Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (8): 1-8.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2023-0522
• Reviews and Special Topics • Next Articles
Research progress on regeneration utilization of LiFePO4 materials in retired power batteries of electric vehicles
XU Jing1( ), WANG Dahui1,2(
), WANG Dahui1,2( ), CHEN Huaijing1,3, GUO Yongqi1, ZHENG Yang1
), CHEN Huaijing1,3, GUO Yongqi1, ZHENG Yang1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Advance Processing and Processing of Nonferrous Metals,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
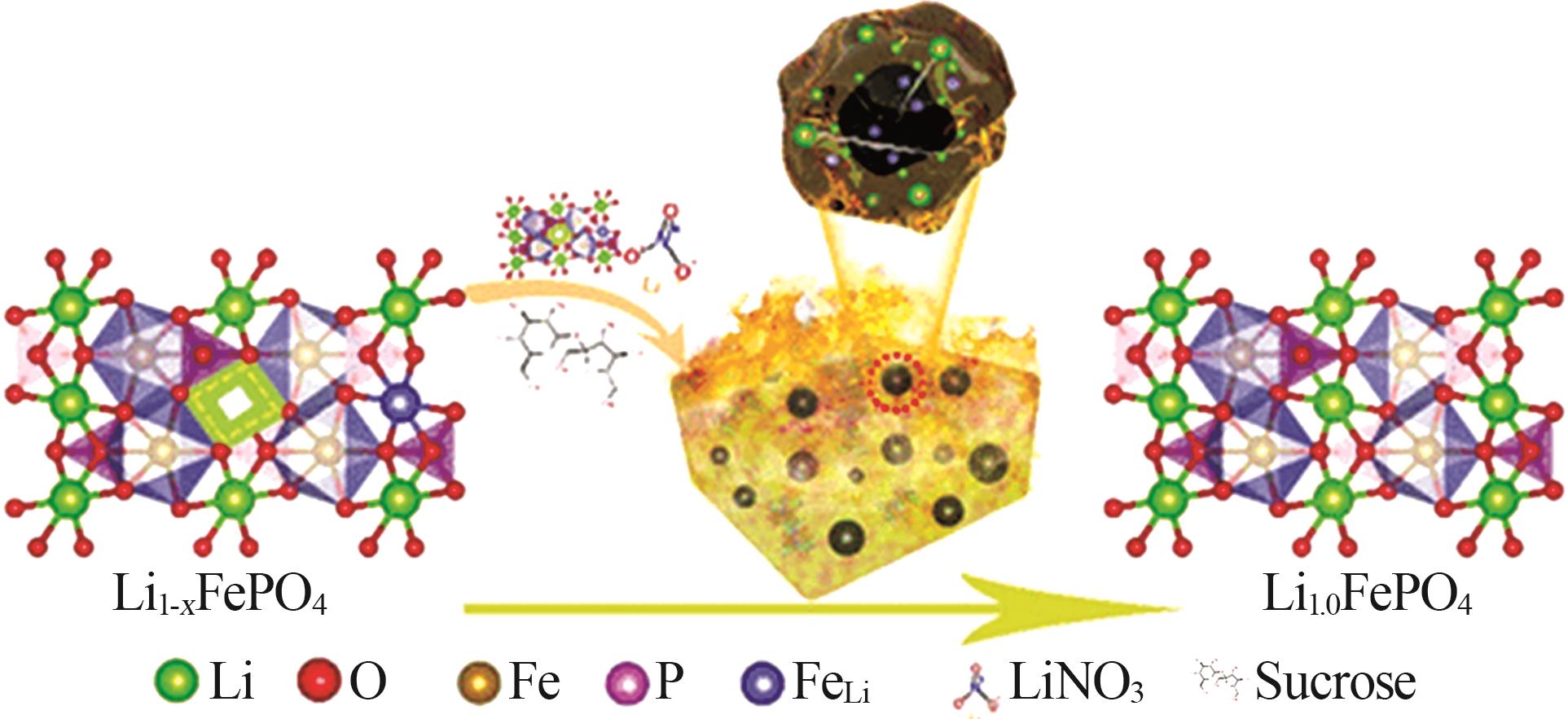
2.College of Materials Science and Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
3.College of Science,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
-
Received:2023-11-02Online:2024-08-10Published:2024-09-26 -
Contact:WANG Dahui E-mail:1531780162@qq.com;wangdh@lut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XU Jing, WANG Dahui, CHEN Huaijing, GUO Yongqi, ZHENG Yang. Research progress on regeneration utilization of LiFePO4 materials in retired power batteries of electric vehicles[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(8): 1-8.
share this article
Table 1
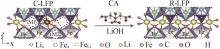
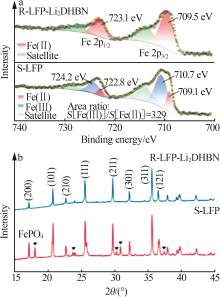
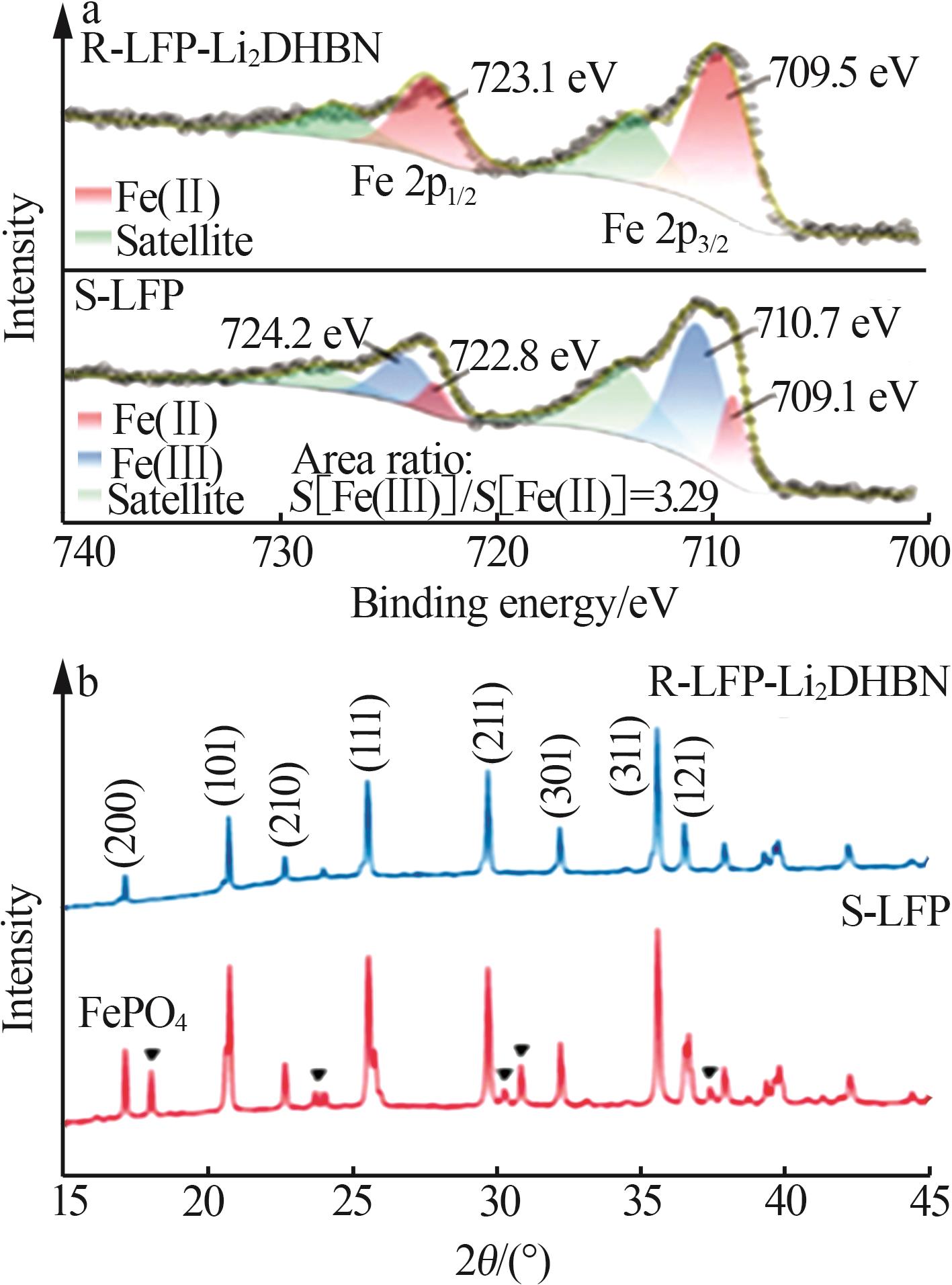
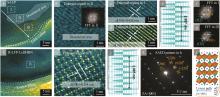
Elemental contents and elemental molar ratiosof S-LFP,R-LFP and C-LFP materials[7]"
| 元素质量分数/% | 元素物质的量比 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | P | Fe | n(Li)/ n(P) | n(Li)/n(Fe) | ||
| C-LFP材料 | 4.44 | 18.48 | 33.27 | 1.07 | 1.07 | |
| R-LFP-Li2DHBN材料 | 4.14 | 18.2 | 30.98 | 1.01 | 1.07 | |
| R-LFP-Li2CO3材料 | 4.41 | 18.11 | 32.36 | 1.08 | 1.09 | |
| R-LFP-LiOH材料 | 4.46 | 18.41 | 32.14 | 1.08 | 1.11 | |
| S-LFP材料 | 3.84 | 18.5 | 32.26 | 0.92 | 0.98 | |
Table 2
Comparison of electrochemical performance of S-LFP materials and R-LFP materials"
| 再生方法 | S-LFP材料电化学性能 | R-LFP材料电化学性能 |
|---|---|---|
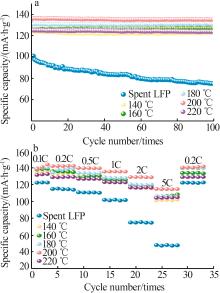
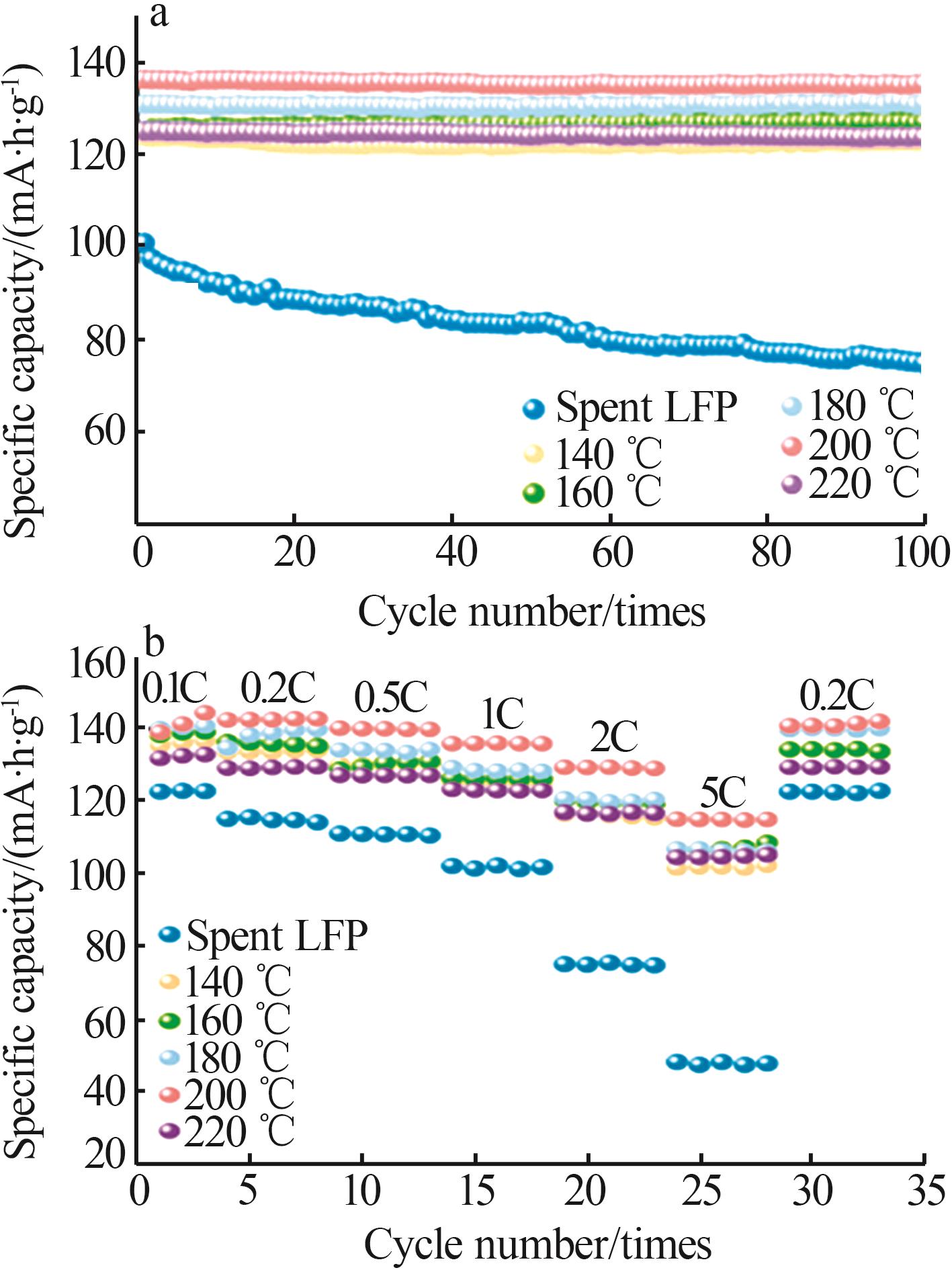
| 高温固相法[ | 0.2C时100 mA·h/g;100次循环后容量保持率达到95% | 0.2C时147.3 mA·h/g;100次循环后容量保持率达到95% |
| 水热法[ | 0.2C时100.7 mA·h/g;100次循环后容量保持率达到76.2% | 1C时135.9 mA·h/g;100次循环后容量保持率达到99% |
| 电化学锂化法[ | 1C时135.2 mA·h/g;500次循环后容量保持率达到95.3% | |
| 石墨预锂化法[ | 0.5C时65.3 mA·h/g;200次循环后容量保持率达到16.8% | 0.5C时126.6 mA·h/g;200次循环后容量保持率达到65.5% |
| 隔膜预锂化法[ | 1C时78.5 mA·h/g;292次循环后容量保持率达到18.1% | 0.05C时152 mA·h/g;150次循环后容量保持率达到85.3% |
| 低共熔溶剂[ | 0.5C时129 mA·h/g;100次循环后容量保持率达到83% | 0.5C时145 mA·h/g;100次循环后容量保持率达到90% |
| 1 | 陈光宇.新能源汽车时代开启[J].四川省情,2017(10):55. |
| CHEN Guangyu.The era of new energy vehicles opens[J].Sichuan Provincial Conditions,2017(10):55. | |
| 2 | 朱学帅,郝廷秀,黄雪,等.退役动力锂离子电池循环回收技术研究进展[J].矿业科学学报,2022,7(5):585-594. |
| ZHU Xueshuai, HAO Tingxiu, HUANG Xue,et al.Research progress on recycling technologies of lithium⁃ion batteries from electric vehicles[J].Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2022,7(5):585-594. | |
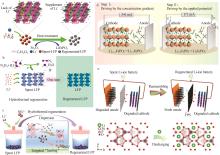
| 3 | CHEN Biaobing, LIU Min, CAO Shuang,et al.Regeneration and performance of LiFePO4 with Li2CO3 and FePO4 as raw materials recovered from spent LiFePO4 batteries[J].Materials Chemistry and Physics,2022,279:125750. |
| 4 | CHEN Biaobing, LIU Min, CAO Shuang,et al.Direct regeneration and performance of spent LiFePO4 via a green efficient hydrothermal technique[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,924:166487. |
| 5 | 费子桐,刘佩文,董鹏,等.退役磷酸铁锂材料资源化循环利用研究进展[J].有色设备,2021,35(4):7-11. |
| FEI Zitong, LIU Peiwen, DONG Peng,et al.Trend of research on recycle of used lithium iron phosphate batteries[J].Nonferrous Metallurgical Equipment,2021,35(4):7-11. | |
| 6 | 刘佩文,董鹏,孟奇,等.废旧磷酸铁锂电池正极材料固相法再生研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(9):6-8,14. |
| LIU Peiwen, DONG Peng, MENG Qi,et al.Research development of solid phase regeneration of cathode material of spent lithium iron phosphate batteries[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(9):6-8,14. | |
| 7 | JI Guanjun, WANG Junxiong, LIANG Zheng,et al.Direct regeneration of degraded lithium⁃ion battery cathodes with a multifunctional organic lithium salt[J].Nature Communications,2023,14: 584. |
| 8 | XU Yunlong, ZHANG Baichao, GE Zhaofei,et al.Direct recovery of degraded LiFePO4 cathode via mild chemical relithiation strategy [J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,477:147201. |
| 9 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M.Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J].Nature Chemistry,2015,7:19-29. |
| 10 | PAUL N, WANDT J, SEIDLMAYER S,et al.Aging behavior of lithium iron phosphate based 18650-type cells studied by in situ neutron diffraction[J].Journal of Power Sources,2017,345:85-96. |
| 11 | OUANECHE T, COURTY M, STIEVANO L,et al.Room temperature efficient regeneration of spent LiFePO4 by direct chemical lithiation[J].Journal of Power Sources,2023,579:233248. |
| 12 | PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, MASQUELIER C,et al.Effect of structure on the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple in iron phosphates[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1997,144(5):1609-1613. |
| 13 | ISLAM M S, DRISCOLL D J, FISHER C A J,et al.Atomic⁃scale investigation of defects,dopants,and lithium transport in the LiFePO4 olivine⁃type battery material[J].Chemistry of Materials,2005,17(20):5085-5092. |
| 14 | WANG Yi, CHEN Xuebing, WANG Yuanxi,et al.Overview of multilevel failure mechanism and analysis technology of energy storage lithium⁃ion batteries[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2023,12(7):2079-2094. |
| 15 | TANG DI, JI Guanjun, WANG Junxiong,et al.A multifunctional amino acid enables direct recycling of spent LiFePO4 cathode material[J].Advanced Materials,2024,36(5):e2309722. |
| 16 | XU Panpan, DAI Qiang, GAO Hongpeng,et al.Efficient direct recycling of lithium⁃ion battery cathodes by targeted healing[J].Joule,2020,4(12):2609-2626. |
| 17 | LIANG Qian, YUE Haifeng, WANG Shaofeng,et al.Recycling and crystal regeneration of commercial used LiFePO4 cathode materials[J].Electrochimica Acta,2020,330:135323. |
| 18 | YANG Yingpan, LIU Zixiao, ZHANG Jialiang,et al.Economical and low⁃carbon regeneration of spent LiFePO4 materials by hydrothermal relithiation[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2023,947:169660. |
| 19 | PENG Dezhao, WANG Xiaowei, WANG Shubin,et al.Efficient regeneration of retired LiFePO4 cathode by combining spontaneous and electrically driven processes[J].Green Chemistry,2022,24(11):4544-4556. |
| 20 | WANG Tao, YU Xiaoshuang, FAN Min,et al.Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO4 via a graphite prelithiation strategy[J].Chemical Communications,2019,56(2):245-248. |
| 21 | FAN Min, MENG Qinghai, CHANG Xin,et al. In situ electrochemical regeneration of degraded LiFePO4 electrode with functionalized prelithiation separator[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2022,12(18):2103630. |
| 22 | LIU Xiang, WANG Mengmeng, DENG Longping,et al.Direct regeneration of spent lithium iron phosphate via a low⁃temperature molten salt process coupled with a reductive environment[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2022,61(11):3831-3839. |
| 23 | 姚健,刘朝阳,王海,等.正负极混合宏量回收废旧磷酸铁锂电池的探索[J].储能科学与技术,2022,11(12):3759-3767. |
| YAO Jian, LIU Zhaoyang, WANG Hai,et al.Exploration of mixed positive and negative electrodes of spent lithium iron phosphate batteries[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2022,11(12):3759-3767. | |
| 24 | WU Jiawei, ZHENG Mengting, LIU Tiefeng,et al.Direct recovery:A sustainable recycling technology for spent lithium⁃ion battery[J].Energy Storage Materials,2023,54:120-134. |
| 25 | LI Xuelei, ZHANG Jin, SONG Dawei,et al.Direct regeneration of recycled cathode material mixture from scrapped LiFePO4 batteries[J].Journal of Power Sources,2017,345:78-84. |
| 26 | KUMAR J, SHEN Xing, LI Bo,et al.Selective recovery of Li and FePO4 from spent LiFePO4 cathode scraps by organic acids and the properties of the regenerated LiFePO4 [J].Waste Management,2020,113:32-40. |
| 27 | YANG Jinyi, ZHOU Kai, GONG Rui,et al.Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO4 materials via a green and economical one⁃step hydrothermal process[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2023,348:119384. |
| 28 | JIN Hao, ZHANG Jialiang, WANG Duoduo,et al.Facile and efficient recovery of lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries via air oxidation⁃water leaching at room temperature[J].Green Chemistry,2022,24(1):152-162. |
| 29 | WANG Zixuan, WU Dandan, WANG Xi,et al.Green phosphate route of regeneration of LiFePO4 composite materials from spent lithium⁃ion batteries[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2023,62(2):1181-1194. |
| 30 | ZHOU Shiyu, DU Jingzhen, XIONG Xiaosong,et al.Direct recovery of scrapped LiFePO4 by a green and low⁃cost electrochemical re⁃lithiation method[J].Green Chemistry,2022,24(16):6278-6286. |
| 31 | WU Chen, XU Mingli, ZHANG Chengyi,et al.Cost⁃effective recycling of spent LiMn2O4 cathode via a chemical lithiation strategy[J].Energy Storage Materials,2023,55:154-165. |
| 32 | QI Cai, WANG Shuhan, ZHU Xukun,et al.Environmental⁃friendly low⁃cost direct regeneration of cathode material from spent LiFePO4 [J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,924:166612. |
| 33 | JIANG Zhenyu, SUN Jing, JIA Pingshan,et al.A sustainable strategy for spent Li-ion battery regeneration:Microwave⁃hydrothermal relithiation complemented with anode⁃revived graphene to construct a LiFePO4/MWrGO cathode material[J].Sustainable Energy & Fuels,2022,6(9):2207-2222. |
| 34 | 靳星,贾美丽,杜浩,等.废旧磷酸铁锂正极材料回收再生研究进展[J].有色金属工程,2020,10(11):64-72. |
| JIN Xing, JIA Meili, DU Hao,et al.Research progress on recovery of spent lithium iron phosphate cathode materials[J].Nonferrous Metals Engineering,2020,10(11):64-72. | |
| 35 | JING Qiankun, ZHANG Jialiang, LIU Yubo,et al.Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO4 cathode material by a green and efficient one⁃step hydrothermal method[J].ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2020,8(48):17622-17628. |
| 36 | 王猛,张家靓,陈永强,等.退役磷酸铁锂电池回收技术综述[J].有色金属(冶炼部分),2023(5):100-110. |
| WANG Meng, ZHANG Jialiang, CHEN Yongqiang,et al.Review on recycling technology of retired LiFePO4 batteries[J].Nonferrous Metals,2023(5):100-110. | |
| 37 | YANG Tairan, LU Yingqi, LI Liurui,et al.An effective relithiation process for recycling lithium⁃ion battery cathode materi⁃als[J].Advanced Sustainable Systems,2020,4(1):1900088. |
| 38 | WENG Suting, YANG Gaojing, ZHANG Simeng,et al.Kinetic limits of graphite anode for fast⁃charging lithium⁃ion batteries[J].Nano⁃Micro Letters,2023,15(1):215. |
| 39 | DOSE W M, JOHNSON C S.Cathode pre⁃lithiation/sodiation for next⁃generation batteries[J].Current Opinion in Electrochemistry,2022,31:100827. |
| 40 | ZHONG Wei, ZHANG Ce, LI Siwu,et al.Mo2C catalyzed low⁃voltage prelithiation using nano⁃Li2C2O4 for high⁃energy lithium⁃ion batteries[J].Science China Materials,2023,66(3):903-912. |
| 41 | HOLTSTIEGE F, BÄRMANN P, NÖLLE R,et al.Pre⁃lithiation strategies for rechargeable energy storage technologies:Concepts,promises and challenges[J].Batteries,2018,4(1):4. |
| 42 | SMITH E L, ABBOTT A P, RYDER K S.Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications[J].Chemical Reviews,2014,114(21):11060-11082. |
| 43 | SVIGELJ R, DOSSI N, GRAZIOLI C,et al.Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their application in biosensor development[J].Sensors,2021,21(13):4263. |
| 44 | 程明强,汝娟坚,华一新,等.低共熔溶剂在废旧锂离子电池正极材料回收中的研究进展[J].化工进展,2022,41(6):3293-3305. |
| CHENG Mingqiang, RU Juanjian, HUA Yixin,et al.Progress of deep eutectic solvents in recovery of cathode materials from spent lithium ion batteries[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2022,41(6):3293-3305. | |
| 45 | WANG Junxiong, ZHANG Qi, SHENG Jinzhi,et al.Direct and green repairing of degraded LiCoO2 for reuse in lithium⁃ion batteries[J].National Science Review,2022,9(8):nwac097. |
| 46 | JIN Yachao, ZHANG Tong, ZHANG Mingdao.Advances in intelligent regeneration of cathode materials for sustainable lithium⁃ion batteries[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2022,12(36):2201526. |
| 47 | YANG Huimeng, DENG Bowen, JING Xiaoyun,et al.Direct recovery of degraded LiCoO2 cathode material from spent lithium⁃ion batteries:Efficient impurity removal toward practical applications[J].Waste Management,2021,129:85-94. |
| 48 | YINGNAKORN T, HARTLEY J, TERREBLANCHE J S,et al.Direct re⁃lithiation strategy for spent lithium iron phosphate battery in Li-based eutectic using organic reducing agents[J].RSC Sustainability,2023,1(9):2341-2349. |
| 49 | YANG Juan, WANG Wenyu, YANG Huimeng,et al.One⁃pot compositional and structural regeneration of degraded LiCoO2 for directly reusing it as a high⁃performance lithium⁃ion battery cathode[J].Green Chemistry,2020,22(19):6489-6496. |
| 50 | SHI Yang, ZHANG Minghao, MENG Y S,et al.Ambient⁃pressure relithiation of degraded Li x Ni0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 (0<x<1) via eutectic solutions for direct regeneration of lithium⁃ion battery cathod⁃es[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2019,9(20):1900454. |
| [1] | GE Jianhua, XIE Minyan, OUYANG Quansheng, SHAO Jiaojing. Advances in regeneration processes of cathode materials for spent power batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(12): 79-87. |
| [2] | TANG Di,WANG Junxiong,CHEN Wen,JI Guanjun,MA Jun,ZHOU Guangmin. Research status and prospect on direct regeneration of cathode materials from retired lithium-ion batteries [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(1): 15-25. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||