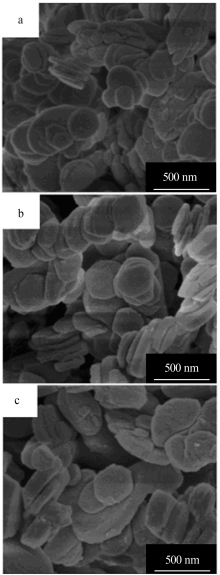
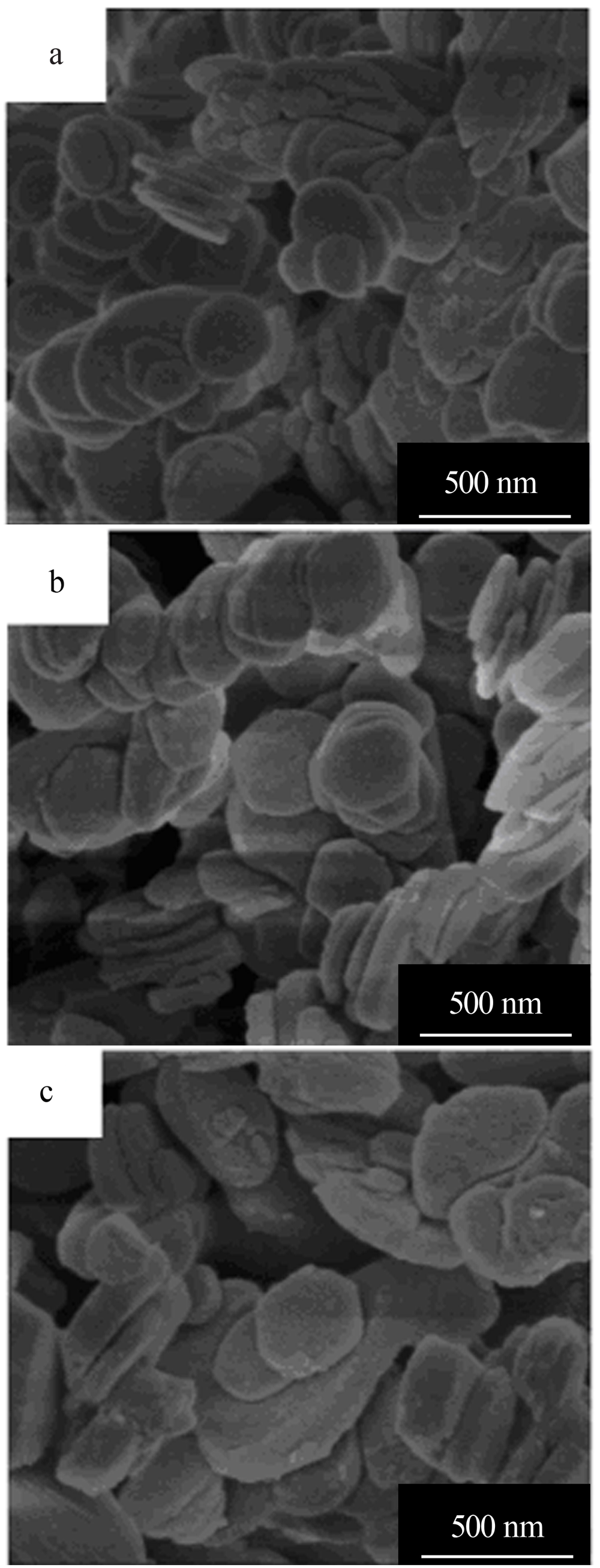
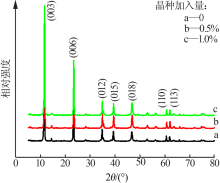
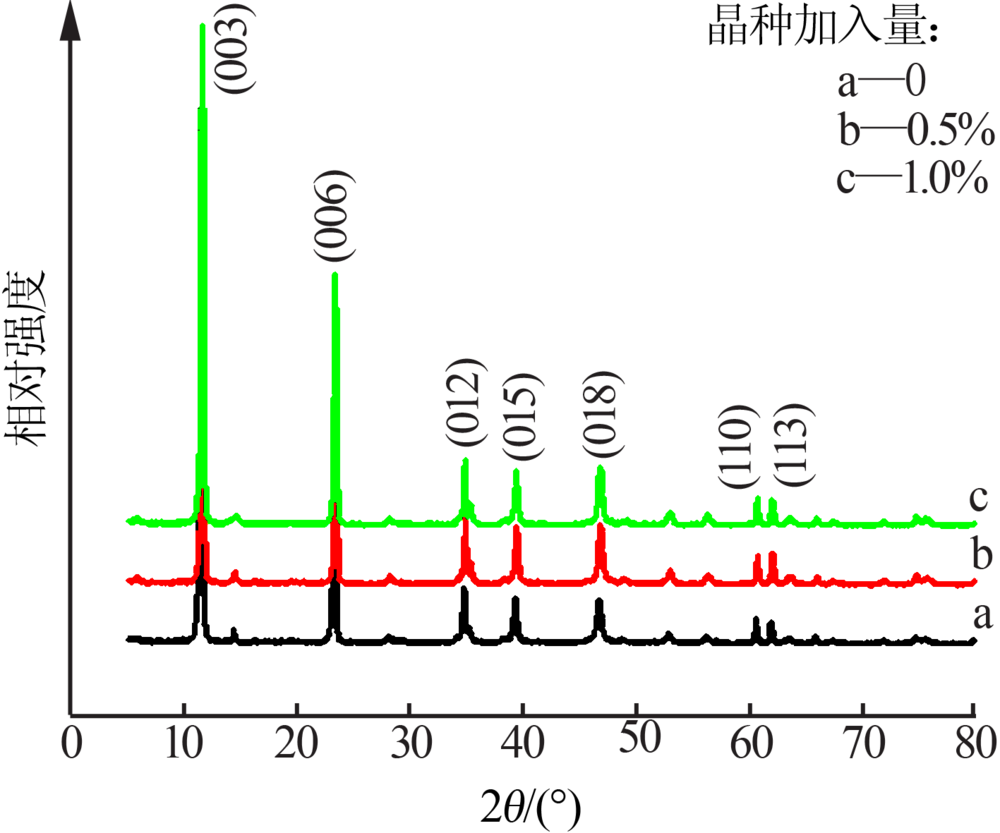
| [1] |
Adachi P M, Forano C, Besse J P . Synjournal of Al-rich hydrotalcite-like compounds by using the urea hydrolysis reaction-control of size and morphology[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2003,13(8):1988-1993.
|
| [2] |
Xu Z P, Stevenson G S, Lu C Q , et al. Stable suspension of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006,128(1):36-37.
doi: 10.1021/ja056652a
pmid: 16390109
|
| [3] |
Lin Y, Wang J, Evans D G , et al. Layered and intercalated hydrotal-cite-like materials as thermal stabilizers in PVC resin[J]. Journal of Physics & Chemistry of Solids, 2006,67(5):998-1001.
|
| [4] |
Wen R, Yang Z, Chen H , et al. Zn-Al-La hydrotalcite-like compo-unds as heating stabilizer in PVC resin[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012,30(9):895-902.
|
| [5] |
Yi S, Yang Z H, Wang S W , et al. Effects of MgAlCe-CO3 layered double hydroxides on the thermal stability of PVC resin[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2011,119(5):2620-2626.
|
| [6] |
Gupta G, Agarwal D D, Banerjee S . Role of hydrotalcites cations in thermal stabilization of poly(vinyl chloride)[J]. International Jour-nal of Polymeric Materials, 2012,61(2):124-135.
|
| [7] |
张宁, 李先铭 . 十四烷酸插层稀土类水滑石的合成及其对PVC的热稳定作用[J]. 中国塑料, 2015,29(6):93-97.
|
| [8] |
吴茂英, 罗勇新 . PVC热稳定剂的发展趋势与锌基无毒热稳定剂技术进展[J]. 聚氯乙烯, 2006(10):1-6.
|
| [9] |
Labajos F M, Rives V, Ulibarri M A . Effect of hydrothermal and the-rmal treatments on the physicochemical properties of Mg-Al hydro-talcite-like materials[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1992,27(6):1546-1552.
|
| [10] |
Hibino T, Yamashita Y, Kosuge K . Decarbonation behavior of Mg-Al-CO3 hydrotalcite-like compounds during heat treatment[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1995,43(4):427-432.
|
| [11] |
Cosimo J I D, DíEz V K, Xu M , et al. Structure and surface and ca-talytic properties of Mg-Al basic oxides[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1998,178(2):499-510.
doi: 10.1002/chem.200400409
pmid: 15584078
|
| [12] |
Velu S, Suzuki K, Osaki T , et al. Synjournal of new Sn incorporated layered double hydroxides and their evolution to mixed oxides[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1999,34(10/11):1707-1717.
|
| [13] |
周园, 李丽娟, 吴志坚 , 等. 青海盐湖资源开发及综合利用[J]. 化学进展, 2013,25(10):1613-1624.
|
 )
)