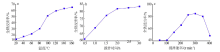
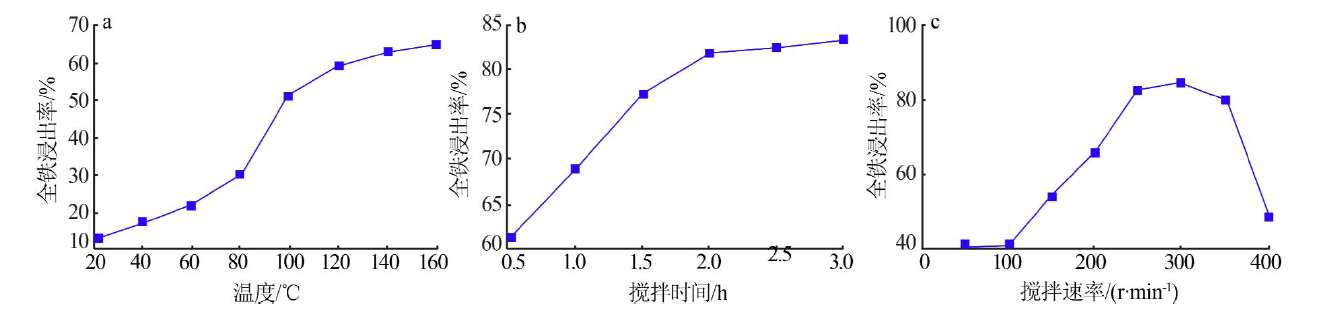
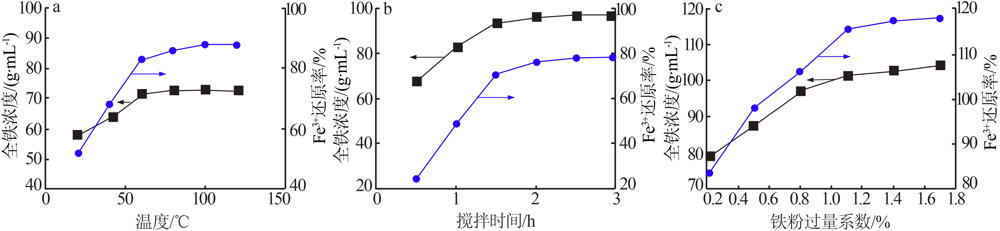
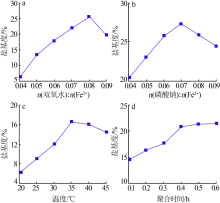
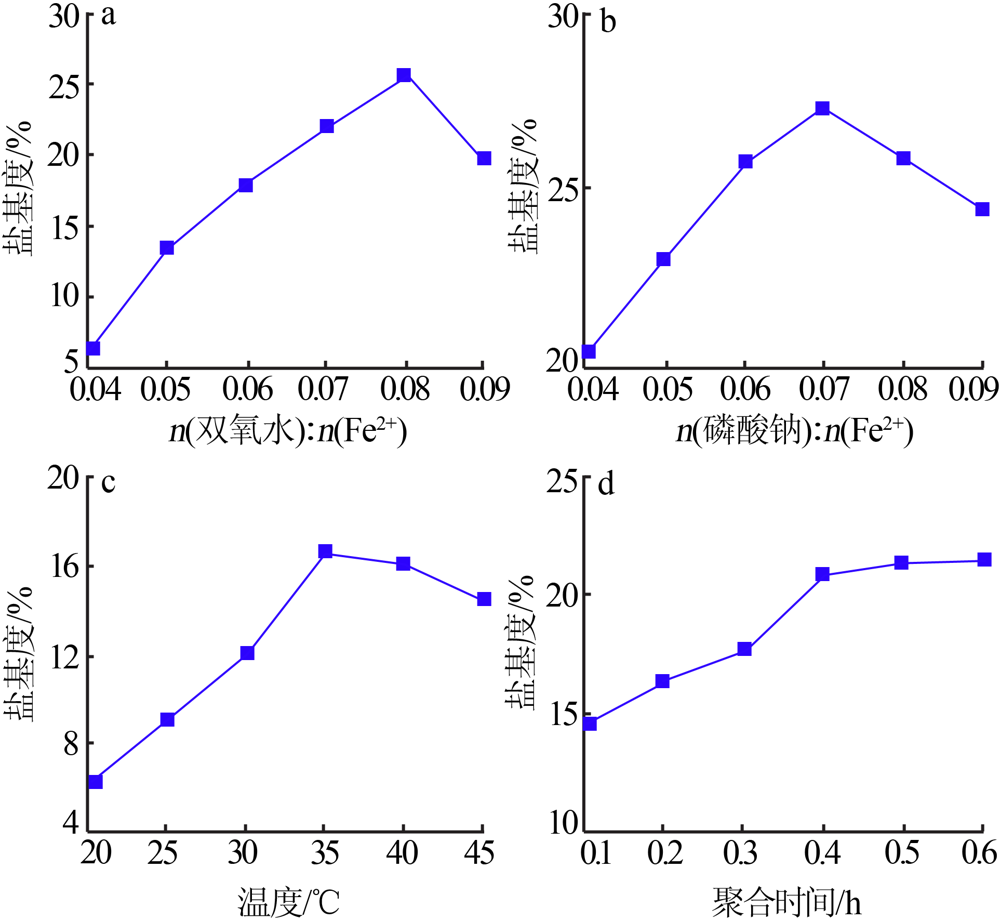
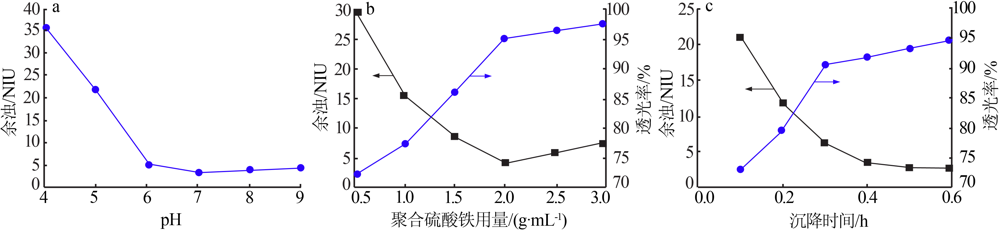
| [1] |
蔺能, 石晓雪, 袁媛, 等. 外磁场调控的聚合硫酸铁水解过程研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(7):2978-2984.
|
| [2] |
拜俊岑, 吴烈善, 周阳波, 等. 稀土镧改性聚合硫酸铁机理分析及其应用[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4):859-868.
|
| [3] |
张骁, 刘海刚, 杨卓然, 等. 利用铝箔废酸液制备聚合硫酸铁铝的工艺研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2019, 39(12):37-40.
|
| [4] |
宋晓乔, 刘罡, 宋少花, 等. 聚合硫酸铁对麦草浆造纸废水预处理的效果研究[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(8):1866-1868.
|
| [5] |
卢素敏, 田一哲, 王汉昌, 等. 聚合硫酸铁-瓜尔胶复合絮凝剂的制备及絮凝效果研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(7):141-146.
|
| [6] |
董林辉, 李杨, 周雪芳, 等. 聚合硫酸铁铝的制备及除磷性能研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(5):57-60.
|
| [7] |
周耘, 武书彬. Fenton污泥制备聚合硫酸铁的中试实验研究[J]. 中国造纸, 2019, 38(5):75-81.
|
| [8] |
陈居玲, 肖景波. 用石棉尾矿制备聚合硫酸铁工艺研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2015, 34(5):385-389.
|
| [9] |
拜俊岑, 吴烈善, 周阳波, 等. 稀土镧改性聚合硫酸铁机理分析及其应用[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4):859-868.
|
| [10] |
吕燕, 韩建华, 田智灏, 等. 双极膜电渗析法连续制备聚合硫酸铁[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(3):1524-1529.
|
| [11] |
秦险峰, 全学军, 叶鹏, 等. 铬铁矿酸浸过程强化及铬铁分离研究进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2020, 52(6):13-19.
|
| [12] |
李超, 覃忠祥, 宋振纶, 等. 刚果(金)某氧化钴矿还原酸浸实验[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(4):93-96.
|
| [13] |
喻文超, 郭亚丹, 陈锦全, 等. 生物聚合硫酸铁絮凝剂去除废水中氟氯的实验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(34):166-173.
|
| [14] |
刘维, 吴冰, 曹江林, 等. 钛对聚合硫酸铁制备与性能的影响. 环境化学, 2012; 31(4):437-442.
|
| [15] |
蒋银峰, 蒋浩. 钢铁酸洗废液污染物质对污水处理效果的影响[J]. 工业水处理, 2019, 39(9):54-57.
|
| [16] |
蒋贞贞, 朱俊任. 聚合硫酸铁铝在污水处理厂二级出水处理中的应用[J]. 工业水处理, 2014, 34(7):27-30.
|
 ),Li Yunzhen2,Zhou Yu1
),Li Yunzhen2,Zhou Yu1