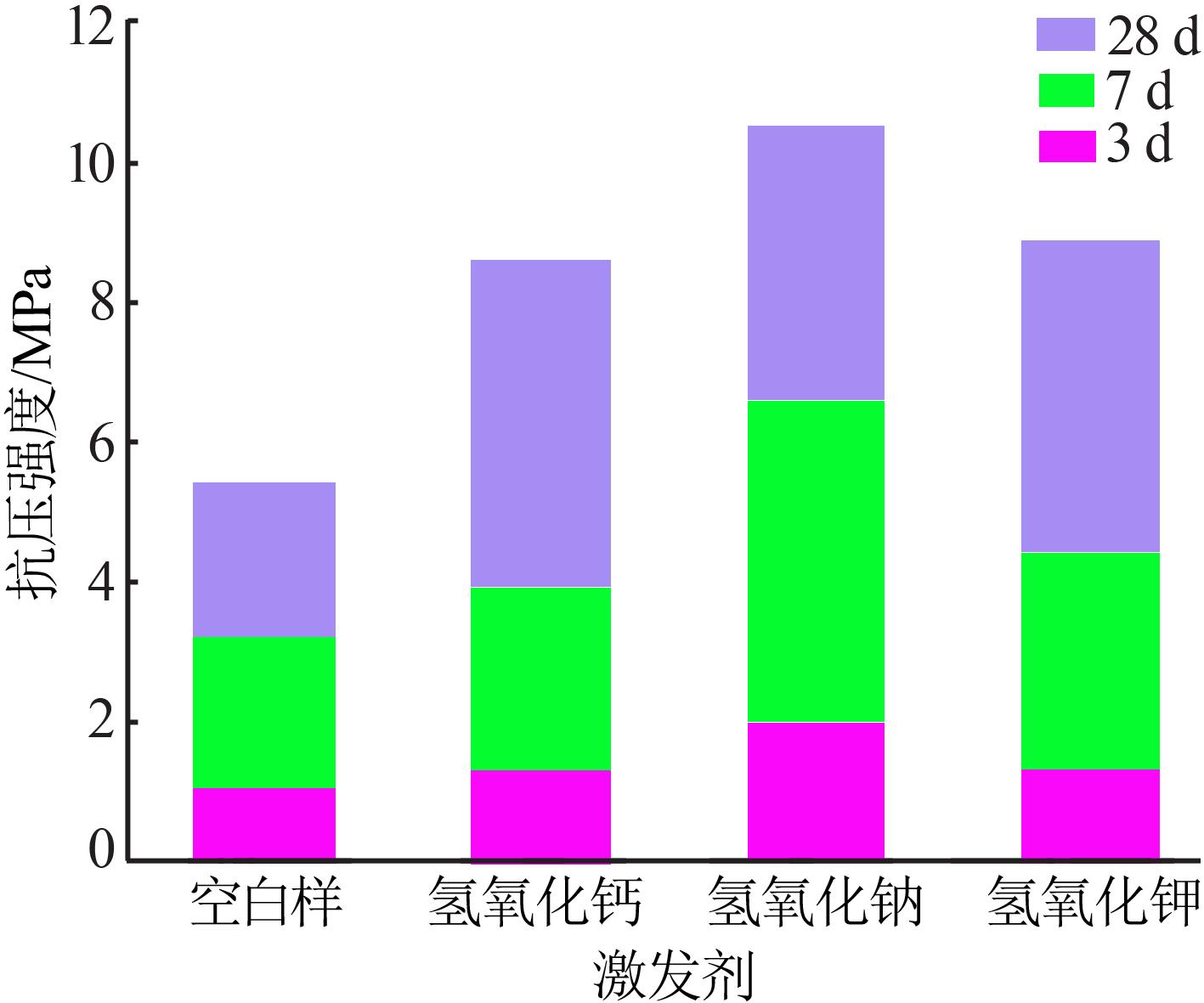
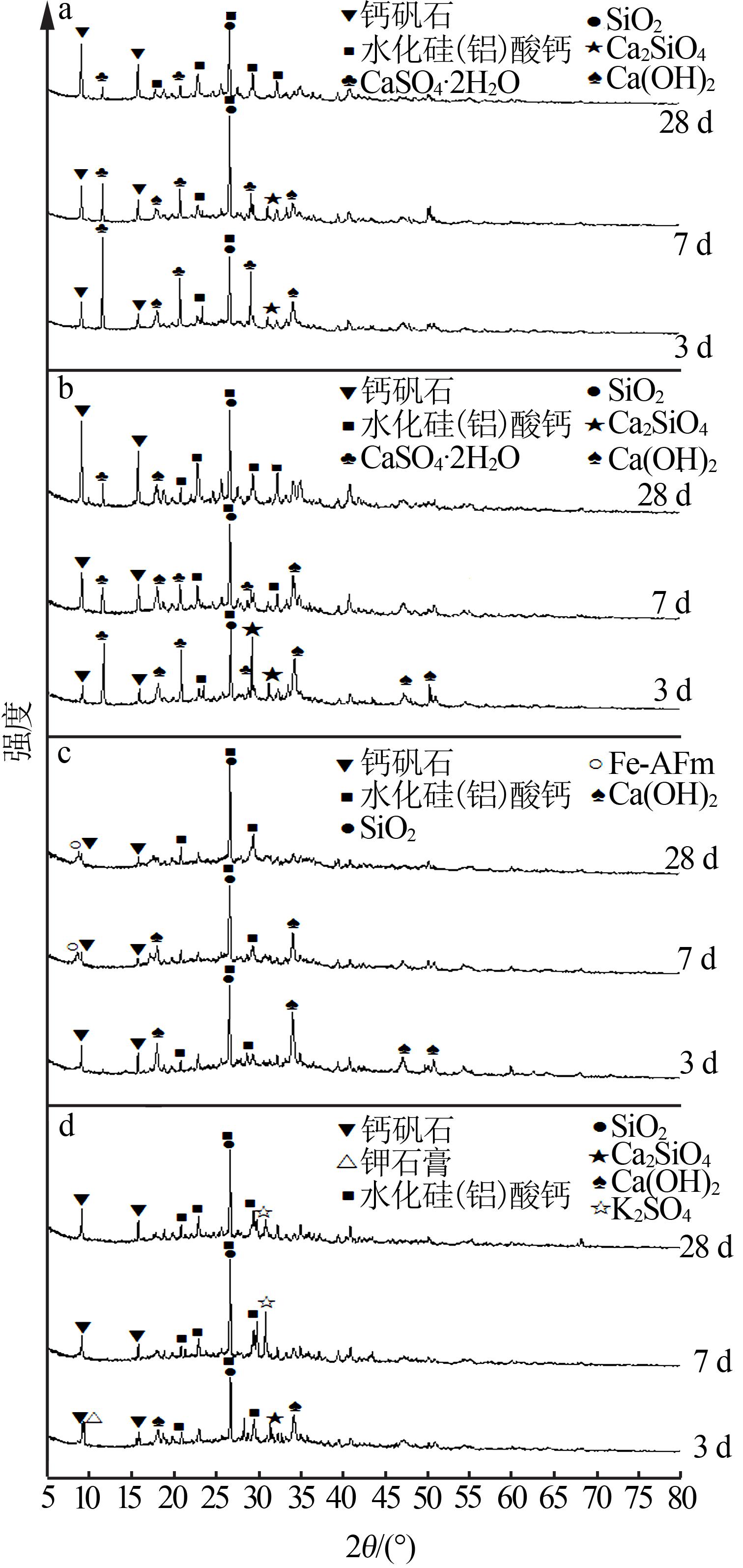
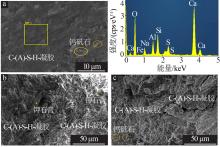
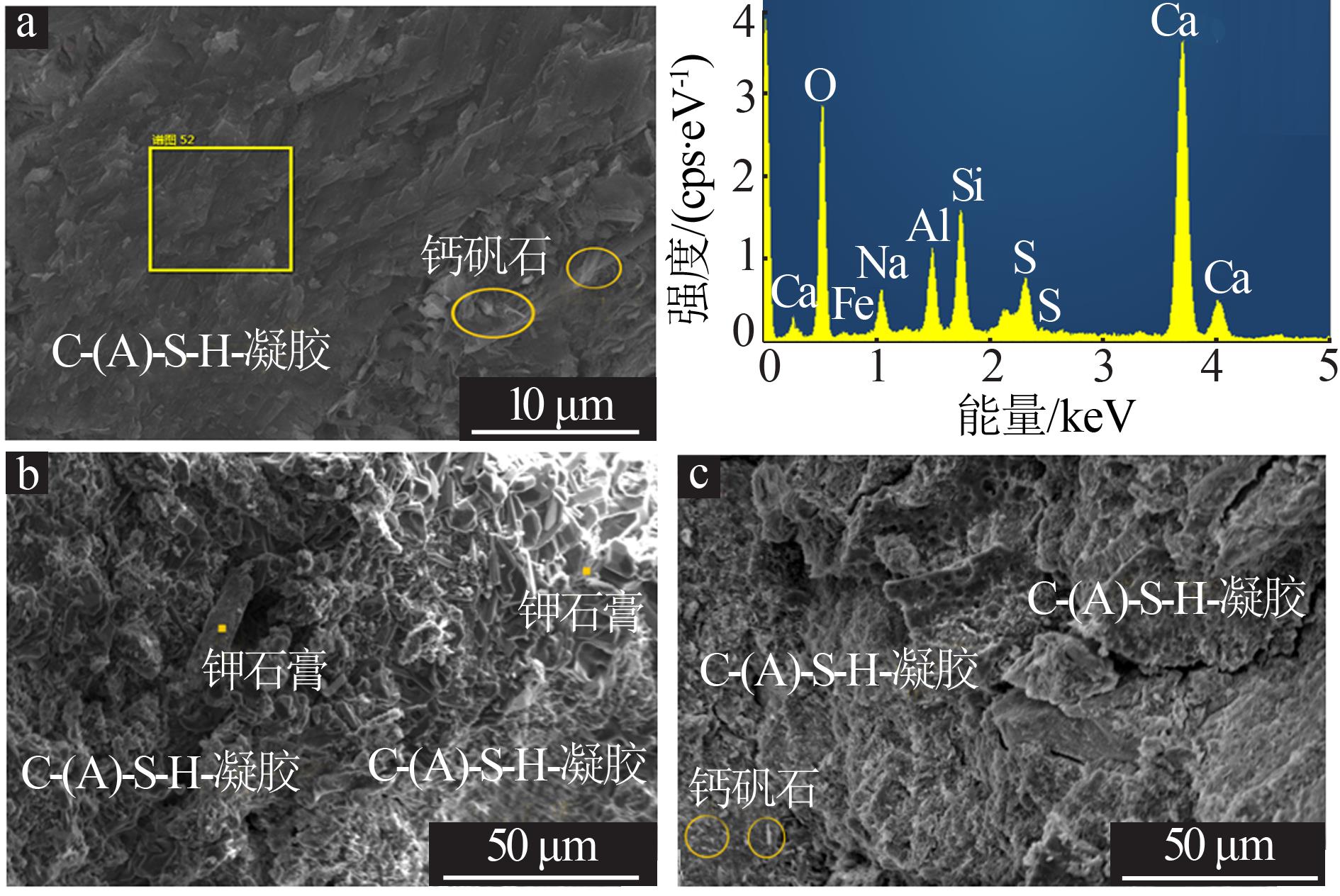
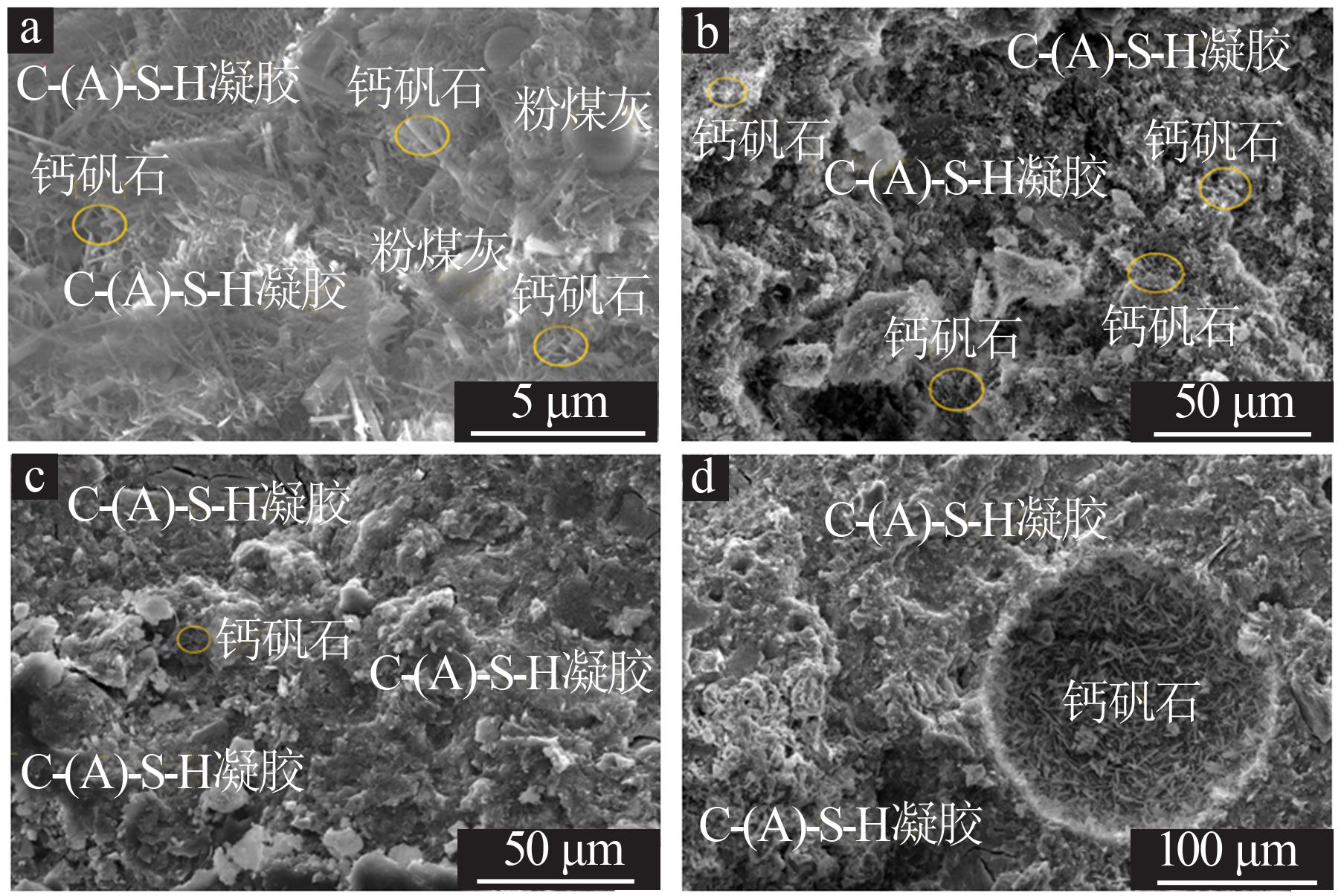
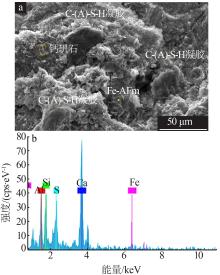
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 115-119.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2021-0581
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
Activation of activator on fly ash?titanium gypsum?calcium carbide slag system and its hydration mechanism
WANG Youyou1,2( ),YUAN Hao1,HAN Qingqing1,CHEN Shiying1,2(
),YUAN Hao1,HAN Qingqing1,CHEN Shiying1,2( )
)
- 1.Institute of Resources and Environment,Henan Polytechnic University,Jiaozuo 454000,China
2.Henan Key Laboratory of Coal Green Conversion(Henan Polytechnic University)
-
Received:2021-08-12Online:2022-06-10Published:2022-06-22 -
Contact:CHEN Shiying E-mail:wanguu120@163.com;chensy@hpu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Youyou,YUAN Hao,HAN Qingqing,CHEN Shiying. Activation of activator on fly ash?titanium gypsum?calcium carbide slag system and its hydration mechanism[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(6): 115-119.
share this article
| 1 | 马远,樊传刚,吴悠,等.过硫钛石膏矿渣水泥的制备与性能表征[J].非金属矿,2016,39(6):41-44. |
| MA Yuan, FAN Chuangang, WU You,et al.Preparation and characterization of persulfur titanium gypsum slag cement[J].Non-Metallic Mines,2016,39(6):41-44. | |
| 2 | 王晓琪,姚媛媛,陈宝成,等.硫酸法钛石膏作为土壤调理剂在油菜上的施用效果研究[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(4):333-338,345. |
| WANG Xiaoqi, YAO Yuanyuan, CHEN Baocheng,et al.Effects of titanium gypsum produced by sulfuric acid method as soil conditioner on rape seedlings[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,32(4):333-338,345. | |
| 3 | 杨冬蕾.我国磷石膏和钛石膏资源化利用进展及展望[J].硫酸工业,2018(10):5-10. |
| YANG Donglei.Progress and prospect of resource utilization of phosphogypsum and titanium gypsum in China[J].Sulphuric Acid Industry,2018(10):5-10. | |
| 4 | ZHANG Jiufu, YAN Yun, HU Zhihua,et al.Properties and hydration behavior of Ti-extracted residues⁃red gypsum based cementitious materials[J].Construction and Building Materials,2019, 218:610-617. |
| 5 | 魏长河,孙玉壮,高兴保,等.钛石膏中重金属元素的浸出特性研究[J].环境工程,2015,33(5):131-135. |
| WEI Changhe, SUN Yuzhuang, GAO Xingbao,et al.Study on leaching characteristics of heavy metals in titanium gypsum[J].Environmental Engineering,2015,33(5):131-135. | |
| 6 | AZDARPOUR A, ASADULLAH M, JUNIN R,et al.Direct carbonation of red gypsum to produce solid carbonates[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2014,126:429-434. |
| 7 | 张宁.利用钛石膏阻抗半刚性基层开裂的应用技术研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2016. |
| ZHANG Ning.Research on mechanism and application technology titanium gypsum impedance semi⁃rigid base cracking[D].Chongqing:Chongqing Jiaotong University,2016. | |
| 8 | 杜传伟,李国忠,陈娟.利用天然石膏形态组成模拟钛石膏及其性能研究[J].建筑材料学报,2014,17(3):511-516. |
| DU Chuanwei, LI Guozhong, CHEN Juan.Simulation of titanium gypsum with morphology and composition of natural gypsum and its property[J].Journal of Building Materials,2014,17(3):511-516. | |
| 9 |
CHEN Qiuju, DING Wenjin, SUN Hongjuan,et al.Synthesis of anhydrite from red gypsum and acidic wastewater treatment[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,278.Doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020 .
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020 |
|
124026.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020 |
|
| 10 | 陈书锐,杨绍利,马兰,等.盐酸浸出钛石膏实验研究[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(2):65-68. |
| CHEN Shurui, YANG Shaoli, MA Lan,et al.Study on leaching of titanium gypsum with hydrochloric acid[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(2):65-68. | |
| 11 | 汪路,谭宏斌,李玉龙,等.Ⅱ型无水石膏制备及水泥对其性能影响研究[J].非金属矿,2020,43(5):52-54,63. |
| WANG Lu, TAN Hongbin, LI Yulong,et al.Preparation of Ⅱ-anhydrite gypsum and effect of cement on its properties[J].Non-Metallic Mines,2020,43(5):52-54,63. | |
| 12 | 蒋美雪,孙红娟,彭同江.钛石膏硫酸浸取法提取铁质氧化物及石膏的物相变化[J].化工进展,2019,38(4):2030-2036. |
| JIANG Meixue, SUN Hongjuan, PENG Tongjiang.Extraction of iron oxide from titanium gypsum by sulfuric acid leaching and phase transform of gypsum[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2019,38(4):2030-2036. | |
| 13 | 刘妍,李国忠.不同激发剂对钛石膏-粉煤灰复合胶凝材料力学性能影响的研究[J].粉煤灰,2015,27(2):8-11. |
| LIU Yan, LI Guozhong.Effect of different activators on mechanical performance of titanium gypsum⁃fly ash compound cementitious material[J].Coal Ash,2015,27(2):8-11. | |
| 14 | 刘虎林,王昭,伍媛婷,等.固硫灰渣的基本特性及其作水泥混合材的关键问题研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报,2021,40(6):2052-2061,2069. |
| LIU Hulin, WANG Zhao, WU Yuanting,et al.Review on characteristics of fluidized bed combustion ashes and key issues in their application as cement admixtures[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(6):2052-2061,2069. | |
| 15 | 钱觉时,余金城,孙化强,等.钙矾石的形成与作用[J].硅酸盐学报,2017,45(11):1569-1581. |
| QIAN Jueshi, YU Jincheng, SUN Huaqiang,et al.Formation and function of ettringite in cement hydrates[J].Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2017,45(11):1569-1581. | |
| 16 | 阎培渝,韩建国.复合胶凝材料的初期水化产物和浆体结构[J].建筑材料学报,2004,7(2):202-206. |
| YAN Peiyu, HAN Jianguo.Early⁃age hydrates and paste structure of complex binders[J].Journal of Building Materials,2004,7(2):202-206. | |
| 17 | BROWN P W, BOTHE J V Jr.The stability of ettringite[J].Advances in Cement Research,1993,5(18):47-63. |
| 18 | 王智,郑洪伟,钱觉时,等.硫酸盐对粉煤灰活性激发的比较[J].粉煤灰综合利用,1999,12(3):15-18. |
| WANG Zhi, ZHENG Hongwei, QIAN Jueshi,et al.A study on comparison of sulfate activating fly ash[J].Fly Ash Comprehensive Utilization,1999,12(3):15-18. | |
| 19 | 陈宇,季军荣,周洲,等.超硫酸盐水泥早期强度影响因素及提高途径[J].硅酸盐通报,2021,40(5):1413-1419. |
| CHEN Yu, JI Junrong, ZHOU Zhou,et al.Influencing factors and enhancement methods of early strength of supersulfated cement[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(5):1413-1419. | |
| 20 | WAN Dawei, ZHANG Wenqin, TAO Yong,et al.The impact of Fe dosage on the ettringite formation during high ferrite cement hydration[J].Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2021,104(7):3652-3664. |
| [1] | YU Zhou, HE Zhaoyi, TANG Liang, HE Sheng, XIAO Haixin, XIAO Yixun. Study on preparation and microscopic properties of typical sulfate solid waste composite cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 90-97. |
| [2] | XIANG Mengqi, MENG Hua, WANG Ye, MENG Xianzhang, BAI Yuhang, WANG Yujunyao, ZHANG Yidan. Study on kinetic of iron leaching from titanium gypsum and its cyclic acid leaching process [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(1): 114-120. |
| [3] | XU Li, ZHANG Qiang. Experimental study on properties of iron tailings powder cement-based materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 116-123. |
| [4] | WEI Kang, ZHANG Hao, GAN Shunpeng. Research on mechanical drive enhancement crystallization process for titanium gypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(11): 78-85. |
| [5] | ZHANG Taiyue,XIE Fan,GUO Junyuan. Study on performance optimization and mechanism of phosphogypsum based composite cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(9): 136-142. |
| [6] | MA Lei,SHENG Yu,ZHOU Junhong,YANG Yujun,LUO Hui,PAN Chunying,WANG Guo. Study on new process of comprehensive utilization and separation of sulfur and calcium of titanium gypsum [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(7): 124-128. |
| [7] | LIU Yingqiang,GUO Runhua,LIU Xijie. Influence of silica fume and metakaolin on properties of slag?fly ash microbead cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(6): 102-108. |
| [8] | FU Rusong,LU Yuexian,AN Hongfang,KONG Dewen,FU Rubin. Study on preparation of cementitious materials from raw phosphogypsum cured by hemihydrate phosphogypsum and their properties [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(6): 109-114. |
| [9] | MIAO Xun,LU Yuexian,FU Rusong,KONG Dewen,FU Rubin,HU Qun. Hemihydrate phosphogypsum as used to solidify the raw phosphogypsum to prepare composite cementitious material [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 10-16. |
| [10] | HU Xiuquan,ZHANG Li,ZHANG Jin,YOU Dahai,LI Guodong,ZHANG Chaohong. Modification experiment of non-calcined phosphogypsum based cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 29-33. |
| [11] | Meng Hua,Zhao Jingyi,Nie Chaoyang,Wang Ye. Study on simulation process of reducing titanium dioxide gypsum by sulfur fluidization [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(9): 61-66. |
| [12] | Liu Junxia,Yang Yanmeng,Wang Shuaiqi,Liu Pan,Zhang Maoliang,Hai Ran. Effect of chemical activator on mechanical property of red mud geopolymer mortar [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(6): 72-75. |
| [13] | Chen Shurui,Yang Shaoli,Ma Lan,Hou Jing. Study on leaching of titanium gypsum with hydrochloric acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(2): 65-68. |
| [14] | Luo Shuang,Fu Rubin,Kong Dewen,Xie Lang,Zhou Yinsheng,Zhao Yan. Summary on effects of admixtures on water resistance and strength of phosphogypsum-based composite cementitious materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(11): 6-6. |
| [15] | Li Jiansheng,Gao Changqing,Wang Xue,Li Shizeng,Liu Bingguang. Inorganic activators utilized in development and production of high performance activated carbon [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(8): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||