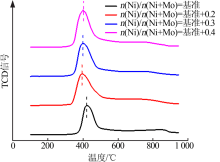
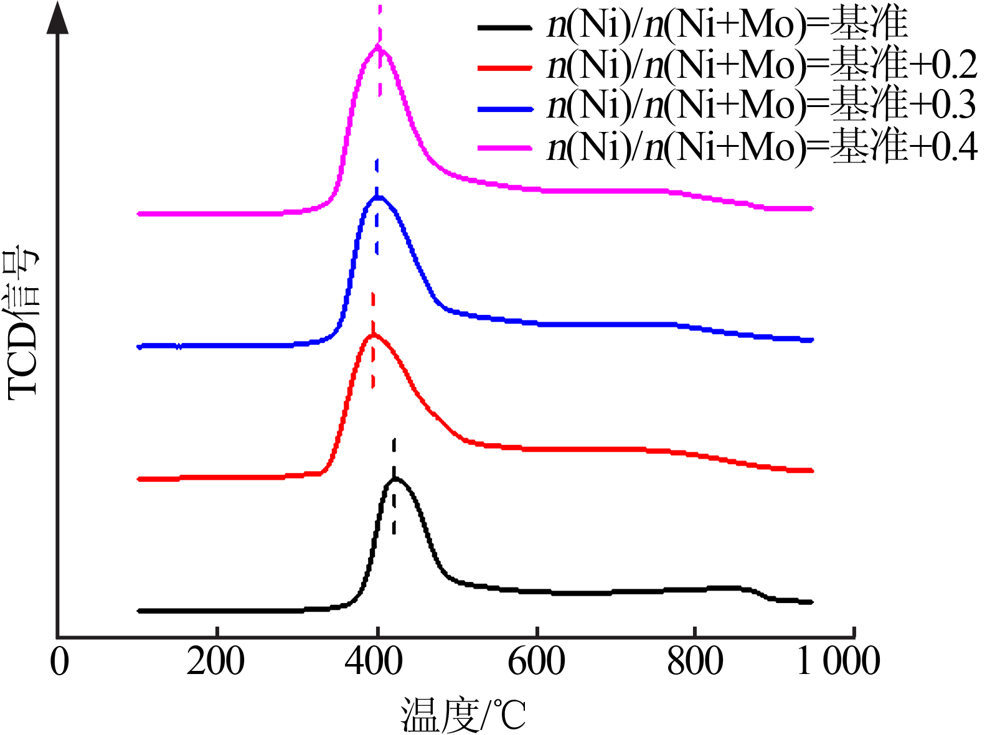
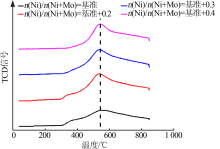
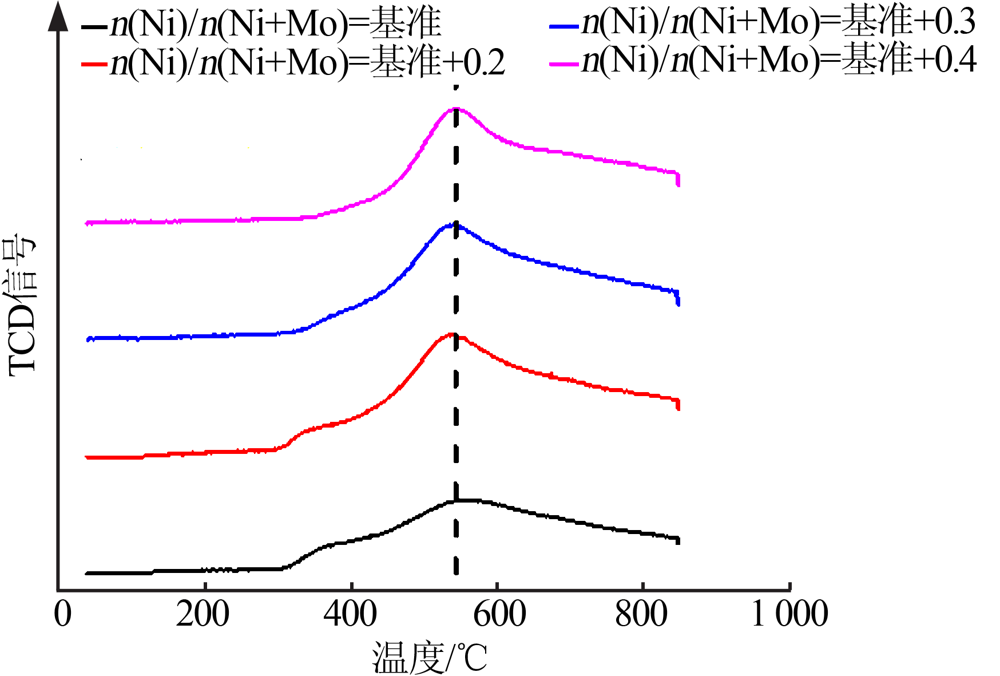
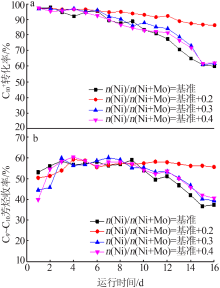
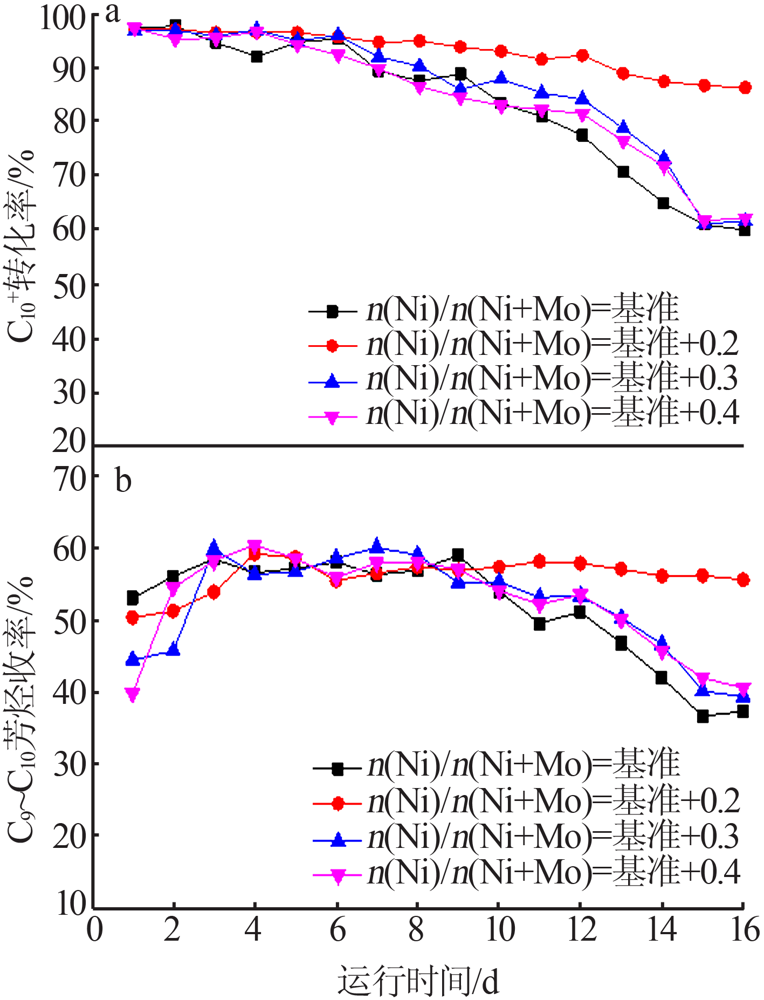
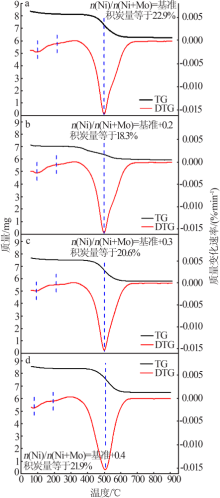
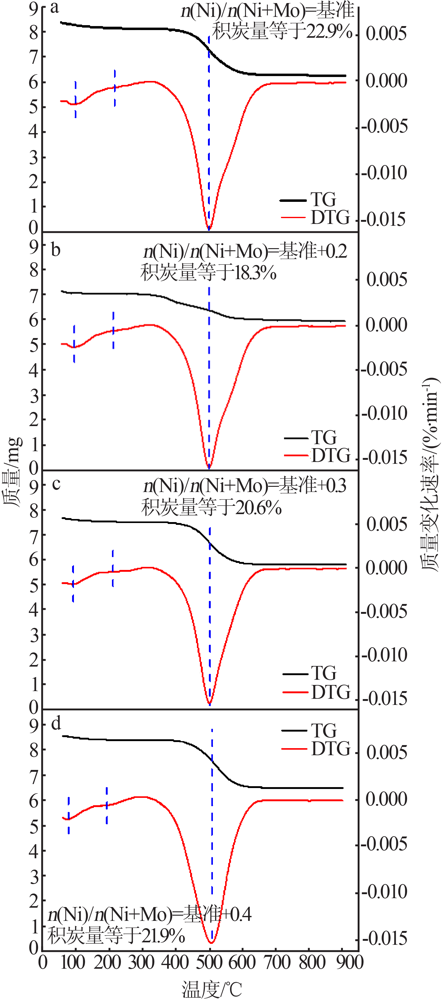
| [1] |
臧甲忠, 郭春垒, 范景新, 等. C9+重芳烃增产BTX技术进展[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(4):1278-1287.
|
| [2] |
孔德金, 祁晓岚, 朱志荣, 等. 重芳烃轻质化技术进展[J]. 化工进展, 2006, 25(9):983-987.
|
| [3] |
刘杰, 刘岗. C9芳烃深加工技术进展[J]. 精细化工原料及中间体, 2005(6):3-4,11.
|
| [4] |
曹根, 李东胜. 重芳烃的加工和应用[J]. 辽宁化工, 2007, 36(2):120-122.
|
| [5] |
宋夕平, 宋金富. 国内外苯、甲苯及二甲苯的增产技术[J]. 齐鲁石油化工, 2000, 28(2):138-141.
|
| [6] |
陈庆龄, 孔德金, 杨卫胜. 对二甲苯增产技术发展趋向[J]. 石油化工, 2004, 33(10):909-915.
|
| [7] |
KWAK B S. Applications of heterogeneous catalytic processes to the environmentally friendly synjournal of fine chemicals[J]. Catalysis Surveys from Asia, 2005, 9(2):103-116.
doi: 10.1007/s10563-005-5996-y
|
| [8] |
ICHIOKA R, YAMAKAWA S, OKINO H. Process for producing xylene:US, 5847256[P]. 1998-12-08.
|
| [9] |
王秋. 重芳烃轻质化工艺研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2001, 30(4):154-156.
|
| [10] |
刘永存, 肖寒, 王帅, 等. Ni-Mo-P/Beta-ZSM-5催化剂对四氢萘加氢裂化性能的研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2018, 50(6):81-85.
|
| [11] |
MAITY S K. Effect of preparation methods and content of phosphorus on hydrotreating activity[J]. Catalysis Today, 2008, 130:374-381.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2007.10.100
|
| [12] |
YANG Lei, PENG Chong, FANG Xiangchen, et al. Hierarchically macro-mesoporous Ni-Mo/Al2O3 catalysts for hydrod-esulfurization of dibenzothiophene[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2019, 121:68-72.
doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.12.020
|
| [13] |
ATANASOVA P, TABAKOVA T, VLADOV C, et al. Effect of pho- sphorus concentration and method of preparation on the structure of the oxide form of phosphorus-nickel-tungsten/alumina hydrotrea- ting catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 1997, 161(1/2):105-119.
doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(96)00392-4
|
| [14] |
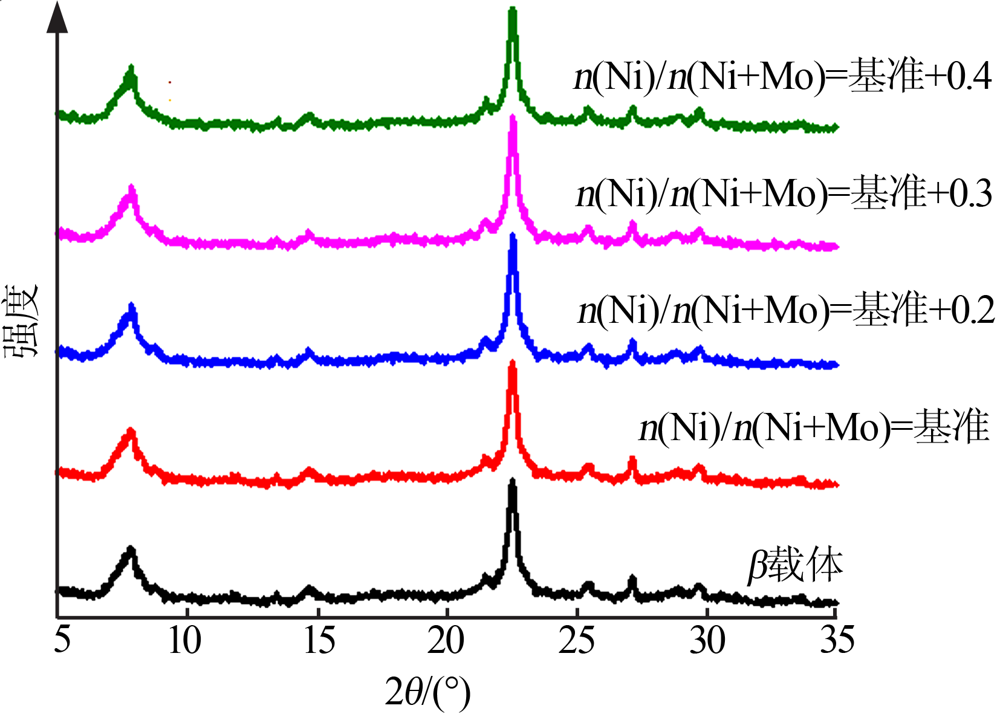
周同娜, 尹海亮, 柳云骐, 等. 磷含量对NiMo/γ-Al2O3催化剂活性相结构的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(1):69-74.
|
| [15] |
QU Lianglong, ZHANG Weiping, KOOYMAN P J, et al. MAS NMR, TPR,and TEM studies of the interaction of NiMo with alumina and silica-alumina supports[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2003, 215(1):7-13.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9517(02)00181-1
|
| [16] |
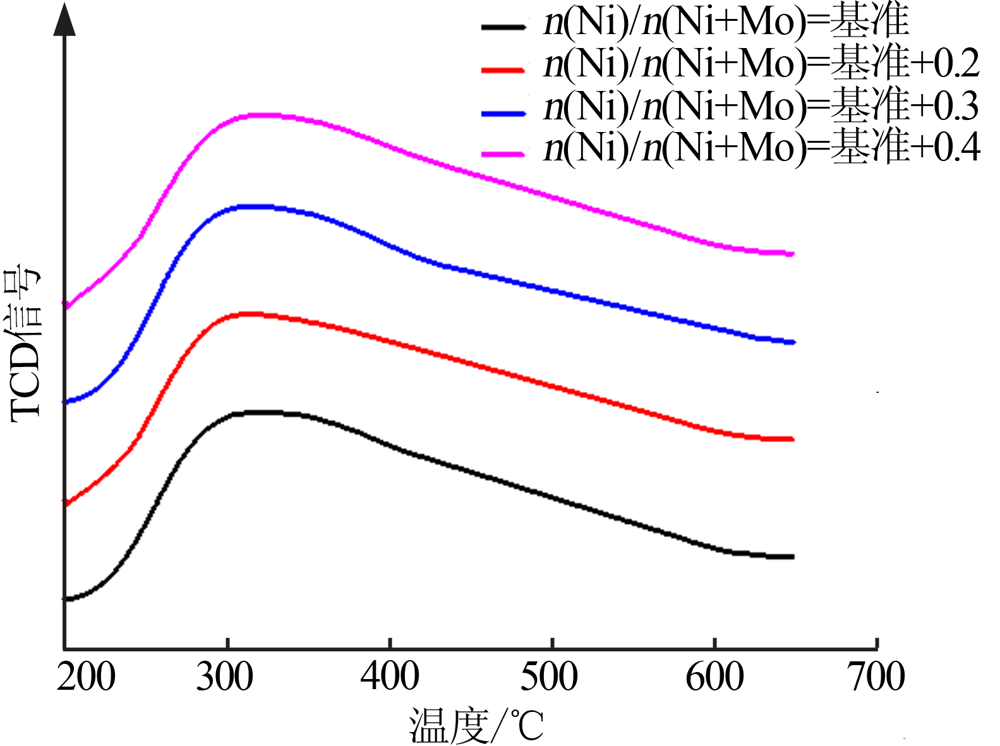
ARNOLDY P, JONGE J C M D, MOULIJN J A. Temperature-pro- grammed reduction of MoO3 and MoO2[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1985, 89(21):4517-4526.
doi: 10.1021/j100267a021
|
| [17] |
BRITO J L, LAINE J, PRATT K C. Temperature-programmed re- duction of Ni-Mo oxides[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1989, 24(2):425-431.
doi: 10.1007/BF01107422
|
| [18] |
BURCH R, COLLINS A. Reducibility of Ni-Mo/Al2O3 catalysts:A TPR study[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1993, 139(2):540-550.
doi: 10.1006/jcat.1993.1047
|
| [19] |
BURCH R, COLLINS A. Temperature-programmed reduction of Ni/Mo hydrotreating catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis, 1985, 18(2):389-400.
doi: 10.1016/S0166-9834(00)84015-4
|
| [20] |
LACROIX M, DUMONTEIL C, BREYSSE M, et al. Hydrogen acti-vation on alumina supported MoS2 based catalysts:Role of the promoter[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1999, 185(1):219-222.
doi: 10.1006/jcat.1999.2505
|
| [21] |
王雪, 孙昱东, 张强, 等. 催化剂上积炭结构和组成的分析研究方法[J]. 分析测试技术与仪器, 2013, 19(1):6-11.
|
| [22] |
张一卫. 以ZSM-5分子筛为载体的新型丙烷脱氢催化剂的研究[D]. 南京:东南大学, 2006.
|
 ),ZANG Jiazhong1,2(
),ZANG Jiazhong1,2( ),FAN Jingxin1,2,GUO Chunlei1,2,JIN Fengying1,2,ZHAO Xunzhi1,2
),FAN Jingxin1,2,GUO Chunlei1,2,JIN Fengying1,2,ZHAO Xunzhi1,2