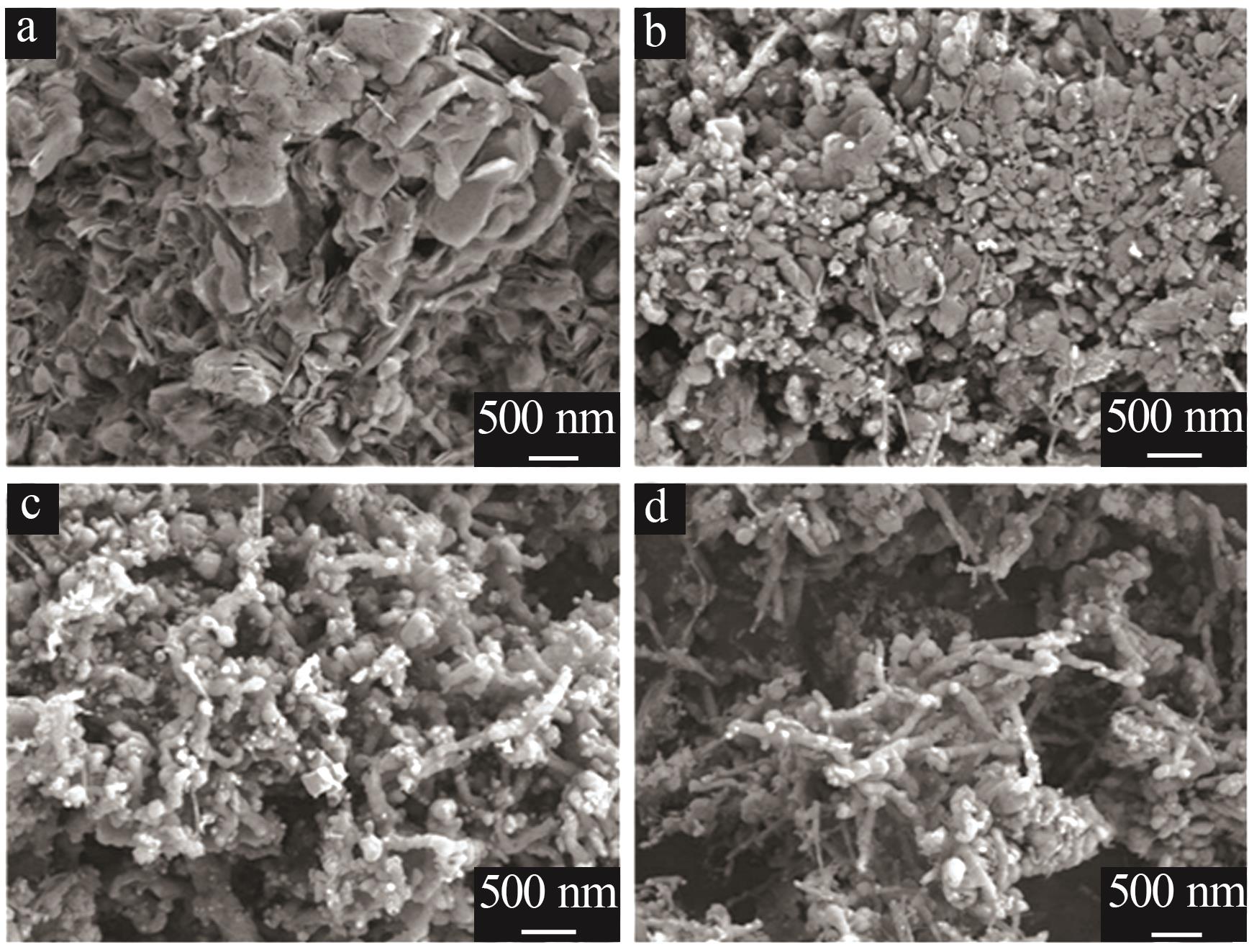
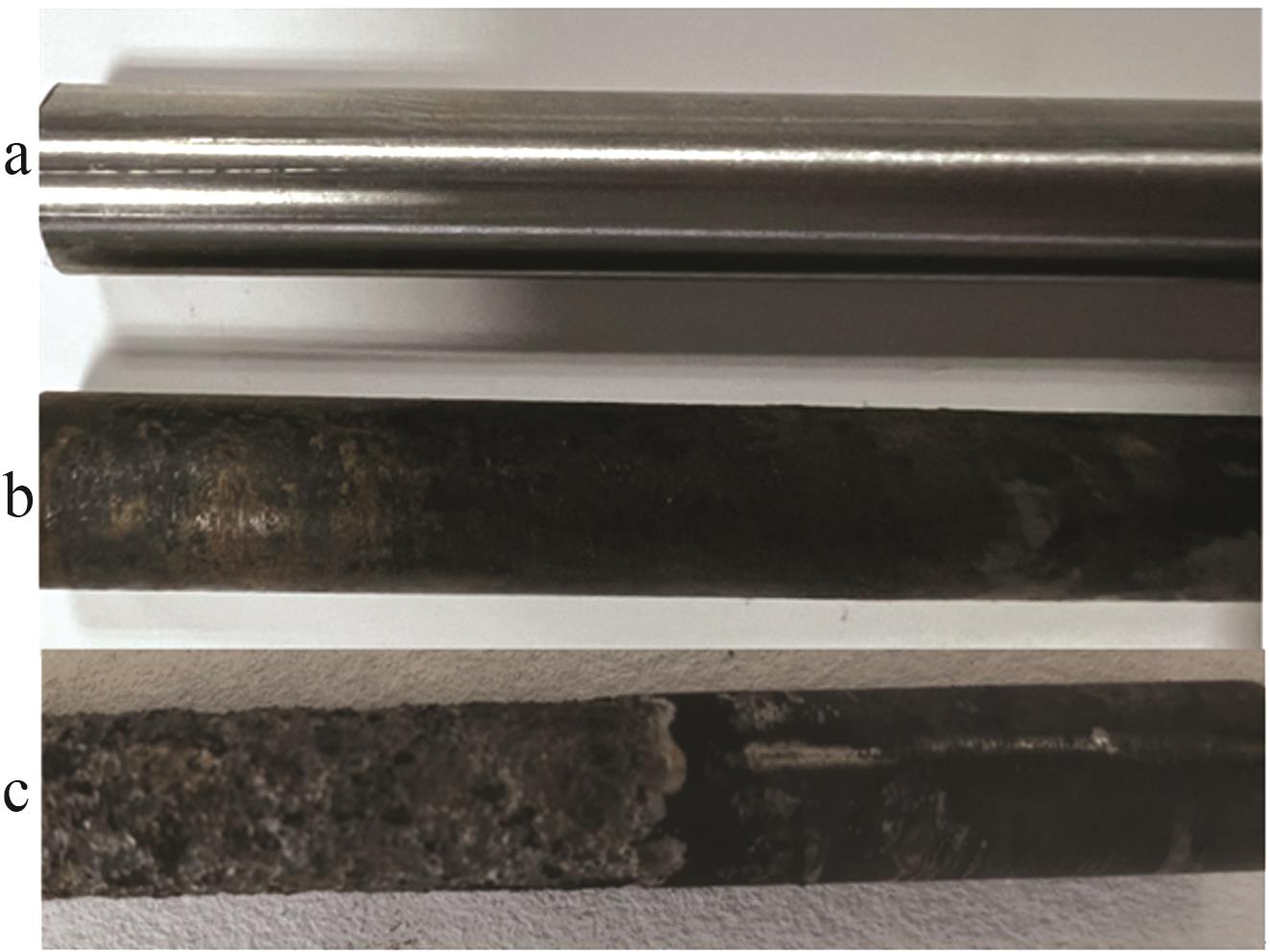
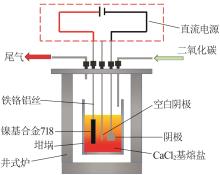
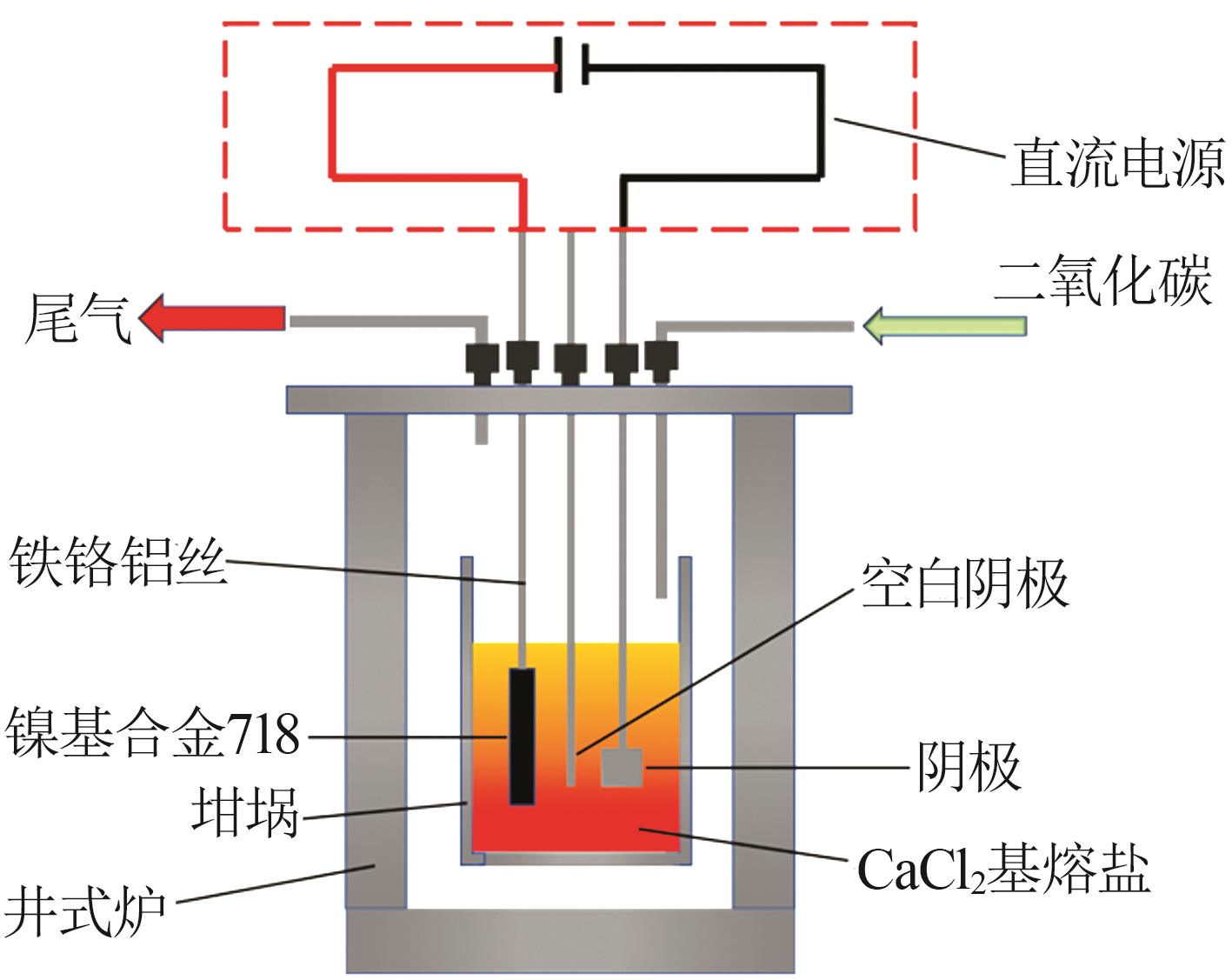
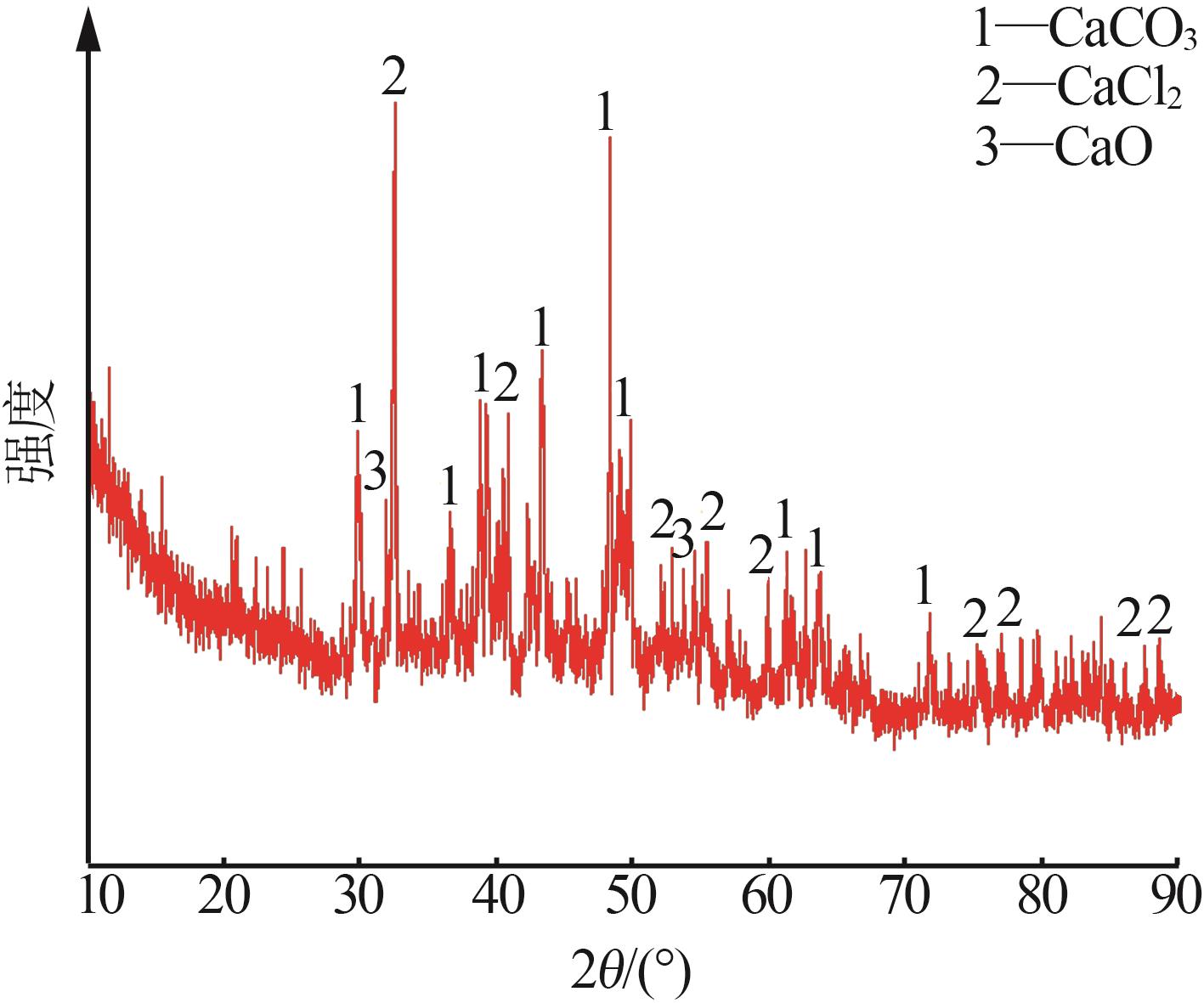
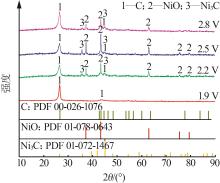
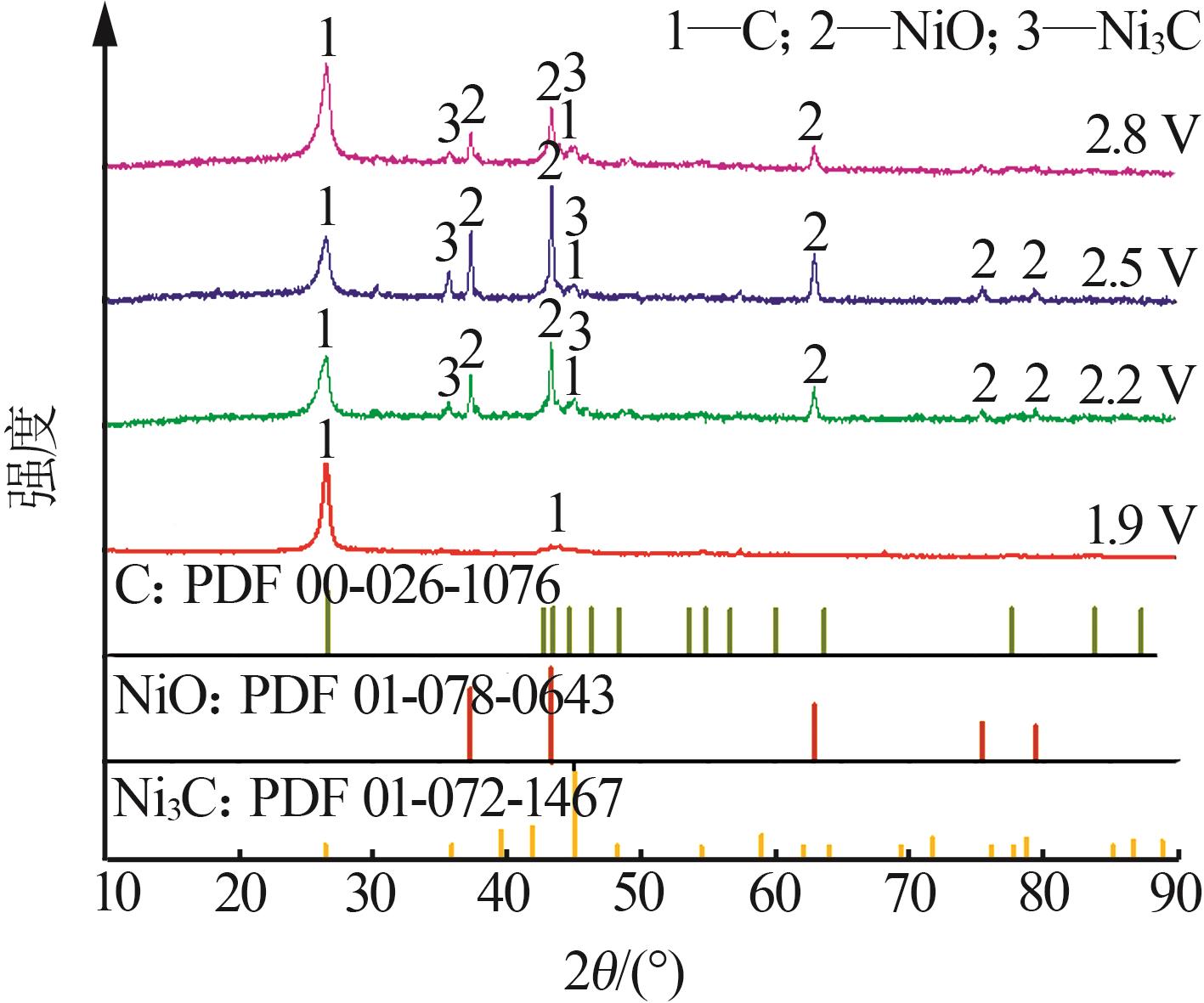
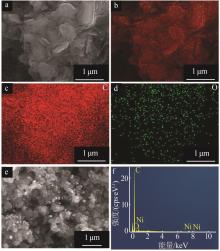
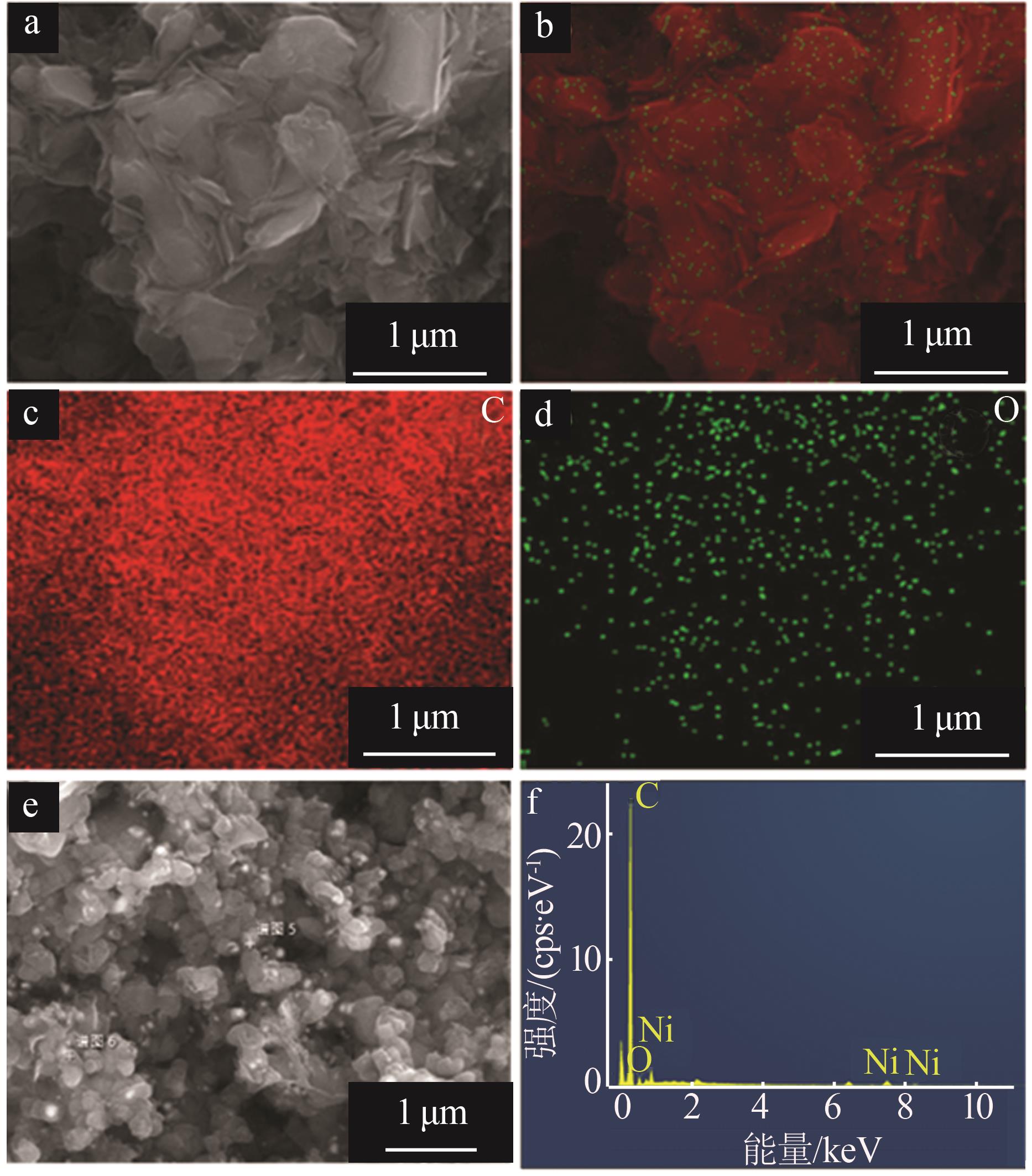
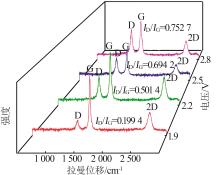
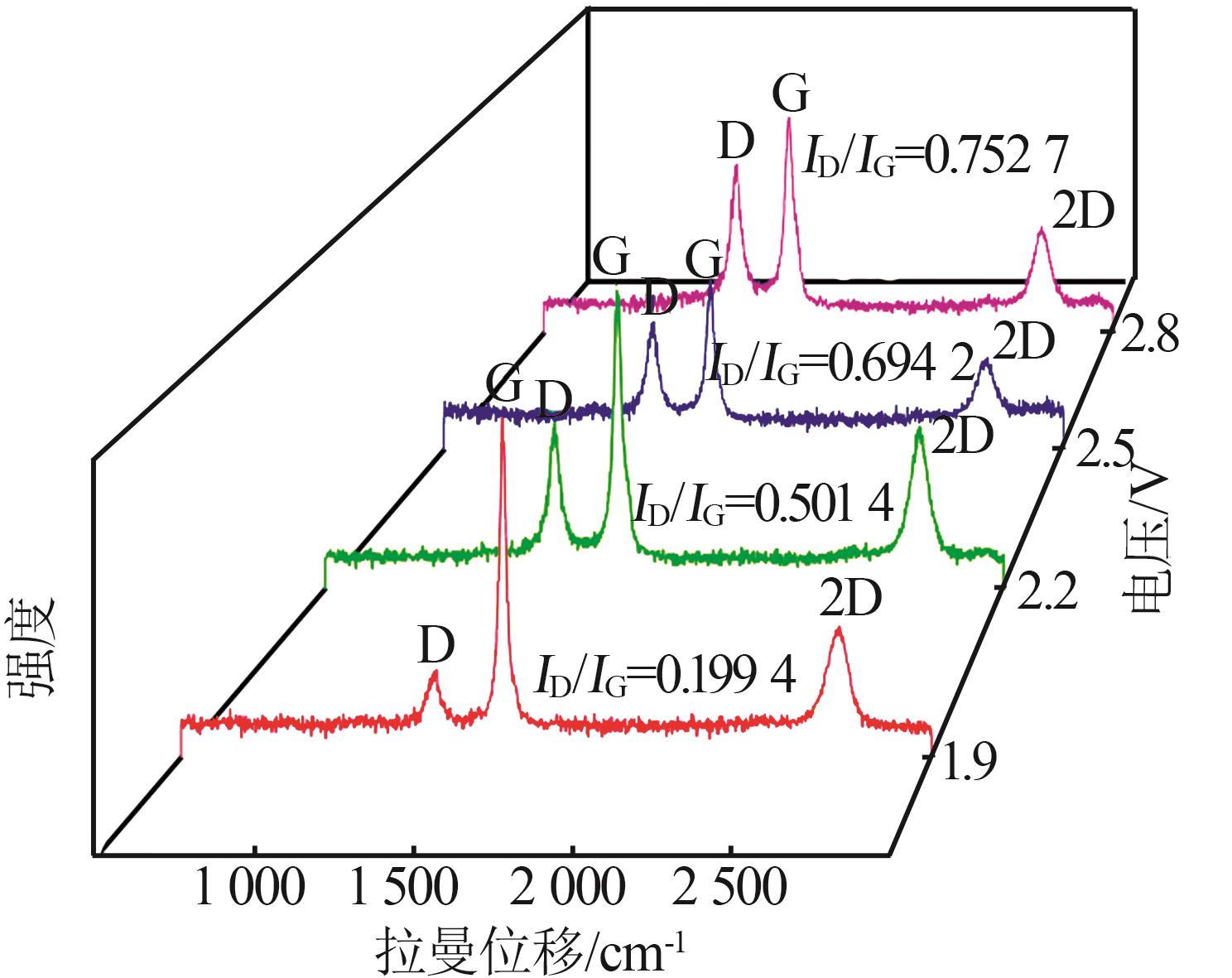
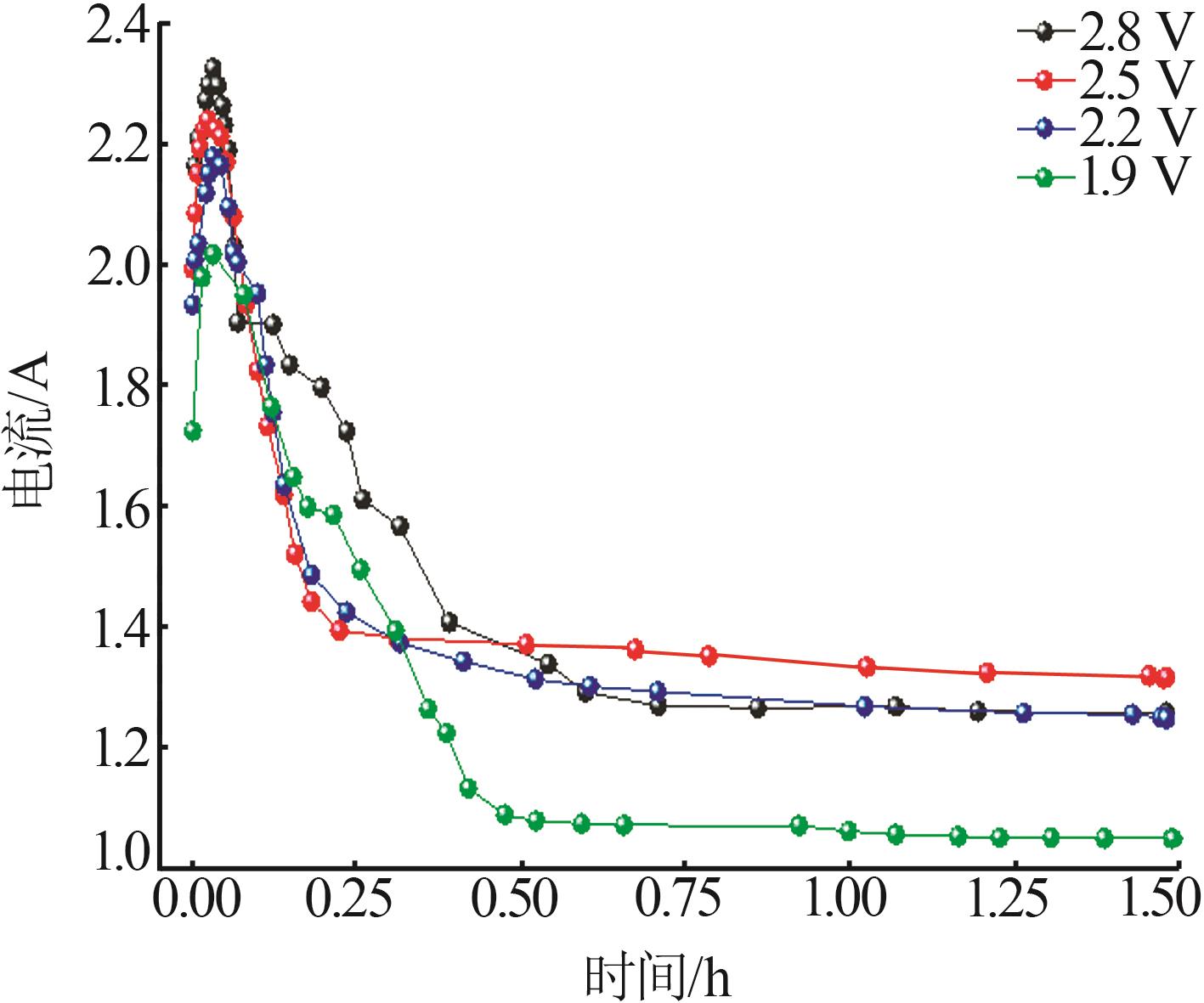
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 40-46.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0095
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
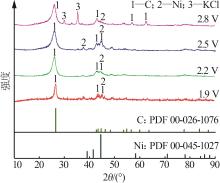
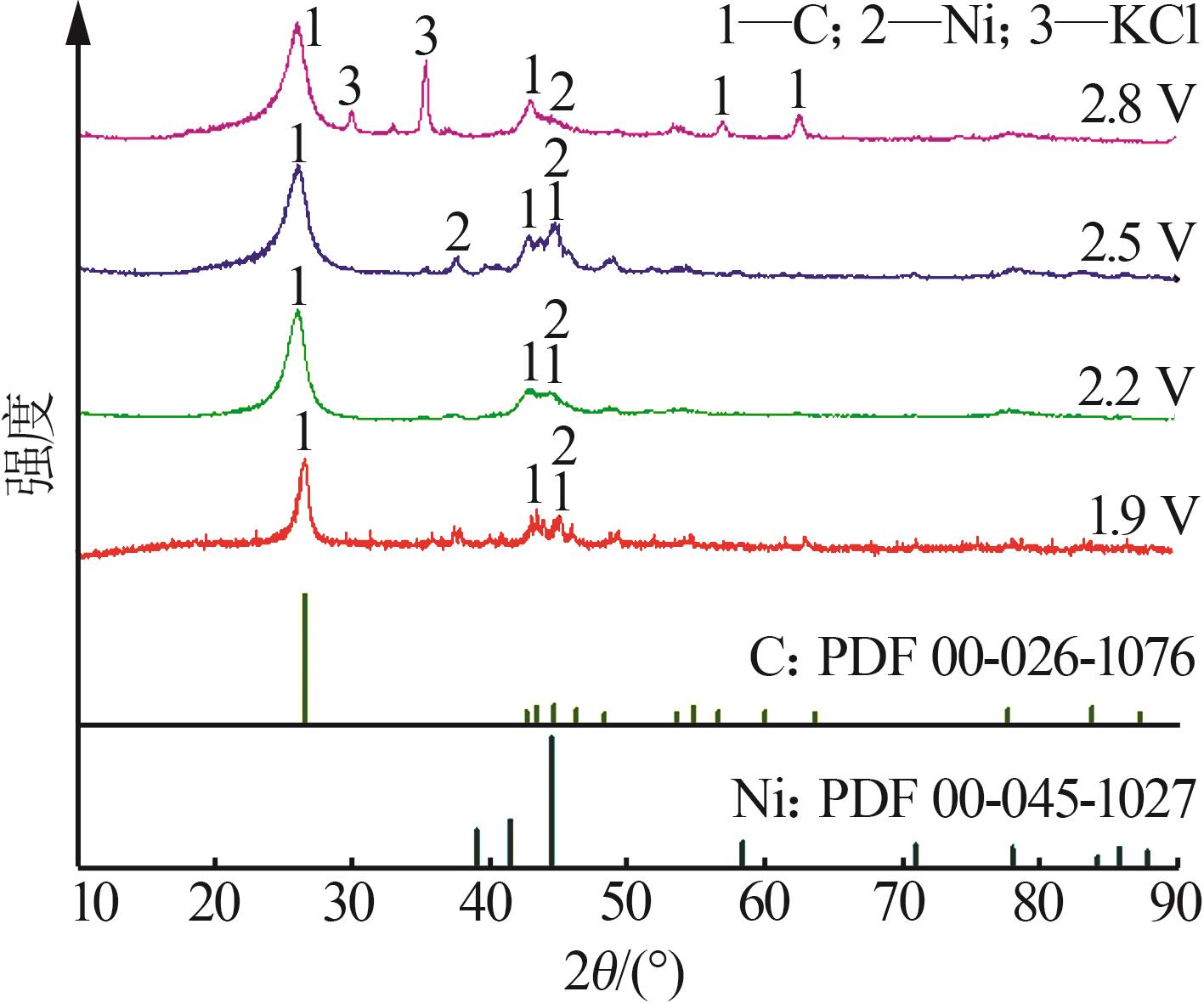
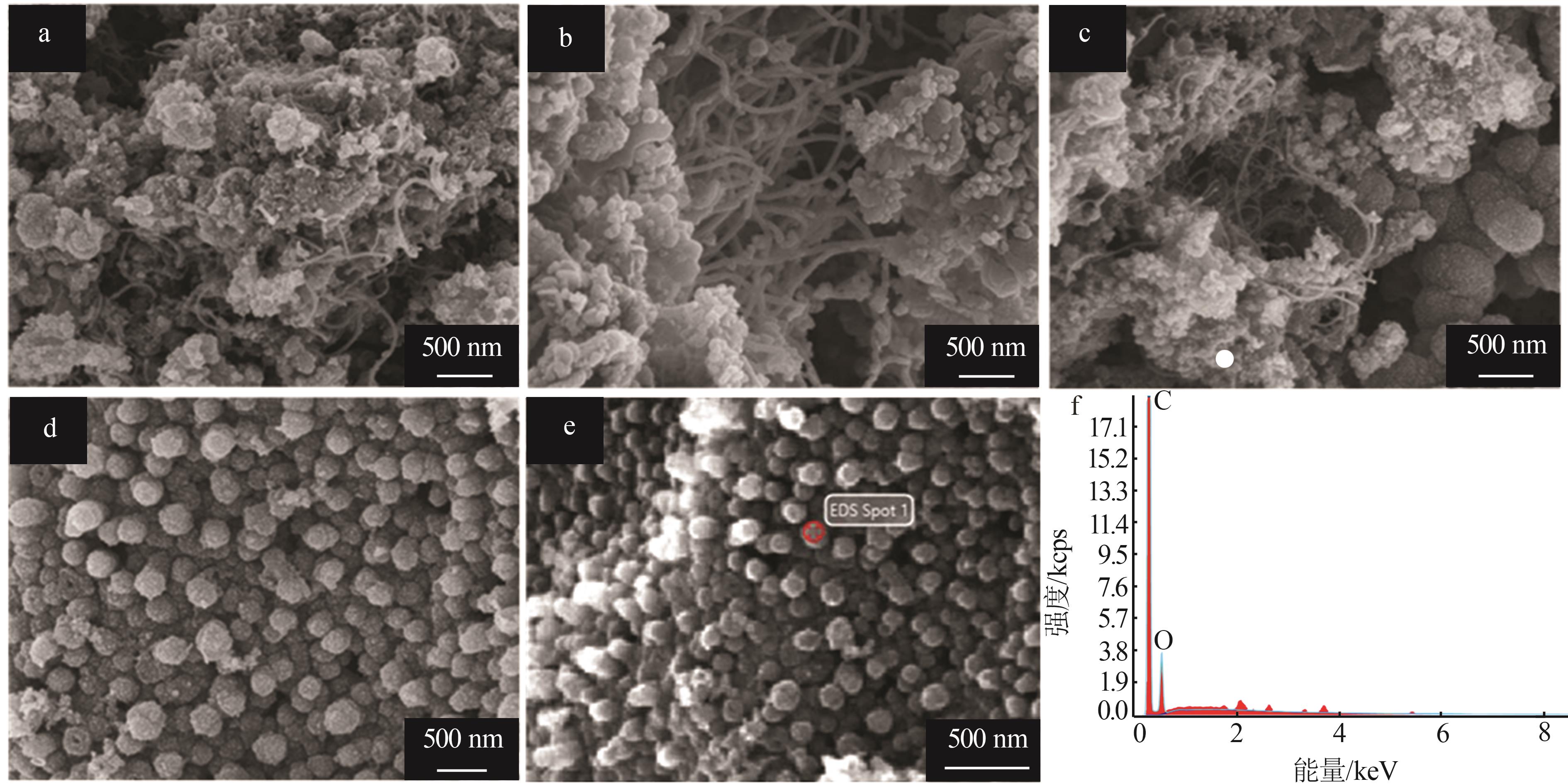
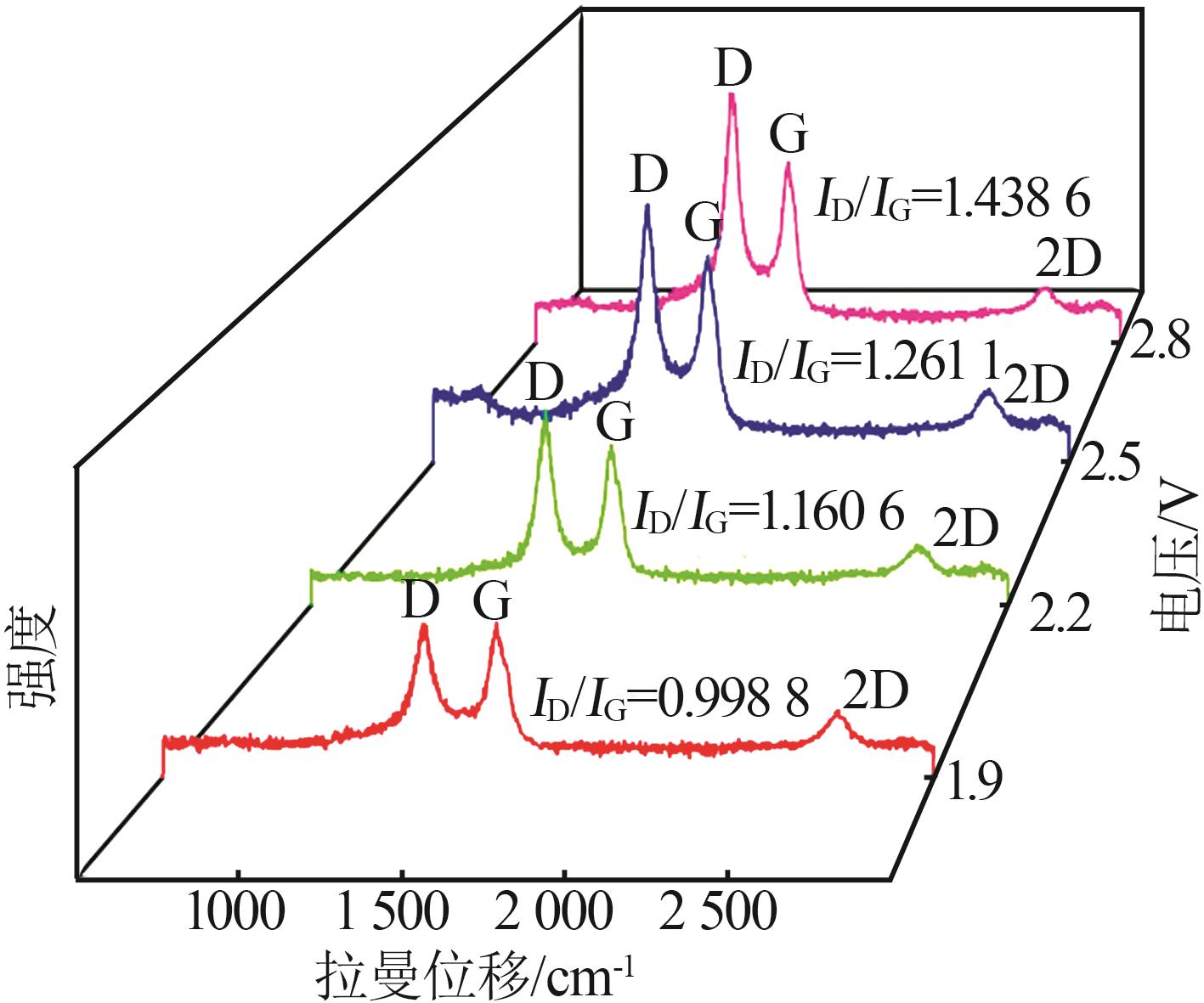
Effect of cell voltage on electrochemical conversion of CO2 to carbon materials in CaCl2 based molten salt
DENG Yinxiang1,2( ), CHEN Chaoyi1,2(
), CHEN Chaoyi1,2( ), WANG Shiyu1,2, GAO Yingxue1,2, PENG Shuang1,2
), WANG Shiyu1,2, GAO Yingxue1,2, PENG Shuang1,2
- 1. College of Materials and Metallurgy,Guizhou University,Guiyang 550025,China
2. Guizhou Province Key Laboratory of Metallurgical Engineering and Process Energy Saving,Guiyang 550025,China
-
Received:2023-02-26Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-18 -
Contact:CHEN Chaoyi E-mail:dengyinxiang3@163.com;ccy197715@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
DENG Yinxiang, CHEN Chaoyi, WANG Shiyu, GAO Yingxue, PENG Shuang. Effect of cell voltage on electrochemical conversion of CO2 to carbon materials in CaCl2 based molten salt[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(1): 40-46.
share this article
| 1 | CHEN Yunfei, WANG Mingyong, ZHANG Jintao,et al.Green and sustainable molten salt electrochemistry for the conversion of secondary carbon pollutants to advanced carbon materials[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2021,9(25):14119-14146. |
| 2 | YANG Yang, AJMAL S, ZHENG Xiuzhen,et al.Efficient nanomaterials for harvesting clean fuels from electrochemical and photoelectrochemical CO2 reduction[J].Sustainable Energy & Fuels,2018,2(3):510-537. |
| 3 | 刘丹,马哲,刘梦晓,等.CO2的电驱动还原[J].化学工业与工程,2021,38(5):1-12. |
| LIU Dan, MA Zhe, LIU Mengxiao,et al.Electricity-driven CO2 reduction[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering,2021,38(5):1-12. | |
| 4 | JIANG Rui, GAO Muxing, MAO Xuhui,et al.Advancements and potentials of molten salt CO2 capture and electrochemical transformation(MSCC-ET) process[J].Current Opinion in Electrochemistry,2019,17:38-46. |
| 5 | HU Liwen, SONG Yang, JIAO Shuqiang,et al.Direct conversion of greenhouse gas CO2 into graphene via molten salts electrolysis[J].ChemSusChem,2016,9(6):588-594. |
| 6 | HU Liwen, SONG Yang, GE Jianbang,et al.Electrochemical deposition of carbon nanotubes from CO2 in CaCl2-NaCl-based me-lts[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(13):6219-6225. |
| 7 | WANG Xirui, SHARIF F, LIU Xinye,et al.Magnetic carbon nanotubes:Carbide nucleated electrochemical growth of ferromagnetic CNTs from CO2 [J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2020,40:101218. |
| 8 | WANG Xirui, LIU Xinye, LICHT G,et al.Exploration of alkali cation variation on the synthesis of carbon nanotubes by electrolysis of CO2 in molten carbonates[J].Journal of CO2 Utilization,2019,34:303-312. |
| 9 | LIU Xinye, REN Jiawen, LICHT G,et al.Carbon nano-onions made directly from CO2 by molten electrolysis for greenhouse gas mitigation[J].Advanced Sustainable Systems,2019,3(10):201900056. |
| 10 | YU Ao, MA Guoming, JIANG Jintian,et al.Bio-inspired and eco-friendly synthesis of 3D spongy meso-microporous carbons from CO2 for supercapacitors[J].Chemistry:A European Journal,2021, 27(40):10405-10412. |
| 11 | TANG Diyong, DOU Yanpeng, YIN Huayi,et al.The capacitive performances of carbon obtained from the electrolysis of CO2 in molten carbonates:Effects of electrolysis voltage and temperatu-re[J].Journal of Energy Chemistry,2020,51:418-424. |
| 12 | CHEN Xiang, ZHAO Zhuqing, QU Jiakang,et al.Electrolysis of lithium-free molten carbonates[J].ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2021,9(11):4167-4174. |
| 13 | YIN Huayi, MAO Xuhui, TANG Diyong,et al.Capture and electrochemical conversion of CO2 to value-added carbon and oxygen by molten salt electrolysis[J].Energy & Environmental Science,2013,6(5):1538-1545. |
| 14 | TANG Diyong, YIN Huayi, MAO Xuhui,et al.Effects of applied voltage and temperature on the electrochemical production of carbon powders from CO2 in molten salt with an inert anode[J].Electrochimica Acta,2013,114:567-573. |
| 15 | CHEN Xiang, ZHAO Haijia, QU Jiakang,et al.A molten calcium carbonate mediator for the electrochemical conversion and absorption of carbon dioxide[J].Green Chemistry,2020,22(22):7946-7954. |
| 16 | GE Jianbang, HU Liwen, SONG Yang,et al.An investigation into the carbon nucleation and growth on a nickel substrate in LiCl-Li2CO3 melts[J].Faraday Discussions,2016,190:259-268. |
| 17 | OTAKE K, KINOSHITA H, KIKUCHI T,et al.CO2 gas decomposition to carbon by electro-reduction in molten salts[J].Electrochimica Acta,2013,100:293-299. |
| 18 | PARK J H, YANG J, KIM D,et al.Review of recent technologies for transforming carbon dioxide to carbon materials[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,427:130980. |
| 19 | NOVOSELOVA I A, KULESHOV S V, VOLKOV S V,et al.Electrochemical synthesis,morphological and structural characteristics of carbon nanomaterials produced in molten salts[J].Electrochimica Acta,2016,211:343-355. |
| 20 | CHOUBEY P K, KIM M S, SRIVASTAVA R R,et al.Advance review on the exploitation of the prominent energy-storage element:Lithium.Part I:From mineral and brine resources[J].Minerals Engineering,2016,89:119-137. |
| 21 | TOMKUTE V, SOLHEIM A, OLSEN E.Investigation of high-temperature CO2 capture by CaO in CaCl2 molten salt[J].Energy & Fuels,2013,27(9):5373-5379. |
| 22 | IJIJE H V, LAWRENCE R C, CHEN G Z.Carbon electrodeposition in molten salts:Electrode reactions and applications[J].RSC Advances,2014,4(67):35808-35817. |
| 23 | DENG Bowen, TANG Juanjuan, MAO Xuhui,et al.Kinetic and thermodynamic characterization of enhanced carbon dioxide absorption process with lithium oxide-containing ternary molten car-bonate[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(19):10588-10595. |
| 24 | IJIJE H V, CHEN G Z.Electrochemical manufacturing of nanocarbons from carbon dioxide in molten alkali metal carbonate salts:Roles of alkali metal cations[J].Advances in Manufacturing,2016,4(1):23-32. |
| 25 | 胡蒙均.电解钛过程碳污染机理及碳材料制备研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2020. |
| HU Mengjun.Study on the mechanism of carbon pollution and the preparation of carbon materials in deoxidation of titanium dioxide by electrochemical process[D].Chongqing:Chongqing University,2020. | |
| 26 | MAO Xuhui, YAN Zhiping, SHENG Tian,et al.Characterization and adsorption properties of the electrolytic carbon derived from CO2 conversion in molten salts[J].Carbon,2017,111:162-172. |
| 27 | WANG Xirui, LICHT G, LIU Xinye,et al.One pot facile transformation of CO2 to an unusual 3-D nano-scaffold morphology of carbon[J].Scientific Reports,2020,10:21518. |
| 28 | DENG Bowen, MAO Xuhui, XIAO Wei,et al.Microbubble effect-assisted electrolytic synthesis of hollow carbon spheres from CO2 [J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(25):12822-12827. |
| 29 | 李志达,李金莲,吴红军.熔盐体系组成对二氧化碳电化学合成新型碳材料形貌影响[J].化工进展,2019,38(9):4174-4182. |
| LI Zhida, LI Jinlian, WU Hongjun.Impact of molten salts conformation on the morphology of the electrochemically synthesized carbon materials[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2019,38(9):4174-4182. |
| [1] | HU Mingliang, ZHOU Wei, LI Bin, LAI Xiaoling. Research progress of synergistic effect catalytic reforming of methane and carbon dioxide [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(1): 23-32. |
| [2] | XU Chunhui, WANG Feng, LING Changjian, WANG Zirui, TANG Zhongfeng. Research progress of CO2 capture by metal oxides modified by molten salts [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(5): 1-7. |
| [3] | WU Luming, YU Haibin, WANG Yaquan. Study on preparation of porous carbon materials and oxygen reduction properties of their metal phosphide [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 104-110. |
| [4] | JI Hongfeng, LI Canhua, DU Gang, ZHANG Yongzhu, XU Wenzhen, LI Minghui. Research progress of preparation and sintering resistance of calcium-based CO2 trapping materials from solid waste sources [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 28-35. |
| [5] | WU Luming, YU Haibin, WANG Yaquan. Research progress of porous carbon-based non noble metal electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(10): 13-23. |
| [6] | YAN Shuo,YU Haibin,CHEN Zan. Technology development status of carbon dioxide removal from natural gas by membrane process [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(5): 38-46. |
| [7] | LI Jiahui,WANG Huan,LI Keyan,GUO Xinwen. Study on photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of Co doped polymeric carbon nitride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(11): 124-130. |
| [8] | Chang Ruopeng,Hu Xu,He Lei,Hao Guangping. Preparation of nickel-nitrogen co-doped carbon-based carbon dioxide electrocatalyst through complex-assisted method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(9): 97-103. |
| [9] | Hao Yuehui,Cheng Huaigang,Qian Aniu. Research progress of hetero-structured carbon materials for metal-O2 batteries applications [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(6): 23-30. |
| [10] | Hu Caixia,Hu Chenxin,Peng Jianlong,Zhong Xing. Preparation of porous spherical calcium carbonate with soluble starch as crystallization controller [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(5): 51-55. |
| [11] | Ye Weihui,Lü Qi,Long Changjiang. Study on rapid preparation process of high-density spherical basic nickel carbonate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(5): 69-72. |
| [12] | Li Yiyi,Sun Qiaoyi,Ma Linge,Zhuo Jinde,Song Weiguo. Study on mineralization-desorption and regeneration of post-CO2 capture by glycine salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(2): 38-41. |
| [13] | CHEN Jingjuan,LÜ Lin,WAN Houzhao,WANG Hao. Recent progress on Cu-based chalcogenides for electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction to formate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12): 14-20. |
| [14] | LI Jiahui,LI Keyan,SONG Chunshan,GUO Xinwen. Study on preparation,modification and carbon dioxide photocatalytic reduction performance of polymeric carbon nitride [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12): 21-28. |
| [15] | GUO Wei,SHI Han,YUAN Biao. Research progress of inorganic solid adsorbents in carbon dioxide capture [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12): 29-34. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||