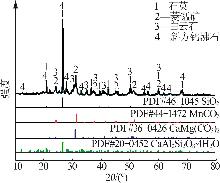
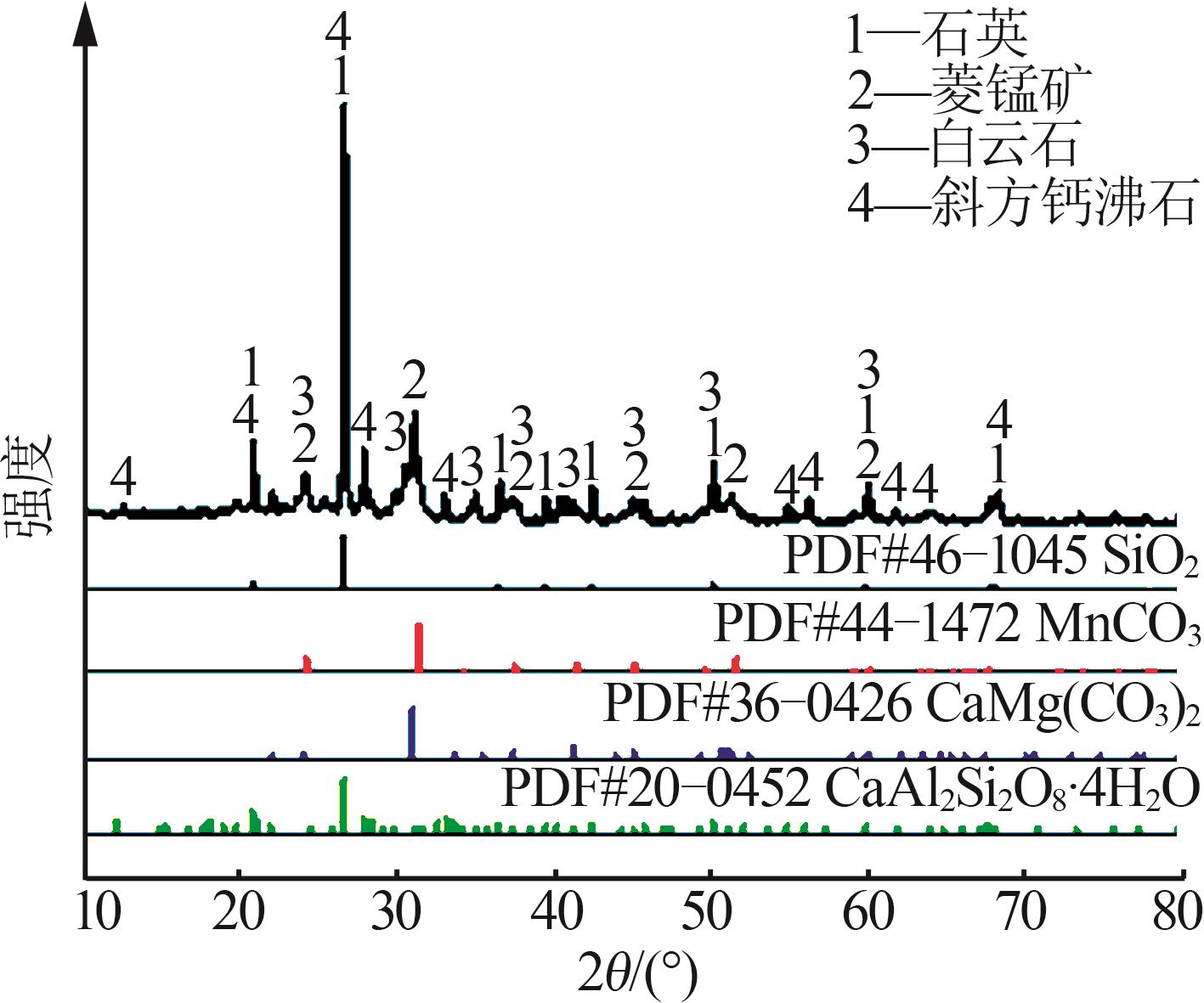
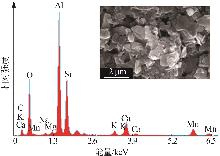
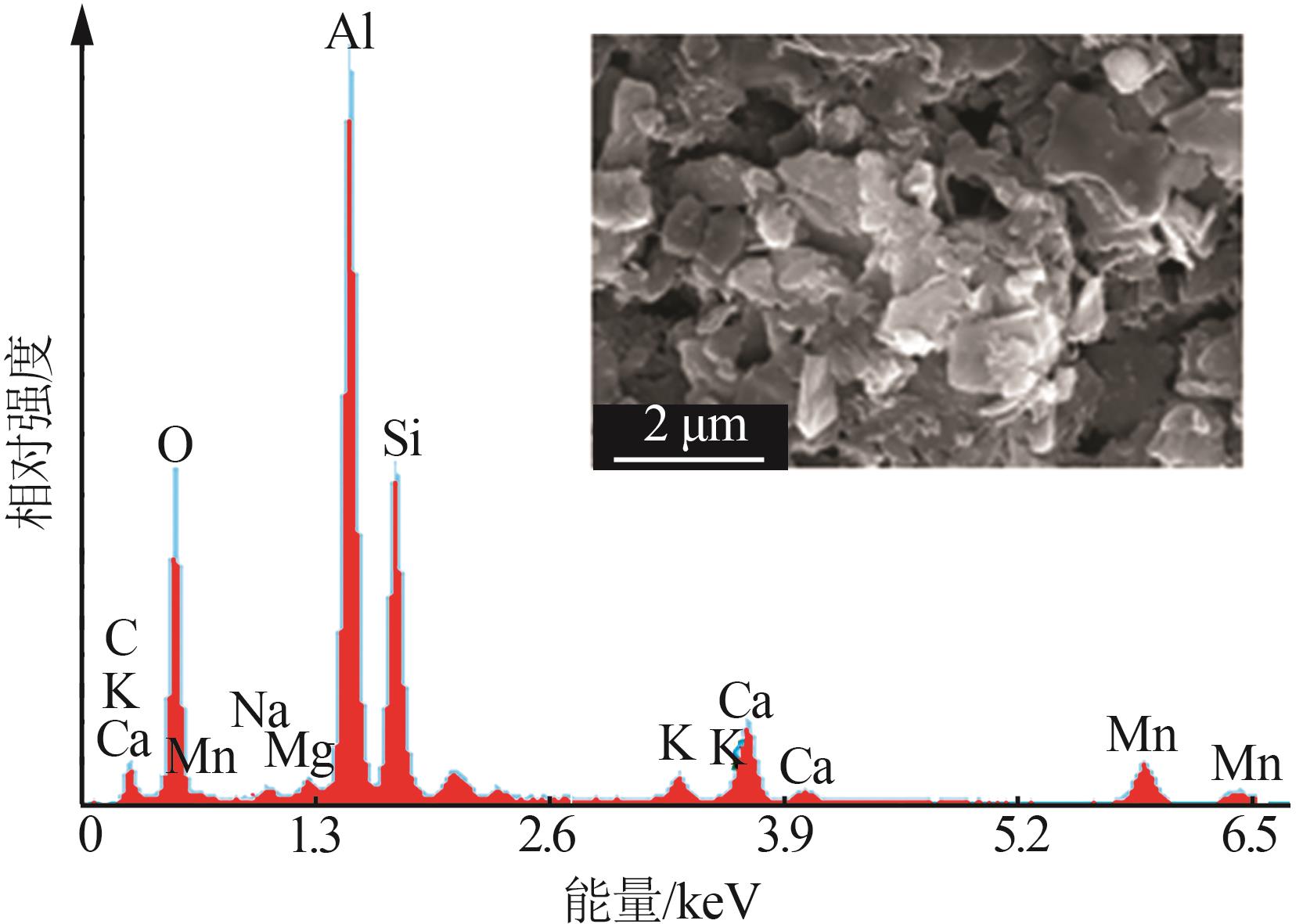
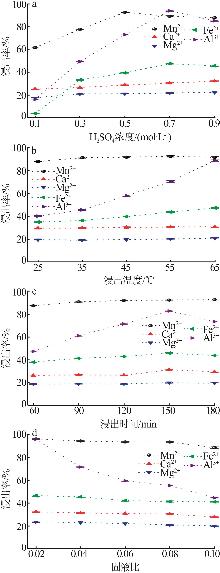
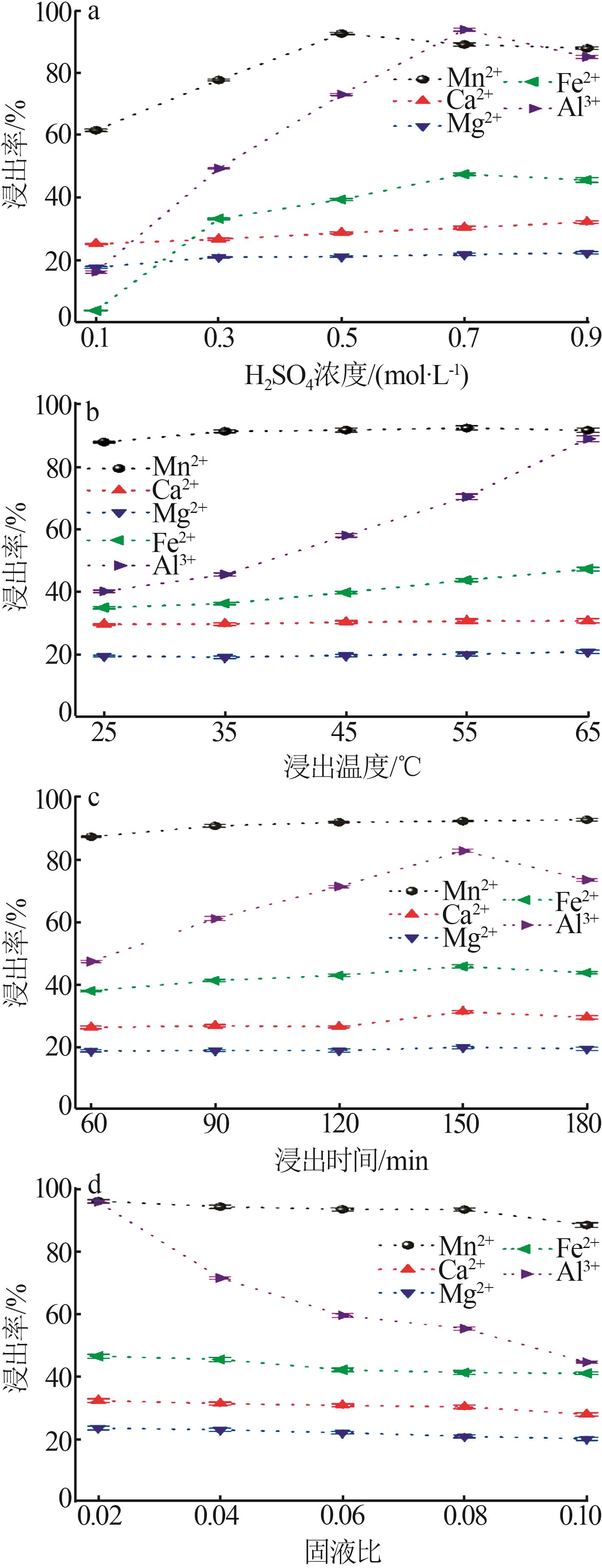
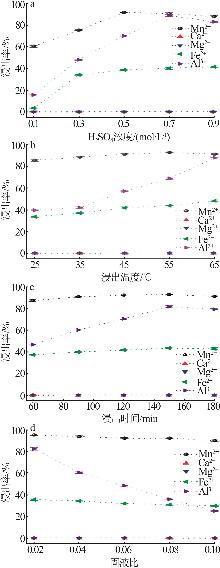
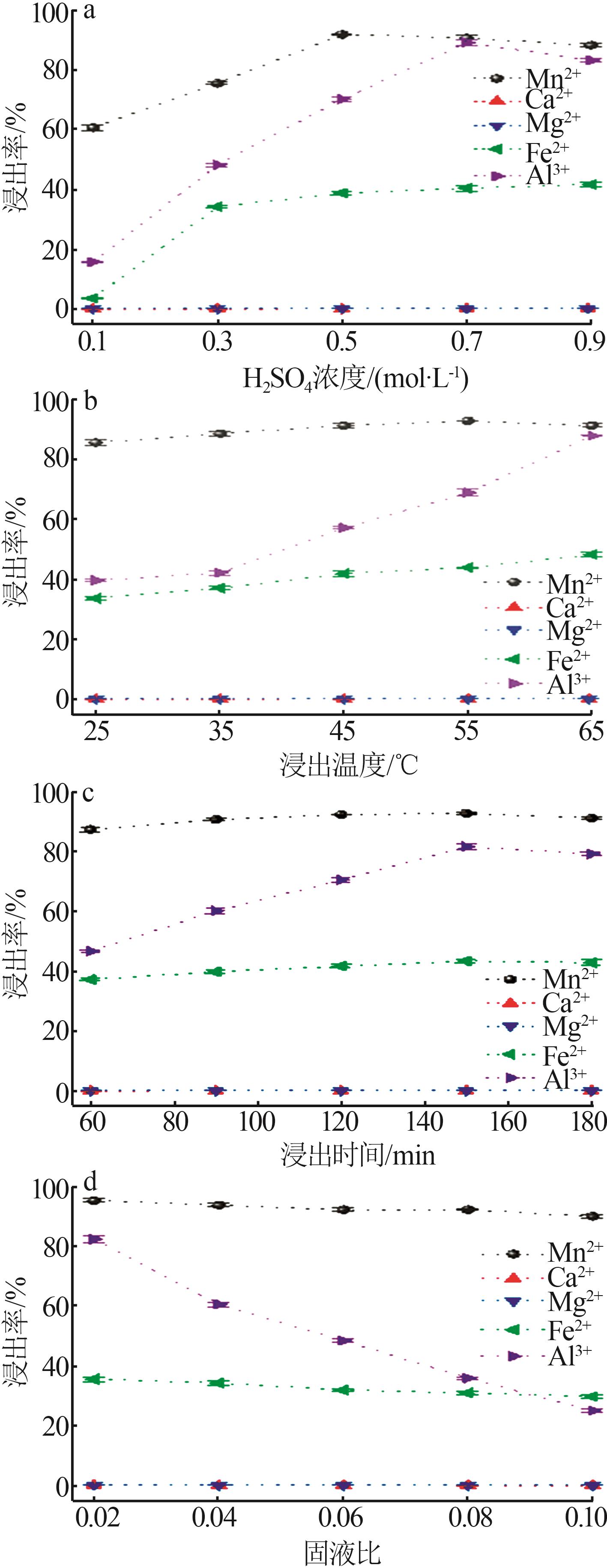
| [1] |
任辉,刘敏,王自国,等.我国锰矿资源及产业链安全保障问题研究[J].中国工程科学,2022,24(3):20-28.
|
|
REN Hui, LIU Min, WANG Ziguo,et al.Security of manganese resources and industrial chain in China[J].Strategic Study of CAE,2022,24(3):20-28.
|
| [2] |
朱志刚.中国锰矿资源开发利用现状[J].中国锰业,2016,34(2):1-3.
|
|
ZHU Zhigang.Exploitation and utilization of resources of Mn ore[J].China’s Manganese Industry,2016,34(2):1-3.
|
| [3] |
涂忠兵.氨法处理高磷低品位菱锰矿的理论及工艺研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2021.
|
|
TU Zhongbing.Theoretical and technological study on ammonia leaching of high-phosphorus and low-grade rhodochrosite ore[D].Chongqing:Chongqing University,2021.
|
| [4] |
WU Tianyi, MA Baozhong, AN Yarui,et al.Improvement of manganese electrolytic process and secondary resources recovery of manganese:A review[J].Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2024,186:895-909.
|
| [5] |
林伟志,付成兵,胡平,等.铜仁地区菱锰矿矿物学特征及其元素赋存状态研究[J].无机盐工业,2024,56(6):73-79.
|
|
LIN Weizhi, FU Chengbing, HU Ping,et al.Study on mineralogical characteristics and occurrence state of elements of rhodochrosite in Tongren area[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2024,56(6):73-79.
|
| [6] |
TU Zhongbing, LIANG Xiaoping, WU Chengbo,et al.Thermal decomposition characteristics of low-grade rhodochrosite ore in N2,CO2 and air atmosphere[J].Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,2022,147(11):6481-6488.
|
| [7] |
REYES I A, FLORES M, PALACIOS E G,et al.Kinetics of the thermal decomposition of rhodochrosite[J].Minerals,2021,11(1): 34.
|
| [8] |
曾祥菲,舒建成,王继钦,等.超声波强化菱锰矿中锰的浸出[J].有色金属(冶炼部分),2022(2):8-15.
|
|
ZENG Xiangfei, SHU Jiancheng, WANG Jiqin,et al.Ultrasonic-assisted leaching of manganese from rhodochrosite[J].Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy),2022(2):8-15.
|
| [9] |
李子寒,舒建成,曹文星,等.菱锰矿浸出前后理化特性及界面水化行为变化规律[J].化工进展,2024,43(9):5320-5328.
|
|
LI Zihan, SHU Jiancheng, CAO Wenxing,et al.Physicochemical properties of rhodochrosite before and after leaching and the changing law of interface hydration behavior[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2024,43(9):5320-5328.
|
| [10] |
AHMED A.Optimization of carbothermal reduction of low-grade manganese ore utilizing microwave heating[J].Journal of Alloys and Metallurgical Systems,2023,3:100019.
|
| [11] |
HE Shichao, WANG Tao, LIU Zhiyong,et al.Mechanochemistry enhanced low-temperature molten salt synergistic treatment of low-grade pyrolusite and waste salts from the electrolytic manganese metal industry[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2025,506:159338.
|
| [12] |
CHEN Guo, LING Yeqing, LI Qiannan,et al.Investigation on microwave carbothermal reduction behavior of low-grade pyrolusite[J].Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2020,9(4):7862-7869.
|
| [13] |
MA Ruiyu, FENG Yali, LI Haoran,et al.An environmentally friendly approach for the extraction and recovery of Mn from pyrolusite by ammonium sulfate roasting-water leaching and ammonium carbonate precipitation[J].Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering,2024,19:e2999.
|
| [14] |
郑可欣,王海峰,王家伟,等.广西靖西地区菱锰矿浸出及其动力学研究[J].无机盐工业,2025,57(1):51-57.
|
|
ZHENG Kexin, WANG Haifeng, WANG Jiawei,et al.Study on leaching and kinetics of rhododengite in Jingxi area of Guangxi[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2025,57(1):51-57.
|
| [15] |
赵云浩,吴睿林,胡平,等.高纯硫酸锰中的杂质特性及净化工艺研究[J].世界有色金属,2020(1):186-188.
|
|
ZHAO Yunhao, WU Ruilin, HU Ping,et al.Study on impurity characteristics and purification process of high purity manganese sulfate[J].World Nonferrous Metals,2020(1):186-188.
|
| [16] |
何银晖,张海静,熊珊.MnSO4溶液的净化及制备电池级高纯硫酸锰[J].湿法冶金,2019,38(5):380-384.
|
|
HE Yinhui, ZHANG Haijing, XIONG Shan.Purification of MnSO4 solution and preparation of battery-level high purity manganese sulfate[J].Hydrometallurgy of China,2019,38(5):380- 384.
|
| [17] |
YANG Peng, LIANG Xiaoping, WU Chengbo,et al.Improve manganese leaching efficiency by adding different complexants during ammonia leaching of low-grade rhodochrosite[J].Minerals Engineering,2022,188:107834.
|
| [18] |
LUO Zhenggang, SHU Jiancheng, CHEN Mengjun,et al.Enhanced leaching of manganese from low-grade pyrolusite using ball milling and electric field[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,211:111893.
|
| [19] |
GHOSH S, MOHANTY S, AKCIL A,et al.A greener approach for resource recycling:Manganese bioleaching[J].Chemosphere,2016,154:628-639.
|
| [20] |
YAN Yaoyu, SUN Shuchen, WEI Jing,et al.Enhanced sulfuric acid leaching and kinetics of rhodochrosite in the presence of trisodium citrate and EDTA[J].Minerals Engineering,2025,228:109323.
|
| [21] |
谢子楠,吴思展,吴运东,等.添加剂对菱锰矿中各离子的浸出影响情况分析[J].无机盐工业,2018,50(11):16-19.
|
|
XIE Zinan, WU Sizhan, WU Yundong,et al.Impact analysis of additives on ions leaching in rhodochrosite[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2018,50(11):16-19.
|
| [22] |
谭善宜,文惠子,何淑玉,等.磷石膏中磷的浸出行为及其动力学研究[J].无机盐工业,2025,57(2):105-112.
|
|
TAN Shanyi, WEN Huizi, HE Shuyu,et al.Study on leaching behavior and kinetics of phosphorus from phosphogypsum[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2025,57(2):105-112.
|
 ), GONG Tingting, PENG Shouhong, CHEN Cheng, YANG Yingchang(
), GONG Tingting, PENG Shouhong, CHEN Cheng, YANG Yingchang( ), SHI Wei(
), SHI Wei( )
)