Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (10): 11-23.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0586
• Reviews and Special Topics • Previous Articles Next Articles
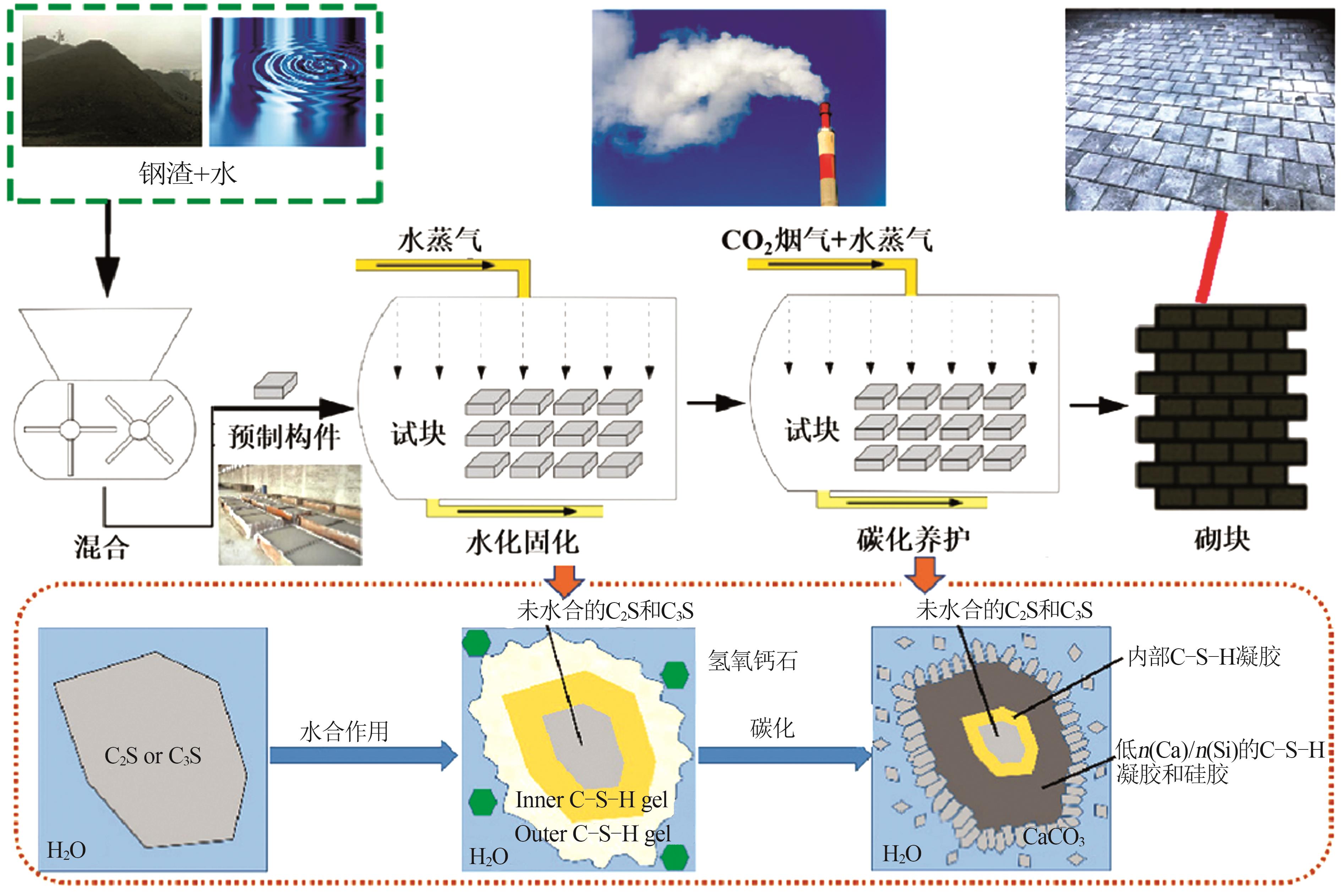
Research progress on typical calcium-based industrial solid waste mineralization process and utilization in building materials
JIN Zhouzheng1,2( ), ZHANG Donghui1, PENG Xueping2, LIN Minyan2, DAI Zhongyuan2, CHEN Changhua2(
), ZHANG Donghui1, PENG Xueping2, LIN Minyan2, DAI Zhongyuan2, CHEN Changhua2( )
)
- 1. School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300350,China
2. Tianjin Cement Ind Design & Res Inst Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300131,China
-
Received:2024-11-05Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-10-27 -
Contact:CHEN Changhua E-mail:jinzhouzheng@sinoma-tianjin.cn;chenchanghua@sinoma-tianjin.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIN Zhouzheng, ZHANG Donghui, PENG Xueping, LIN Minyan, DAI Zhongyuan, CHEN Changhua. Research progress on typical calcium-based industrial solid waste mineralization process and utilization in building materials[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2025, 57(10): 11-23.
share this article
| [1] | DUNANT C F, JOSEPH S, PRAJAPATI R,et al.Electric recycling of Portland cement at scale[J].Nature,2024,629(8014):1055-1061. |
| [2] | BANG J, CHOI J, HONG W T,et al.Influences of binder composition and carbonation curing condition on the compressive strength of alkali-activated cementitious materials:A review[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2023,74:102551. |
| [3] | VAN VUUREN D P, STEHFEST E, GERNAAT D E H J,et al.Alternative pathways to the 1.5 ℃ target reduce the need for negative emission technologies[J].Nature Climate Change,2018,8(5):391-397. |
| [4] | AGENCY I E.Cement technology roadmap:Carbon emissions reductions up to 2050[M].Paris:OECD,2009. |
| [5] | SHAH I H, MILLER S A, JIANG Daqian,et al.Cement substitution with secondary materials can reduce annual global CO2 emissions by up to 1.3 gigatons[J].Nature Communications,2022,13:5758. |
| [6] | 王栋民,许栋,张祖华,等.水泥基胶凝材料演变与展望[J/OL].建筑材料学报,2025[2025-08-07].https://link.cnki.net/urlid/31.1764.TU.20250507.0945.002. |
| WANG Dongmin, XU Dong, ZHANG Zuhua,et al.The evolution and prospects of cement-based cementitious materials[J/OL].Journal of Building Materials,2025[2025-08-07].https://link.cnki.net/urlid/31.1764.TU.20250507.0945.002. | |
| [7] | POPIELAK P, MAJCHRZAK-KUCĘBA I, WAWRZYŃCZAK D.Climate change mitigation with CCUS:A case study with benchmarking for selected countries in adapting the European Union′s Green Deal[J].International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2024,132:104057. |
| [8] | NATH F, MAHMOOD M N, YOUSUF N.Recent advances in CCUS:A critical review on technologies,regulatory aspects and economics[J].Geoenergy Science and Engineering,2024,238:212726. |
| [9] | ZHANG Zheyuan, LEI Ying, RICHARD LIEW J Y,et al.Embodied carbon saving potential of using recycled materials as cement substitute in Singapore′s buildings[J].NPJ Materials Sustainability,2024,2:27. |
| [10] | BAKER R W, FREEMAN B, KNIEP J,et al.CO2 capture from cement plants and steel mills using membranes[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(47):15963-15970. |
| [11] | METZ B, DAVIDSON O, De CONINCK H C,et al.IPCC special report on carbon dioxide capture and storage[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,2005. |
| [12] | BOBICKI E R, LIU Qingxia, XU Zhenghe,et al.Carbon capture and storage using alkaline industrial wastes[J].Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2012,38(2):302-320. |
| [13] | SANNA A, UIBU M, CARAMANNA G,et al.A review of mineral carbonation technologies to sequester CO2 [J].Chemical Society Reviews,2014,43(23):8049-8080. |
| [14] | MIN Yujia, JUN Y S.Wollastonite carbonation in water-bearing supercritical CO2:Effects of water saturation conditions,temperature,and pressure[J].Chemical Geology,2018,483:239-246. |
| [15] | DAVAL D, MARTINEZ I, CORVISIER J,et al.Carbonation of Ca-bearing silicates,the case of wollastonite:Experimental investigations and kinetic modeling[J].Chemical Geology,2009,265(1/2):63-78. |
| [16] | WANG Fei, DREISINGER D, JARVIS M,et al.Kinetics and mechanism of mineral carbonation of olivine for CO2 sequestration[J].Minerals Engineering,2019,131:185-197. |
| [17] | 季洪峰,李灿华,都刚,等.固废源钙基碳捕集剂制备及抗烧结性研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(3):28-35. |
| JI Hongfeng, LI Canhua, DU Gang,et al.Research progress of preparation and sintering resistance of calcium-based CO2 trapping materials from solid waste sources[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(3):28-35. | |
| [18] | SKOCEK J, ZAJAC M, HAHA M BEN.Carbon Capture and Utilization by mineralization of cement pastes derived from recycled concrete[J].Scientific Reports,2020,10:5614. |
| [19] | WANG Min, CHEN Dong, WANG Hui,et al.A review on fly ash high-value synthesis utilization and its prospect[J].Green Energy and Resources,2024,2(1):100062. |
| [20] | WANG Chenglong, JIANG Huayu, MIAO Endong,et al.Accelerated CO2 mineralization technology using fly ash as raw material:Recent research advances[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2024,488:150676. |
| [21] | LIU Jun, WANG Zhengdong, XIE Guangming,et al.Resource utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash-cement and alkali-activated cementitious materials:A review[J].Science of the Total Environment,2022,852:158254. |
| [22] | RAKHIMOVA N R, RAKHIMOV R Z.Toward clean cement technologies:A review on alkali-activated fly-ash cements incorporated with supplementary materials[J].Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids,2019,509:31-41. |
| [23] | MCCARTHY M J, YAKUB H I, CSETENYI L J.Fly ash from modern coal-fired power technologies:Chloride ingress and carbonation of concrete[J].Magazine of Concrete Research,2020,72(10):486-498. |
| [24] | 张祥成,孟永彪.浅析中国粉煤灰的综合利用现状[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(2):1-5. |
| ZHANG Xiangcheng, MENG Yongbiao.Brief analysis on present situation of comprehensive utilization of fly ash in China[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(2):1-5. | |
| [25] | FENG Wei, WAN Zhijian, DANIELS J,et al.Synthesis of high quality zeolites from coal fly ash:Mobility of hazardous elements and environmental applications[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2018,202:390-400. |
| [26] | 冯文丽,吕学斌,熊健,等.粉煤灰高附加值利用研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(4):25-31. |
| FENG Wenli, Xuebin Lü, XIONG Jian,et al.Research progress of high added value utilization of coal fly ash[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(4):25-31. | |
| [27] | ELONEVA S, SAID A, FOGELHOLM C J,et al.Preliminary assessment of a method utilizing carbon dioxide and steelmaking slags to produce precipitated calcium carbonate[J].Applied Energy,2012,90(1):329-334. |
| [28] | MONTES-HERNANDEZ G, PÉREZ-LÓPEZ R, RENARD F,et al.Mineral sequestration of CO2 by aqueous carbonation of coal combustion fly-ash[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2008,161:1347-1354. |
| [29] | ULIASZ-BOCHEŃCZYK A, MOKRZYCKI E.The potential of FBC fly ashes to reduce CO2 emissions[J].Scientific Reports,2020,10:9469. |
| [30] | SANNA A,DRI M, HALL M R,et al.Waste materials for carbon capture and storage by mineralisation(CCSM):A UK perspecti- ve[J].Applied Energy,2012,99:545-554. |
| [31] | SANNA A, RAMLI I, MAROTO-VALER M M.Development of sodium/lithium/fly ash sorbents for high temperature post-combustion CO2 capture[J].Applied Energy,2015,156:197-206. |
| [32] | NYAMBURA M G, MUGERA G W, FELICIA P L,et al.Carbonation of brine impacted fractionated coal fly ash:Implications for CO2 sequestration[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2011,92(3):655-664. |
| [33] | TAMILSELVI DANANJAYAN R R, KANDASAMY P, ANDIMUTHU R.Direct mineral carbonation of coal fly ash for CO2 sequestration[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2016,112:4173-4182. |
| [34] | PAN Shuyuan, LIU H L, CHANG E E,et al.Multiple model approach to evaluation of accelerated carbonation for steelmaking slag in a slurry reactor[J].Chemosphere,2016,154:63-71. |
| [35] | MAYES W, RILEY A L, GOMES H I,et al.Atmospheric CO2 sequestration in iron and steel slag:Consett,County Durham,Unit-ed Kingdom[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(14):7892-7900. |
| [36] | MOHAMED A O, GAMAL M EL, HAMEEDI S M,et al.Carbonation of steel slag[M]//Sustainable Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Waste Management.Amsterdam:Elsevier,2023:327-372. |
| [37] | HUANG Xiaoli, ZHANG Junfei, ZHANG Lei.Accelerated carbonation of steel slag:A review of methods,mechanisms and influencing factors[J].Construction and Building Materials,2024,411:134603. |
| [38] | ZHANG Yongpeng, YING Yimei, XING Lei,et al.Carbon dioxide reduction through mineral carbonation by steel slag[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2025,152:664-684. |
| [39] | UKWATTAGE N L, RANJITH P G, LI X.Steel-making slag for mineral sequestration of carbon dioxide by accelerated carbonation[J].Measurement,2017,97:15-22. |
| [40] | MAHOUTIAN M, GHOULEH Z, SHAO Y.Carbon dioxide activated ladle slag binder[J].Construction and Building Materials,2014,66:214-221. |
| [41] | QUAGHEBEUR M, NIELSEN P, HORCKMANS L,et al.Accelerated carbonation of steel slag compacts:Development of high-strength construction materials[J].Frontiers in Energy Research,2015,3:52. |
| [42] | FANG Yanfeng, SHAN Jinxue, WANG Qinghe,et al.Semi-dry and aqueous carbonation of steel slag:Characteristics and properties of steel slag as supplementary cementitious materials[J].Construction and Building Materials,2024,425:135981. |
| [43] | SANTOS R M, FRANÇOIS D, MERTENS G,et al.Ultrasound-intensified mineral carbonation[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2013,57(1/2):154-163. |
| [44] | SANTOS R M, VAN BOUWEL J, VANDEVELDE E,et al.Accelerated mineral carbonation of stainless steel slags for CO2 storage and waste valorization:Effect of process parameters on geochemical properties[J].International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2013,17:32-45. |
| [45] | VAN ZOMEREN A, VAN DER LAAN S R, KOBESEN H B A,et al.Changes in mineralogical and leaching properties of converter steel slag resulting from accelerated carbonation at low CO2 pressure[J].Waste Management,2011,31(11):2236-2244. |
| [46] | JIANG Yi, LING T C, SHI Caijun,et al.Characteristics of steel slags and their use in cement and concrete:A review[J].Resources,Conservation and Recycling,2018,136:187-197. |
| [47] | GHOULEH Z, GUTHRIE R I L, SHAO Yixin.High-strength KOBM steel slag binder activated by carbonation[J].Construction and Building Materials,2015,99:175-183. |
| [48] | NAIDU T S, SHERIDAN C M, VAN DYK L D.Basic oxygen furnace slag:Review of current and potential uses[J].Minerals Engineering,2020,149:106234. |
| [49] | ZHAO Zhiguang, QU Xiaoling, LI Fangxian,et al.Effects of steel slag and silica fume additions on compressive strength and thermal properties of lime-fly ash pastes[J].Construction and Building Materials,2018,183:439-450. |
| [50] | GAO Pengfei, WANG Jian, CUI Jianjun,et al.Experimental study on the effects of carbonated steel slag fine aggregate on the expansion rate,mechanical properties and carbonation depth of mortar[J].Materials,2024,17(13):3279. |
| [51] | BRAND A S, ROESLER J R.Steel furnace slag aggregate expansion and hardened concrete properties[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2015,60:1-9. |
| [52] | PAN Shuyuan, CHIANG P C, CHEN Y H,et al.Performance evaluation of aqueous carbonation for steelmaking slag:Process chemistry[J].Energy Procedia,2013,37:115-121. |
| [53] | YI Yuanrong, LIN Yue, DU Yuncong,et al.Accelerated carbonation of ladle furnace slag and characterization of its mineral phase[J].Construction and Building Materials,2021,276:122235. |
| [54] | PAN Shuyuan, CHIANG P C, CHEN Y H,et al. Ex situ CO2 capture by carbonation of steelmaking slag coupled with metalworking wastewater in a rotating packed bed[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(7):3308-3315. |
| [55] | ZHANG Zhenqing, ZHENG Keren, CHEN Lou,et al.Review on accelerated carbonation of calcium-bearing minerals:Carbonation behaviors,reaction kinetics,and carbonation efficiency improvement[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2024,86:108826. |
| [56] | KODAMA S, NISHIMOTO T, YAMAMOTO N,et al.Development of a new pH-swing CO2 mineralization process with a recyclable reaction solution[J].Energy,2008,33(5):776-784. |
| [57] | MOHAMED A O, EL-GAMAL M, HAMEEDI S.Advanced mineral carbonation:An approach to accelerate CO2 sequestration using steel production wastes and integrated fluidized bed react-or[M]//Energy Geotechnics.Cham:Springer International Publishing,2018:387-393. |
| [58] | MA Hang, FENG Xiao, YANG Yabin,et al.Preparation of feed grade calcium formate from calcium carbide residue[J].Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy,2016,18(6):1905-1915. |
| [59] | MA Hailong, CUI Chong, MA Wentao,et al.Enhancement mechanism of new type autoclaved calcium carbide residue shell-aggregate on concrete[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2016,72:146-154. |
| [60] | HORPIBULSUK S, MUNSRAKEST V, UDOMCHAI A,et al.Strength of sustainable non-bearing masonry units manufactured from calcium carbide residue and fly ash[J].Construction and Building Materials,2014,71:210-215. |
| [61] | 赵娜,郭小惠,伍永福,等.二次铝灰与工业废渣共处理研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2025:57(8):21-27. |
| ZHAO Na, GUO Xiaohui, WU Yongfu,et al.Research progress on co-treatment of secondary aluminum dross and industrial waste residues[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2025,57(8):21-27. | |
| [62] | JIMOF O A, ARIFFIN K S, HUSSIN H B,et al.Synthesis of precipitated calcium carbonate:A review[J].Carbonates and Evaporites,2018,33(2):331-346. |
| [63] | MOHAMED A O, GAMAL M EL, HAMEEDI S M,et al.Carbonation of calcium carbide residue[M]//Sustainable Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Waste Management.Amsterdam:Elsevier,2023:373-413. |
| [64] | RAMASAMY P, PERIATHAMBY A, IBRAHIM S.Carbide sludge management in acetylene producing plants by using vacuum filtration[J].Waste Management & Research:The Journal for a Sustainable Circular Economy,2002,20(6):536-540. |
| [65] | MAKARATAT N, JATURAPITAKKUL C, NAMARAK C,et al.Effects of binder and CaCl2 contents on the strength of calcium carbide residue-fly ash concrete[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2011,33(3):436-443. |
| [66] | ABDULMATIN A, KHONGPERMGOSON P, JATURAPITAKKUL C,et al.Use of eco-friendly cementing material in concrete made from bottom ash and calcium carbide residue[J].Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2018,43(4):1617-1626. |
| [67] | LI Wenxiu, HUANG Yan, WANG Tao,et al.Preparation of calcium carbonate nanoparticles from waste carbide slag based on CO2 mineralization[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,363:132463. |
| [68] | LIU Kai, ZHAO Bosheng, WU Yu,et al.Bubbling synthesis and high-temperature CO2 adsorption performance of CaO-based adsorbents from carbide slag[J].Fuel,2020,269:117481. |
| [69] | ZHOU Jun, SHENG Zimo, LI Tiantian,et al.Preparation of hardened tiles from waste phosphogypsum by a new intermittent pressing hydration[J].Ceramics International,2016,42(6):7237-7245. |
| [70] | 董泽,翟延波,任志威,等.磷石膏建材资源化利用研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2022,54(4):5-9. |
| DONG Ze, ZHAI Yanbo, REN Zhiwei,et al.Research progress on phosphogypsum utilization in building materials[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2022,54(4):5-9. | |
| [71] | WANG Jinman, YANG Peiling.Potential flue gas desulfurization gypsum utilization in agriculture:A comprehensive review[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018,82:1969-1978. |
| [72] | KORALEGEDARA N H, PINTO P X, DIONYSIOU D D,et al.Recent advances in flue gas desulfurization gypsum processes and applications:A review[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2019,251:109572. |
| [73] | LIU Weizao, WANG Xiaomei, LU Zhenpu,et al.Preparation of synthetic rutile via selective sulfation of ilmenite with (NH4)2SO4 followed by targeted removal of impurities[J].Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2017,25(6):821-828. |
| [74] | SONG K, JANG Y N, KIM W,et al.Precipitation of calcium carbonate during direct aqueous carbonation of flue gas desulfurization gypsum[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,213:251- 258. |
| [75] | DING Wenjin, CHEN Qiuju, SUN Hongjuan,et al.Modified phosphogypsum sequestrating CO2 and characteristics of the carbonation product[J].Energy,2019,182:224-235. |
| [76] | DLUGOGORSKI B Z, BALUCAN R D.Dehydroxylation of serpentine minerals:Implications for mineral carbonation[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2014,31:353-367. |
| [77] | LEE M G, JANG Y N, RYU K W,et al.Mineral carbonation of flue gas desulfurization gypsum for CO2 sequestration[J].Energy,2012,47(1):370-377. |
| [78] | ZHAO Hongtao, LI Huiquan, BAO Weijun,et al.Experimental study of enhanced phosphogypsum carbonation with ammonia under increased CO2 pressure[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2015,11:10-19. |
| [79] | AZDARPOUR A, ASADULLAH M, MOHAMMADIAN E,et al.Mineral carbonation of red gypsum via pH-swing process:Effect of CO2 pressure on the efficiency and products characteristics[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,264:425-436. |
| [80] | AZDARPOUR A, ASADULLAH M, JUNIN R,et al.Direct carbonation of red gypsum to produce solid carbonates[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2014,126:429-434. |
| [81] | CLARK C, JAMBECK J, TOWNSEND T.A review of construction and demolition debris regulations in the United States[J].Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology,2006,36(2):141-186. |
| [82] | PHIL R.The negative emission potential of alkaline materials[J].Nature Communications,2019,10:1401. |
| [83] | TOWNSEND T G, INGWERSEN W W, NIBLICK B,et al.CDDPath:A method for quantifying the loss and recovery of construction and demolition debris in the United States[J].Waste Management,2019,84:302-309. |
| [84] | MOHAMED A O, GAMAL M EL, HAMEEDI S M,et al.Carbonation of cement-based construction waste[M]//Sustainable Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Waste Management.Amsterdam:Elsevier,2023:415-448. |
| [85] | KATSUYAMA Y, YAMASAKI A, IIZUKA A,et al.Development of a process for producing high-purity calcium carbonate (CaCO3) from waste cement using pressurized CO2 [J].Environmental Progress,2005,24(2):162-170. |
| [86] | HUNTZINGER D N, GIERKE J S, KAWATRA S K,et al.Carbon dioxide sequestration in cement kiln dust through mineral carbonation[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2009,43(6):1986-1992. |
| [87] | KLEE H, COLES E.The cement sustainability initiative-implementing change across a global industry[J].Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management,2004,11(2):114-120. |
| [88] | ROTH H R, LEWIS M, HANCOCK L.The green building materials manual:A reference to environmentally sustainable initiatives and evaluation methods[M].Cham:Springer International Publishing,2021. |
| [89] | JIAN Simin, WU Bo, HU Nan.Environmental impacts of three waste concrete recycling strategies for prefabricated components through comparative life cycle assessment[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,328:129463. |
| [90] | KOU Shicong, ZHAN Baojian, POON C S.Use of a CO2 curing step to improve the properties of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2014,45:22- 28. |
| [91] | DUAN Zhenhao, SUN Rui.An improved model calculating CO2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions from 273 to 533 K and from 0 to 2 000 bar[J].Chemical Geology,2003,193(3/4):257-271. |
| [92] | ISMAIL R, CIONITA T, SHING W L,et al.Synthesis and characterization of calcium carbonate obtained from green musseland crab shells as a biomaterials candidate[J].Materials,2022,15(16):5712. |
| [93] | SHUTO D, IGARASHI K, NAGASAWA H,et al.CO2 fixation process with waste cement powder via regeneration of alkali and acid by electrodialysis:Effect of operation conditions[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2015,54(25):6569-6577. |
| [1] | LI Yang, LOU Feijian, SUI Xin, LI Keyan, LIU Fei, GUO Xinwen. Preparation of amine-functionalized fumed SiO2 materials and their performance for CO2 adsorption [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(2): 38-43. |
| [2] | NI Dong, TANG Liang, HE Zhaoyi, WANG Jian, PEI Shanshan, XIA Lei. Study on sulfate activation performance of electrolytic manganese residue in hydrated lime-slag system [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(11): 151-157. |
| [3] | JI Hongfeng, LI Canhua, DU Gang, ZHANG Yongzhu, XU Wenzhen, LI Minghui. Research progress of preparation and sintering resistance of calcium-based CO2 trapping materials from solid waste sources [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 28-35. |
| [4] | TIAN Yijuan,YAN Chaoqun,CHENG Zhiliang,QUAN Xuejun,LI Gang. Detoxification of Cr(Ⅵ) from chromite ore processing residue by pyrolysis with citrus peel [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12): 129-134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||