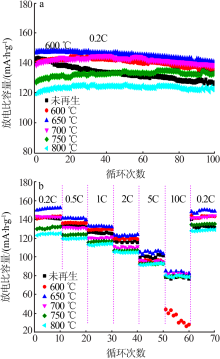
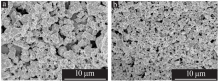
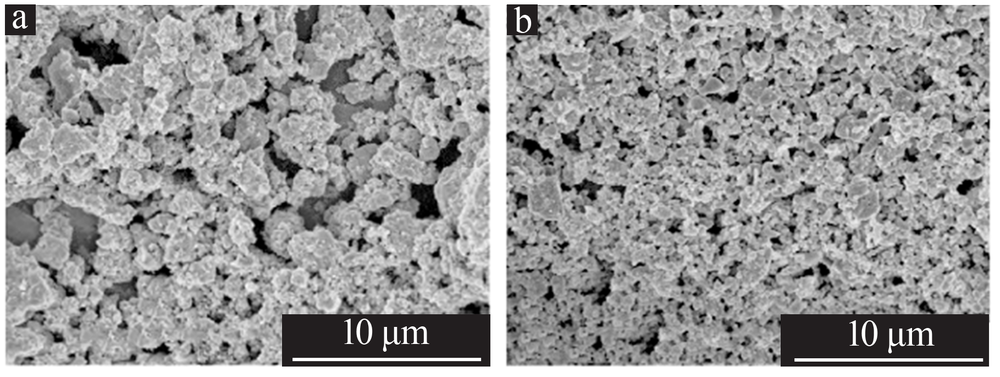
| [1] |
Wang L H, Li J, Zhou H M, et al. Regeneration cathode material mi-xture from spent lithium iron phosphate batteries[J]. Journal of Ma-terials Science:Materials in Electronics, 2018,29(11):9283-9290.
|
| [2] |
冉敬文, 刘鑫, 裴军, 等. 我国锂资源开发的生产工艺现状[J]. 广州化工, 2016,44(13):4-5,37.
|
| [3] |
Kim H S, Shin E J. Re-synjournal and electrochemical characteris-tics of LiFePO4 cathode materials recycled from scrap electrodes[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2013,34(3):851-855.
doi: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.3.851
|
| [4] |
陈江平, 宋大卫, 宋继顺, 等. 废旧磷酸铁锂电池中的正极材料的绿色回收和高效利用[C]// 第31届全国化学与物理电源学术年会论文集.天津:中国电子学会化学与物理电源技术分会, 2015: 171-172.
|
| [5] |
Li X, Zhang J, Song D, et al. Direct regeneration of recycled cathode material mixture from scrapped LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Journal of Po-wer Sources, 2017,345:78-84.
|
| [6] |
Song X, Hu T, Liang C, et al. Direct regeneration of cathode materi-als from spent lithium iron phosphate batteries using a solid phase sintering method[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7(8):4783-4790.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA27210J
|
| [7] |
杨秋菊, 赵世超, 王楠, 等. 废旧动力锂离子电池中磷酸铁锂的再生[J]. 电池, 2014,44(1):60-62.
|
| [8] |
卞都成, 刘树林, 孙永辉, 等. 废旧LiFePO4正极材料的循环利用及电化学性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2015,43(11):1511-1516.
|
| [9] |
谢英豪, 余海军, 欧彦楠, 等. 从废旧动力电池中回收制备磷酸铁锂[J]. 电源技术, 2014,38(12):2239-2241,2257.
|
| [10] |
陈永珍, 黎华玲, 宋文吉, 等. 废旧磷酸铁锂材料的固相再生及电化学性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2018,69(12):5316-5325.
|
| [11] |
Pei F, Wu Y, Zhang W H, et al. Preparing LiFePO4 using recovered materials from waste Li-ion battery[J]. Advanced Materials Rese-arch, 2013, 726-731:2940-2944.
|
| [12] |
董重瑞, 赵光金, 赵栋, 等. 废旧电池磷酸铁锂正极的中温回收及再生[J]. 电源技术, 2019,43(2):201-203,240.
|
| [13] |
卞都成, 刘树林, 田院. 固相补锂法再利用废旧LiFePO4正极材料及电化学性能[J]. 无机盐工业, 2016,48(2):71-74.
|
| [14] |
陈永珍, 黎华玲, 宋文吉, 等. 废旧磷酸铁锂材料碳热还原固相再生方法[J]. 化工进展, 2018,37(S1):133-140.
|
 ),Dong Peng2,3,4,Meng Qi2,3,4(
),Dong Peng2,3,4,Meng Qi2,3,4( ),Yang Xuan1,3,4,Zhou Siyuan1,3,4
),Yang Xuan1,3,4,Zhou Siyuan1,3,4