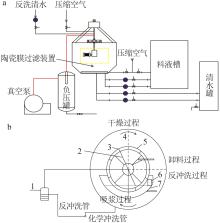
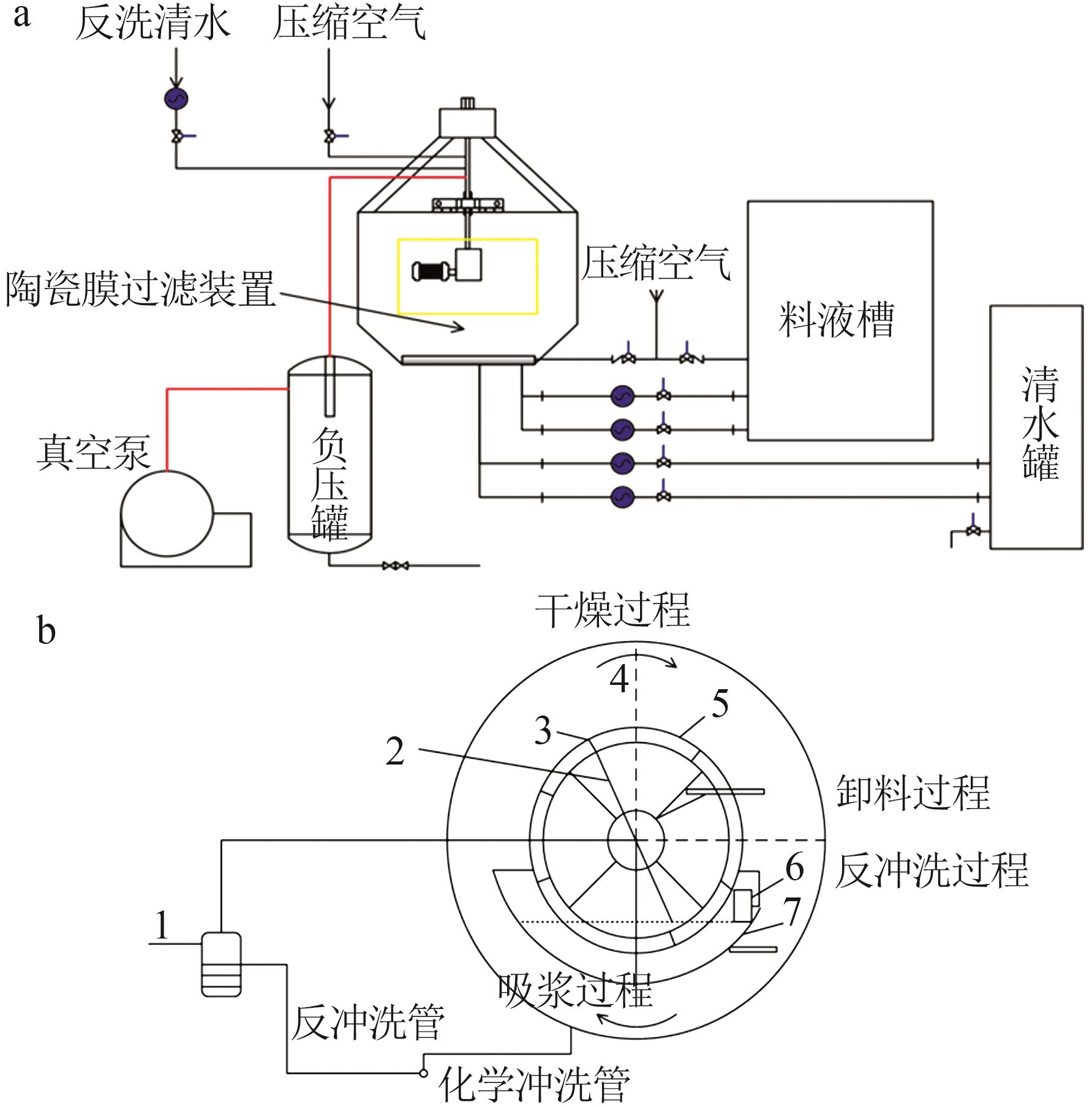
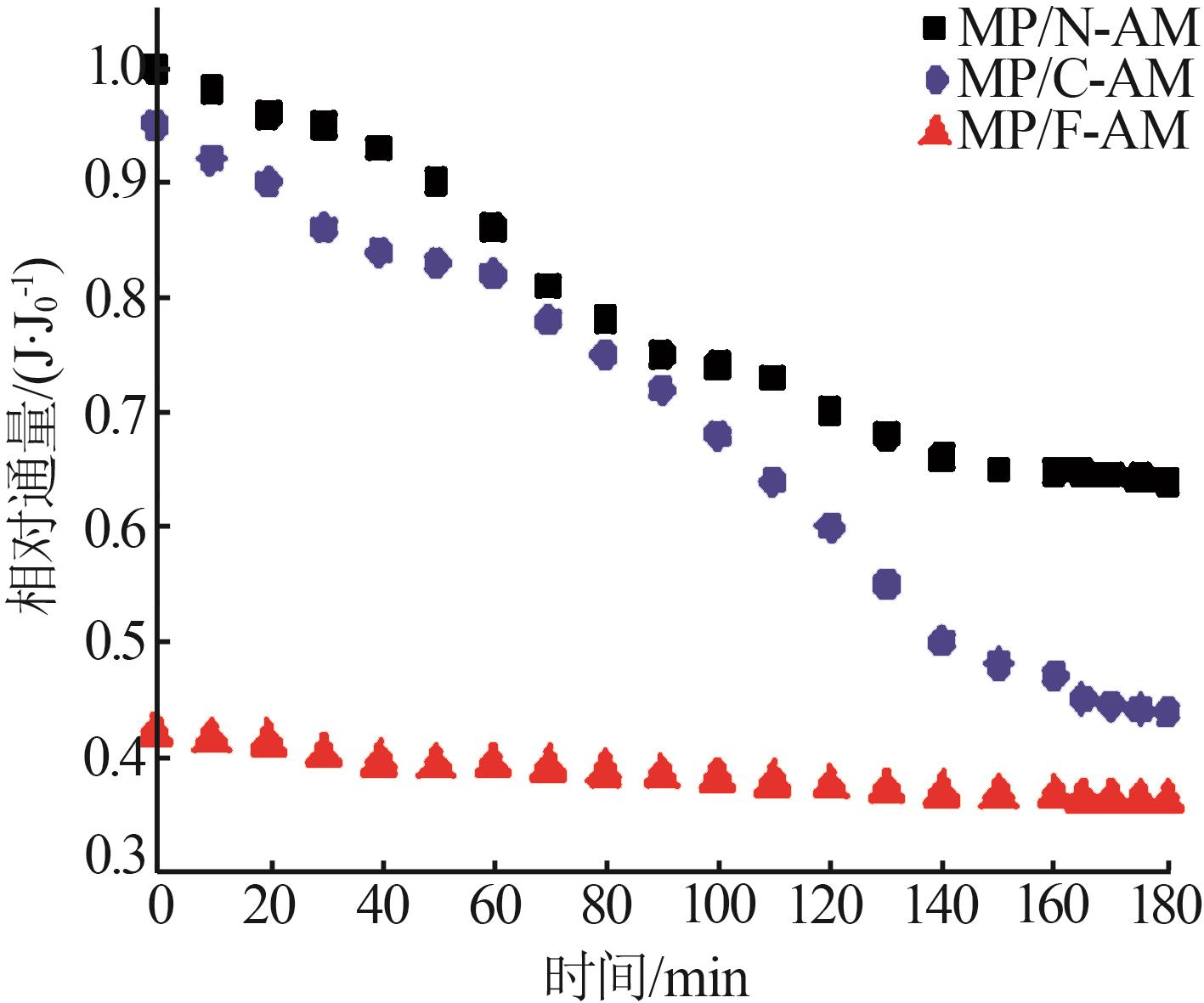
| 1 |
CEVALLOS-MENDOZA J, AMORIM C G, RODRÍGUEZ-DÍAZ J M,et al.Removal of contaminants from water by membrane filtration:A review[J].Membranes,2022,12(6):570.
|
| 2 |
林钰青,张以任,邱宇隆,等.膜技术在盐湖提锂中的进展和展望[J].无机盐工业,2023,55(1):33-45.
|
|
LIN Yuqing, ZHANG Yiren, QIU Yulong,et al.Progress and prospect of membrane technology in lithium extraction from salt lake brine[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2023,55(1):33-45.
|
| 3 |
DONG Yingchao, WU Hui, YANG Fenglin,et al.Cost and efficiency perspectives of ceramic membranes for water treatment[J].Water Research,2022,220:118629.
|
| 4 |
SHI Yaoke, WANG Zhiwen, DU Xianjun,et al.Membrane fouling diagnosis of membrane components based on multi-feature information fusion[J].Journal of Membrane Science,2022,657:120670.
|
| 5 |
TIAN Jiayu, PAN Hui, BAI Zhaoyu,et al.Alleviated membrane fouling of corundum ceramic membrane in MBR:As compared with alumina membrane[J].Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2022,10(6):108949.
|
| 6 |
MENG Shujuan, ZHANG Minmin, YAO Meng,et al.Membrane fouling and performance of flat ceramic membranes in the application of drinking water purification[J].Water,2019,11(12):2606.
|
| 7 |
WU Haichao, KANORA A, SCHWARTZ D K.Fouling of microfiltration membranes by bidisperse particle solutions[J].Journal of Membrane Science,2022,641:119878.
|
| 8 |
ZHANG Bing, TANG Heli, SHEN Yu,et al.Comparative analysis of membrane fouling mechanisms induced by colloidal polymer:Effects of sodium and calcium ions[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2022,608(Pt 1):780-791.
|
| 9 |
YANG Haiyan, YU Xuri, LIU Junxia,et al.A concise review of theoretical models and numerical simulations of membrane fouli- ng[J].Water,2022,14(21):3537.
|
| 10 |
LIN Tao, LU Zijian, CHEN Wei.Interaction mechanisms and predictions on membrane fouling in an ultrafiltration system,using the XDLVO approach[J].Journal of Membrane Science,2014,461:49-58.
|
| 11 |
LI Haigang, XIA Huanjin, MEI Yingxin.Modeling organic fouling of reverse osmosis membrane:From adsorption to fouling layer formation[J].Desalination,2016,386:25-31.
|
| 12 |
MA Zhun, ZHANG Lu, LIU Ying,et al.Influential mechanism of natural organic matters with calcium ion on the anion exchange membrane fouling behavior via xDLVO theory[J].Membranes,2021,11(12):968.
|
| 13 |
BAI Zhaoyu, ZHANG Ruijun, WANG Songxue,et al.Membrane fouling behaviors of ceramic hollow fiber microfiltration(MF) membranes by typical organic matters[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2021,274:118951.
|
| 14 |
周鸣天,张干伟,寇朝卫,等.XDLVO理论分析混合有机污染物的膜污染[J].水处理技术,2020,46(4):73-77,96.
|
|
ZHOU Mingtian, ZHANG Ganwei, KOU Chaowei,et al.XDLVO theory analysis of membrane fouling by mixture organic pollutan-ts[J].Technology of Water Treatment,2020,46(4):73-77,96.
|
| 15 |
LI Renjie, LOU Yang, XU Yanchao,et al.Effects of surface morphology on alginate adhesion:Molecular insights into membrane fouling based on XDLVO and DFT analysis[J].Chemosphere,2019,233:373-380.
|
| 16 |
唐和礼,张冰,黄冬梅,等.XDLVO理论在膜污染解析中的应用研究[J].化工学报,2021,72(3):1230-1241.
|
|
TANG Heli, ZHANG Bing, HUANG Dongmei,et al.Advances in membrane fouling analysis based on XDLVO theory[J].CIESC Journal,2021,72(3):1230-1241.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG Tong, ZHANG Jie, WANG Qiaoying,et al.Evaluating of the performance of natural mineral vermiculite modified PVDF membrane for oil/water separation by membrane fouling model and XDLVO theory[J].Journal of Membrane Science,2022,641:119886.
|
| 18 |
LIU Junxia, FAN Yaqian, SUN Yuhui,et al.Modelling the critical roles of zeta potential and contact angle on colloidal fouling with a coupled XDLVO-collision attachment approach[J].Journal of Membrane Science,2021,623:119048.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG Jun, WANG Pengfei, BORG M K,et al.A critical assessment of the line tension determined by the modified Young′s equation[J].Physics of Fluids,2018,30(8):82003.
|
| 20 |
屈晓璐.任意粗糙膜表面的构建及其与膜污染界面作用力的关系研究[D].金华:浙江师范大学,2018.
|
|
QU Xiaolu.Construction of random rough membrane surface and its relationship with interfacial interactions in membrane fouli-ng[D].Jinhua:Zhejiang Normal University,2018.
|
| 21 |
KRUPP H, SPERLING G.Theory of adhesion of small particles[J].Journal of Applied Physics,1966,37(11):4176-4180.
|
| 22 |
赵应许,纵瑞强,高欣玉,等.XDLVO理论解析不同离子条件下海藻酸钠微滤膜污染[J].环境科学,2014,35(4):1343-1350.
|
|
ZHAO Yingxu, ZONG Ruiqiang, GAO Xinyu,et al.Fouling behavior of sodium alginate during microfiltration at various ionic co-mpositions:XDLVO approach[J].Environmental Science,2014,35(4):1343-1350.
|
| 23 |
YUAN Xiaotong, WU Lei, GENG Hongzhang,et al.Polyaniline/polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes with improved permeability and anti-fouling behavior[J].Journal of Water Process Engineering,2021,40:101903.
|
| 24 |
王可,樊华,侯得印,等.XDLVO理论解析有机物在膜蒸馏过程中的膜污染行为机制[J].膜科学与技术,2022,42(2):25-33.
|
|
WANG Ke, FAN Hua, HOU Deyin,et al.Mechanism of membrane fouling in membrane distillation process by organic compounds:XDLVO theory[J].Membrane Science and Technology,2022,42(2):25-33.
|
| 25 |
吴欢欢,沈飞,万印华,等.XDLVO理论解析膜蒸馏回收离子液体过程中的膜污染研究[J].膜科学与技术,2019,39(5):9-17.
|
|
WU Huanhuan, SHEN Fei, WAN Yinhua,et al.Analysis of membrane fouling by XDLVO theory in vacuum membrane distillation for ionic liquid recycling[J].Membrane Science and Technology,2019,39(5):9-17.
|
 ), TIAN Mengkui1(
), TIAN Mengkui1( ), LIU Hai2
), LIU Hai2