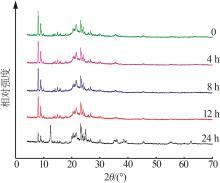
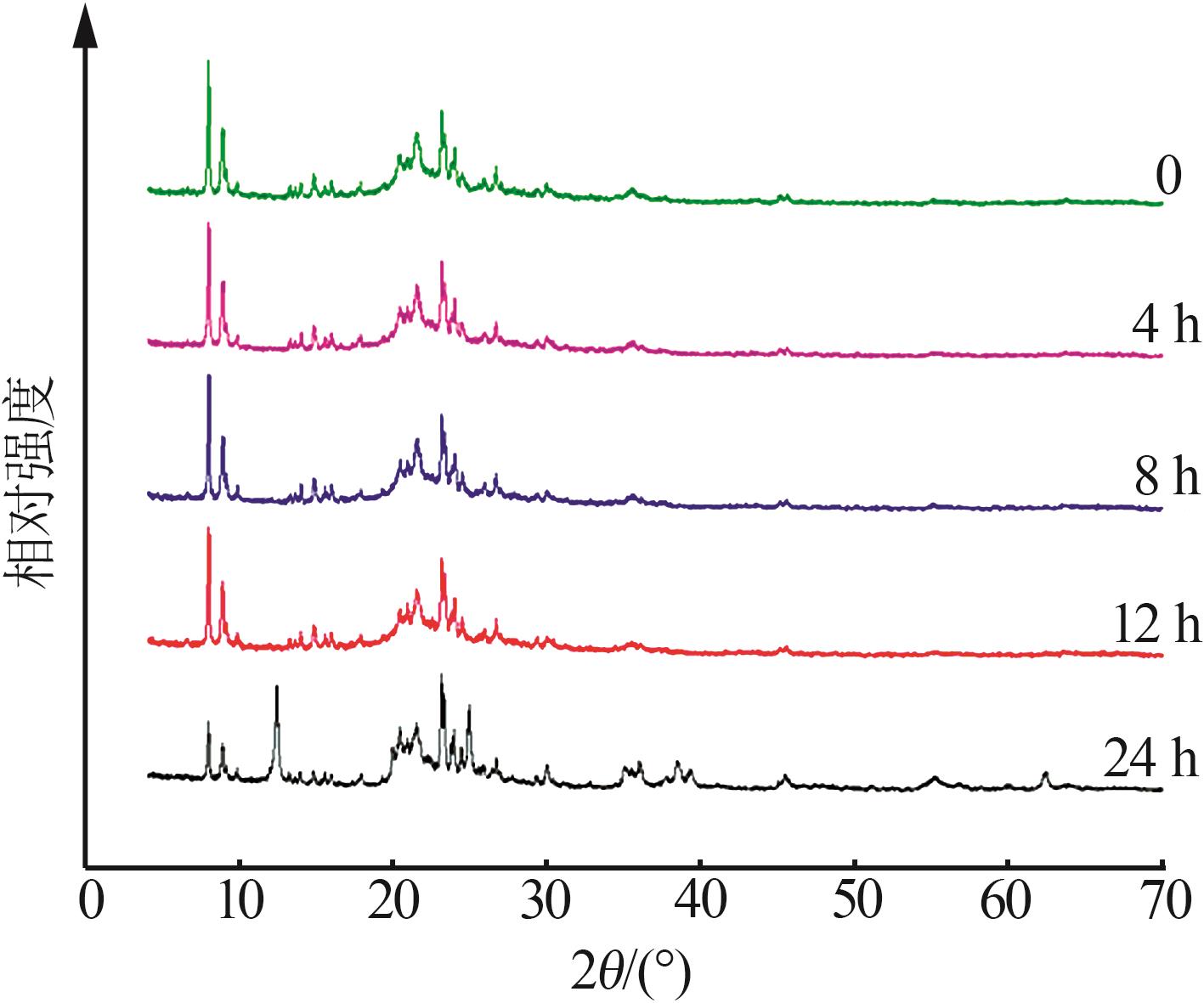
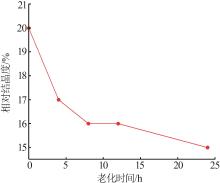
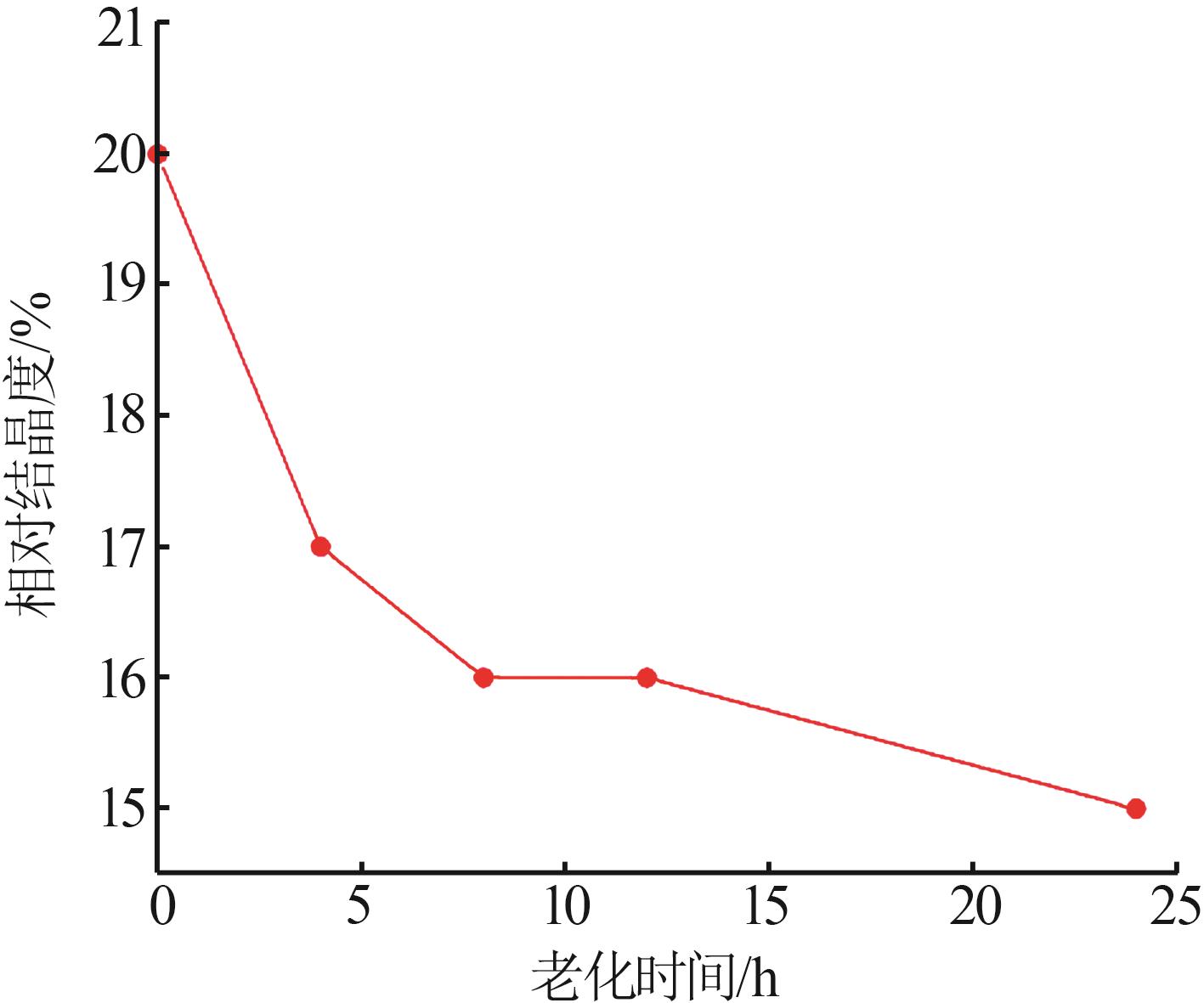
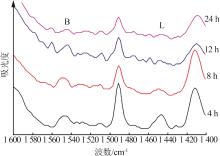
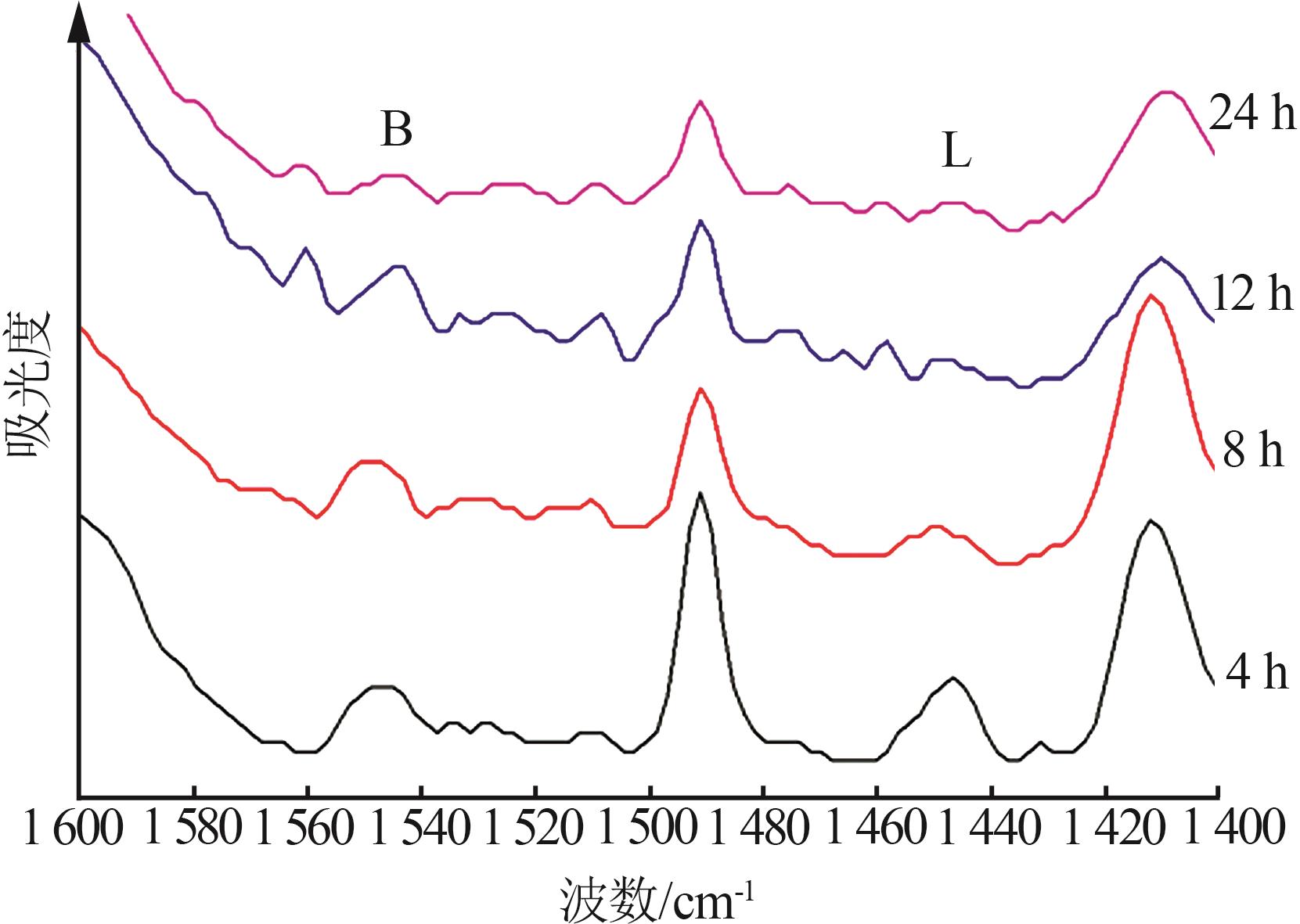
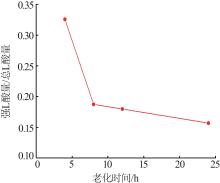
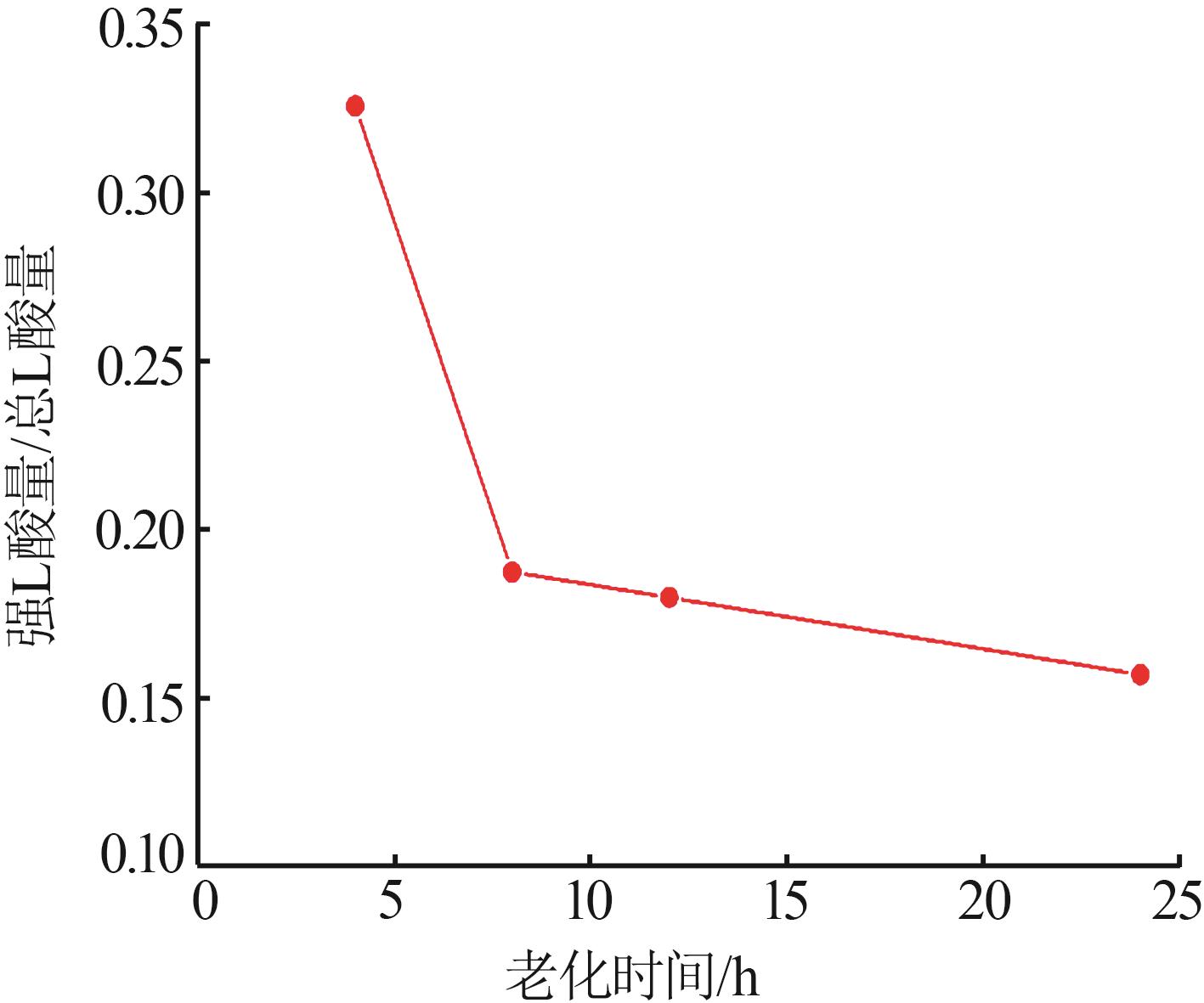
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 55-60.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0445
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on effect of hydrothermal aging on physicochemical properties of propylene additives
ZHAO Mingzhi1( ), DUAN Hongchang1(
), DUAN Hongchang1( ), SUN Xueqin1, LÜ Penggang1, LI Xueli2, LIU Tao1, CAO Gengzhen1
), SUN Xueqin1, LÜ Penggang1, LI Xueli2, LIU Tao1, CAO Gengzhen1
- 1.Lanzhou Petrochemical Research Center, Petrochemical Research Institute, PetroChina, Lanzhou 730060, China
2.School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yan′an University, Yan′an 716000, China
-
Received:2023-09-06Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:DUAN Hongchang E-mail:zhaomingzhi123@petrochina.com.cn;duanhongchang@petrochina.com.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHAO Mingzhi, DUAN Hongchang, SUN Xueqin, LÜ Penggang, LI Xueli, LIU Tao, CAO Gengzhen. Study on effect of hydrothermal aging on physicochemical properties of propylene additives[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(7): 55-60.
share this article
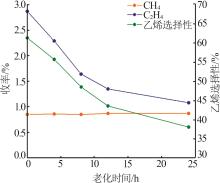
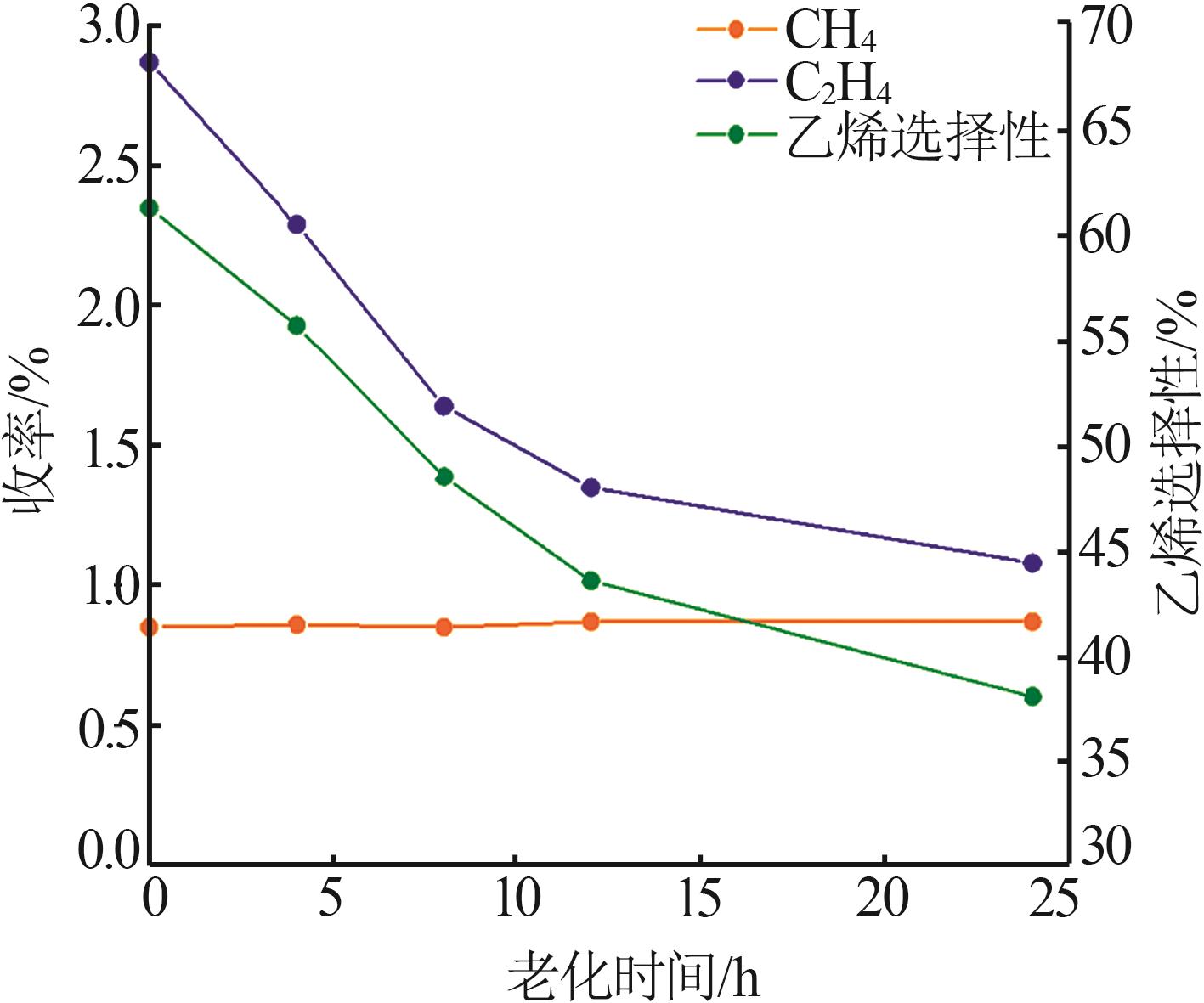
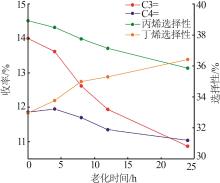
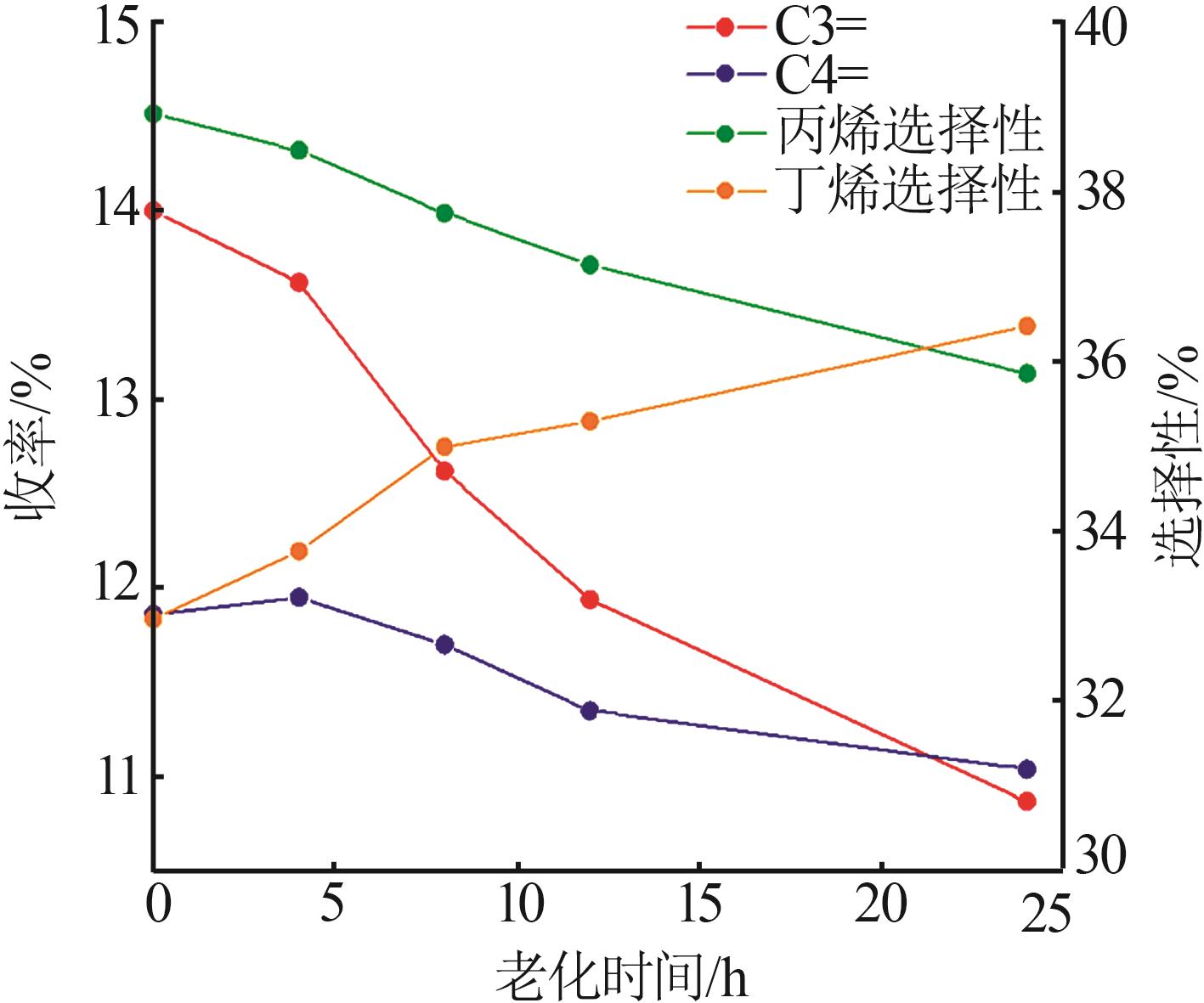
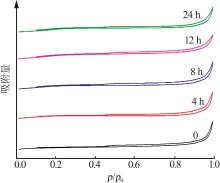
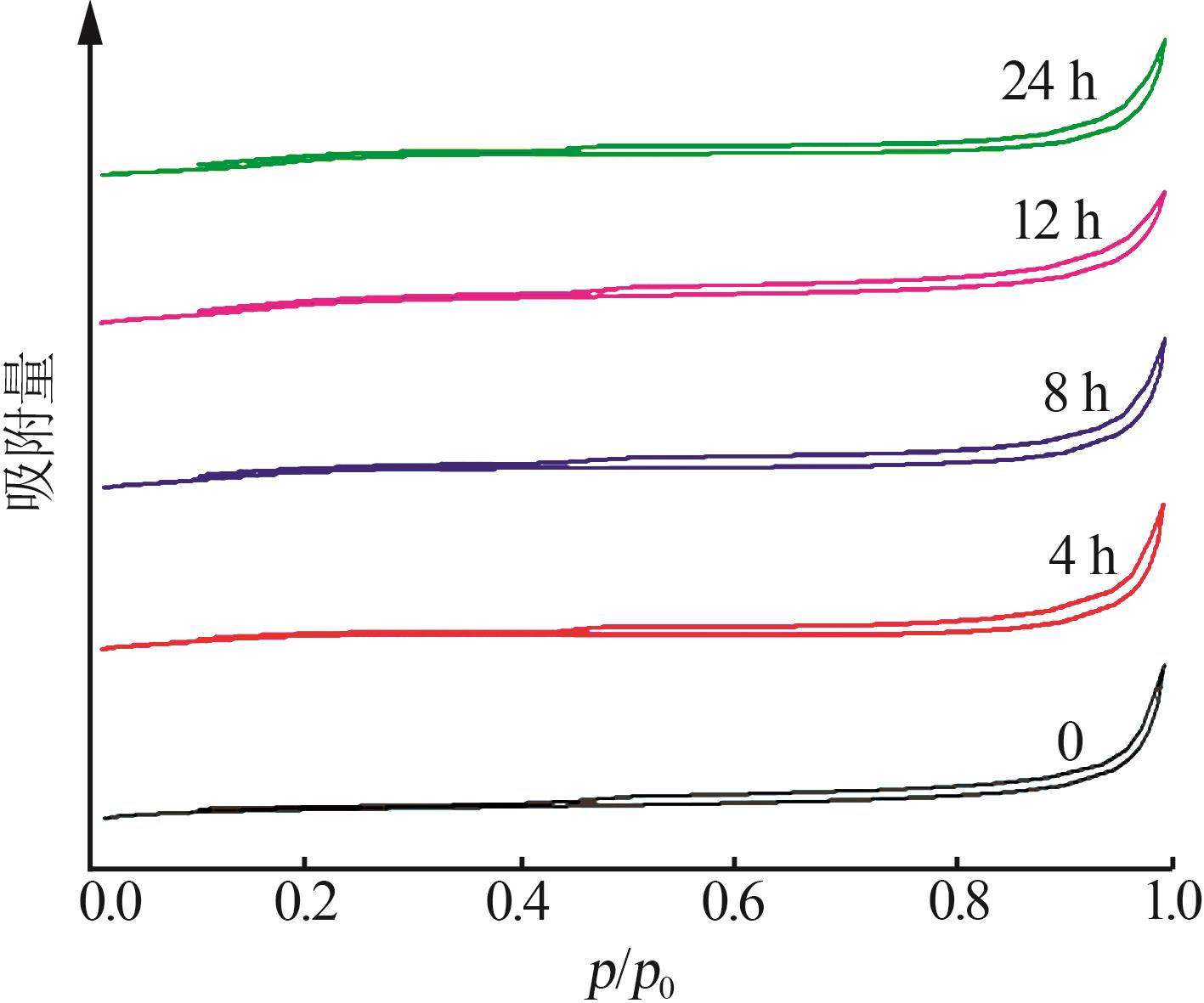
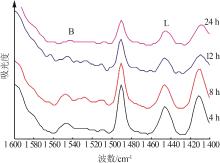
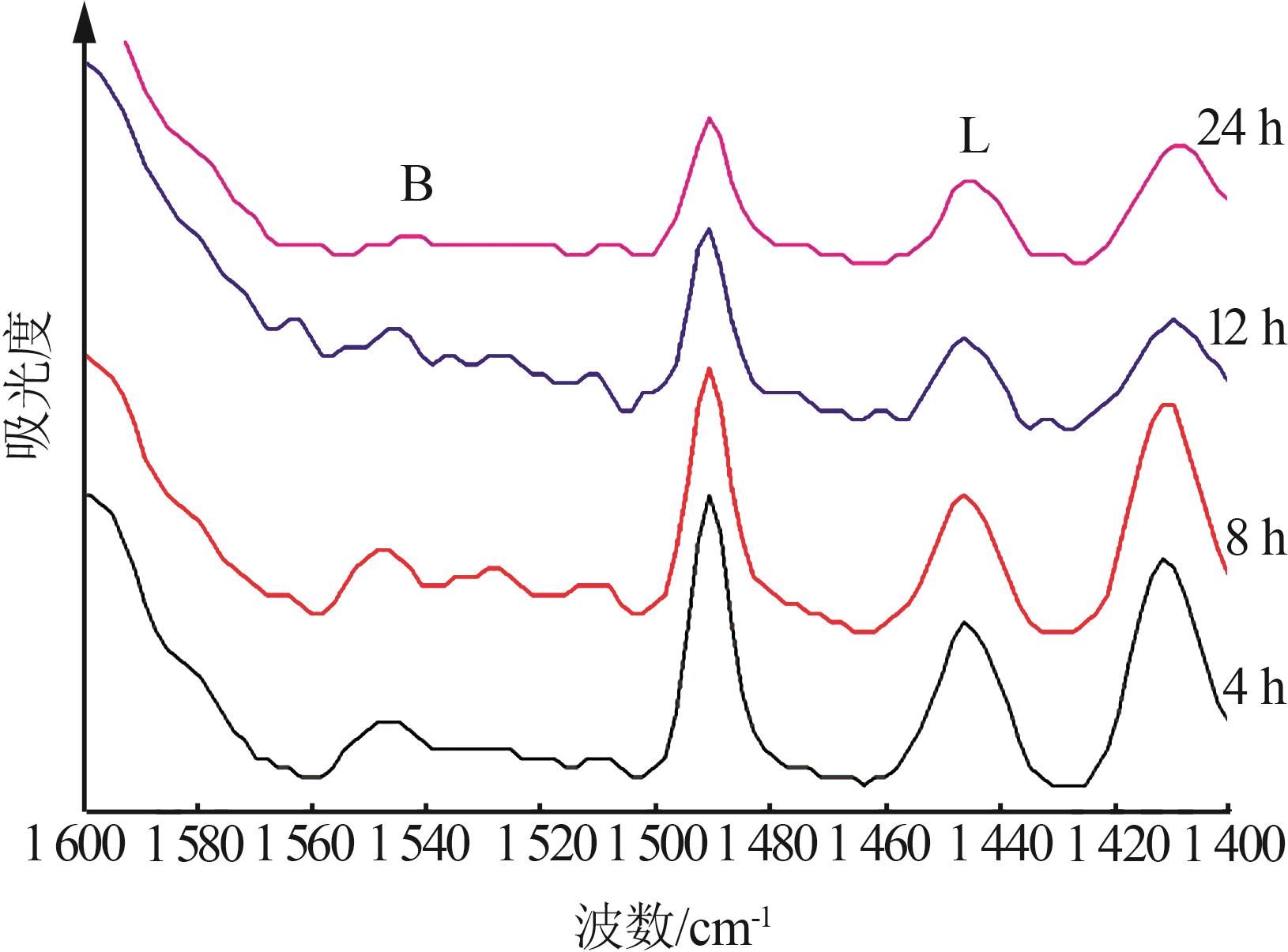
Table 4
ACE evaluation results of main agent and propylene additive compound with 20% by mass at different aging times"
| 编号 | 转化率/ % | 产物分布/% | 轻收/ % | 总液收/% | 丙烯选 择性/% | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干气 | 液化气 | 汽油 | 柴油 | 重油 | 焦炭 | |||||||||||
| H2 | CH4 | C2H4 | C3 | C3= | n-C4 | i-C4 | C4= | |||||||||
| 主剂+助剂-1 | 82.47 | 0.07 | 0.85 | 2.87 | 2.29 | 14.00 | 1.29 | 6.53 | 11.86 | 35.79 | 11.91 | 5.62 | 6.03 | 47.7 | 83.67 | 38.92 |
| 主剂+助剂-2 | 82.87 | 0.06 | 0.86 | 2.29 | 2.05 | 13.62 | 1.26 | 6.51 | 11.95 | 37.29 | 11.59 | 5.54 | 6.08 | 48.88 | 84.27 | 38.49 |
| 主剂+助剂-3 | 82.32 | 0.06 | 0.85 | 1.64 | 1.84 | 12.62 | 1.18 | 6.10 | 11.70 | 39.55 | 12.13 | 5.55 | 5.96 | 51.68 | 85.11 | 37.75 |
| 主剂+助剂-4 | 82.29 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 1.35 | 1.74 | 11.94 | 1.16 | 5.96 | 11.35 | 41.90 | 12.17 | 5.54 | 5.95 | 53.26 | 85.41 | 37.14 |
| 主剂+助剂-5 | 82.04 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 1.08 | 1.6 | 10.87 | 1.12 | 5.68 | 11.04 | 42.95 | 12.12 | 5.84 | 5.94 | 55.07 | 85.38 | 35.86 |
| 主剂 | 83.91 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 0.73 | 1.36 | 6.85 | 1.21 | 5.31 | 8.59 | 51.51 | 11.28 | 4.81 | 6.37 | 62.79 | 86.11 | 29.37 |
| 1 | ALOTIBI M F, ALSHAMMARI B A, ALOTAIBI M H,et al.ZSM-5 zeolite based additive in FCC process:A review on modifications for improving propylene production[J].Catalysis Surveys from Asia,2020,24(1):1-10. |
| 2 | 何立柱,郑云锋,杨玉峰,等.多产丙烯高辛烷值助剂LHP-A的工业应用[J].石化技术与应用,2020,38(4):255-258. |
| HE Lizhu, ZHENG Yunfeng, YANG Yufeng,et al.Industrial application of propylene maximizing and high octane number additive LHP-A[J].Petrochemical Technology & Application,2020,38(4):255-258. | |
| 3 | VELTHOEN M E Z, PAIONI A L, TEUNE I E,et al.Matrix effects in a fluid catalytic cracking catalyst particle:Influence on structure,acidity,and accessibility[J].Chemistry,2020,26(52):11995-12009. |
| 4 | 陈永利,陈浩,郭振宇.丙烯产业发展现状及趋势分析[J].炼油技术与工程,2019,49(12):1-5. |
| CHEN Yongli, CHEN Hao, GUO Zhenyu.Present situation and trend analysis of propylene industry[J].Petroleum Refinery Engineering,2019,49(12):1-5. | |
| 5 | 高明军,王涛,郭卡莉,等.ZSM-5分子筛母液回用及晶貌对其催化裂解性能的影响[J].现代化工,2023,43(3):203-208. |
| GAO Mingjun, WANG Tao, GUO Kali,et al.Influence of mother liquor reuse and crystal morphology of ZSM-5 molecular sieve on its catalytic cracking performance[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2023,43(3):203-208. | |
| 6 | KONNO H, OHNAKA R, NISHIMURA J I,et al.Kinetics of the catalytic cracking of naphtha over ZSM-5 zeolite:Effect of reduced crystal size on the reaction of naphthenes[J].Catalysis Science & Technology,2014,4(12):4265-4273. |
| 7 | 王晓兰.催化裂化增产丙烯助剂经济效益分析[J].炼油技术与工程,2005,35(6):34-35. |
| WANG Xiaolan.Economical benefits analysis for the assistant increasing propene yield of FCC unit[J].Petroleum Refinery Engineering,2005,35(6):34-35. | |
| 8 | 吕鹏刚,刘涛,叶行,等.FCC工艺中提升增产丙烯助剂性能研究进展[J].化工进展,2022,41(1):210-220. |
| Penggang LYU, LIU Tao, YE Hang,et al.Advances in improving the performance of additives for increasing propylene production in FCC process[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2022,41(1):210-220. | |
| 9 | HUSSAIN A I, AITANI A M, KUBŮ M,et al.Catalytic cracking of Arabian light VGO over novel zeolites as FCC catalyst additives for maximizing propylene yield[J].Fuel,2016,167:226-239. |
| 10 | 刘倩倩,任飞,朱玉霞.循环污染老化法模拟FCC平衡剂金属年龄分布[J].石油炼制与化工,2018,49(5):55-59. |
| LIU Qianqian, REN Fei, ZHU Yuxia.Recycling metal contamination and aging method for simulating metal age distribution of FCC equilibrium catalyst[J].Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals,2018,49(5):55-59. | |
| 11 | DENTON P, CHAJAR Z, BAINIER-DAVIAS N,et al.Selective reduction of nitrogen oxide with hydrocarbons and hydrothermal aging of Cu-ZSM-5 catalysts[J].Studies in Surface Science & Catalysis,1998,116:335-345. |
| 12 | LIU Zhongqing, WANG Yimeng, FU Jun,et al.Highly efficient synthesis of zeolite MCM-22 under static hydrothermal crystallization conditions[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2002,23(5):439-442. |
| 13 | 王达锐,孙洪敏,薛明伟,等.微波法高效合成全结晶ZSM-5分子筛催化剂及其催化性能[J].化工进展,2023,42(7):3582-3588. |
| WANG Darui, SUN Hongmin, XUE Mingwei,et al.Efficient synthesis of fully crystalline ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst by microwave method and its catalytic performance[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2023,42(7):3582-3588. | |
| 14 | 包立业.ZSM-5分子筛芳构化功能的水热稳定性研究[D].北京:中国石油大学(北京),2017. |
| BAO Liye.Study on hydrothermal stability of ZSM-5 zeolite for aromatization[D].Beijing:China University of Petroleum(Beijing),2017. | |
| 15 | 魏艳飞,管斌,吴星泽,等.水热老化温度和时长对Cu-SSZ-13分子筛催化剂性能和理化特性影响的研究[J].内燃机工程,2022,43(4):100-108. |
| WEI Yanfei, GUAN Bin, WU Xingze,et al.Study on the influence of hydrothermal aging temperature and time on the performance and physical and chemical characteristics of Cu-SSZ-13 molecular sieve catalyst[J].Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering,2022,43(4):100-108. | |
| 16 | 宋绍彤,李天舒,鞠雅娜,等.不同硅/铝比La/ZSM-5分子筛对催化裂化轻汽油异构化/芳构化性能的影响[J].石油学报(石油加工),2022,38(3):553-563. |
| SONG Shaotong, LI Tianshu, JU Yana,et al.Effect of La/ZSM-5 zeolites with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios on the isomerization/aromatization performance of FCC light gasoline[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing Section),2022,38(3):553-563. | |
| 17 | 任杰,任勇默,袁海宽.催化裂化再生器中平衡催化剂年龄分布及水热失活模拟[J].计算机与应用化学,2015,32(9):1099-1103. |
| REN Jie, REN Yongmo, YUAN Haikuan.Mathematical simulations of age distribution and hydrothermal deactivation for equilibrium catalyst in regenerator of catalytic cracking unit[J].Computers and Applied Chemistry,2015,32(9):1099-1103. | |
| 18 | 侯硕旻,段宏昌,郭静静,等.磷改性ZSM-5及其对催化裂化增产丙烯的影响[J].石油炼制与化工,2022,53(10):58- 65. |
| HOU Shuomin, DUAN Hongchang, GUO Jingjing,et al.Effect of phosphorus modification on the ZSM-5 zeolite for increasing propylene production in FCC unit[J].Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals,2022,53(10):58-65. | |
| 19 | PONCELET G.An infrared study of the surface acidity of Germanic near⁃faujasite zeolite by pyridine adsorption[J].Journal of Catalysis,1978,52(2):321-331. |
| 20 | LEE J S, BOUDART M. In situ carburization of metallic molybdenum during catalytic reactions of carbon⁃containing gases[J].Catalysis Letters,1993,20(1):97-106. |
| 21 | 崔守业,许友好,刘新林.不同老化时间催化裂化催化剂上加氢蜡油反应性能[J].石油炼制与化工,2020,51(7):27-32. |
| CUI Shouye, XU Youhao, LIU Xinlin.Reaction performance of hydrogenation VGO on catalytic cracking catalysts with different aging time[J].Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals,2020,51(7):27-32. |
| [1] | WANG Jianjie, SHU Xiaolong, XIAO Xia, WANG Peng, FAN Xiaoqiang, KONG Lian, XIE Zean, ZHAO Zhen. Study on synthesis of hierarchical flower⁃like ZSM-5 zeolite and its catalytic performance for n-octane cracking [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 139-146. |
| [2] | HAN Wenhua, HONG Luwei, LI Bin, ZHOU Wei, LIU Guanfeng, WANG Yinbin. Study on synthesis of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite by seed method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 128-134. |
| [3] | LI Yongheng, MI Xiaotong, ZHANG Peipei. Synthesis of holycrystalline nano-ZSM-5 aggregate and its application in methylation of toluene [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(5): 135-140. |
| [4] | MI Xiaotong, LI Xiaoguo, CHANG Yang, ZHANG Yongkun, LI Yongheng, CAO Hui, HOU Zhanggui. Collaborative construction of nanoscale ZSM-5 aggregates by crystal seeds and templates [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 130-135. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yongkun, CHANG Yang, LI Xiaoguo, LIU Yan, XING Changxin, GAO Jinping, XIAO Jiawang, HOU Zhanggui. Study on modification of HZSM-5 catalyst and its pilot catalytic performance for alkylation of benzene with dilute ethylene [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(5): 137-142. |
| [6] | ZHOU Wei,ZHANG Gengrui,YU Haibin,MA Xinbin,LIU Fei,LIU Jiaxu. Study on solvent effect on preparation of MnO x -ZSM-5 deNO x catalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(8): 138-144. |
| [7] | WANG Yinzhong,QIN Dongling,YANG Gang. Study on preparation of hierarchical ZSM-5/SAPO-34 composite molecular sieve and its MTO performance [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 119-124. |
| [8] | XIE Zhuohan,HAN He,LI Xiaoguo,ZHANG Yongkun,HOU Zhanggui,BIAN Kai,ZHANG Anfeng,GUO Xinwen,SONG Chunshan. Synthesis of nano Ga-ZSM-5 zeolite and its application in alkylation of benzene with dilute ethylene [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(2): 123-128. |
| [9] | LI Xiaoguo,MI Xiaotong,CAO Hui,CHANG Yang,ZHANG Yongkun,LI Yongheng. Synthesis of ZSM-5 aggregates assembled by oriented stacking nanosheets [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(1): 112-116. |
| [10] | Su Shaolong,Qu Xiaolong,Zhong Dule,Sun Yanmin,Nan Jun,Li Shipeng. Study on preparation and denitration performance of Cu-Ce/ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(6): 190-193. |
| [11] | Li Xiaoguo, Li Yongheng, Hou Zhanggui, Han Guodong, Xiao Jiawang, Gao Jinping, Chang Yang. Study on pilot catalytic performance of the modified catalyst for alkylation of toluene with methanol to p-xylene [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(3): 97-101. |
| [12] | Hou Zhanggui,Zhu Qianqian,Li Xiaoguo,Li Yongheng,Chang Yang,Zhang Anfeng,Guo Xinwen. Preparation of modificated micro-mesoporous ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst and its catalytic performance for alkylation of toluene with methanol [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(9): 96-99. |
| [13] | Chen Yanguang,Han Tong,Zhang Yanan,Yang Xiuqi,Han Hongjing,Wang Hao. Process regulation of ZSM-5 zeolite synthesis from hydrolyzed tetraethyl orthosilicate as silicon source in acidic medium [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(7): 88-93. |
| [14] | Chang Yang,Li Xiaoguo,Hou Zhanggui,Mi Xiaotong,Wei Linlin. Study on synthetic technology of nano-sized ZSM-5 aggregates with low Si/Al ratio [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(6): 92-95. |
| [15] | Li Xiaoguo,Mi Xiaotong,Hou Zhanggui. Synthesis of aggregated nano-sized ZSM-5 zeolite with ternary pore structure [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(12): 104-108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||