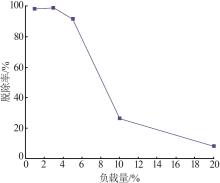
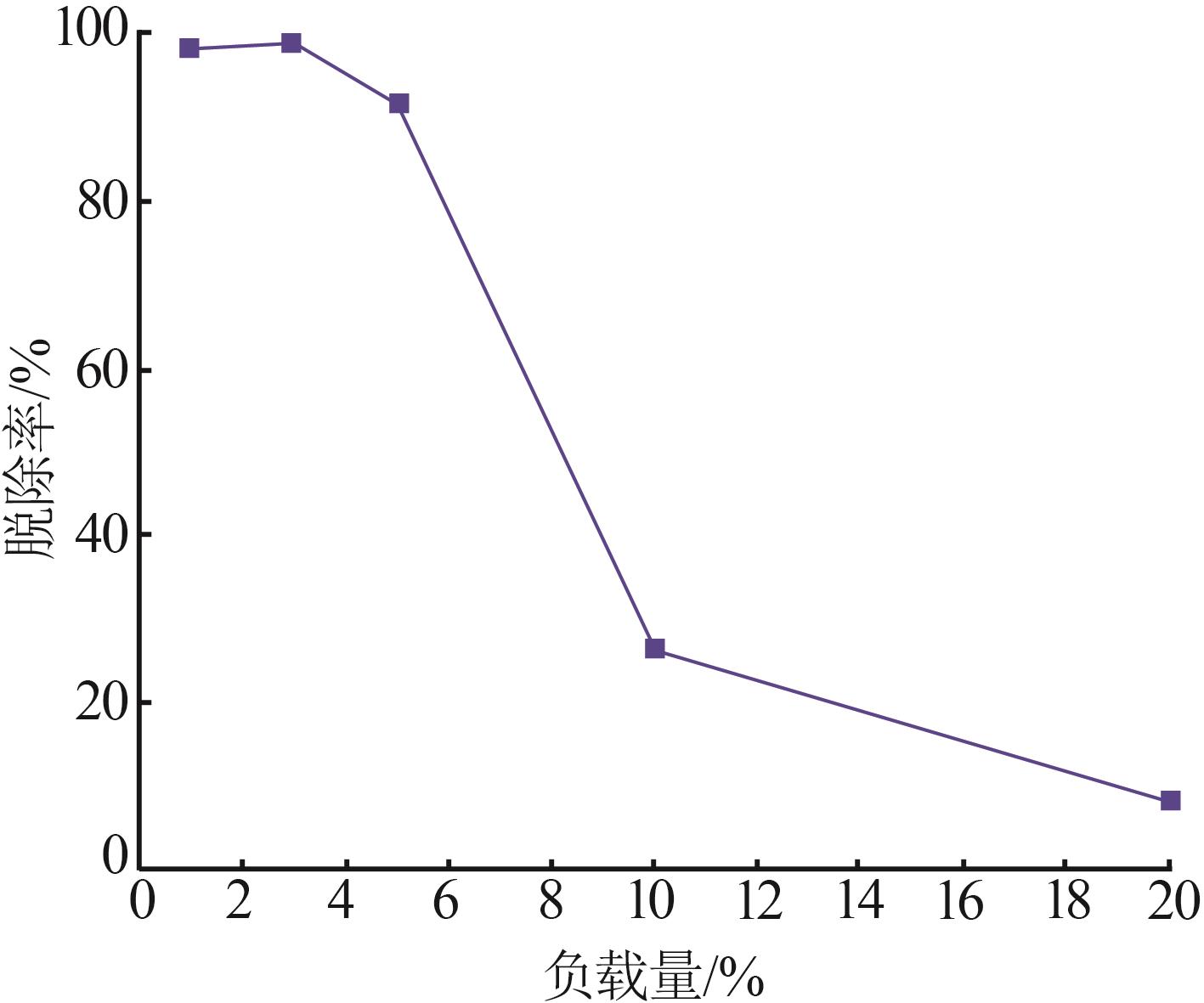
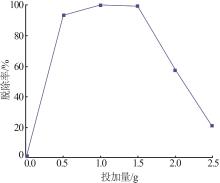
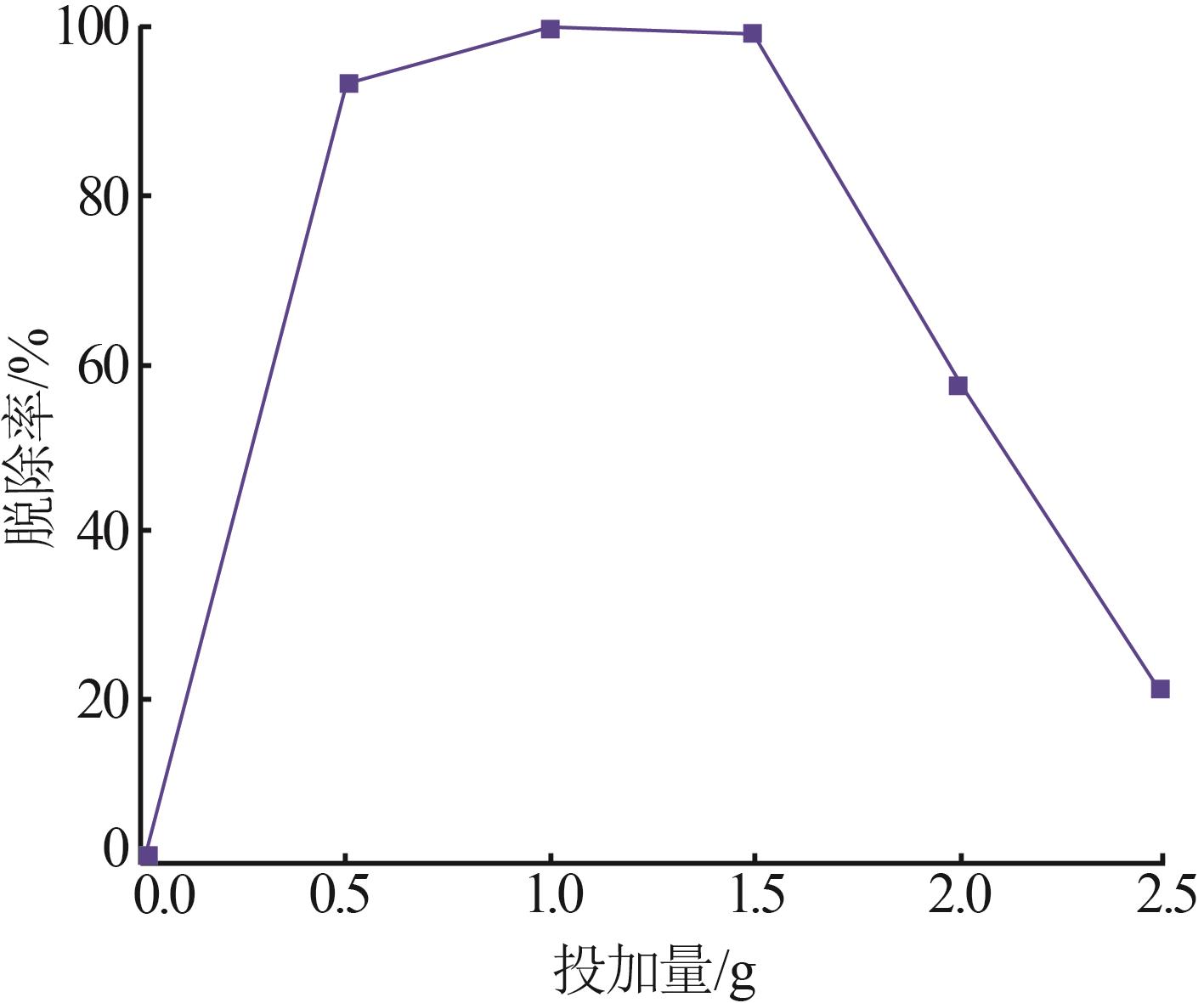
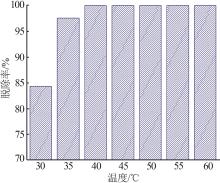
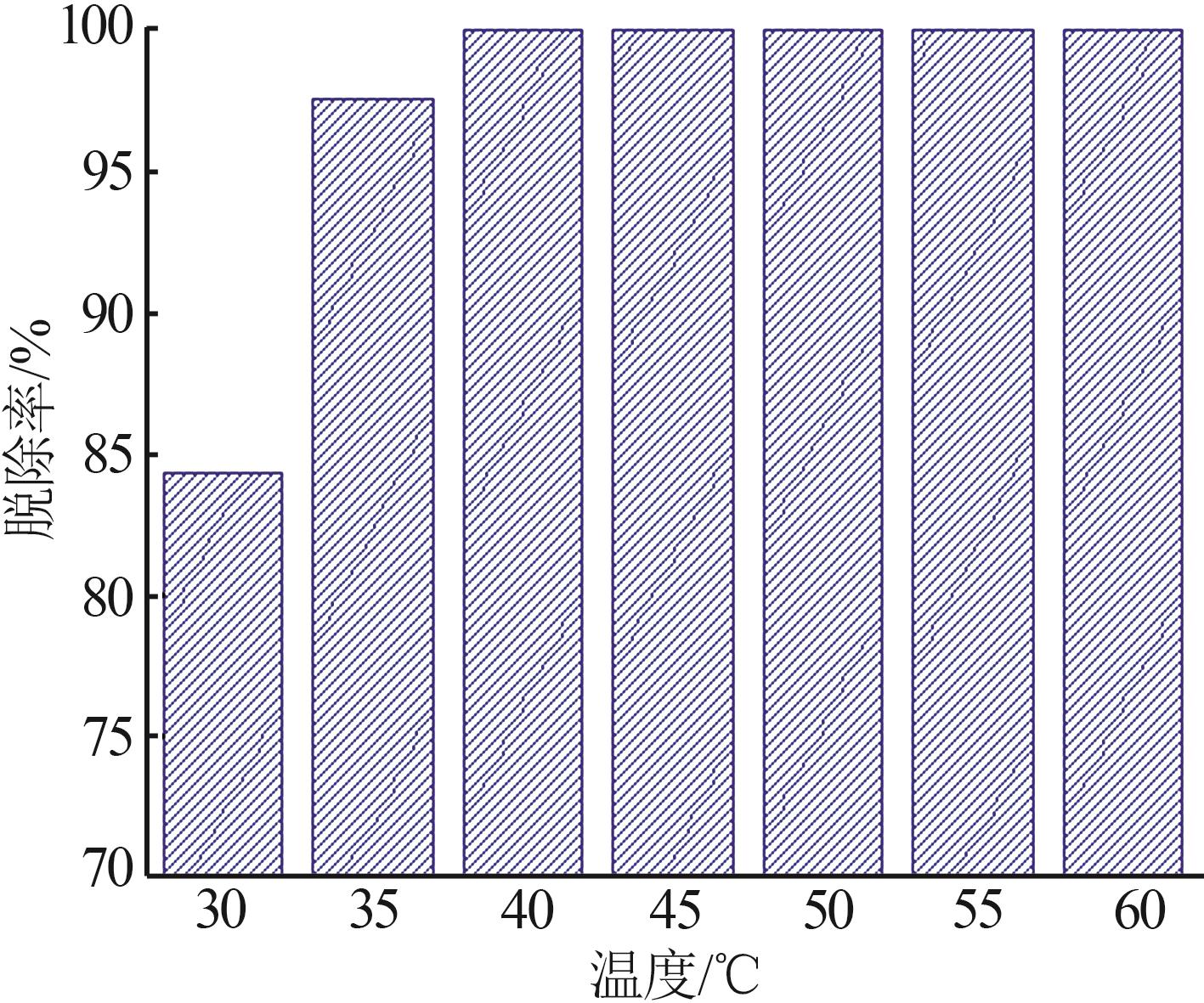
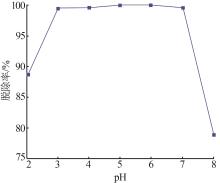
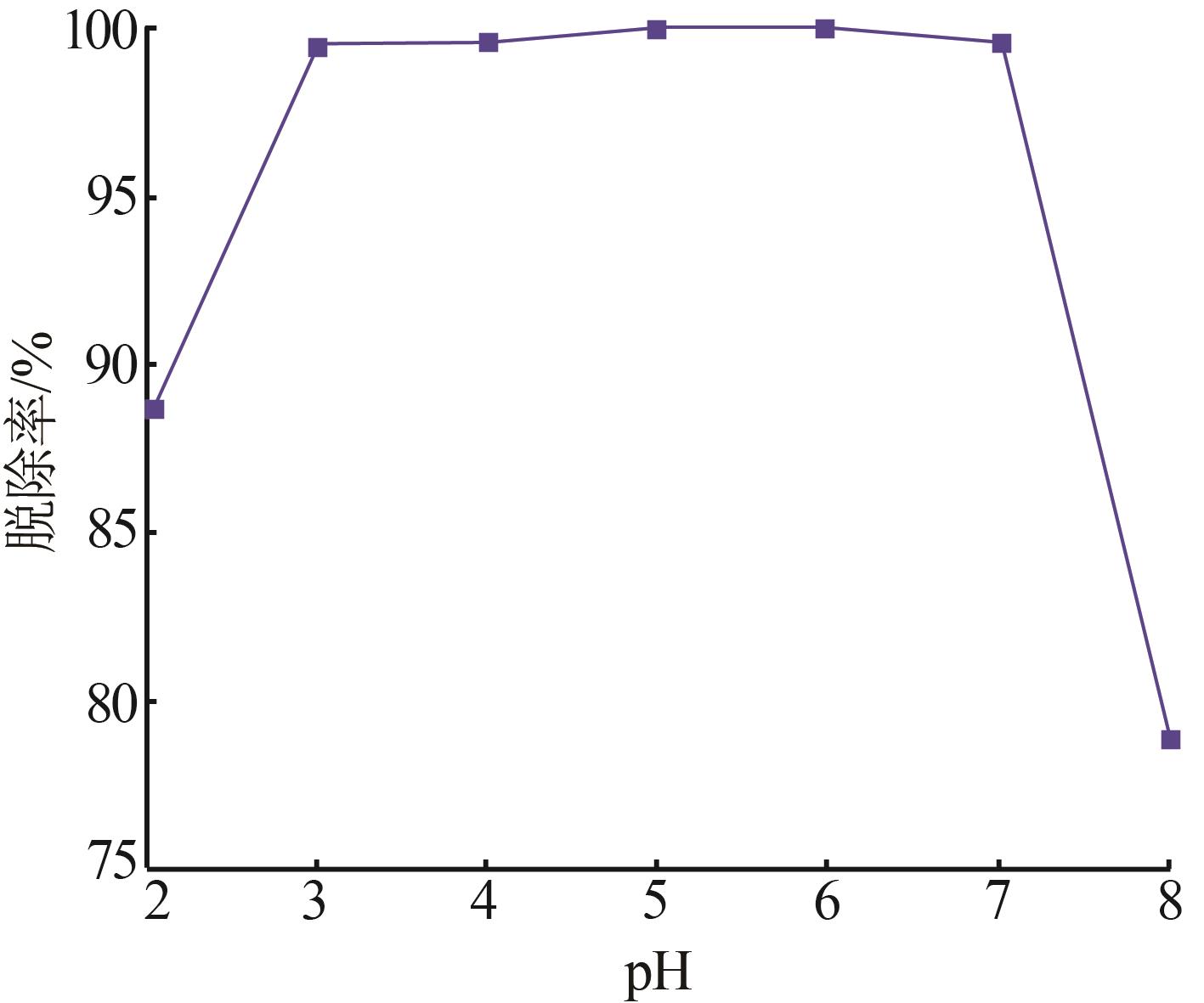
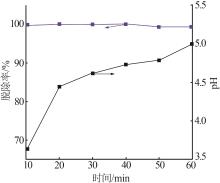
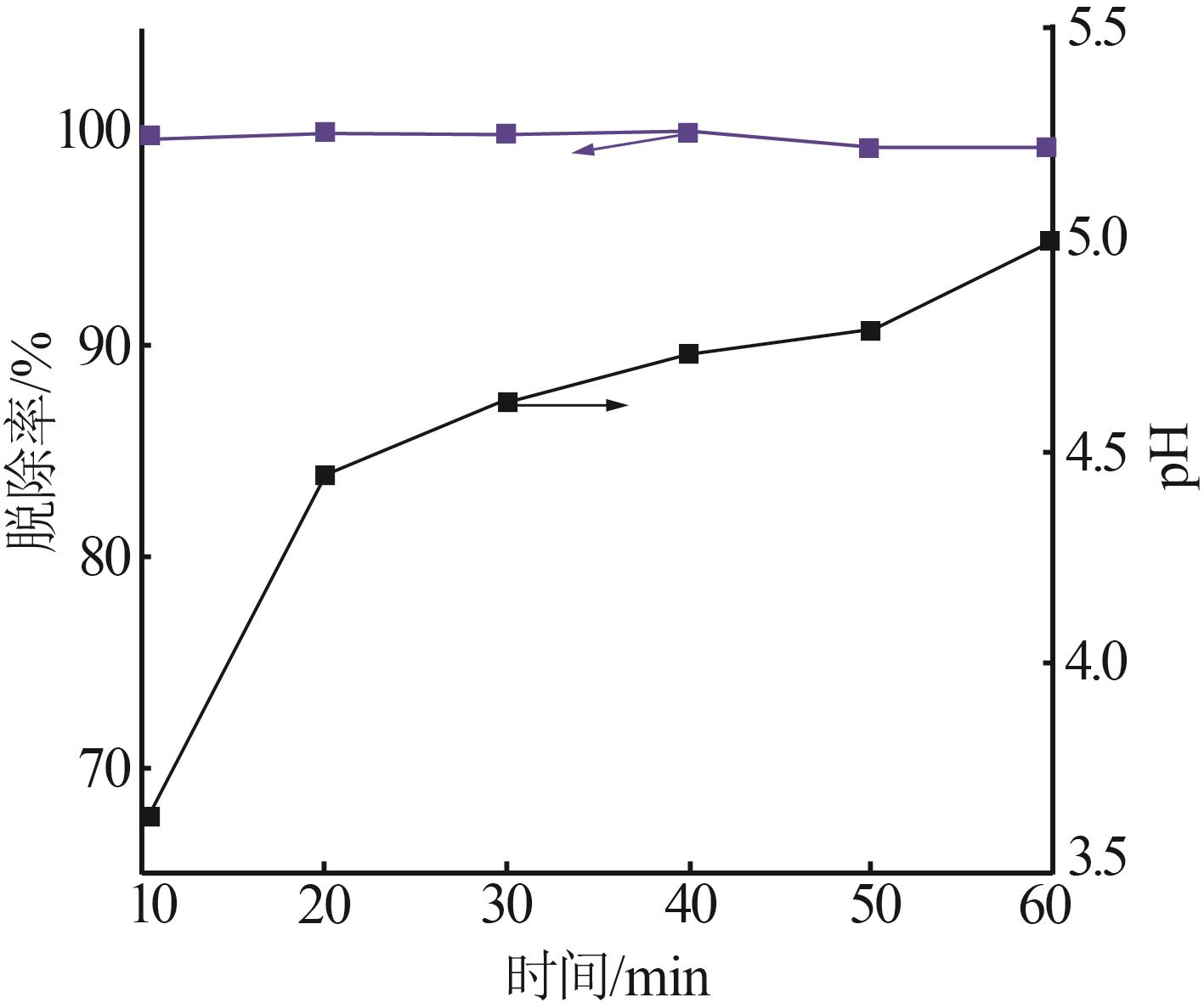
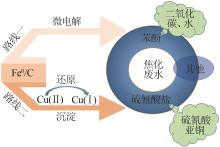
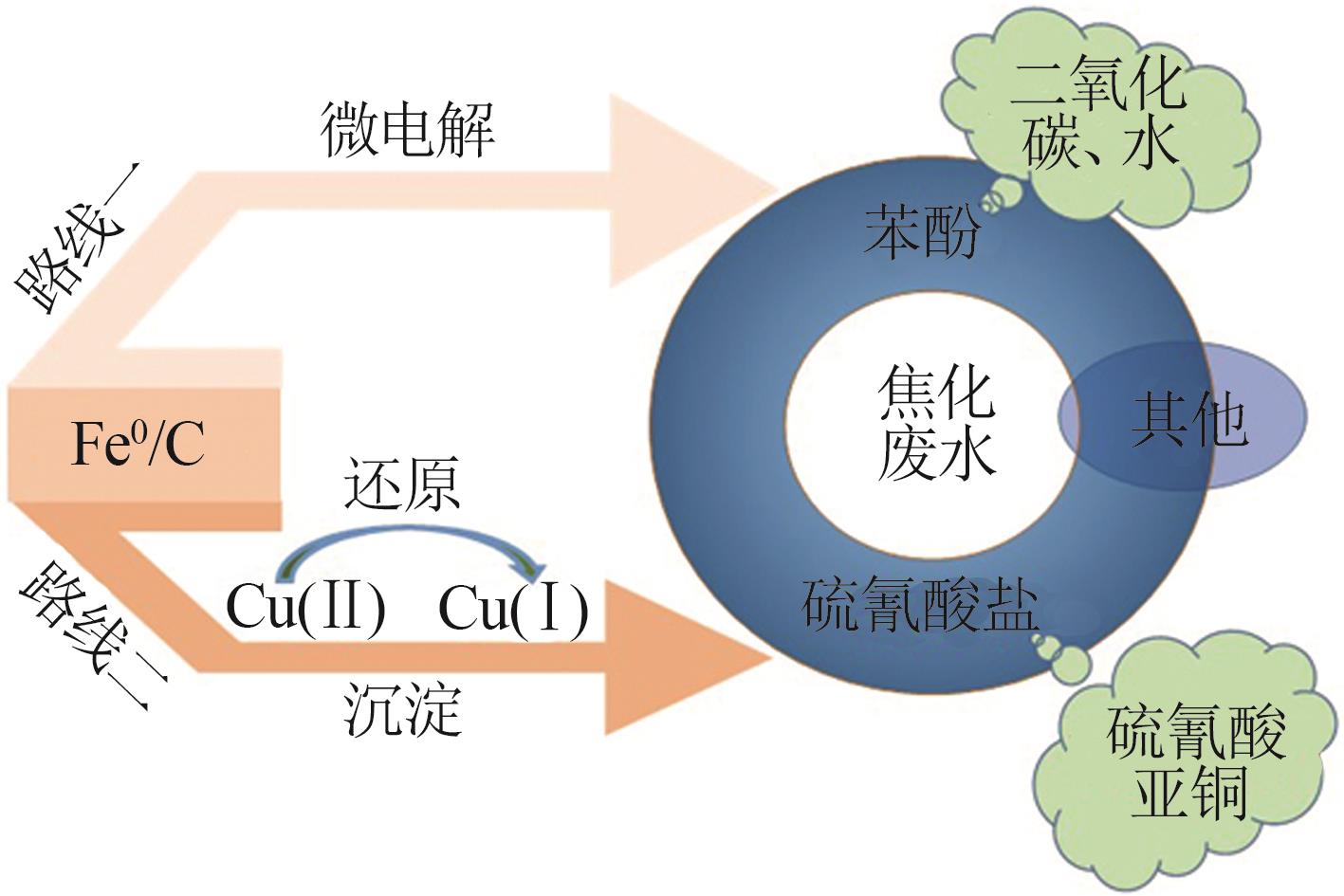
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 129-135.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0116
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
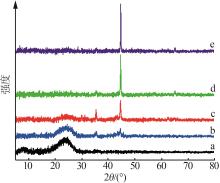
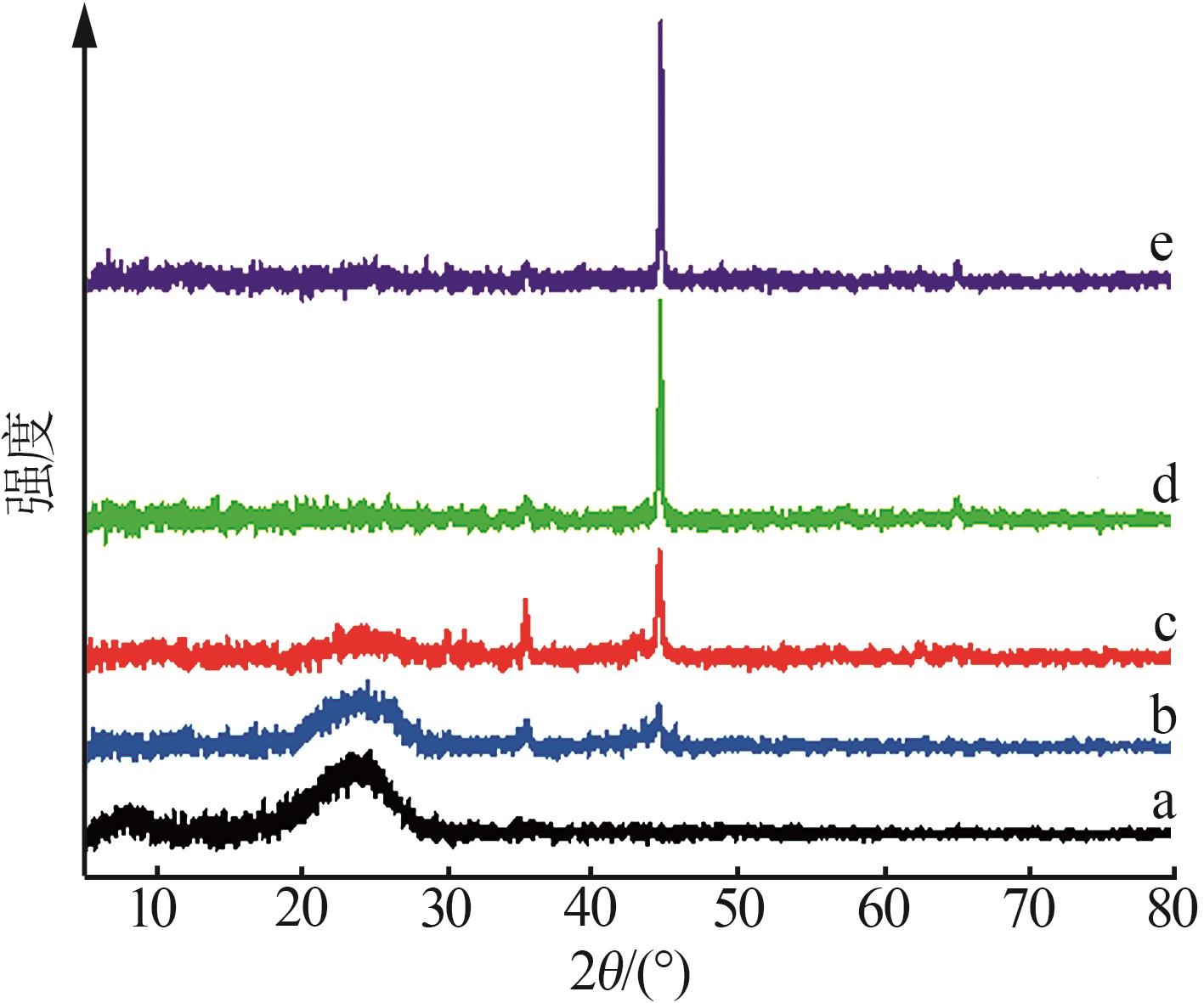
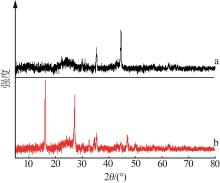
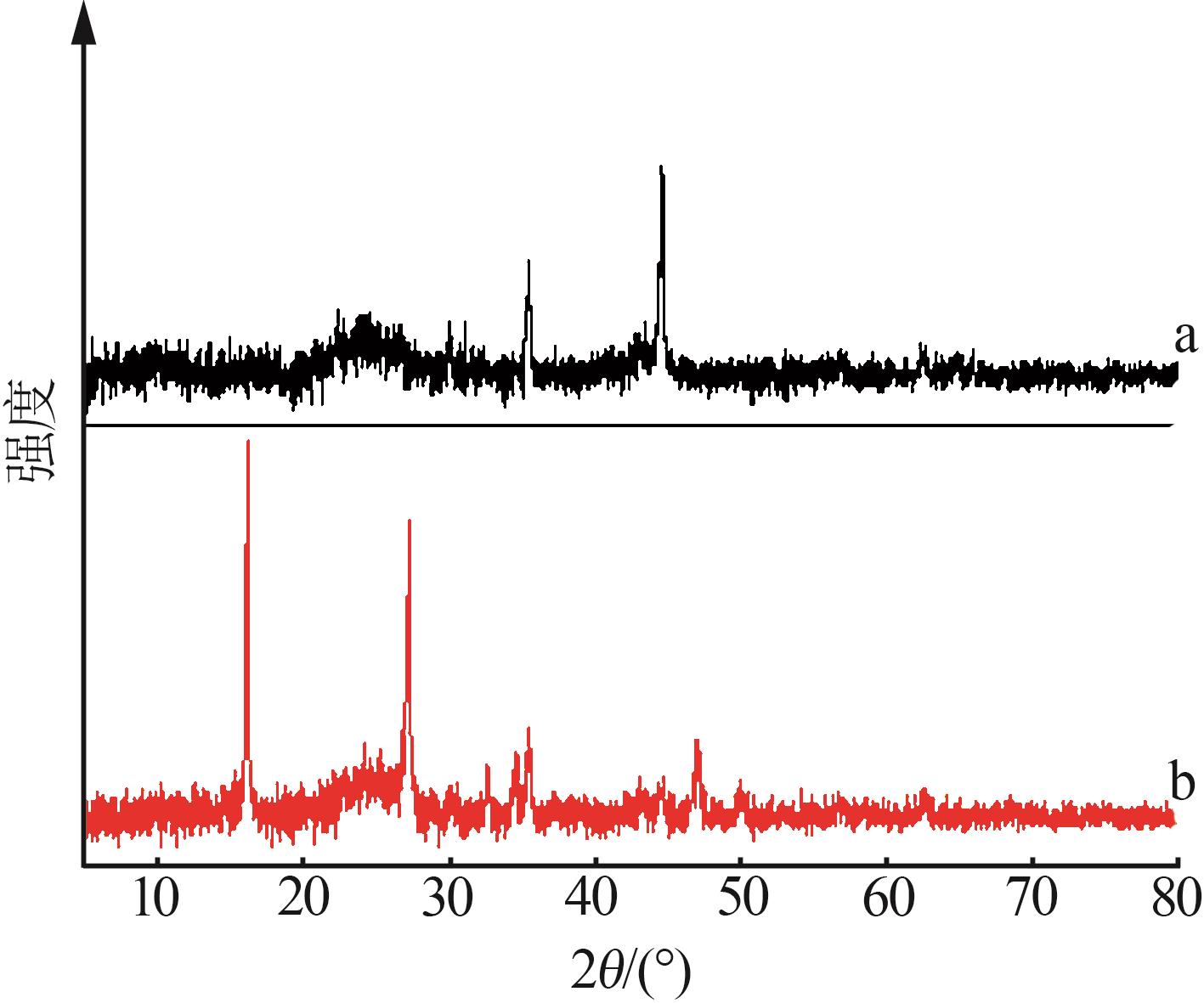
Fe0/C induced copper salt reduction coupled with chemical precipitation method to remove thiocyanate from wastewater
JIA Zhiqi1( ),NIE Huimin1,ZHAO Yongxiang1,2
),NIE Huimin1,ZHAO Yongxiang1,2
- 1. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China
2. Engineering Research Center of Fine Chemicals,Ministry of Education,Taiyuan 030006,China
-
Received:2022-03-14Online:2023-01-10Published:2023-01-17
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIA Zhiqi,NIE Huimin,ZHAO Yongxiang. Fe0/C induced copper salt reduction coupled with chemical precipitation method to remove thiocyanate from wastewater[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 129-135.
share this article
| 1 | 刘莎, 陈康康. 焦化废水深度处理技术研究进展[J].中国资源综合利用, 2020, 38(9):132-134. |
| LIU Sha, CHEN Kangkang. Research progress on advanced treatment technology of coking wastewater[J].China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2020, 38(9):132-134. | |
| 2 | 肖小双, 安雪姣, 叶晗媛, 等. 废水中硫氰酸盐的微生物降解研究进展[J].生物技术通报, 2021, 37(2):224-235. |
| XIAO Xiaoshuang, AN Xuejiao, YE Hanyuan, et al. Research progress on microbial degradation of thiocyanate in wastewater[J].Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(2):224-235. | |
| 3 | YANG Wenlan, WANG Jicheng, HUA Ming, et al. Characterization of effluent organic matter from different coking wastewater treatment plants[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 203:68-75. |
| 4 | 何绪文, 张斯宇, 何灿. 焦化废水深度处理现状及技术进展[J].煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(1):100-107. |
| HE Xuwen, ZHANG Siyu, HE Can. Status and progress of coking wastewater advanced treatment technology[J].Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(1):100-107. | |
| 5 |
RAPER E, STEPHENSON T, FISHER R, et al. Characterisation of thiocyanate degradation in a mixed culture activated sludge process treating coke wastewater[J].Bioresource Technology, 2019, 288.Doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121524.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121524 |
| 6 | PAN Jianxin, MA Jingde, WU Haizhen, et al. Application of metabolic division of labor in simultaneous removal of nitrogen and thiocyanate from wastewater[J].Water Research, 2019, 150:216- 224. |
| 7 |
ÁLVAREZ J R, ANTÓN F E, ÁLVAREZ-GARCÍA S, et al. Treatment of aqueous effluents from steel manufacturing with high thiocyanate concentration by reverse osmosis[J].Membranes, 2020, 10(12).Doi:10.3390/membranes10120437.
doi: 10.3390/membranes10120437 |
| 8 | 范铃琴, 马欣, 任静, 等. Fenton氧化去除焦化废水纳滤浓水中有机物的研究[J].工业用水与废水, 2020, 51(2):11-16. |
| FAN Lingqin, MA Xin, REN Jing, et al. Study on organic matters removal from nanofiltration concentrated coking wastewater by Fenton oxidation[J].Industrial Water & Wastewater, 2020, 51(2):11-16. | |
| 9 | 张恒, 李淑敏, 刘媛, 等. 微波强化Fenton技术对焦化废水生化出水的深度处理[J].环境工程学报, 2020, 14(6):1495-1502. |
| ZHANG Heng, LI Shumin, LIU Yuan, et al. Advanced treatment of bio-treated coking wastewater by microwave-enhanced Fenton process[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(6):1495-1502. | |
| 10 | 何灿, 黄祁, 何文丽, 等. 臭氧催化氧化深度处理焦化废水的研究及应用[J].给水排水, 2020, 56(10):65-71. |
| HE Can, HUANG Qi, HE Wenli, et al. Study on ozone catalytic oxidation in advanced treatment of coking wastewater and its application[J].Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2020, 56(10):65-71. | |
| 11 | 强喆林, 王玲, 吴迪, 等. 含酚废水处理技术研究进展[J].当代化工, 2021, 50(9):2206-2210. |
| QIANG Zhelin, WANG Ling, WU Di, et al. Research progress of phenolic wastewater treatment technology[J].Contemporary Che- | |
| Industry mical,2021, 50(9):2206-2210. | |
| 12 | 孙培杰, 王林平, 徐乐瑾. 焦化废水中氰化物的处理技术研究进展[J].化工进展, 2021, 40(S1):386-396. |
| SUN Peijie, WANG Linping, XU Lejin. Advances in the treatment of cyanide in coking wastewater[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(S1):386-396. | |
| 13 | 金玉涛, 史大勇, 郭利华, 等. 酚氰废水处理工程实践[J].工业水处理, 2021, 41(10):133-136. |
| JIN Yutao, SHI Dayong, GUO Lihua, et al. Engineering practice of phenol cyanide wastewater treatment[J].Industrial Water Treat-ment, 2021, 41(10):133-136. | |
| 14 | 高富聪, 陈国宝, 马云瑞, 等. 废水中硫氰酸根的脱除研究现状[J].有色金属:冶炼部分, 2021(3):143-149, 154. |
| GAO Fucong, CHEN Guobao, MA Yunrui, et al. Research status of removal of thiocyanate from wastewater[J].Nonferrous Metals:Extractive Metallurgy, 2021(3):143-149, 154. | |
| 15 | CHO Y, CATTRALL R W, KOLEV S D. A novel polymer inclusion membrane based method for continuous clean-up of thiocyanate from gold mine tailings water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 341:297-303. |
| 16 | REN Gengbo, ZHOU Minghua, ZHANG Qizhan, et al. Cost-efficient improvement of coking wastewater biodegradability by multi-stages flow through peroxi-coagulation under low current load[J].Water Research, 2019, 154:336-348. |
| 17 | 谢莉, 刘吉明, 逯新宇, 等. 电催化氧化法—活性炭深度处理焦化废水[J].工业水处理, 2021, 41(8):69-74. |
| XIE Li, LIU Jiming, LU Xinyu, et al. Advanced treatment of coking wastewater by electrocatalytic oxidation-activated carbon adsorption[J].Industrial Water Treatment, 2021, 41(8):69-74. | |
| 18 | 初永宝, 陈德林, 刘生, 等. 分体式流化床催化臭氧—絮凝工艺深度处理焦化废水生化尾水[J].北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 58(1):177-185. |
| CHU Yongbao, CHEN Delin, LIU Sheng, et al. Split fluidized bed catalytic ozone-flocculation process for advanced treatment of biochemical tail water from coking wastewater[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2022, 58(1):177- 185. | |
| 19 | 邹晓爽, 李江, 李彦澄, 等. 两级A/O工艺处理焦化废水有机污染物转化特征及细菌群落响应[J].环境科学研究, 2022, 35(5):1245-1256. |
| ZOU Xiaoshuang, LI Jiang, LI Yancheng, et al. Two-stage anoxic/oxic(A/O) process to remove organic pollutants and bacterial community in coking wastewater[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(5):1245-1256. | |
| 20 | 曾婧. 活性炭处理含硫氰酸钠废水的研究[J].江西化工, 2019(4):138-140. |
| ZENG Jing. Study on treatment of wastewater containing sodium thiocyanate by activated carbon[J].Jiangxi Chemical Industry, 2019(4):138-140. | |
| 21 |
TURAN A, KEYIKOGLU R, KOBYA M, et al. Degradation of thiocyanate by electrochemical oxidation process in coke oven wastewater:Role of operative parameters and mechanistic stu-dy[J].Chemosphere, 2020, 255.Doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127014.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127014 |
| 22 | 周钦灵, 冯凡让, 王武雄, 等. 含硫氰酸根废液综合利用及无害化处置技术路线研究[J].广东化工, 2021, 48(11):90-91, 130. |
| ZHOU Qinling, FENG Fanrang, WANG Wuxiong, et al. Study on comprehensive utilization and harmless disposal technology of thiocyanate wastewater[J].Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2021, 48(11):90-91, 130. | |
| 23 | 谢佳兵. M x O y /C复合材料的制备及在酚类废水处理中应 用[D].太原:山西大学, 2019. |
| XIE Jiabing. Preparation of M x O y /C composites and its application in phenol wastewater treatment[D].Taiyuan:Shanxi University, 2019. | |
| 24 | 席乔悦. 氧化亚铜和硫氰酸亚铜纳米材料的制备及其光电性质研究[D].北京:中国科学院大学, 2018. |
| XI Qiaoyue. Preparation and photoelectric properties of cuprous oxide and cuprous cyanide nanomaterials[D].Beijing:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. | |
| 25 | 李明威, 李金汞. 硫氰酸亚铜及其应用[J].无机盐工业, 1985, 17(4):36-37. |
| 26 | LIU Wujun, JIANG Hong, YU Hanqing. Emerging applications of biochar-based materials for energy storage and conversion[J].Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(6):1751-1779. |
| 27 | YUAN Ye, DING Yujie, WANG Chunhui, et al. Multifunctional stiff carbon foam derived from bread[J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(26):16852-16861. |
| 28 | DONG Yongqiang, CHEN Yingmei, YOU Xu, et al. High photoluminescent carbon based dots with tunable emission color from orange to green[J].Nanoscale, 2017, 9(3):1028-1032. |
| 29 | 杨惠芳. 纳米CuSCN的制备及其在复合涂料中的应用研究[D].天津:天津大学, 2007. |
| YANG Huifang. Study on the preparation of cuprous thiocyanate nanoparticles and application in nano-compound paint[D].Tianjin:Tianjin University, 2007. | |
| 30 | 雷乐成, 汪大翚. 水处理高级氧化技术[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2001. |
| 31 | 孙凤. 流化床非均相催化氧化处理工业废水中的硫氰酸盐[D].大连:大连工业大学, 2016. |
| SUN Feng. Fluidised bed heterogeneous catalytic oxidation treatment of industrial wastewater thiocyanate[D].Dalian:Dalian Poly-technic University, 2016. | |
| 32 |
LI Mingxin, LI Binchuan, CHEN Jianshe, et al. A novel green method for copper recovery from cuprous thiocyanate-containing acidified sediments in the gold industry[J].Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 329.Doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129729.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129729 |
| [1] | LU Ju, WANG Jiawei, WANG Haifeng, PEI Zhengqing, ZHOU Xingjie, ZHENG Kexin, MA Dehua. Study on purification of magnesium from manganese electrolyte by fluorine salt method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(6): 40-45. |
| [2] | Liang Ning,Mo Fujin,Zhou Jierong,Wang Junzheng. Study on preparation of sludge biochar and its adsorption performance for phosphorus [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(6): 174-179. |
| [3] | Zhang Yanyan,Liu Yonghe,Li Donghong,Wang Yi. Research on preparation and expanding test of AlN power [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(11): 56-59. |
| [4] | Li Pufang,Mu Lin,Wang Shebin. Carbon thermal reduction/melting separation of valuable metals from spent SCR catalysts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(1): 93-98. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lin-Jin, CHEN Xiao-Juan, PANG Huan-Jun. Preliminary research on magnesium oxide thermal reduction in annular shaft kiln [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2014, 46(12): 34-. |
| [6] | LIU Yu, LIU Bing-Guo, XING Xiao-Zhong. Research on dezincification of blast furnace flue slime by carbothermal reduction method [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2013, 45(10): 39-. |
| [7] | LUO Xu-Dong, ZHANG Guo-Dong, QU Dian-Li, LIU Hai-Xiao, 吕Nan- . Research on preparation of magnesium oxide powder by carbothermal reduction oxidation method [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2011, 43(5): 55-. |
| [8] | LONG Hai-Bo, ZHANG Ning, HOU Jing, LIANG Bin. Effect of lanthanum on synthesis temperature and particle size of ultrafine SiC [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2011, 43(4): 27-. |
| [9] | LONG Hai-Bo, ZHANG Ning, HOU Jing, LIANG Bin. Effect of lanthanum on synthesis temperature and particle size of ultrafine SiC [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2011, 43(4): 27-. |
| [10] | Jiang Caibin;Tan Fangxiang;Li Meilin;Lü Xiaoyan;Wang Fan;Wen Yanxuan. Process optimization for carbothermal reduction synthesis of LiFePO4 by uniform design [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2010, 0(10): 0-0. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||