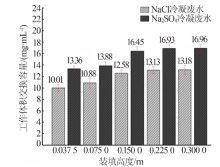
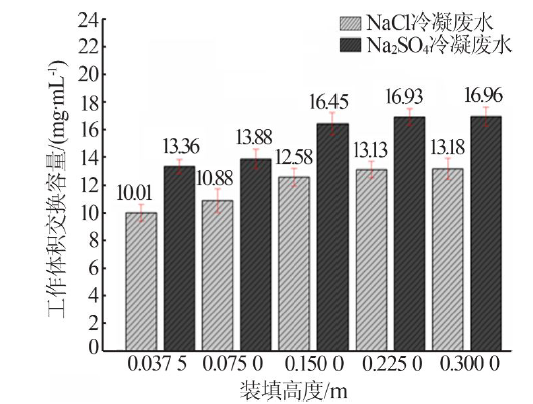
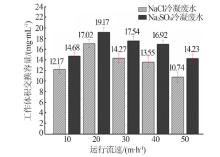
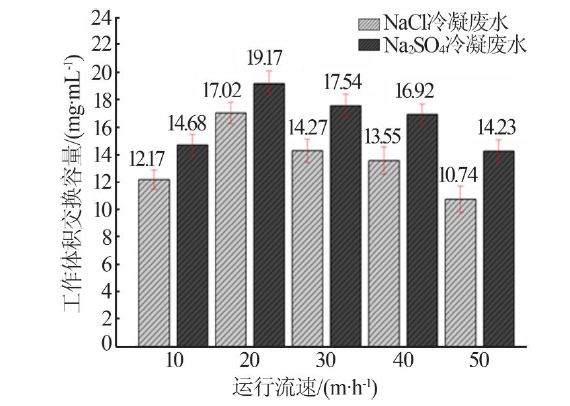
| [1] |
黄祥浩. 湿法冶金提取废弃电脑线路板中金的研究[D]. 武汉:武汉科技大学, 2019.
|
| [2] |
何健俊. MVR处理高浓度废水产生的冷凝水水质研究[J]. 低碳世界, 2017(3):30-31.
|
| [3] |
张成琳, 刘清风. 钢筋混凝土中氯盐和硫酸盐耦合侵蚀研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(1):65-73.
|
| [4] |
王霄. 电厂给水处理中不同除盐工艺研究、经济性比较与针对不同水质的方案设计[D]. 青岛:青岛科技大学, 2015.
|
| [5] |
程浩, 陈亚中, 崔鹏. A222型阴离子交换树脂脱除HPPH+体系中的SO42-、NO3-[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(S1):316-320.
|
| [6] |
SARBATLY R, CHIAM C K. Evaluation of geothermal energy in desalination by vacuum membrane distillation[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 112:737-746.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.12.028
|
| [7] |
李长海, 党小建, 张雅潇. 电渗析技术及其应用[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2012, 28(4):27-30.
|
| [8] |
STRATHMANN H. Electrodialysis,a mature technology with a multitude of new applications[J]. Desalination, 2010, 264:268-288.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.04.069
|
| [9] |
XU P, DREWES J E, KIM T U, et al. Effect of membrane fouling on transport of organic contaminants in NF/RO membrane applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2005, 279(1):165-175.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.001
|
| [10] |
NGHIEM L D, SCHÄFER A I. Critical risk points of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis processes in water recycling applications[J]. Desalination, 2005, 187(1):303-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.089
|
| [11] |
李宏鹏. 基于离子交换的低盐废水处理技术研究[D]. 济南:济南大学, 2020.
|
| [12] |
徐勇, 陈青柏, 王建友. 离子交换水软化技术研究与应用进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(S2):319-328.
|
| [13] |
陈仁. 大孔阴离子交换树脂去除溴酸盐的研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学, 2015.
|
| [14] |
李恺雄, 池勇志, 付翠莲, 等. 湿法冶金MVR废水中溶解性有机溶剂和萃取剂的去除[J]. 工业水处理, 2021, 41(2):33-37.
|
| [15] |
YUAN C Y, SUN Y Z, YANG Y, et al. Performance and modeling of bromide dynamic adsorption onto D301 anion exchange resin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2020, 20(6):655-666
|
| [16] |
吴赵敏, 杨林, 王辛龙, 等. 动态离子交换法处理电子行业蚀刻含铝废酸工艺研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2021, 53(2):61-65,70.
|
| [17] |
庄海波, 杨林, 邓强, 等. 离子交换法脱除磷酸中锰离子的动态吸附研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2021, 53(1):18-23.
|
| [18] |
王璐, 冯京京, 陶敏莉. 季铵离子化腈纶纤维对染料的动态吸附性能[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2020, 37(2):73-79.
|
| [19] |
GB/T 50109—2014 工业用水软化除盐设计规范[S].
|
| [20] |
张拿慧. 201×7强碱性阴离子交换树脂吸附浓海水中溴的应用基础研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工业大学, 2009.
|
 ),CHI Yongzhi1,2(
),CHI Yongzhi1,2( ),LI Kaixiong1,2,TIAN Sufeng1,2,LIU Muzhi3
),LI Kaixiong1,2,TIAN Sufeng1,2,LIU Muzhi3