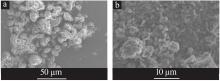
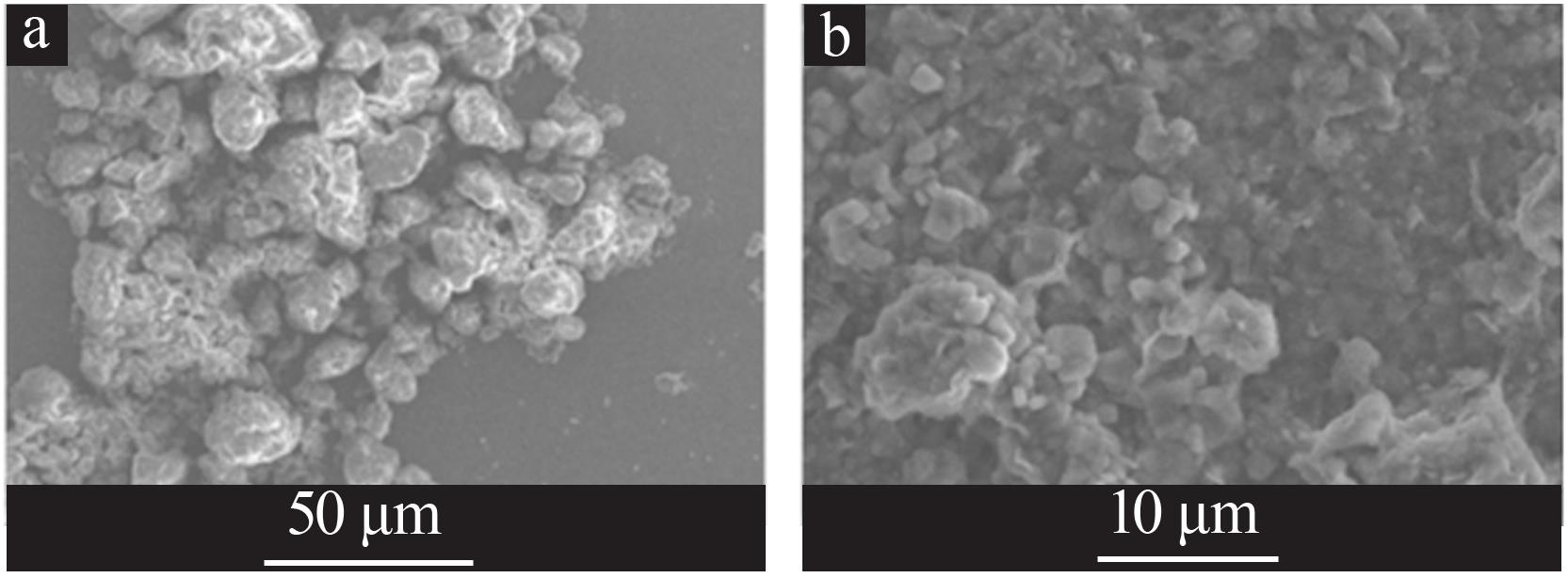
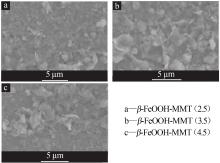
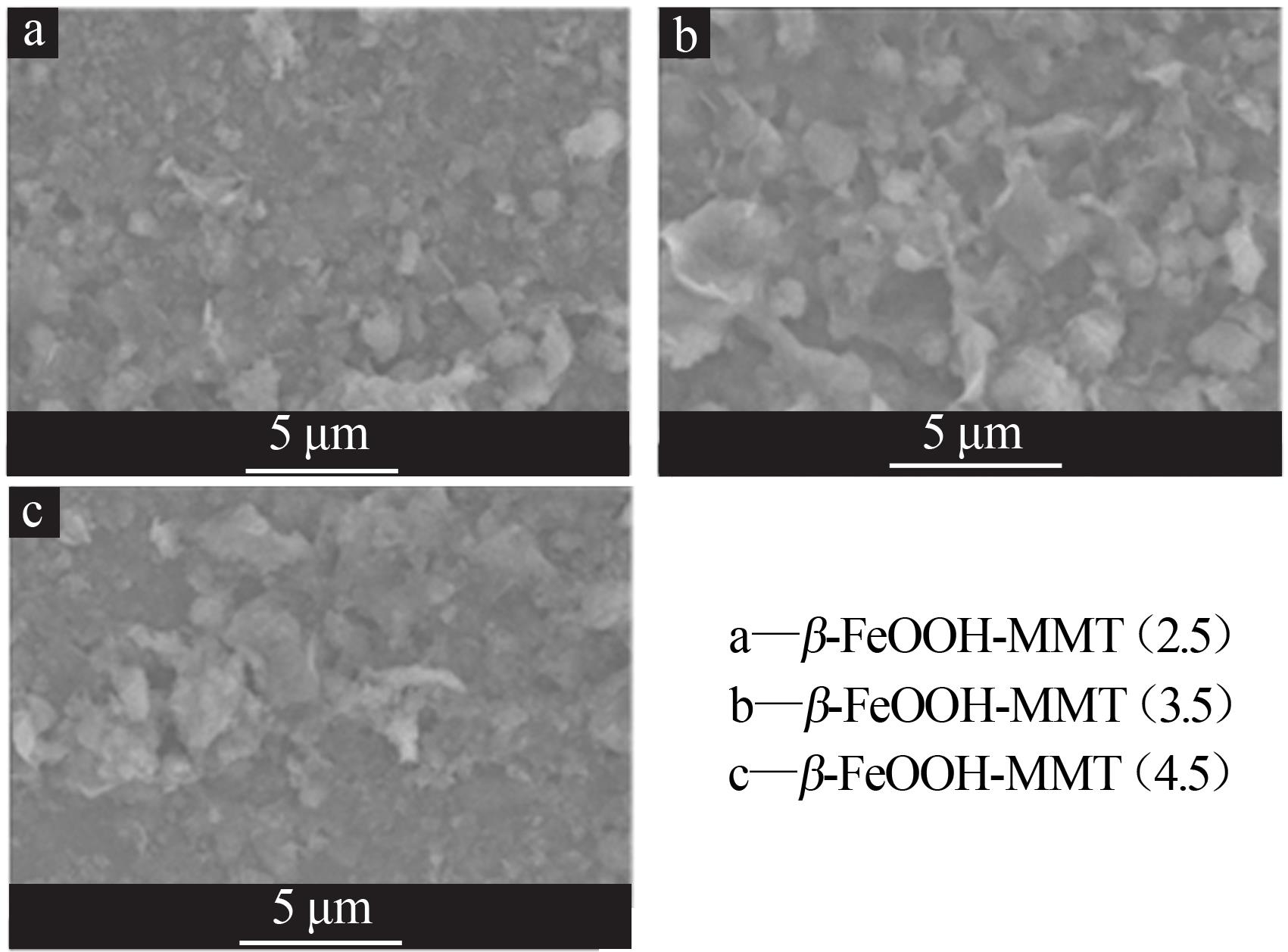
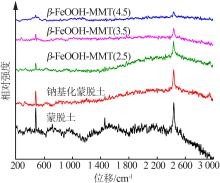
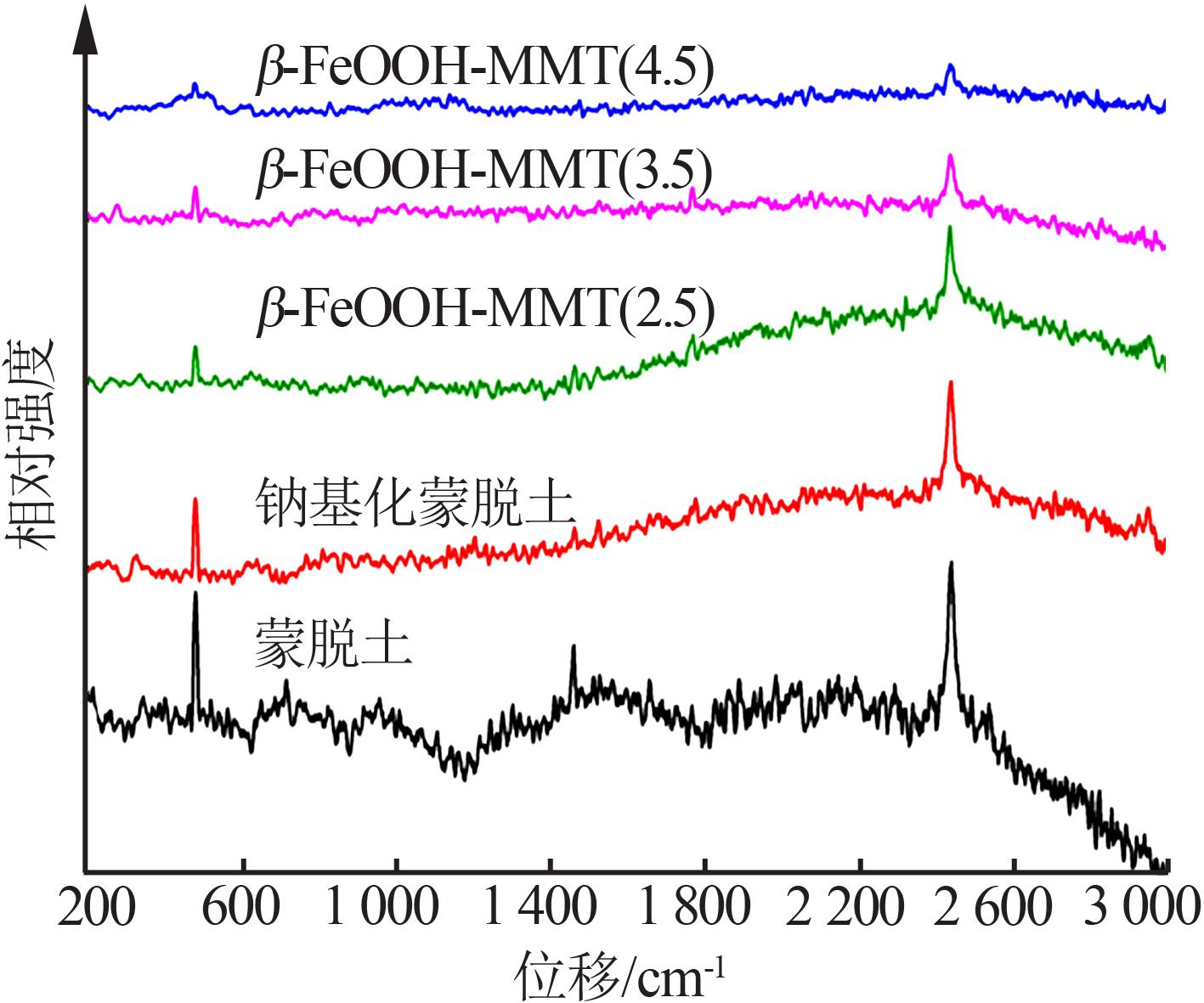
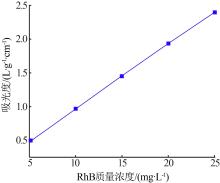
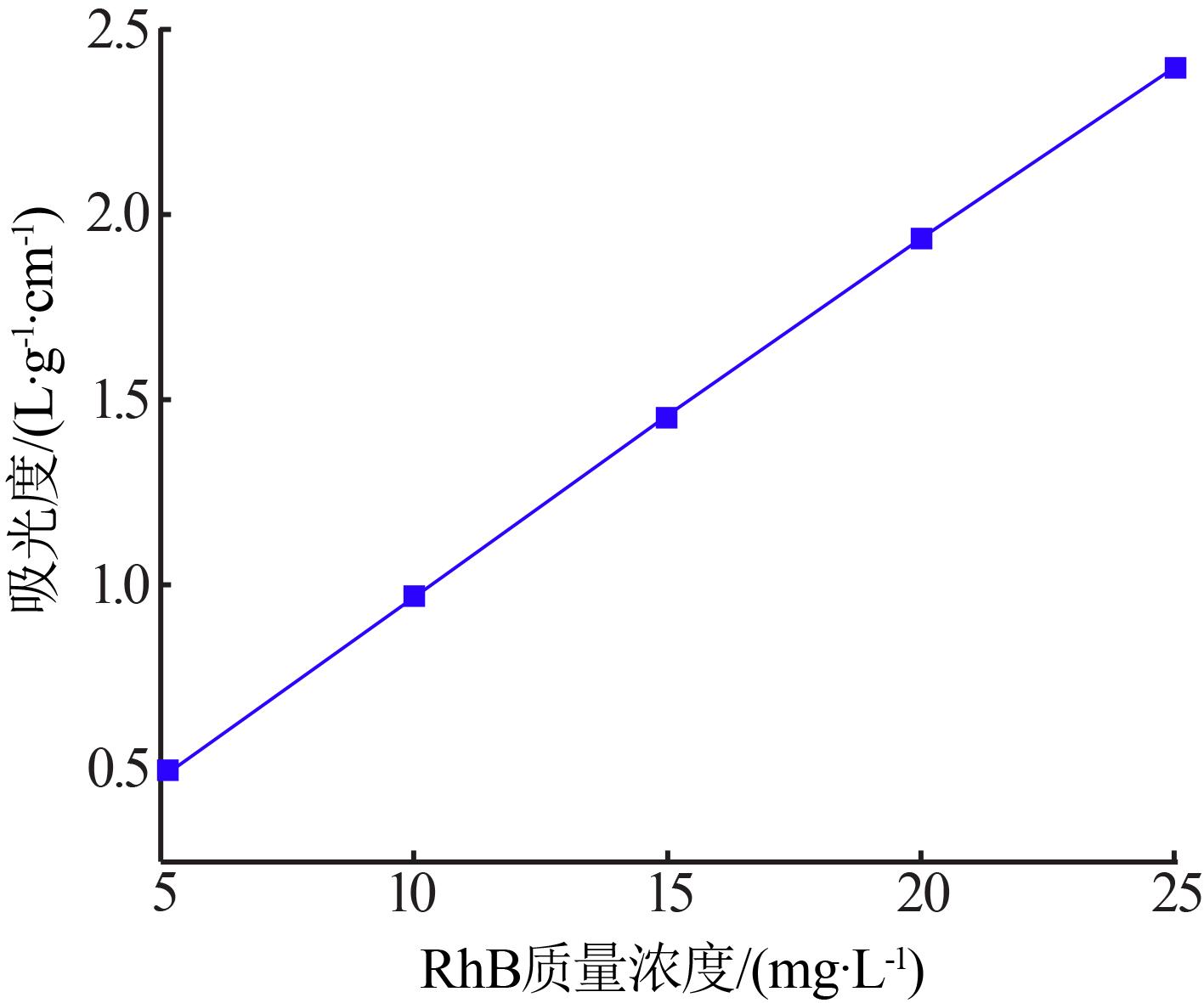
| 1 |
孔张亮,成先雄,连军锋,等.Fe/C微电解+Fenton试剂处理酸性品红废水的研究[J].应用化工,2019,48(5):1080-1083,1088.
|
|
KONG Zhangliang, CHENG Xianxiong, LIAN Junfeng,et al.Treatment of acid fuchsin wastewater by Fe/C micro electrolysis+Fenton reagent[J].Applied Chemical Industry,2019,48(5):1080-1083,1088.
|
| 2 |
徐辉,彭丹莉,郑致力,等.Fenton-纳米TiO2/UV氧化法处理高浓度农药废水效果研究[J].能源环境保护,2018,32(6):34-39.
|
|
XU Hui, PENG Danli, ZHENG Zhili,et al.Study on high concentration pesticide wastewater treatment by Fenton and nano⁃tio2/uv photocatalysis oxidation[J].Energy Environmental Protection,2018,32(6):34-39.
|
| 3 |
YUAN Peng, WANG Zhi, AHMAD M S,et al.Enhanced oxidative removal of NO by UV/in situ Fenton:Factors,kinetics and simulation[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,778.Doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146202 .
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146202
|
| 4 |
REN Bin, MIAO Junfeng, WANG Shasha,et al.Facilely synthesized porous 3D coral⁃like Fe-based N-doped carbon composite as effective Fenton catalyst in methylene blue degradation[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2021,618.Doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126439 .
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126439
|
| 5 |
李光明,邱珊,马放.均相与非均相超声-芬顿催化降解水中罗丹明B[J].水处理技术,2020,46(5):19-23.
|
|
LI Guangming, QIU Shan, MA Fang.Homogeneous and heterogeneous ultrasound-Fenton for degradation of RhB in water[J].Technology of Water Treatment,2020,46(5):19-23.
|
| 6 |
陈修栋,邹洪涛,毛海立,等.超声波辅助Al-Fe柱撑蒙脱土催化降解茜素红[J].山东化工,2016,45(11):149-150,154.
|
|
CHEN Xiudong, ZOU Hongtao, MAO Haili,et al.Ultrasonic⁃assist⁃
|
|
ed Al-Fe pillared montmorillonite catalytic degradation of alizarin
|
|
red[J].Shandong Chemical Industry,2016,45(11):149-150,154.
|
| 7 |
陈修栋,初本莉,王嘉承,等.微波辅助Fe-Al柱撑蒙脱土的制备及其对亚甲基蓝的吸附[J].化工环保,2012,32(6):565-
|
| 568 |
CHEN Xiudong, CHU Benli, WANG Jiacheng,et al.Microwave⁃assisted preparation of Fe-Al pillared montmorillonite and its adsorption of methylene blue[J].Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry,2012,32(6):565-568.
|
| 8 |
杨科,王锦成,郑晓昱.蒙脱土的结构、性能及其改性研究现状[J].上海工程技术大学学报,2011,25(1):65-70.
|
|
YANG Ke, WANG Jincheng, ZHENG Xiaoyu.Current study of structure,property and modification of montmorillonite[J].Journal of Shanghai University of Engineering Science,2011,25(1):65-70.
|
| 9 |
AN Junjian, HU Chenyan, WANG Yin,et al.Preparation of activated carbon fibers-α-FeOOH as a high⁃performance heterogeneous Fenton⁃like catalyst for efficient removal of hydrotropic lignin model compound[J].ChemistrySelect,2021,6(10).2492-2503.
|
| 10 |
樊凯悦.可见光照下BiOI/FeOOH复合光催化剂催化H2O2降解罗丹明B研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2020.
|
|
FAN Kaiyue.Degradation of rhodamine B using H2O2 catalyzed by BiOI/FeOOH with visible light[D].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology,2020.
|
| 11 |
宋思扬,吴丹,赵焕新,等.Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4的制备及其在非均相光芬顿反应中的催化性能[J].环境工程学报,2020,14(12):3262-3269.
|
|
SONG Siyang, WU Dan, ZHAO Huanxin,et al.Fabrication of Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4 composite and its catalytic performance on heterogeneous photo-Fenton[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2020,14(12):3262-3269.
|
| 12 |
JIANG Zhikang, ZHANG Fen, SHEN Li,et al.Facile pH-controlled synthesis of MnWO4 nanoparticles and nanorods and their heterogeneous Fenton⁃like catalytic activity[J].Materials Letters,2021,293.Doi:10.1016/j.mattet.2021.129662 .
doi: 10.1016/j.mattet.2021.129662
|
| 13 |
李荣. γ-FeOOH的制备及其对活性黄X-R染料废水的催化降解的研究[D].天津:天津科技大学,2019.
|
|
LI Rong.Peparation of γ-FeOOH and catalytic performance in degradation of reactive yellow X-R dye[D].Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science & Technology,2019.
|
| 14 |
BAO Yan, YAN Qingyun, JI Jiahui,et al.Graphene⁃based photo⁃Fenton catalysts for pollutant control[J].Transactions of Tianjin University,2021,27(2):110-126.
|
| 15 |
徐其鹏,罗志龙,李萌,等.超声协同Fenton氧化法降解HMX废水及动力学研究[J].火炸药学报,2016,39(2):102-106.
|
|
XU Qipeng, LUO Zhilong, LI Meng,et al.Study on the kinetics of degrading the HMX wastewater by ultrasonic/Fenton oxidation method[J].Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants,2016,39(2):102-106.
|
 ),ZHANG Yihuan1,ZHANG Haodong1,SHENG Donghe1,WU Jiawei1,LIU Jinhang1,YAN Ping1,ZHAN Changchao2(
),ZHANG Yihuan1,ZHANG Haodong1,SHENG Donghe1,WU Jiawei1,LIU Jinhang1,YAN Ping1,ZHAN Changchao2( )
)