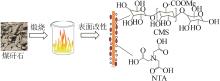
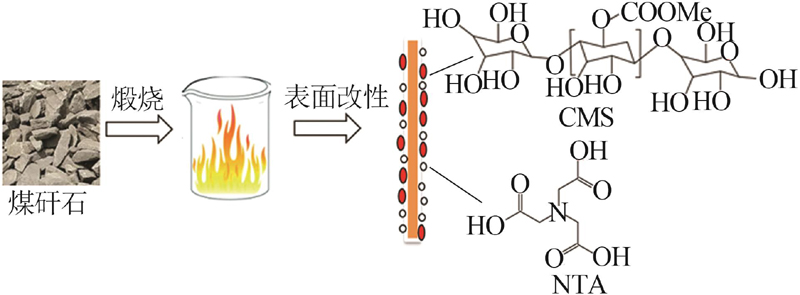
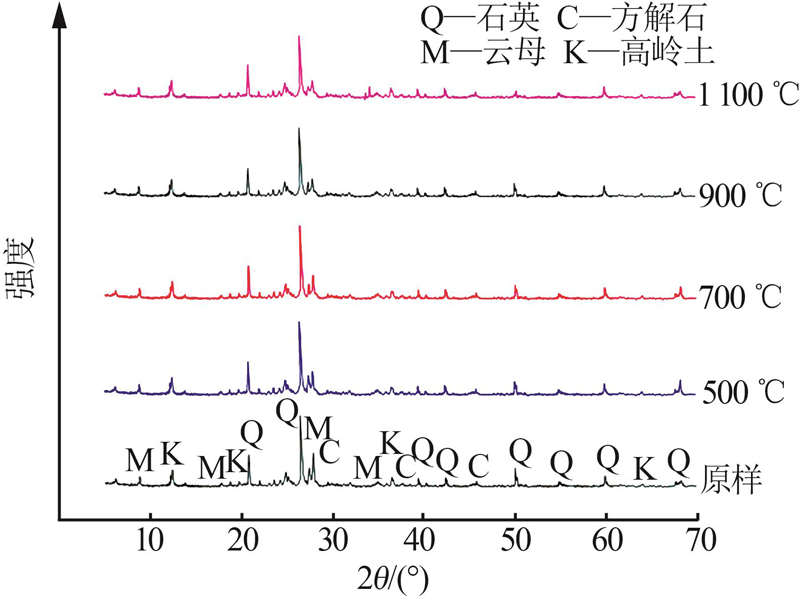
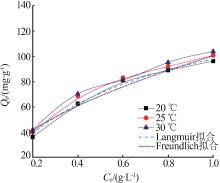
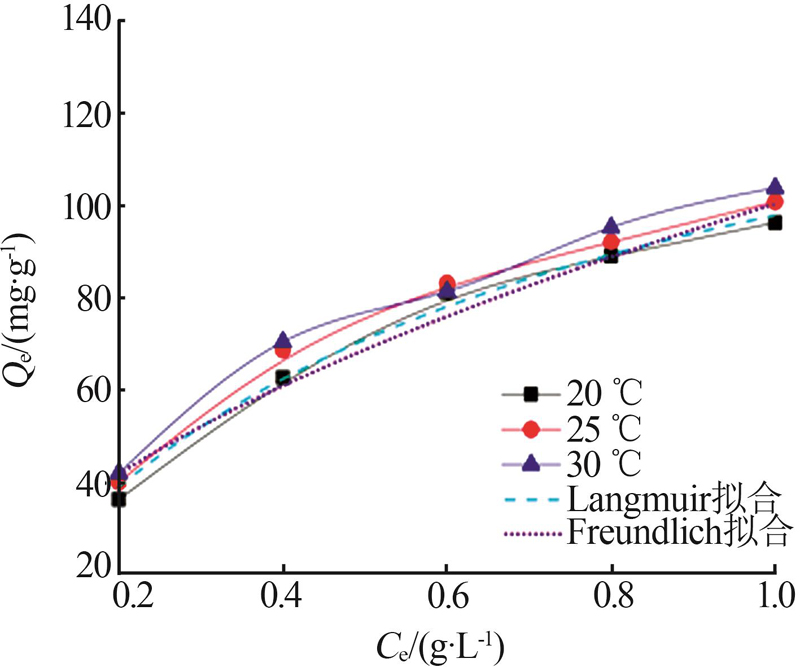
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 97-103.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0375
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on adsorption of heavy metal ions in mineral processing wastewater by chelating modified coal gangue
ZHANG Chenhu1,3( ), MA Yi2, ZHU Shan1,3, CHEN Peng1,3, WANG Chengyong1,3, LI Ziwen1,3
), MA Yi2, ZHU Shan1,3, CHEN Peng1,3, WANG Chengyong1,3, LI Ziwen1,3
- 1. School of Mining and Mechanical Engineering,Liupanshui Normal University,Liupanshui 553004,China
2. Liupanshui Zhonglian Industry and Trade Co. ,Ltd. ,Liupanshui 553000,China
3. Guizhou Provincial Key Laboratory;of Coal Clean Utilization,Liupanshui 553004,China
-
Received:2022-06-20Online:2023-04-10Published:2023-04-13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Chenhu, MA Yi, ZHU Shan, CHEN Peng, WANG Chengyong, LI Ziwen. Study on adsorption of heavy metal ions in mineral processing wastewater by chelating modified coal gangue[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 97-103.
share this article
Table 1
Chemical composition analysis of coal gangue in different areas"
| 样本 | w(SiO2) | w (Al2O3) | w (TFe) | w (CaO) | w (MgO) | w (Na2O) | w (K2O) | w (TiO2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.88 | 11.69 | 8.69 | 2.00 | 3.21 | 1.58 | 2.11 | 2.68 |
| 2 | 46.38 | 12.37 | 7.65 | 1.22 | 2.88 | 1.01 | 1.67 | 4.33 |
| 3 | 45.05 | 10.85 | 8.35 | 1.94 | 2.01 | 1.22 | 1.25 | 2.52 |
| 4 | 43.22 | 11.38 | 5.68 | 1.41 | 0.68 | 1.02 | 1.33 | 3.41 |
| 5 | 43.89 | 14.38 | 7.33 | 0.85 | 1.85 | 1.35 | 1.84 | 3.29 |
| 6 | 45.37 | 13.68 | 9.91 | 1.14 | 2.14 | 1.17 | 1.01 | 4.77 |
| 1 | 贾鲁涛,吴倩云.煤矸石特性及其资源化综合利用现状[J].煤炭技术,2019,38(11):37-40. |
| JIA Lutao, WU Qianyun.Properties and comprehensive utilization status of coal gangue resource[J].Coal Technology,2019,38(11):37-40. | |
| 2 | 郭伟.煤矸石资源化的研究进展[J].中国矿业,2007,16(7):85-87. |
| GUO Wei.Progress on utilization of coal gangue[J].China Mining Magazine,2007,16(7):85-87. | |
| 3 | 程金生,惠冰,孟凌霄,等.公路工程煤矸石填筑路基可行性研究[J].建筑技术开发,2021,48(3):155-156. |
| CHENG Jinsheng, HUI Bing, MENG Lingxiao,et al.Feasibility study of roadbed filling with gangue for highway engineering[J].Building Technology Development,2021,48(3):155-156. | |
| 4 | 徐平坤.利用煤矸石生产耐火材料[J].再生资源与循环经济,2016,9(3):41-44. |
| XU Pingkun.Production of refractory materials by using coal gangue[J].Recyclable Resources and Circular Economy,2016,9(3):41-44. | |
| 5 | 俞心刚,李德军,田学春,等.煤矸石泡沫混凝土的研究[J].新型建筑材料,2008,35(1):16-19. |
| YU Xingang, LI Dejun, TIAN Xuechun,et al.Study on gangue foam concrete[J].New Building Materials,2008,35(1):16-19. | |
| 6 | 张新策,郑波,夏静慧,等.一种煤矸石生产硅酸盐水泥熟料的制备方法:中国,110845159A[P].2020-02-28. |
| 7 | GAO Yajun, HUANG Huijuan, TANG Wenjing,et al.Preparation and characterization of a novel porous silicate material from coal gangue[J].Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2015,217:210-218. |
| 8 | QIAN Tingting, LI Jinhong.Synthesis of Na-A zeolite from coal gangue with the in situ crystallization technique[J].Advanced Powder Technology,2015,26(1):98-104. |
| 9 | CHEN Jianlong, LU Xinwei.Synthesis and characterization of zeolites NaA and NaX from coal gangue[J].Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2018,20(1):489-495. |
| 10 | 邓晓虎,乐英红,高滋.K2CO3活化煤矸石制备活性炭吸附剂[J].应用化学,1997,14(3):49-52. |
| DENG Xiaohu, YUE Yinghong, GAO Zi.Preparation of active carbon adsorbents from elutrilithe via K2CO3 activation[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry,1997,14(3):49-52. | |
| 11 | Qikai LÜ, DONG Xinfa, ZHU Zhiwen,et al.Environment-oriented low-cost porous mullite ceramic membrane supports fabricated from coal gangue and bauxite[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2014,273:136-145. |
| 12 | DONG Weiyang, JIN Yaoyao, ZHOU Kang,et al.Efficient degradation of pharmaceutical micropollutants in water and wastewater by FeIII-NTA-catalyzed neutral photo-Fenton process[J].Science of the Total Environment,2019,688:513-520. |
| 13 | SAINI S, KATNORIA J K, KAUR I.Surface modification of Dendrocalamus strictus charcoal powder using nitrilotriacetic acid as a chelating agent and its application for removal of copper(Ⅱ) from aqueous solutions[J].Separation Science and Technology,2021,56(2):275-289. |
| 14 | 陈亮,陈东辉,李步祥.壳聚糖吸附处理废水的研究进展[J].四川环境,2001,20(3):19-23. |
| CHEN Liang, CHEN Donghui, LI Buxiang.Review on the adsorption of chitosan in wastewater treatment[J].Sichuan Environment,2001,20(3):19-23. | |
| 15 | 周秋生.海藻酸盐凝胶微球的制备及其吸附性能研究[D].绵阳:西南科技大学,2015. |
| ZHOU Qiusheng.Studies on preparation and adsorption performance of alginate gel microspheres[D].Mianyang:Southwest Uni-versity of Science and Technology,2015. | |
| 16 | 何莼,李忠,赵桢霞,等.低成本木质素吸附剂对废水中Pb2+吸附性能的研究[J].离子交换与吸附,2006,22(6):481-488. |
| HE Chun, LI Zhong, ZHAO Zhenxia,et al.Adsorption properties of a low-cost lignin adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions Pb2+ [J].Ion Exchange and Adsorption,2006,22(6):481-488. | |
| 17 | 孔德顺,李志,李琳,等.六盘水矿区煤矸石理化性质及资源化利用分析[J].煤炭工程,2013,45(7):99-101. |
| KONG Deshun, LI Zhi, LI Lin,et al.Analysis on physicochemical properties and resource utilization of coal rejects in Liupanshui mining area[J].Coal Engineering,2013,45(7):99-101. | |
| 18 | 吴红,孔德顺,张绪勇,等.六盘水矿区煤矸石理化特性及热活化研究[J].硅酸盐通报,2016,35(11):3814-3818. |
| WU Hong, KONG Deshun, ZHANG Xuyong,et al.Physicochemical properties and thermal activation of coal gangue in Liupanshui mining area[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2016,35(11):3814-3818. | |
| 19 | ZHANG Ge, YANG Huifen, JIANG Meiling,et al.Preparation and characterization of activated carbon derived from deashing coal slime with ZnCl2 activation[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2022,641.Doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.128124 . |
| 20 | ZHANG Weiqing, DONG Chaowei, HUANG Peng,et al.Experimental study on the characteristics of activated coal gangue and coal gangue-based geopolymer[J].Energies,2020,13(10).Doi:10.3390/en13102504 . |
| 21 | FA'IZZAH M, WIDJIJONO W, KAMIYA Y,et al.Synthesis and characterization of white mineral trioxide aggregate using precipitated calcium carbonate extracted from limestone[J].Key Engineering Materials,2020,840:330-335. |
| 22 | TIAN Xianghui, SONG Dazhao, HE Xueqiu,et al.Investigation on micro-surface adhesion of coals and implications for gas occurrence and coal and gas outburst mechanism[J].Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2021,94.Doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104115 . |
| 23 | MOHAMMADI R, AZADMEHR A, MAGHSOUDI A.Fabrication of the alginate-combusted coal gangue composite for simultaneous and effective adsorption of Zn(Ⅱ) and Mn(Ⅱ)[J].Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2019,7(6).Doi:10.1016/j.jece.2019.103494 . |
| 24 | JIN Yuxuan, LIU Ze, HAN Le,et al.Synthesis of coal-analcime composite from coal gangue and its adsorption performance on heavy metal ions[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,423.Doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127027 . |
| [1] | YANG En, SHEN Hongyan, LIU Youzhi. In situ modification of superfine magnesium hydroxide with silicon polyether [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 42-49. |
| [2] | LI Chao, WANG Liping, DAI Yin, GAO Guimei, ZHANG Yunfeng, HONG Yu, XU Lijun, CUI Yongjie. Study on alkali fusion hydrothermal synthesis of 13X zeolite from high silicon tailings and its adsorption on lead,copper and zinc ions [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(9): 88-93. |
| [3] | WANG Lijuan, YAN Kezhou, GUO Zhiqiang, ZHAO Zhonghe, GUO Yanxia, CHENG Fangqin. Preparation of poly-aluminum chloride from acid leaching liquor of red mud-coal gangue activated by sodium salt [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(4): 76-83. |
| [4] | LIU Xueting, MAO Lingfeng, HU Yun, PENG Xi, FAN Xuemei, CHEN Yanlei, LIU Wenkui. Synergistic dispersion of SiO2 by dispersant and supershear [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(3): 71-77. |
| [5] | TIAN Peng, XU Jingang, XU Qianjin, LIU Kunji, PANG Hongchang, NING Guiling. Preparation of nano-alumina slurry and its application in modifying lithium-ion battery cathode material [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(12): 43-49. |
| [6] | LIANG Chao,LI Chunquan,SUN Zhiming,ZHENG Shuilin. Surface modification effect and mechanism of new organic modifiers on ground calcium carbonate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(7): 70-77. |
| [7] | LI Yalin,HUANG Yu,Li Dongao,SUI Zhaoyi,HE Haiyang,LIU Haozhao. Preparation of Fe-impregnated biochar from food waste by solvothermal method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(11): 96-103. |
| [8] | BAN Liping,MA Min. Study on synthesis and photoluminescence mechanism of CuAl2O4 and CuAl2O4:Cr phosphors [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(1): 56-61. |
| [9] | Jian Mengqi,Zhang Kun,Xie Xin,Chen Xiyong. Research progress of LiMnPO4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(9): 18-23. |
| [10] | Wang Ling,Xiong Yuting,Cui Zhaochun,Jia Lanbo,Fan Chenzi,Liu Shuxian,Nie Yimiao. Modification of ultrafine silica prepared by olivine acid dissolution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(3): 34-37. |
| [11] | Yang Quancheng,Zhang Kaiyong,Guo De,Shi Changsheng,Ma Ruixin,Tang Ligang,Du Zhenyu. Research on adsorption properties of methylene blue by mesoporous calcium silicate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(10): 86-91. |
| [12] | Chen Lijia,Chen Haibin,Li Rongyong. Application progress of mechanical coating technique in preparation of photocatalytic materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(8): 1-5. |
| [13] | Liu Xiaoting,Wen Jiuran,Wang Siyu,Liu Kaiping,Gao Ni,Zhong Jiaqiang. Study on strengthening technology of raw coal gangue aggregate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(4): 65-71. |
| [14] | Yang Quancheng,Gong Zhiming,Mao Yanyu,Li Xiaodong,Zhang Yancheng,Shi Changsheng,Zeng Ming. Preparation of mesoporous calcium silicate with alumina-extracted coal gangue by hydrothermal method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(11): 86-90. |
| [15] | Xie Juan,Xia Runnan,Du Hongxia,Xu Yongquan,Zhao Shuchun,Xu Hong,Kang Wentong. Preparation of α-Fe2O3/coal gangue composite photocatalyst and its application in pentachlorophenol degradation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(5): 74-77. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||