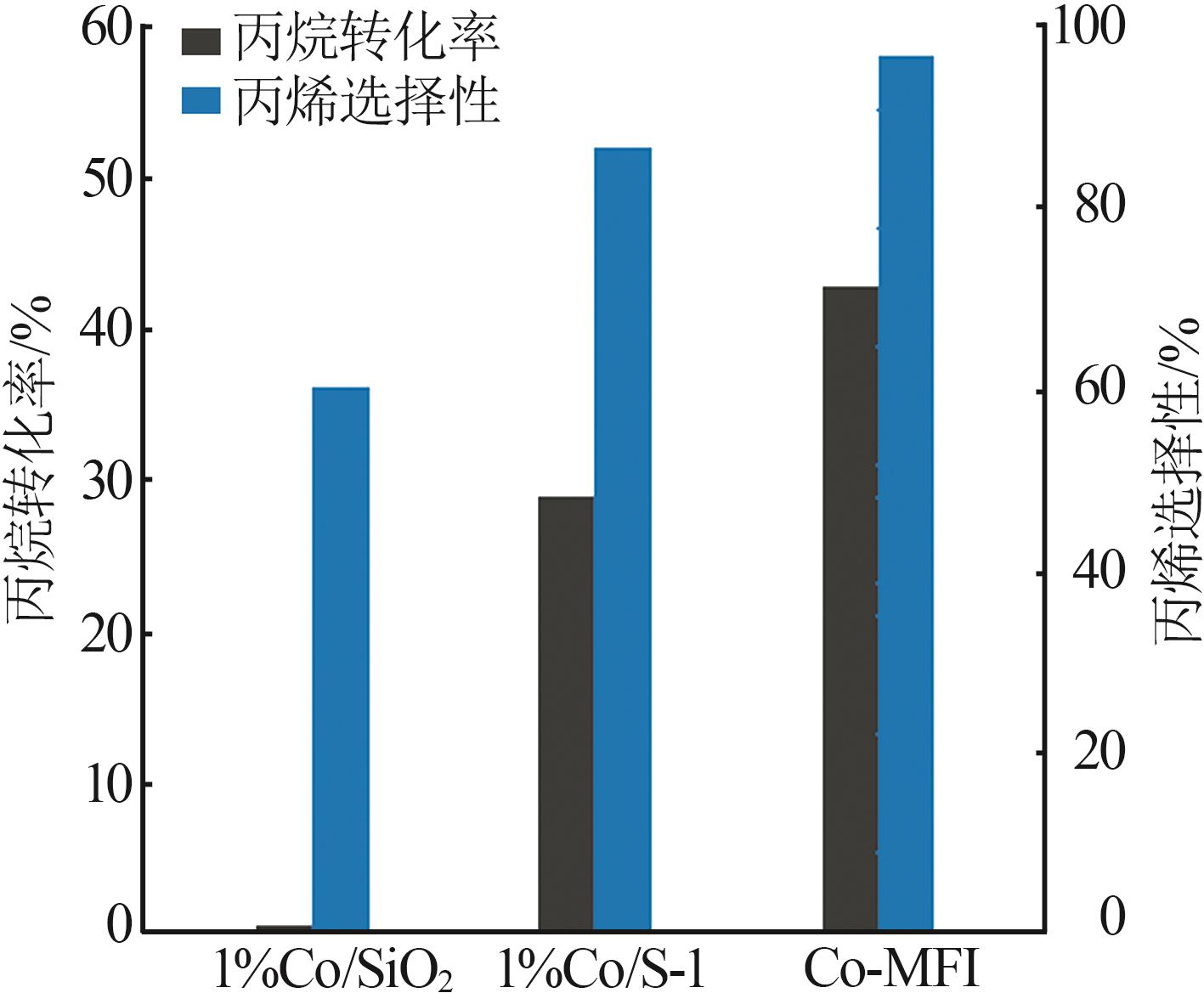
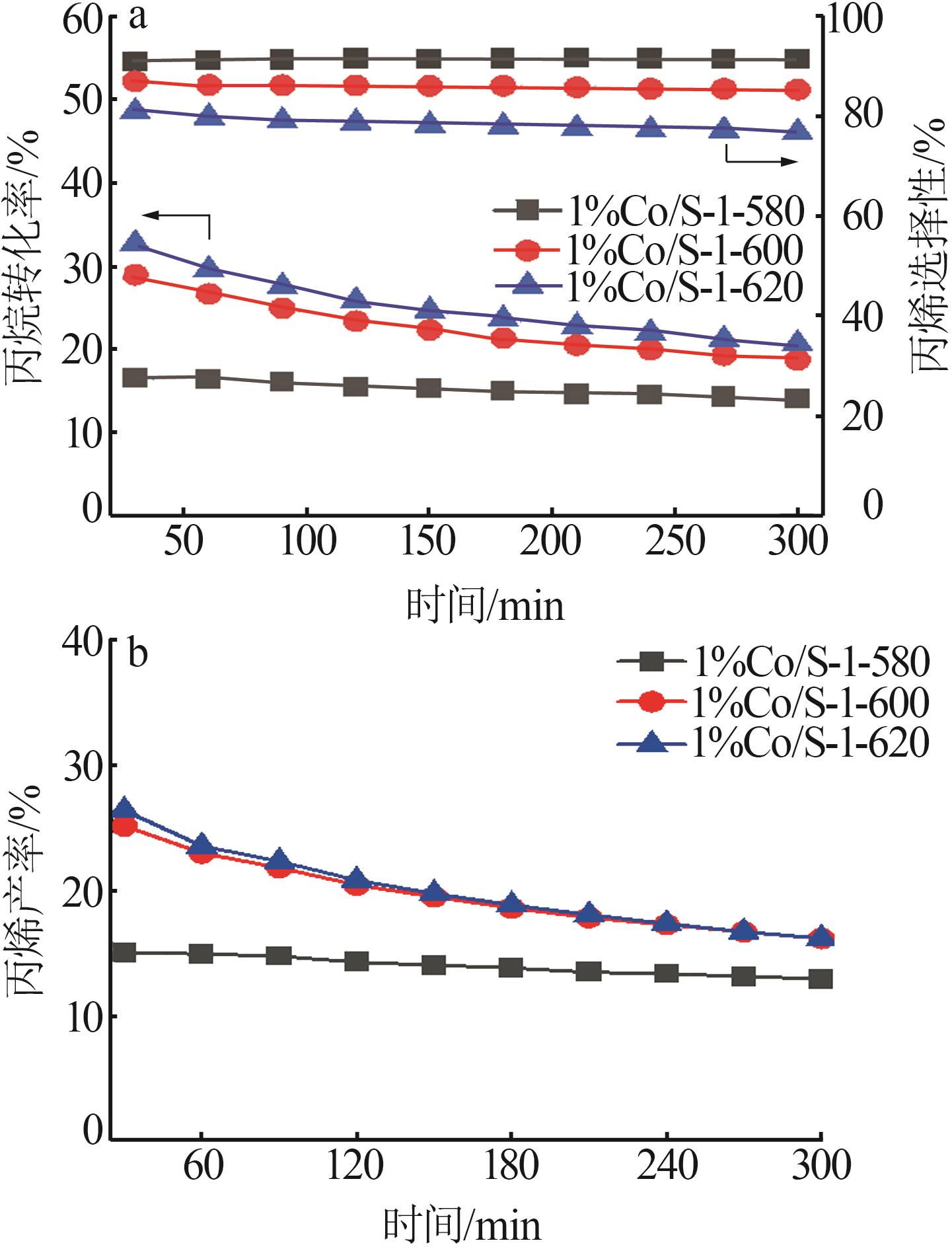
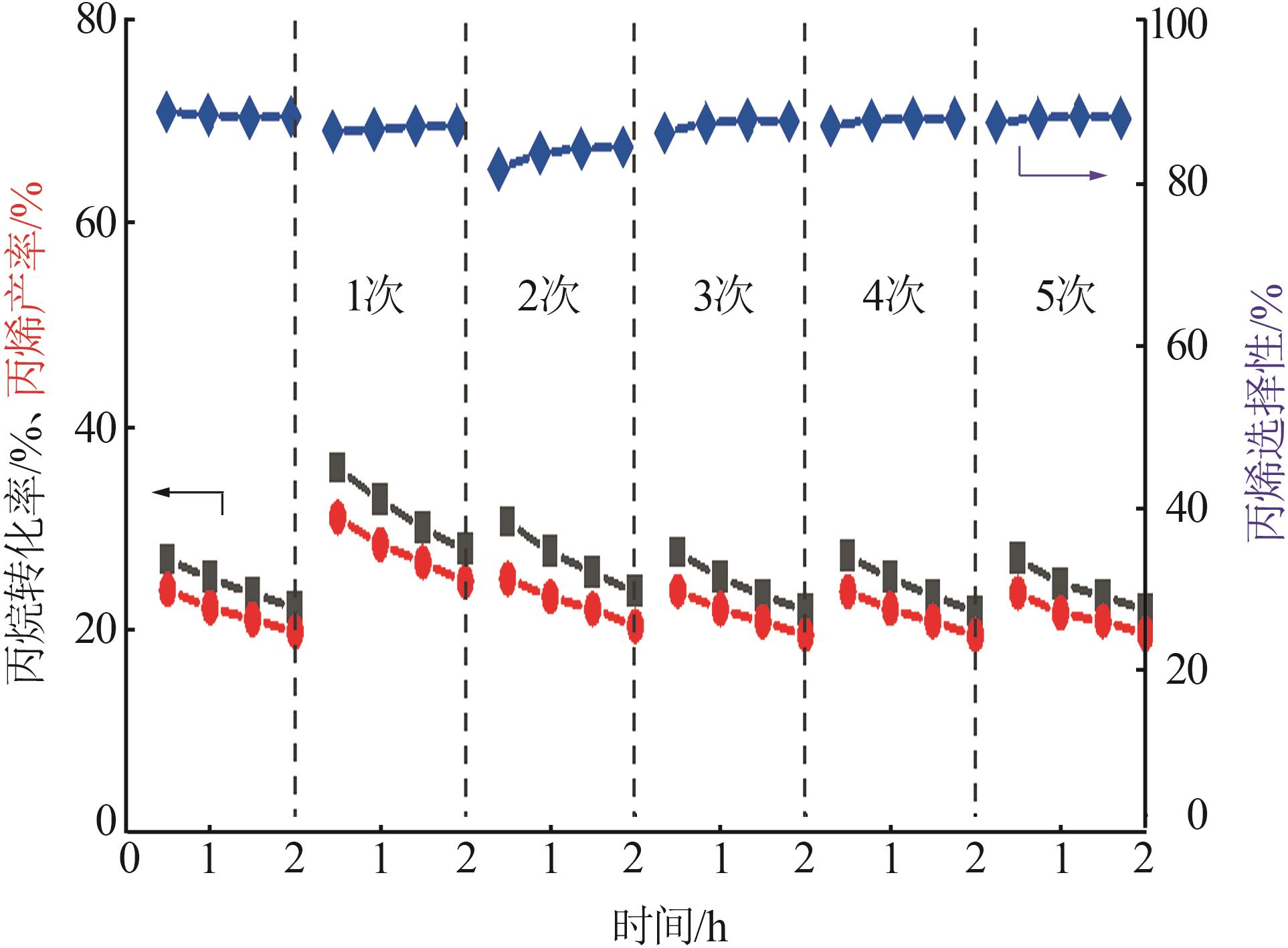
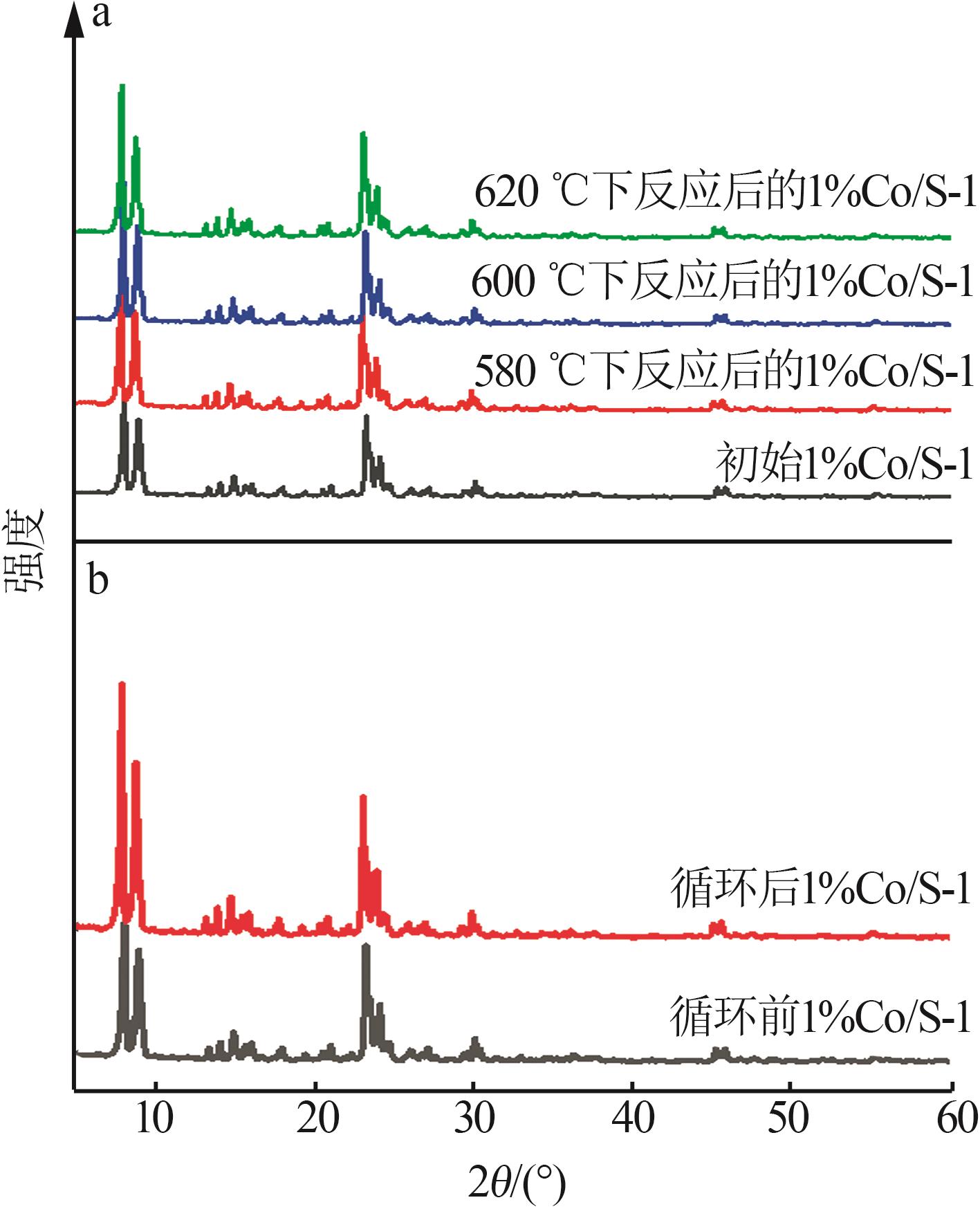
| 1 |
常小虎,赵毅,周帅,等.Fe改性Silicalite-1分子筛铂基催化剂的制备及其丙烷脱氢的催化性能[J].合成化学,2022,30(7):574-582.
|
|
CHANG Xiaohu, ZHAO Yi, ZHOU Shuai,et al.Fe modified silicalite-1 supported Pt-based catalyst for propane dehydrogenati-on[J].Chinese Journal of Synthetic Chemistry,2022,30(7):574-582
|
| 2 |
GOMEZ E, YAN Binhang, KATTEL S,et al.Carbon dioxide reduction in tandem with light-alkane dehydrogenation[J].Nature Reviews Chemistry,2019,3(11):638-649.
|
| 3 |
SATTLER J J H B, RUIZ-MARTINEZ J, SANTILLAN-JIMENEZ E,et al.Catalytic dehydrogenation of light alkanes on metals and metal oxides[J].Chemical Reviews,2014,114(20):10613-10653.
|
| 4 |
MCFARLAND E.Unconventional chemistry for unconventional natural gas[J].Science,2012,338(6105):340-342.
|
| 5 |
周微,于海斌,马新宾.Cr/SSZ-13催化二氧化碳氧化乙烷脱氢反应的研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(12):43-48.
|
|
ZHOU Wei, YU Haibin, MA Xinbin.Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane with carbon dioxide to ethylene over Cr/SSZ-13 catalyst[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(12):43-48.
|
| 6 |
YANG Zhiyuan, LI Huan, ZHOU Hang,et al.Coking-resistant iron catalyst in ethane dehydrogenation achieved through siliceous zeolite modulation[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2020,142(38):16429-16436.
|
| 7 |
李晓云,胡远明,蔡奇,等.铂系低碳烷烃脱氢催化剂研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(5):1-6.
|
|
LI Xiaoyun, HU Yuanming, CAI Qi,et al.Research progress of Pt-based catalysts for dehydrogenation of low-carbon alkanes[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(5):1-6.
|
| 8 |
郭秋双,蔡奇,孙彦民,等.低碳烷烃脱氢催化剂的研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2016,48(8):11-15.
|
|
GUO Qiushuang, CAI Qi, SUN Yanmin,et al.Research progress of low carbon alkane dehydrogenation catalyst[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2016,48(8):11-15.
|
| 9 |
HU Zhongpan, YANG Dandan, WANG Zheng,et al.State-of-the-art catalysts for direct dehydrogenation of propane to propylene[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2019,40(9):1233-1254.
|
| 10 |
MARCINKOWSKI M D, DARBY M T, LIU Jilei,et al.Pt/Cu single-atom alloys as coke-resistant catalysts for efficient C—H activation[J].Nature Chemistry,2018,10(3):325-332.
|
| 11 |
LIU Lichen, LOPEZ-HARO M, LOPES C W,et al.Regioselective generation and reactivity control of subnanometric platinum clusters in zeolites for high-temperature catalysis[J].Nature Materials,2019,18(8):866-873.
|
| 12 |
CHAI Yuchao, WU Guangjun, LIU Xiaoyan,et al.Acetylene-selective hydrogenation catalyzed by cationic nickel confined in zeolite[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019, 141(25):9920-9927.
|
| 13 |
GORDON C P, ENGLER H, TRAGL A S,et al.Efficient epoxidation over dinuclear sites in titanium silicalite-1[J].Nature,2020,586(7831):708-713.
|
| 14 |
HU Zhongpan, HAN Jingfeng, WEI Yingxu,et al.Dynamic evolution of zeolite framework and metal-zeolite interface[J].ACS Catalysis,2022,12(9):5060-5076.
|
| 15 |
WEI Donghui, ZHU Xinju, NIU Junlong,et al.High-valent-cobalt-catalyzed C—H functionalization based on concerted metalation-deprotonation and single-electron-transfer mechanisms[J].ChemCatChem,2016,8(7):1242-1263.
|
| 16 |
HU B, BEAN G A, SCHWEITZER N M,et al.Selective propane dehydrogenation with single-site CoII on SiO2 by a non-redox me-chanism [J].Journal of Catalysis,2015,322:24–37.
|
| 17 |
ESTES D P, SIDDIQI G, ALLOUCHE F,et al.C—H activation on Co,O sites:Isolated surface sites versus molecular analogs[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2016,138(45):14987-14997.
|
| 18 |
DAI Yihu, GU Jingjing, TIAN Suyang,et al. γ-Al2O3 sheet-stabilized isolate Co2+ for catalytic propane dehydrogenation[J].Journal of Catalysis,2020,381:482-492.
|
| 19 |
DAI Yihu, WU Yue, DAI Hua,et al.Effect of coking and propylene adsorption on enhanced stability for Co2+-catalyzed propane dehydrogenation[J].Journal of Catalysis,2021,395:105-116.
|
| 20 |
CHEN Chong, ZHANG Shoumin, WANG Zheng,et al.Ultrasmall Co confined in the silanols of dealuminated beta zeolite:A highly active and selective catalyst for direct dehydrogenation of propane to propylene[J].Journal of Catalysis,2020,383:77-87.
|
| 21 |
WANG Yansu, SUO Yujun, REN Jintao,et al.Spatially isolated cobalt oxide sites derived from MOFs for direct propane dehydrogenation[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,594:113-121.
|
| 22 |
GU Dong, JIA Chunjiang, WEIDENTHALER C,et al.Highly ordered mesoporous cobalt-containing oxides:Structure,catalytic properties,and active sites in oxidation of carbon monoxide[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2015,137(35):11407-11418.
|
| 23 |
LI Xiuyi, WANG Pengzhao, WANG Haoren,et al.Effects of the state of Co species in Co/Al2O3 catalysts on the catalytic performance of propane dehydrogenation[J].Applied Surface Science,2018,441:688-693.
|
| 24 |
HU Bo, KIM W G, SULMONETTI T P,et al.A mesoporous cobalt aluminate spinel catalyst for nonoxidative propane dehydrogenation[J].ChemCatChem,2017,9(17):3330-3337.
|
| 25 |
HU Zhongpan, QIN Gangqiang, HAN Jingfeng,et al.Atomic insight into the local structure and microenvironment of isolated Co-motifs in MFI zeolite frameworks for propane dehydrogenati-on[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2022,144(27):12127-12137.
|
| 26 |
陈利利,邱安定.ZSM-5分子筛掺杂双稀土金属用于低碳烷烃脱氢反应[J].现代化工,2018,38(4):155-159.
|
|
CHEN Lili, QIU Anding.ZSM-5 molecular sieve doped with double rare earth metals for dehydrogenation of low carbon alkanes[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2018,38(4):155-159.
|
| 27 |
KRUK M, JARONIEC M.Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic-inorganic nanocomposite materials[J].Chemistry of Materials,2001,13(10):3169-3183.
|
| 28 |
HU Zhongpan, ZHAO Hui, GAO Zemin,et al.High-surface-area activated red mud supported Co3O4 catalysts for efficient catalytic oxidation of CO[J].RSC Advances,2016,6(97):94748-94755.
|
| 29 |
OTTO T, ZONES S I, HONG Yongchun,et al.Synthesis of highly dispersed cobalt oxide clusters encapsulated within LTA zeolit- es[J].Journal of Catalysis,2017,356:173-185.
|
 ), HU Zhongpan1(
), HU Zhongpan1( ), WANG Kunyuan1(
), WANG Kunyuan1( ), HAN Jingfeng1, WEI Yingxu1, LIU Zhongmin1
), HAN Jingfeng1, WEI Yingxu1, LIU Zhongmin1