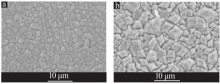
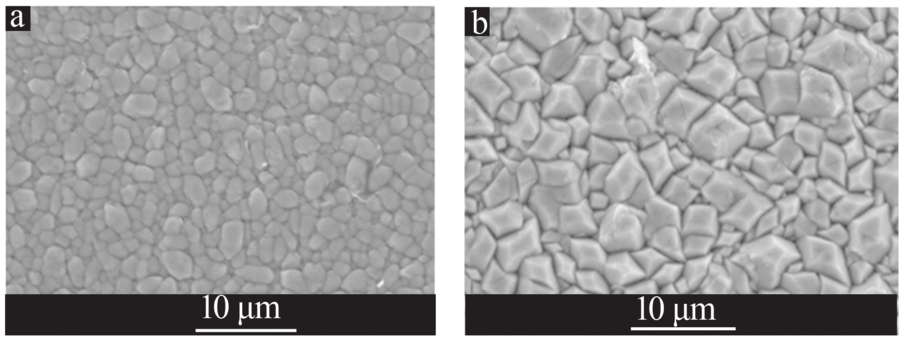
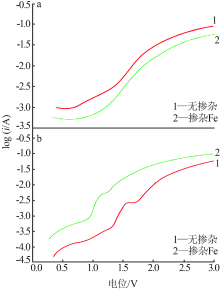
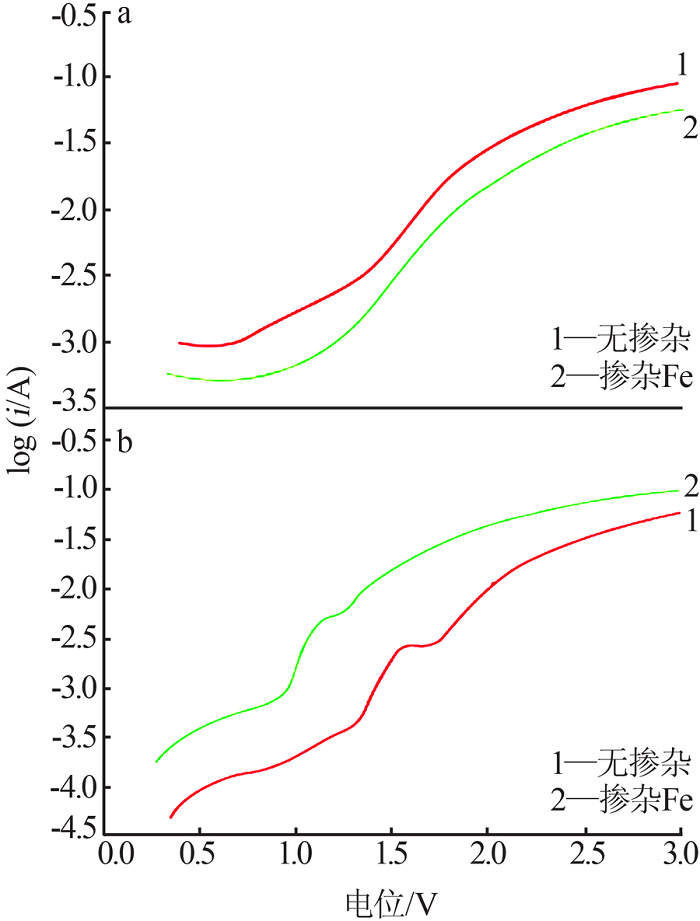
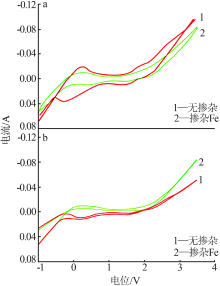
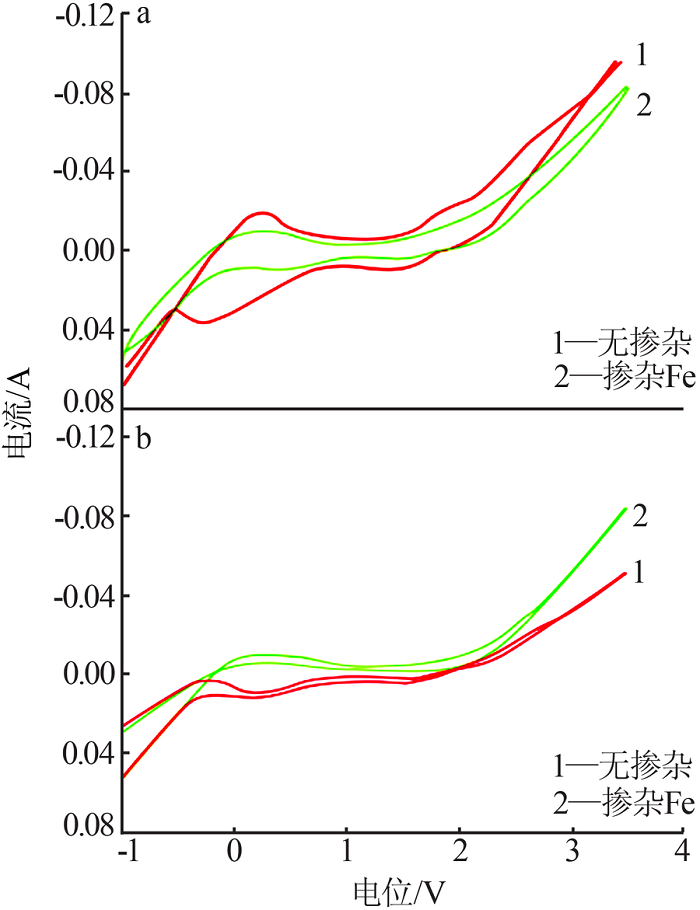
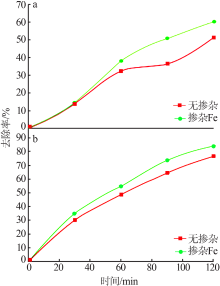
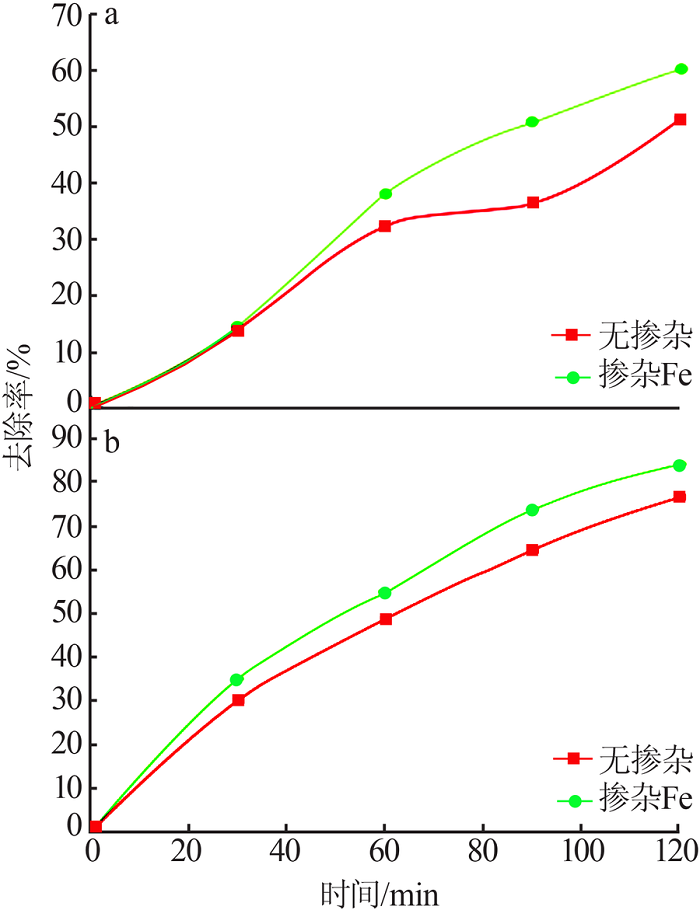
| [1] |
王鸿辉, 马明洁, 冯婕, 等. 钕掺杂二氧化铅复合阳极的电化学性能研究[J]. 电化学, 2018, 24(4):367-374
|
| [2] |
李晓乐, 卢鑫, 张晓杰, 等. 新型钛基PbO2阳极电氧化降解有机污染物的特性研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2016, 48(11):79-82.
|
| [3] |
于锦昭, 柯昌美, 杨金堂, 等. 乙二醇为碳源制备铅炭电池负极材料[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(4):27-31
|
| [4] |
YAO Y, DONG H, YU N, et al. Effects of peak current density on the structure and property of PbO2-CeO2 nanocomposite electrodes pre-pared by pulse electrode position[J]. Russian Journal of Electroche-mistry, 2017, 53(4):411-416.
|
| [5] |
何易, 陈阵, 朱薇, 等. 多壁碳纳米管对钛基二氧化铅电极电化学性能的影响[J]材料保护, 2017, 50(11):14-17
|
| [6] |
张硕嘉, 杨玉彬, 唐宇, 等. 高活性Fe2O3@Ni复合电极制备及电化学性能研究应用[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(7):24-27
|
| [7] |
HE Z, HAYAT MD, HUANG S, et al. PbO2 electrodes prepared by pulse reverse electrodeposition and their application in benzoic acid degradation[J]. Journal of Elec-troanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 812:74-81.
|
| [8] |
YAO Y, CUI L, JIAO L, et al. Effects of duty cycle on the prepara-tion and property of PbO2-CeO2 nanocomposite electrodes[J]. Jour-nal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2016, 20(3):725-731.
|
| [9] |
杨洋, 崔磊磊, 姚颖悟. 电沉积法制备二氧化铅电极的研究进展[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2018, 40:29-32
|
| [10] |
FARINOS R M, RUOTOLO L. Comparison of the electrooxidation performance of three-dimensional RVC/PbO2 and boron-doped dia-mond electrodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 224:32-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.12.025
|
| [11] |
郭爱红, 唐雪娇, 张宝贵. 钛-二氧化铅阳极电解次磷酸钠制备高纯次磷酸[J]. 无机盐工业, 2013, 45(11):18-20
|
| [12] |
邢俊涛, 周秉武. 多孔Ti/SnO2-Sb2O5/CNT-PbO2电极的制备及其电催化氧化有机染料废水的研究[J]. 上海化工, 2018, 43(6):15-22
|
| [13] |
冯建俊, 黎学明, 苏德水, 等. PbO2复合电极预处理甲苯二胺废水[J]. 化工环保, 2017, 37(6):673-678
|
| [14] |
李晓乐, 卢鑫, 张晓杰, 等. 新型钛基PbO2阳极电氧化降解有机污染物的特性研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2016, 48(11):79-82.
|
 ),YANG Yan2,ZHANG Lijun1
),YANG Yan2,ZHANG Lijun1