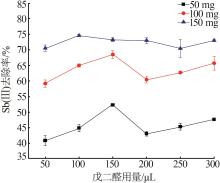
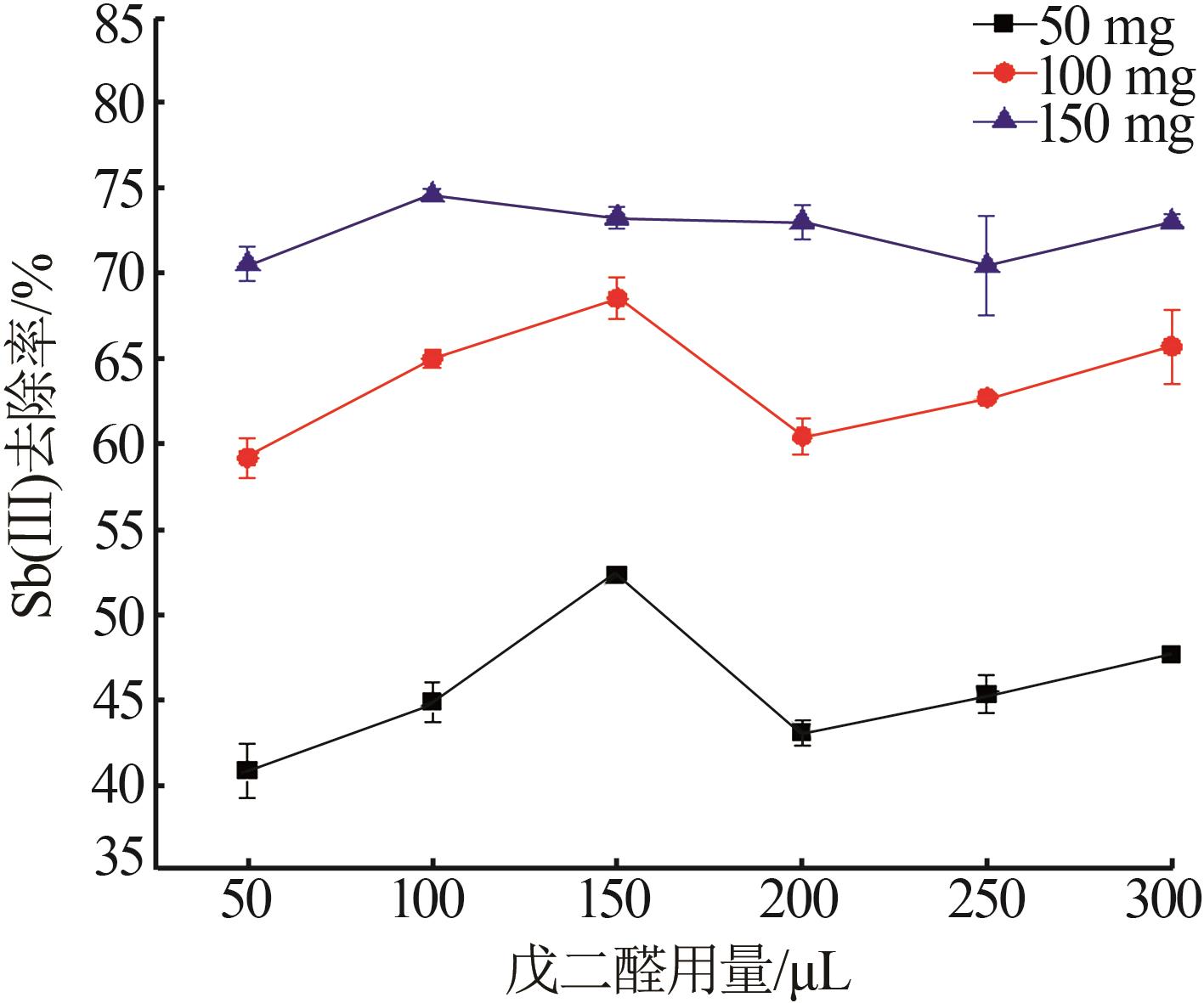
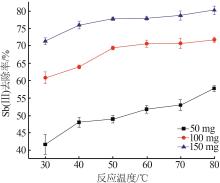
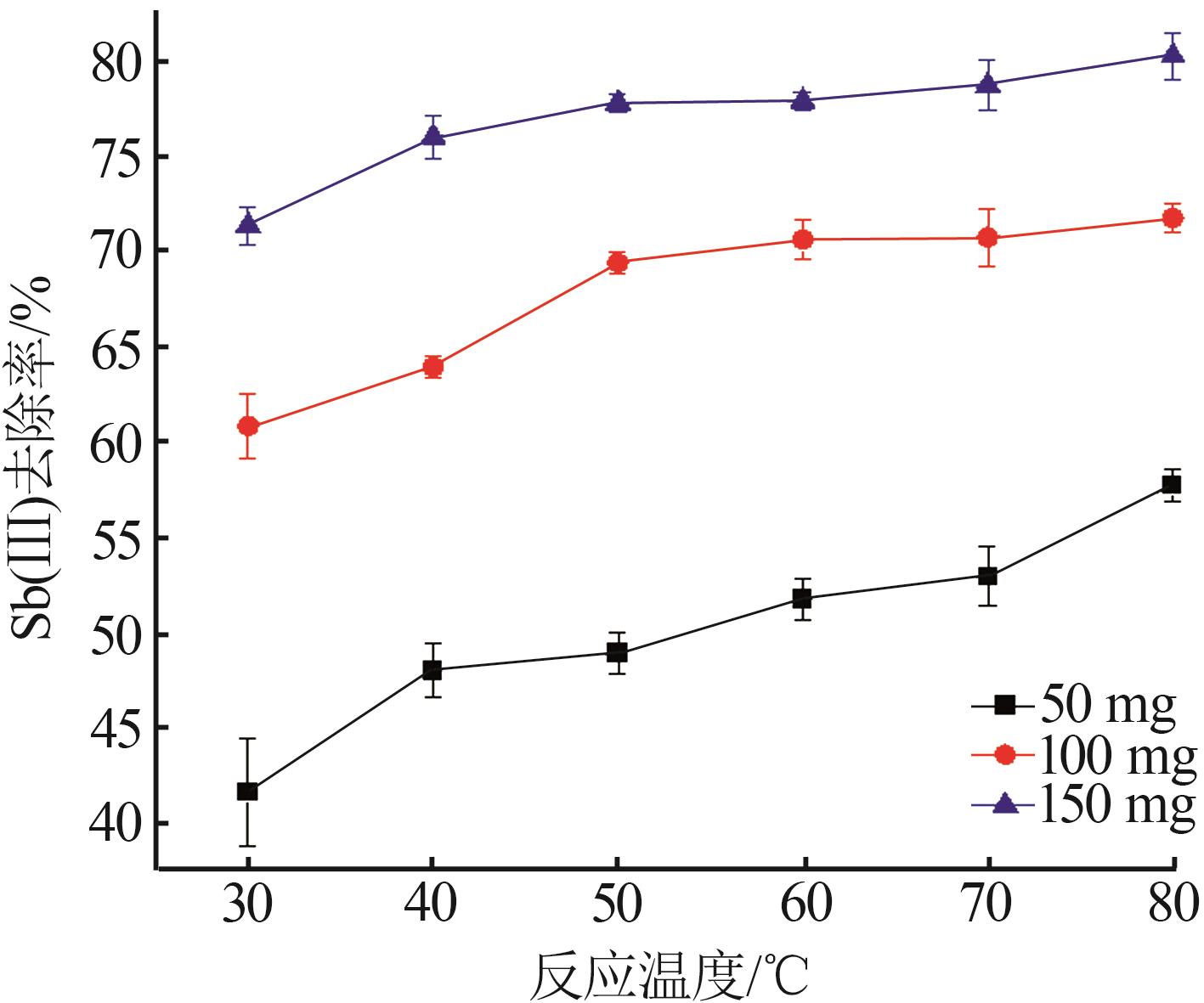
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 89-96.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0598
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
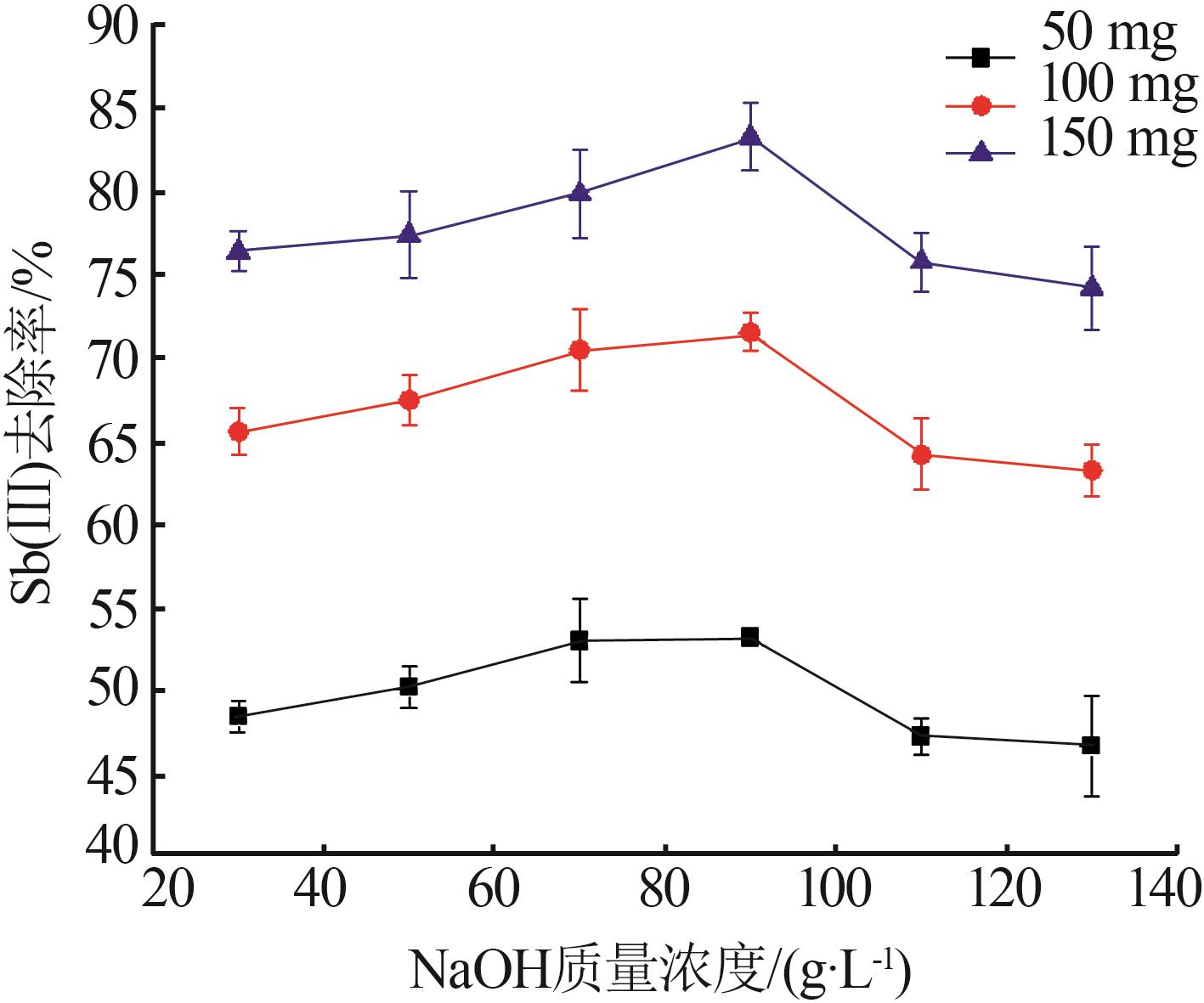
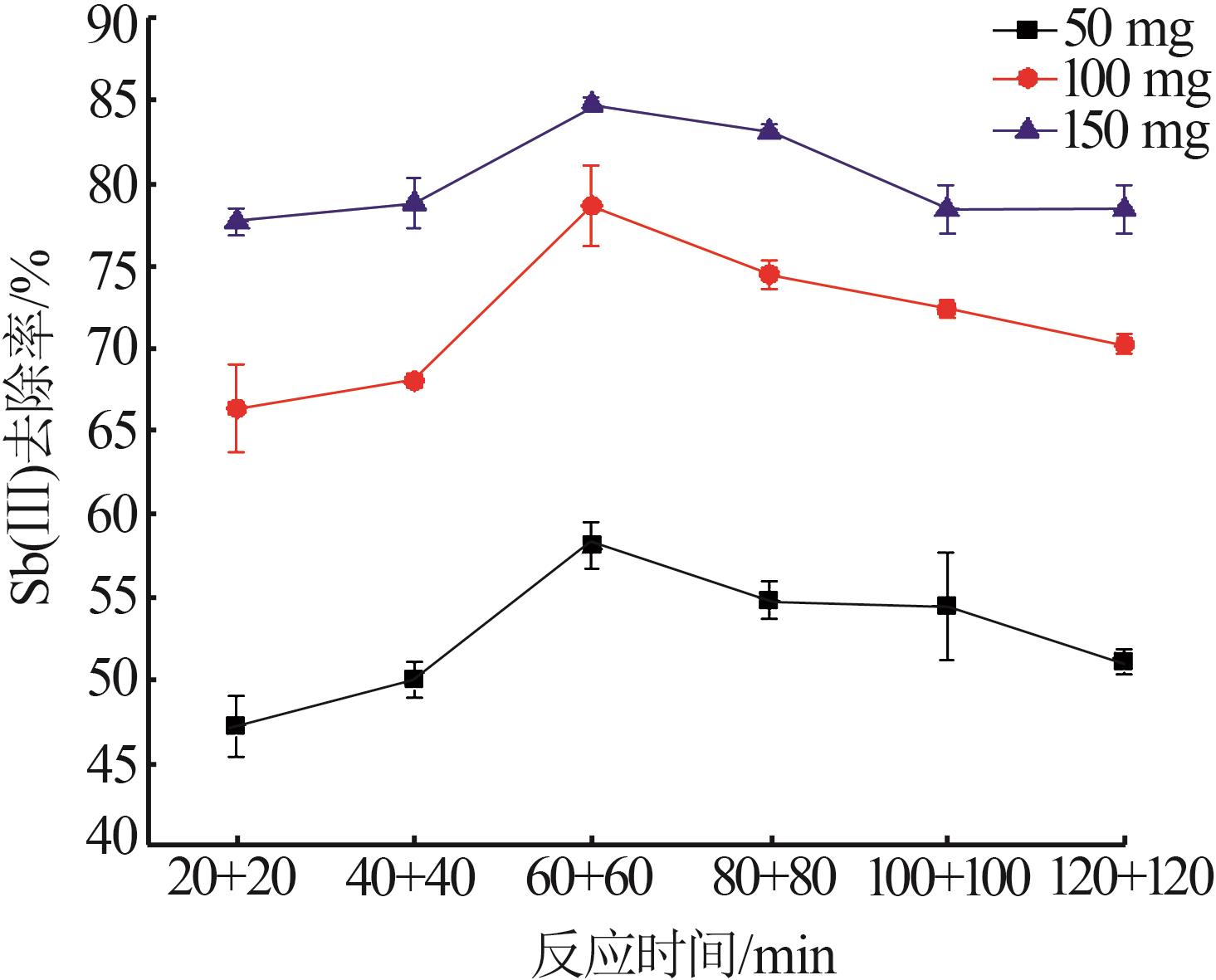
Synthesis and characterization of magnetic xanthogenated chitosan
ZHANG Peng1,2,3( ), DONG Shanshan1, WANG Yulu2, ZHAO Yuelong1
), DONG Shanshan1, WANG Yulu2, ZHAO Yuelong1
- 1. College of Environmental Science and Engineering,Taiyuan University of Technology,Taiyuan 030000,China
2. College of Civil Engineering,Hunan University of Science and Technology,Xiangtan 411201,China
3. Upgrading office of Modern College of Humanities and Sciences of Shanxi Normal University,Linfen 041075,China
-
Received:2022-10-10Online:2023-07-10Published:2023-07-13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Peng, DONG Shanshan, WANG Yulu, ZHAO Yuelong. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic xanthogenated chitosan[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(7): 89-96.
share this article
| 1 | 张天羽,李聪颖,孙赛军,等.锑的地球化学性质与华南锑矿带成因初探[J].岩石学报,2020,36(1):44-54. |
| ZHANG Tianyu, LI Congying, SUN Saijun,et al.Geochemical characteristics of antimony and genesis of antimony deposits in South China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2020,36(1):44-54. | |
| 2 | 杨昆仑,周家盛,吕丹,等.铁基复合材料的制备及其对水中锑的去除[J].化学进展,2017,29(11):1407-1421. |
| YANG Kunlun, ZHOU Jiasheng, Dan LÜ,et al.Preparation and application of iron-based composite materials for the removal of antimony from aqueous solution[J].Progress in Chemistry,2017,29(11):1407-1421. | |
| 3 | Ting LÜ, ZHANG Shuang, QI Dongming,et al.Enhanced demulsification from aqueous media by using magnetic chitosan-based flocculant[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2018,518:76-83. |
| 4 | 向香源,黄阳,冯启明,等.壳聚糖改性纳米FeS除锑性能研究[J].环境工程,2018,36(12):87-92,102. |
| XIANG Xiangyuan, HUANG Yang, FENG Qiming,et al.Study on antimony removal capacity of chitosan modified nano FeS[J].Environmental Engineering,2018,36(12):87-92,102. | |
| 5 | LONG Xiaojing, WANG Tianning, HE Mengchang.Simultaneous removal of antimony and arsenic by nano-TiO2-crosslinked chitosan(TA-chitosan) beads[J].Environmental Technology,2022. Doi:10.1080/09593330.2022.2048084 . |
| 6 | 贾双珠,李长安,刘品祯,等.壳聚糖的应用研究进展[J].精细与专用化学品,2022,30(1):25-30. |
| JIA Shuangzhu, LI Chang'an, LIU Pinzhen,et al.Research progress of application for chitosan[J].Fine and Specialty Chemicals,2022,30(1):25-30. | |
| 7 | 刘义,张淑琴,任大军,等.不同官能团改性壳聚糖吸附重金属的研究进展[J].化学试剂,2022,44(4):495-503. |
| LIU Yi, ZHANG Shuqin, REN Dajun,et al.Research progress on adsorption of heavy metals by modified chitosan with different functional groups[J].Chemical Reagents,2022,44(4):495-503. | |
| 8 | ZHU Hongshan, WU Jin, FANG Ming,et al.Synthesis of a core-shell magnetic Fe3O4-NH2@PmPD nanocomposite for efficient removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from aqueous media[J].RSC Advances,2017,7(58):36231-36241. |
| 9 | LIU Yong, JIA Shaoyi, WU Qian,et al.Studies of Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation under the magnetic field for lipase immobilization[J].Catalysis Communications,2011,12(8):717-720. |
| 10 | DONG Liming, SHAN Chengyang, LIU Yuan,et al.Characterization and mechanistic study of heavy metal adsorption by facile synthesized magnetic xanthate-modified chitosan/polyacrylic acid hydrogels[J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(17):11123. |
| 11 | Long LÜ, CHEN Nan, FENG Chuanping,et al.Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution by xanthate-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) particles[J].RSC Advanc- es,2017,7(45):27992-28000. |
| 12 | TANHAEI B, AYATI A, SILLANPÄÄ M.Magnetic xanthate modified chitosan as an emerging adsorbent for cationic azo dyes removal:Kinetic,thermodynamic and isothermal studies[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:1126-1134. |
| 13 | 李黎,马力,李鹤.磁性壳聚糖微球的制备及表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):577-582. |
| LI Li, MA Li, LI He.Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan microspheres[J].Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2020,24(4):577-582. | |
| 14 | 刘盛,朱红祥,王进,等.超声波法黄原酸化壳聚糖的制备[J].化工进展,2015,34(7):1956-1961. |
| LIU Sheng, ZHU Hongxiang, WANG Jin,et al.Preparation of xanthation chitosan with ultrasonic assistance[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2015,34(7):1956-1961. | |
| 15 | 王馨,王刚,杨凯,等.新型高分子絮凝剂黄原酸化壳聚糖 |
| 的制备及除铜性能[J].环境污染与防治,2018,40(2):133- 138. | |
| WANG Xin, WANG Gang, YANG Kai,et al.Preparation of novel macromolecule flocculant xanthated chitosan and its removal performance for copper ions[J].Environmental Pollution & Control,2018,40(2):133-138. | |
| 16 | 曾淼,张廷安,吕国志,等.黄原酸化交联壳聚糖的制备及表征[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2014,30(6):174-177. |
| ZENG Miao, ZHANG Tingan, Guozhi LÜ,et al.Preparation and characterization of xanthated crosslinked chitosan[J].Polymer Materials Science & Engineering,2014,30(6):174-177. | |
| 17 | 王刚.重金属絮凝剂聚乙烯亚胺基黄原酸钠的制备及性能研究[D].兰州:兰州交通大学,2013. |
| WANG Gang.Study on preparation and properties of heavy metal flocculant sodium polyethyleneimine xanthate[D].Lanzhou:Lanzhou Jiaotong University,2013. | |
| 18 | CHANG Qing, WANG Gang.Study on the macromolecular coagulant PEX which traps heavy metals[J].Chemical Engineering Science,2007,62(17):4636-4643. |
| 19 | 宋庆平,孟祥瑞,王崇侠,等.新型黄原酸壳聚糖对铅离子 |
| 的吸附及机理研究[J].离子交换与吸附,2014,30(2):115- 123. | |
| SONG Qingping, MENG Xiangrui, WANG Chongxia,et al.Adsorption performance and mechanism of lead ions adsorbed on xanthated chitosan[J].Ion Exchange and Adsorption,2014,30(2):115-123. | |
| 20 | 李宏达,张连红,蒋林时,等.超声波合成三(4-乙酰氨基苯基)甲烷[J].辽宁石油化工大学学报,2019,39(5):26-29. |
| LI Hongda, ZHANG Lianhong, JIANG Linshi,et al.Ultrasonic synthesis of tris-(4-acetamidphenyl) methane[J].Journal of | |
| Liaoning Shihua University,2019,39(5):26-29. | |
| 21 | 刘犇,郎印海,朱春苗,等.诺氟沙星吸附剂生物炭-壳聚糖复合微球的制备优化[J].环境科学研究,2018,31(6):1138-1143. |
| LIU Ben, LANG Yinhai, ZHU Chunmiao,et al.Optimal preparation of biochar-chitosan composite microspheres for highly efficient adsorption of norfloxacin[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(6):1138-1143. | |
| 22 | 陈新,邵正中,黄郁芳,等.不同交联剂含量对戊二醛交联壳聚糖膜结构与性能影响的研究[J].化学学报,2000,58(12):1654-1659. |
| CHEN Xin, SHAO Zhengzhong, HUANG Yufang,et al.Influence of crosslinking agent content on structure and properties of glutaraldehyde crosslinked chitosan membranes[J].Acta Chimica Sinica,2000,58(12):1654-1659. | |
| 23 | 郭睿,王超,杨江月,等.螯合絮凝剂EPPCX的制备及对Pb2+、Cu2+捕集性能研究[J].环境科学学报,2017,37(4):1396-1403. |
| GUO Rui, WANG Chao, YANG Jiangyue,et al.Preparation of heavy metal chelating flocculant EPPCX and its removal performance for Pb2+ and Cu2+ [J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2017,37(4):1396-1403. | |
| 24 | SUN Xitong, YANG Liangrong, XING Huifang,et al.Synthesis of polyethylenimine-functionalized poly(glycidyl methacrylate) ma- |
| gnetic microspheres and their excellent Cr(Ⅵ) ion removal properties[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,234:338-345. | |
| 25 | GUO Xueyi, MAO Fangfang, WANG Weijia,et al.Sulfhydryl-modified Fe3O4@SiO2 core/shell nanocomposite:Synthesis and toxicity assessment in vitro[J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(27):14983-14991. |
| 26 | ZHU He, SHEN Yi, WANG Qin,et al.Highly promoted removal of Hg(Ⅱ) with magnetic CoFe2O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles modified by thiol groups[J].RSC Advances,2017,7(62):39204-39215. |
| 27 | MA Jiangya, SHI Jun, DING Houcheng,et al.Synthesis of cationic polyacrylamide by low-pressure UV initiation for turbidity water flocculation[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,312:20-29. |
| 28 | ZHU Guocheng, LIU Junfei, YIN Jun,et al.Functionalized polyacrylamide by xanthate for Cr(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous soluti- |
| on[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,288:390-398. | |
| 29 | 张鹏,张伟,廖为雄.絮凝剂CTS-GSH的合成及其除铬性能[J].过程工程学报,2018,18(2):312-317. |
| ZHANG Peng, ZHANG Wei, LIAO Weixiong.Synthesis of chitosan-glutathione and its performance of chromium removal[J].The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2018,18(2):312-317. | |
| 30 | 高玲玲,王振宇,饶伟丽,等.骨胶原蛋白-壳聚糖共混膜中分子间作用红外光谱分析[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(3):285-291. |
| GAO Lingling, WANG Zhenyu, RAO Weili,et al.Molecular interaction analysis between collagen and chitosan blend film based on infrared spectroscopy[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2018,34(3):285-291. | |
| 31 | 李莉,王震洲,师鹏,等.硫脲νN—C=S红外光谱研究[J].红外技术,2017,39(1):95-102. |
| LI Li, WANG Zhenzhou, SHI Peng,et al.Infrared spectroscopy study of thiourea νN—C=S[J].Infrared Technology,2017,39(1):95-102. | |
| 32 | ILAIYARAJA P, KUMAR SINGHA DEB A, PONRAJU D,et al.Xanthate functionalized PAMAM dendrimer(XFPD) chelating ligand for treatment of radioactive liquid wastes[J].Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2015,3(2):1047-1054. |
| 上接第 88 页) | |
| flotation techniques[J].Chemosphere,2022,287:132231. | |
| 33 | KHATIR M Z, ABDOLLAHY M, KHALESI M R,et al.The selective separation of neodymium from aluminum using ion flotati- on[J].Minerals Engineering,2022,180:107480. |
| 34 | CHO S H, KIM J Y, CHUN J H,et al.Ultrasonic formation of nanobubbles and their zeta-potentials in aqueous electrolyte and surfactant solutions[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2005,269(1/2/3):28-34. |
| 35 | TAKAHASHI M. ζ potential of microbubbles in aqueous solutions:Electrical properties of the gas-water interface[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005,109:21858-21864. |
| 36 | MEEGODA J N, HEWAGE S A, BATAGODA J H.Application of the diffused double layer theory to nanobubbles[J].Langmuir:the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids,2019,35(37):12100-12112. |
| 37 | WILLS B A, FINCH J A.Wills' mineral processing technology[M].8th ed.Boston:Elsevier,2016:265-380. |
| 38 | PENG Weijun, CHANG Luping, LI Peiya,et al.An overview on the surfactants used in ion flotation[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2019,286:110955. |
| 39 | MICHEAU C, SCHNEIDER A, GIRARD L,et al.Evaluation of ion separation coefficients by foam flotation using a carboxylate surfactant[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2015,470:52-59. |
| 40 | SMITH R M, MARTELL A E, MOTEKAITIS R J.NIST critically selected stability constants of metal complexes database[Z].NIST standard reference database 46,2004. |
| 41 | CHIRKST D E, LOBACHEVA O L, BERLINSKII I V,et al.Recovery and separation of Ce3+ and Y3+ ions from aqueous solutions by ion flotation[J].Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry,2009,82(8):1370-1374. |
| 42 | ARSLAN F, BULUT G.Ion flotation and its applications on concentration,recovery,and removal of metal ions from solutions[J].Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing,2022,58(5):152061. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||