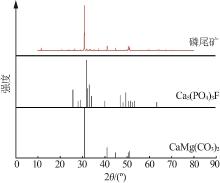
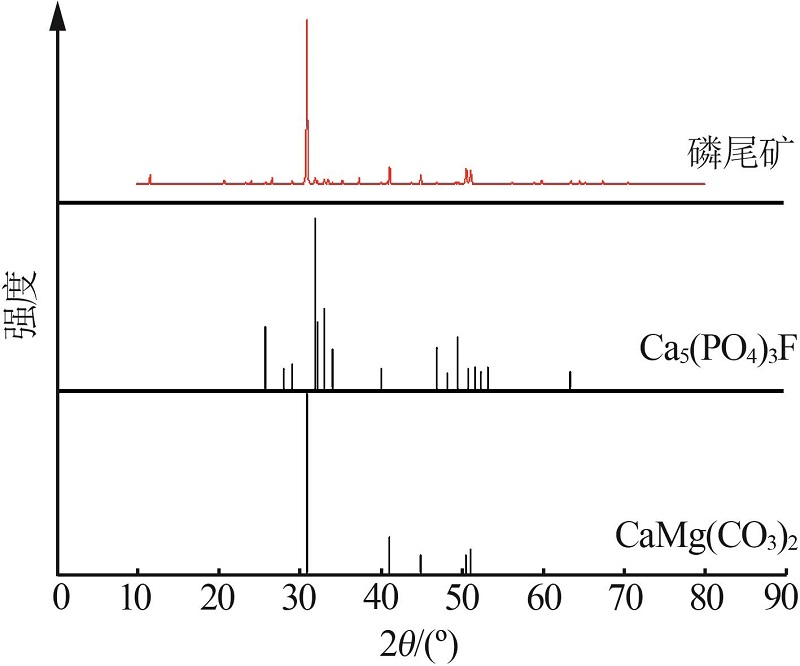
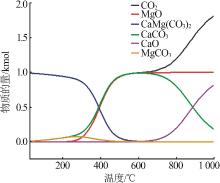
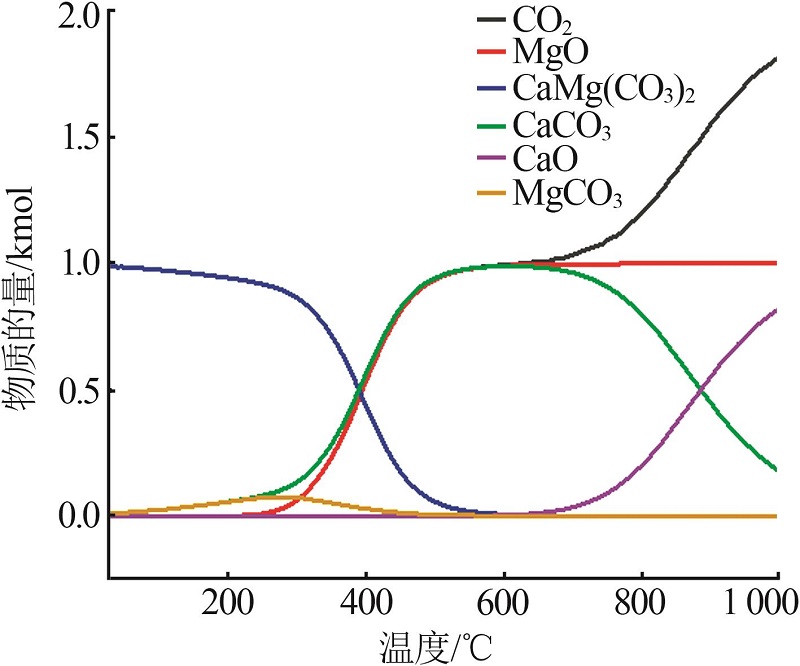
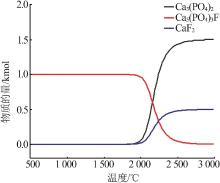
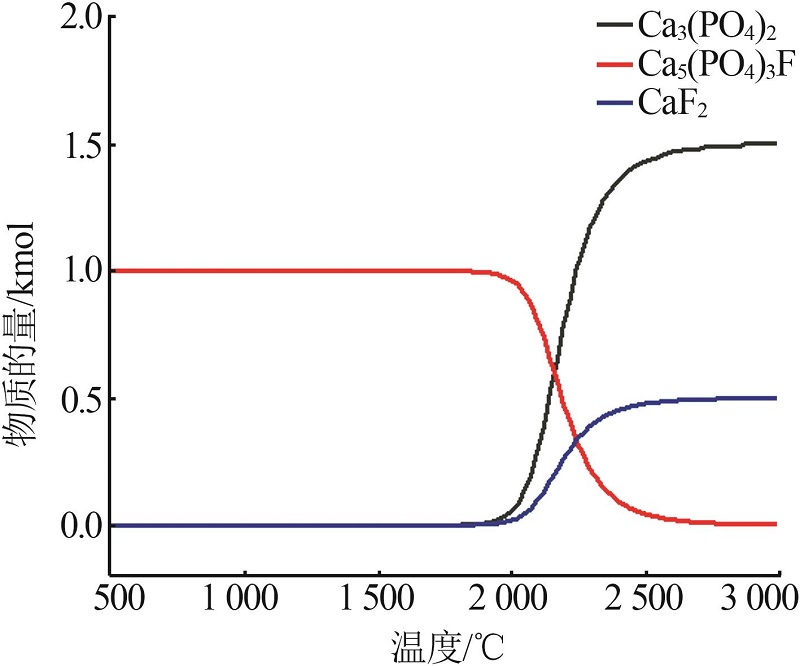
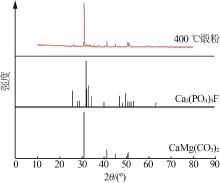
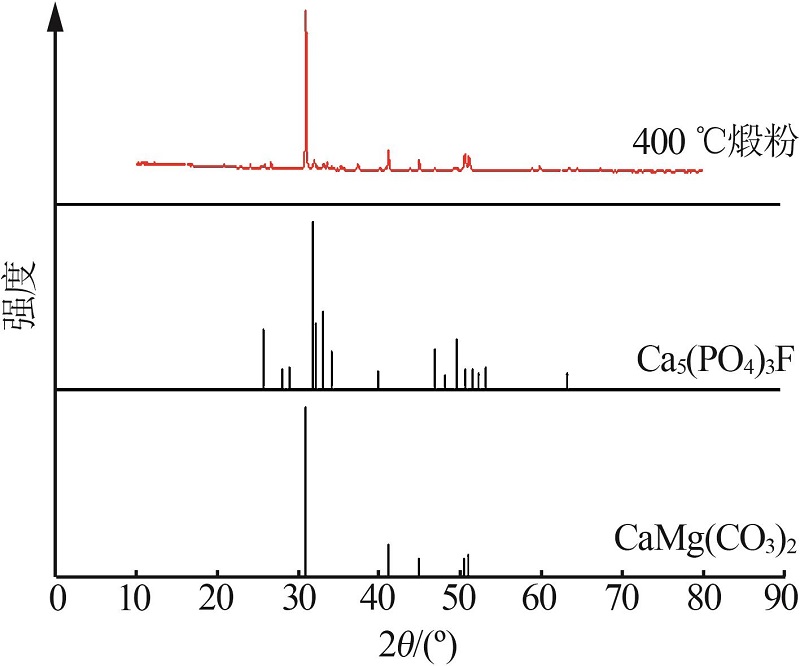
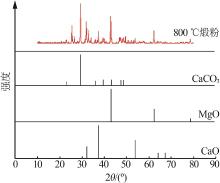
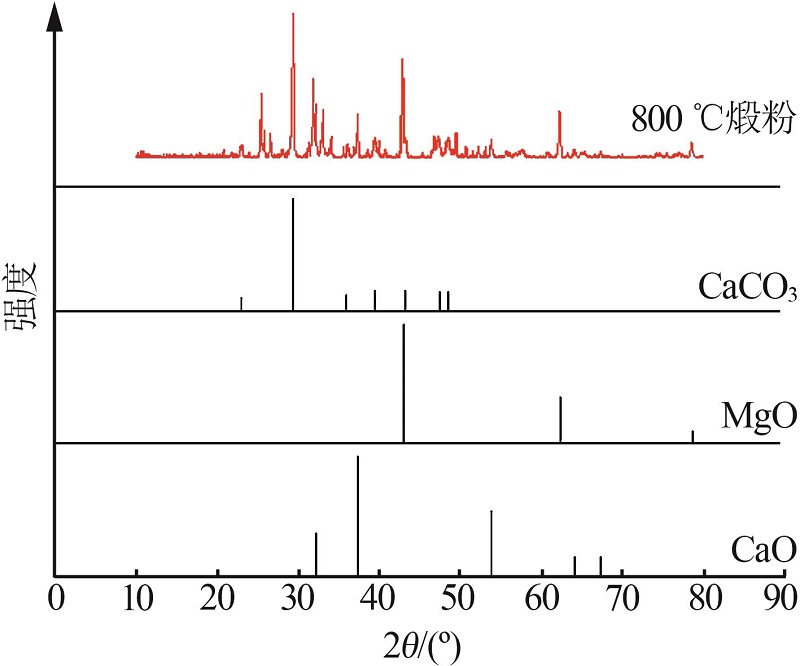
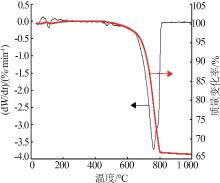
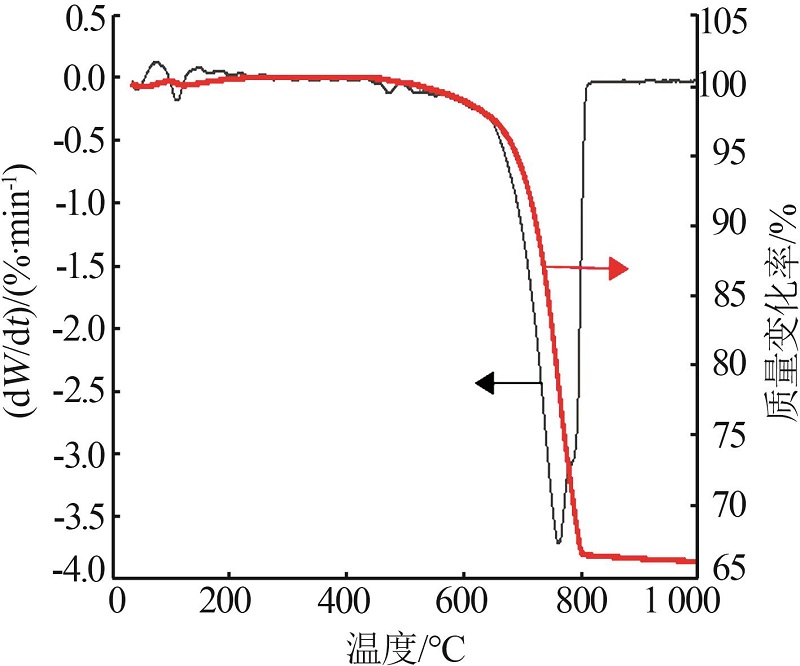
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 47-54.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0295
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
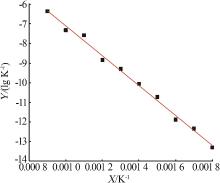
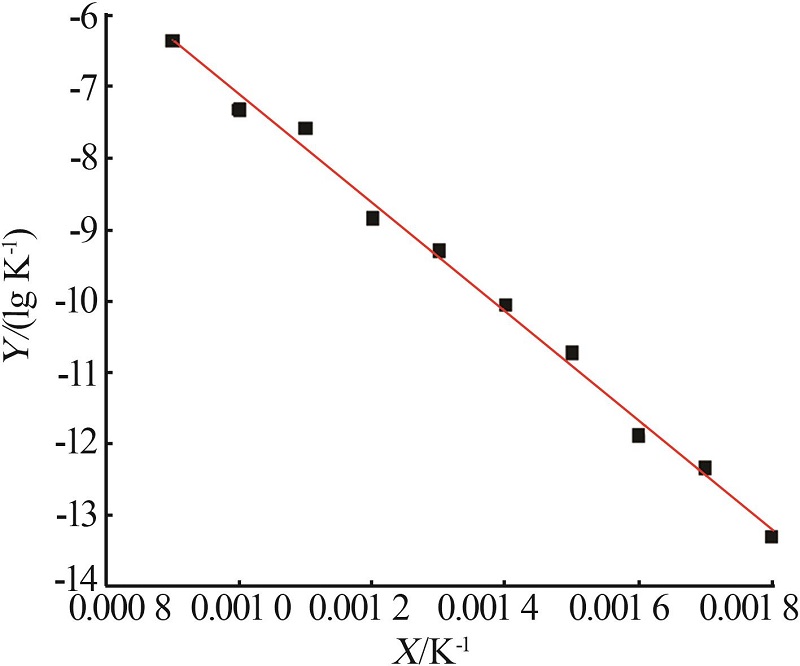
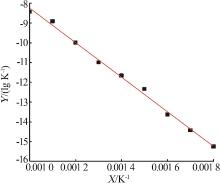
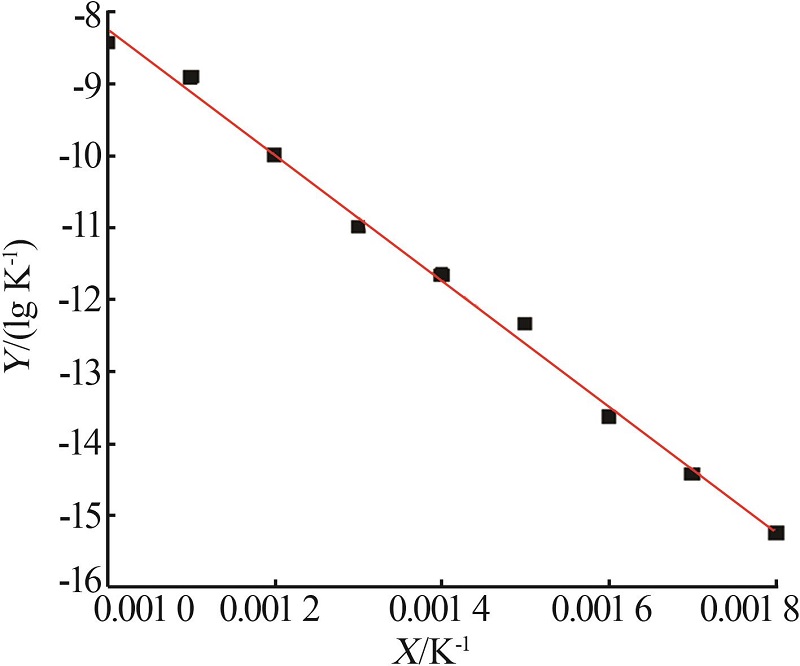
Study on thermal decomposition kinetic mechanism and calcination process of phosphorus tailings
ZHOU Qiang( ), WU Bin(
), WU Bin( ), CHEN Kui, JI Lijun, WU Yanyang
), CHEN Kui, JI Lijun, WU Yanyang
- School of Chemical Engineering,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
-
Received:2022-05-14Online:2023-03-10Published:2023-03-17
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHOU Qiang, WU Bin, CHEN Kui, JI Lijun, WU Yanyang. Study on thermal decomposition kinetic mechanism and calcination process of phosphorus tailings[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 47-54.
share this article
| 1 | 李鹏毅,张冬冬,宁平,等.磷尾矿资源化利用研究[J].化工矿物与加工,2019,48(2):66-70. |
| LI Pengyi, ZHANG Dongdong, NING Ping,et al.Study on resource utilization of phosphate tailings[J].Industrial Minerals & Processing,2019,48(2):66-70. | |
| 2 | 马会娟,杨成,潘志权,等.磷尾矿制备硫酸镁试验研究[J].非金属矿,2017,40(1):93-95. |
| MA Huijuan, YANG Cheng, PAN Zhiquan,et al.Experimental study on the preparation of magnesium sulfate from phosphate tailings[J].Non-Metallic Mines,2017,40(1):93-95. | |
| 3 | 田兴.反浮选磷尾矿的综合利用[D].武汉:武汉工程大学,2013. |
| TIAN Xing.Comprehensive utilization of phosphate tailings from reverse floatation[D].Wuhan:Wuhan Institute of Technology,2013. | |
| 4 | 苗俊艳,王艳语,许秀成.中低品位磷矿及磷尾矿的综合利用现状[J].硫磷设计与粉体工程,2019(6):11-13,27. |
| MIAO Junyan, WANG Yanyu, XU Xiucheng.Current utilization of medium- and low-grade phosphate ore and tailing[J].Sulphur Phosphorus & Bulk Materials Handling Related Engineering,2019(6):11-13,27. | |
| 5 | 高贺然,黄远来,邱跃琴,等.减水剂对磷尾矿胶结充填料浆输送流动性能影响研究[J].矿冶工程,2018,38(1):30-34. |
| GAO Heran, HUANG Yuanlai, QIU Yueqin,et al.Influence of water reducer on fluidity of phosphate tailings cemented paste backfill[J].Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2018,38(1):30-34. | |
| 6 | 黄芳,王华,李军旗,等.萃取-反萃法综合回收磷矿浮选尾矿中磷和镁[J].环境科学与技术,2010,33(4):104-107,140. |
| HUANG Fang, WANG Hua, LI Junqi,et al.Recovering P and Mg from phosphate floatation tailings using extraction-stripping process[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2010,33(4):104-107,140. | |
| 7 | 谢娟,刘松林,陶绍程,等.高镁磷尾矿碳化法制备碱式碳酸镁研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(12):135-139. |
| XIE Juan, LIU Songlin, TAO Shaocheng,et al.Study on preparation of magnesium carbonate hydroxide by carbonization method from high-Mg phosphate tailings[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(12):135-139. | |
| 8 | 周佳琦,陈葵,武斌,等.磷尾矿煅烧及酸浸过程动力学研究[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(1):77-82,108. |
| ZHOU Jiaqi, CHEN Kui, WU Bin,et al.Study on kinetics of phosphate tailings calcination and acid leaching process[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(1):77-82,108. | |
| 9 | 陈永弟.白云石的热分解规律及其应用[D].长春:吉林大学,2012. |
| CHEN Yongdi.The thermal decomposition behavior of dolomite and application[D].Changchun:Jilin University,2012. | |
| 10 | 林小化,张煜,廖裕辉,等.煅烧条件对白云石质磷尾矿热分解规律的影响[J].化工矿物与加工,2019,48(1):31-35,39. |
| LIN Xiaohua, ZHANG Yu, LIAO Yuhui,et al.Effect of calcining conditions on thermal decomposition of dolomite phosphate tailings[J].Industrial Minerals & Processing,2019,48(1):31-35,39. | |
| 11 | 王景峰,胡宏.瓮福磷尾矿热分解过程研究[J].煤炭与化工,2013,36(3):29-31,67. |
| WANG Jingfeng, HU Hong.Study on thermal decompose process of Wengfu phosphorus tailing[J].Coal and Chemical Industry,2013,36(3):29-31,67. | |
| 12 | 李沛伦,邱显扬,胡真,等.复杂Mn-Ag-Cu结合矿的浸出机理及工业优化[J].中国有色金属学报,2022,32(2):563-573. |
| LI Peilun, QIU Xianyang, HU Zhen,et al.Mechanism of leaching on complex Mn-Ag-Cu bound ore and industrial optimizations[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2022,32(2):563-573. | |
| 13 | 魏君,邓强,刘雪梅,等.HSC Chemistry在电动势法测定化学热力学函数中的应用[J].广东化工,2017,44(11):279-280, 283. |
| WEI Jun, DENG Qiang, LIU Xuemei,et al.Application of HSC chemistry software in the determination of chemical thermodynamic function by measuring electromotance[J].Guangdong Chemical Industry,2017,44(11):279-280,283. | |
| 14 | 李宁.HSC Chemistry软件在高校化学科研中的应用[J].化工管理,2016(17):74. |
| LI Ning.The application of HSC Chemistry software in chemical research in colleges and universities[J].Chemical Management,2016(17):74. | |
| 15 | 郭满满,肖卓炳,于华忠,等.热重法研究绿原酸的热稳定性、分解动力学及贮存期[J].药物评价研究,2011,34(5):348-352. |
| GUO Manman, XIAO Zhuobing, YU Huazhong,et al.Study on thermal stability,decomposition kinetics,and shelf life of chlorogenic acid by thermogravimetry method[J].Drug Evaluation Research,2011,34(5):348-352. | |
| 16 | 刘小星,李陇岗,杨建元,等.改进Freeman-Carroll法求算氢氧化镁热分解动力学参数研究[J].广州化工,2012,40(14):32-33. |
| LIU Xiaoxing, LI Longgang, YANG Jianyuan,et al.Studies on the calculation of the kinetic parameters of Mg(OH)2 thermo-decomposition by improved Freeman-carroll method[J].Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2012,40(14):32-33. | |
| 17 | 张英明,王兵毅,余坚,等.三氧化二铝对环氧树脂固化动力学及热降解动力学的影响[J].广东工业大学学报,2019,36(5):63-70. |
| ZHANG Yingming, WANG Bingyi, YU Jian,et al.Effects of aluminum oxide on curing and thermal decomposition kinetics of epoxy resin[J].Journal of Guangdong University of Technology,2019,36(5):63-70. |
| [1] | WANG Shengchang, HAO Jianying, CHEN Jianing, TIAN Bo. Effect of calcination on properties of calcined gypsum prepared from desulphurization gypsum with potassium aluminum sulfate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 105-111. |
| [2] | QIAN Zhihui, ZHU Qin, MA Jiao, GUO Yujiao, XIANG Mingwu, GUO Junming. Study on preparation and electrochemical properties of nano-sized LiNi0.05Mn1.95O4 cathode materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 50-56. |
| [3] | YANG Kun, REN Qixia, DONG Yonggang, LIU Fei, YAO Mengqin, CAO Jianxin. Effect of calcination temperature on catalytic performance of ZnGaZrO x /SAPO-34 [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 136-145. |
| [4] | ZHANG Conghua, YAN Wenbin, XIAO Jiajun, ZHAO Ke, PENG Shangquan, WEI Yuhong. Reductive leaching technology of manganese anode slag using tartaric acid as reducing agent optimized by RSM [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 106-113. |
| [5] | LI Qiang, YOU Xiaomin, SHE Xuefeng, JIANG Zeyi, XUE Qingguo, WANG Jingsong. Effect of calcination temperature and carbon structure on compressive strength of CaO-containing carbon pellets [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 43-49. |
| [6] | XU Li, ZHANG Qiang. Experimental study on properties of iron tailings powder cement-based materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 116-123. |
| [7] | LI Heng, ZHANG Hui, ZI Xuemin. Analysis on calcination process progress of phosphogypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 27-35. |
| [8] | HONG Meihua, GUO Zifeng, LIU Guanfeng, ZANG Jiazhong, YANG Keyu, YU Yonghua, ZHANG Dazhi, HUANG Shengjun. Progress and challenges of alkaline treatment for synthesis of hierarchical zeolites [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 36-42. |
| [9] | TIAN Xiaoli, LI Zhixun, FENG Runtang, ZHANG Jie, ZHENG Quanfu, SHI Xuwu, DU Yongbin. Study on thermal decomposition behavior of Tibetan Kamado microcrystalline magnesite [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 60-65. |
| [10] | LIAO Shengde,YANG Yaofeng,LI Yaxin,WU Hao. Study on flotation experiment and mechanism of desulfurization by-product magnesium sulfite using dodecylamine [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(2): 113-118. |
| [11] | GUO Shuang, XING Dongxian, GUO Xiao, JI Xiaojie, TANG Jianwei, HUA Quanxian, WANG Baoming, LIU Yong. Study on preparation and modification of phosphogypsum-based architectural gypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(12): 102-110. |
| [12] | YUE Yuansui, CHENG Guanwen, XU Min, XU Xiaoyu, ZHANG Zhenlin, NONG Guowu. Function and effect of ferric chloride solution in alkaline regulation of red mud [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 121-129. |
| [13] | DU Guanggang, HE Tong, XU Zehui, LIU Lei. Study on properties of calcium oxide in SCA under different calcination conditions [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 35-41. |
| [14] | PENG Jiaoyu, TAN Yuqin, YANG Keli, DONG Yaping, ZHANG Bo, LI Wu. Study on crystallization mechanism and kinetics of macallisterite synthesized with bischofite from salt lake [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 56-62. |
| [15] | WU Di, LI Laishi, WANG Junkai, WU Yusheng, WANG Yuzheng, LI Mingchun. Study on decomposition process and thermal decomposition kinetics of ammonium sulfate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 86-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||