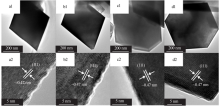
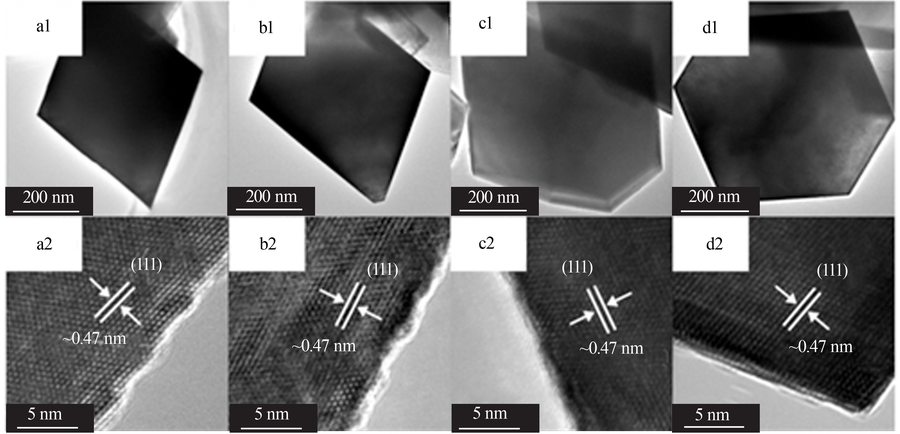
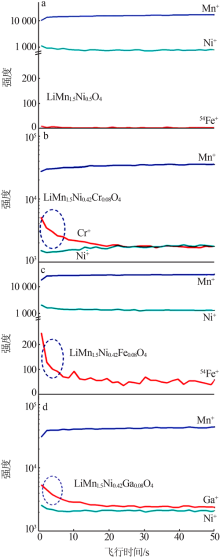
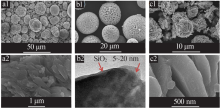
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (11): 17-24.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2021-0184
• Reviews and Special Topics • Previous Articles Next Articles
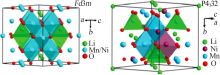
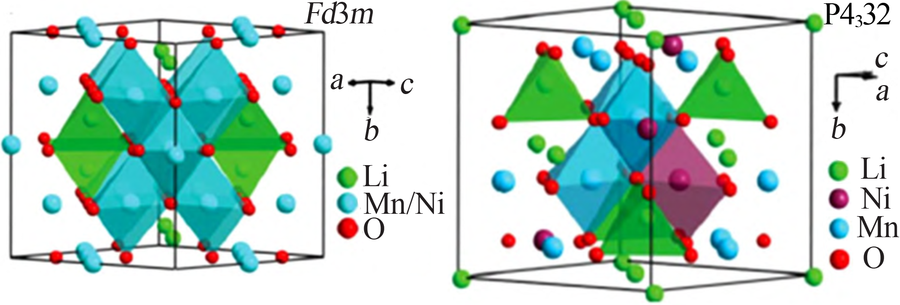
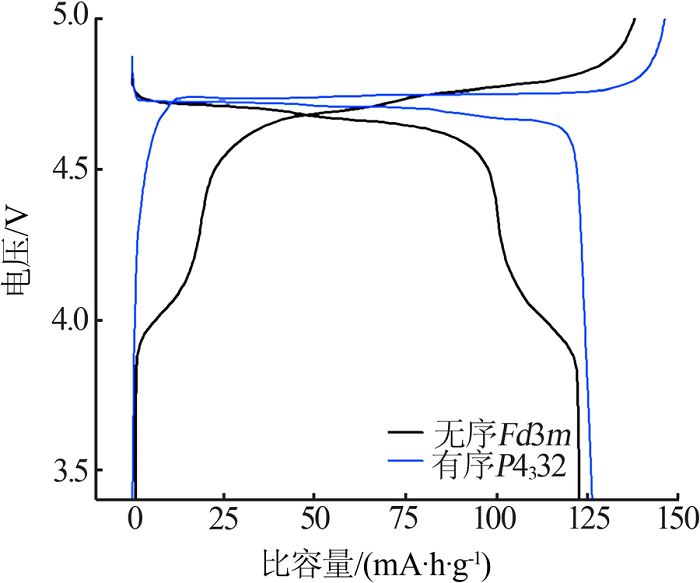
Research status and analysis of effect of interfacial chemistry on electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials
ZHOU Lan( ),LI Wang,LIAO Wenjun
),LI Wang,LIAO Wenjun
- Central Research Academy,Shanghai Electric Group Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai 200070,China
-
Received:2021-03-24Online:2021-11-10Published:2021-11-15
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHOU Lan,LI Wang,LIAO Wenjun. Research status and analysis of effect of interfacial chemistry on electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(11): 17-24.
share this article
| [1] | 李旺, 周兰, 刘佳丽, 等. 镍锰酸锂正极材料制备及其适配性电解液研究最新进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(6):5-10. |
| [2] | 金彦章, 王永和, 刘强, 等. 高电压正极材料LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4制备及性能研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017, 49(6):45-49. |
| [3] | 梁文彪, 李世友, 崔孝玲, 等. 高电压LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4正极材料现状及展望[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 278(11):77-82. |
| [4] |
ZHANG X, CHENG F, ZHANG K, et al. Facile polymer-assisted synjournal of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with a hierarchical micro-nano structure and high rate capability[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(13):5669-5675.
doi: 10.1039/c2ra20669b |
| [5] |
TERADA Y, YASAKA K, NISHIKAWA F, et al. In situ XAFS an-alysis of Li(Mn,M)2O4(M=Cr,Co,Ni) 5V cathode materials for li-thium-ion secondary batteries[J]. Journal Solid State Chemistry, 2001, 156:286-291.
doi: 10.1006/jssc.2000.8990 |
| [6] | ZHOU L, WANG L, WAN L. Preparation,electrochemistry properti-es of LiNi0.5-xFe0.0485Mn1.5-yO4 by Spray-Dry method with different Mn/Ni ratios[J]. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures, 2020, 15(3):857-866. |
| [7] |
HAI B, SHUKLA A K, DUNCAN H, et al. The effect of particle sur-face facets on the kinetic properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode ma-terials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(3):759-769.
doi: 10.1039/C2TA00212D |
| [8] |
DENG Y F, ZHAO S X, XU Y H, et al. Impact of P doped in spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 on degree of disorder,grain morphology,and electro-chemical performance[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27:7734-7742.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b03517 |
| [9] | CHEMELEWSKI K R, SHIN D W, LI W, et al. Octahedral and trunc-uncated high-voltage spinel cathodes:The role of morphology and surface planes in electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Materi-als Chemistry A, 2013, 1:3347-3354. |
| [10] |
GUO J, DENG Z, YAN S, et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4spinels with different particle sizes and surface orientations as cathode materials for lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55:13157-13176.
doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-04973-0 |
| [11] |
WEI Y, TUO K, WANG P, et al. Appropriate proportion truncated octahedron LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with excellent electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries prepared by graphite-assisted calcination method[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26:6003-6012.
doi: 10.1007/s11581-020-03786-0 |
| [12] |
ZHOU M, GONG J, DENG Z, et al. Synjournal and electrochemical performances of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinels with different surface orientations for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(5):2187-2200.
doi: 10.1007/s11581-019-03373-y |
| [13] | CHEN Z, ZHAO R, DU P, et al. Polyhedral LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with exc-ellent electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Jo-urnal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2:12835-12848. |
| [14] | LIU H, KLOEPSCH R, WANG J, et al. Truncated octahedral LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for ultralonglife lithium-ion battery:Positive(100) surfaces in high-voltage spinel system[J]. J.Power Sources, 2015, 300:430-437. |
| [15] |
LIU J, LIU W, JI S, et al. Electrospun spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 hierarc-hical nanofibers as 5 V cathode materials for lithium-ion batteri-es[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2013, 78:636-641.
doi: 10.1002/cplu.v78.7 |
| [16] |
HAO X, AUSTIN M H, BARTLETT B M. Two-step hydrothermal synjournal of submicron Li1+xNi0.5Mn1.5O4-δ for lithium-ion battery ca-thodes(x=0.02,δ=0.12)[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41:8067-8076.
doi: 10.1039/c2dt30351e |
| [17] | 罗英, 王勇, 郭满毅, 等. 基于Mn3+浓度和形貌控制的高性能LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4正极材料[J]. 上海航天, 2020, 224(2):50-57. |
| [18] | XIAO J, CHEN X, SUSHKO P V, et al. High-performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel controlled by Mn3+ concentration and site di-sorder[J]. Adv.Mater., 2012, 24:2109-2116. |
| [19] |
LIU D, LU Y, GOODENOUGH J B. Rate properties and elevated temperature performances of LiNi0.5-xCr2xMn1.5xO4(0≤2x≤0.8) as 5 V cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157:A1269-A1273.
doi: 10.1149/1.3491365 |
| [20] | LEE E S, MANTHIRAM A. Influence of doping on the cation order-ing and charge-discharge behavior of LiMn1.5Ni0.5-xMxO4(M=Cr,Fe,Co,and Ga) spinels between 5.0 and 2.0 V[J]. Journal of Materi-als Chemistry A, 2013, 1:3118-3126. |
| [21] |
LIN M, BEN L, SUN Y, et al. Insight into the atomic structure of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material in the first cy-cle[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27:292-303.
doi: 10.1021/cm503972a |
| [22] | 张文林, 霍宇, 李功伟, 等. 离子液体作为电解液添加剂用于高压锂离子电池[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6):2334-2342. |
| [23] |
XU Y, WAN L, LIU J, et al. γ-butyrolactone and glutaronitrile as 5 V electrolyte additive and its electrochemical performance for LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 698:207-214.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.381 |
| [24] | 陈锐芳, 撒召遥, 苏长伟, 等. 尖晶石LiMn2O4正极材料的研究进展[J]. 电池, 2020, 265(5):91-95. |
| [25] |
PIECZONKA N P, LIU Z, LU P, et al. Understanding transition-metal dissolution behavior in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 high-voltage spinel for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117:15947-15957.
doi: 10.1021/jp405158m |
| [26] |
OKUNO Y, USHIROGATA K, SODEYAMA K, et al. Structures,electronic states,and reactions at interfaces between LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode and ethylene carbonate electrolyte:A first-principles stu-dy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(4):2267-2277.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b10625 |
| [27] |
JARRY A, GOTTIS S, YU Y S, et al. The formation mechanism of fluorescent metal complexes at the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/carbonate ester electrolyte interface[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137:3533-3539.
doi: 10.1021/ja5116698 |
| [28] |
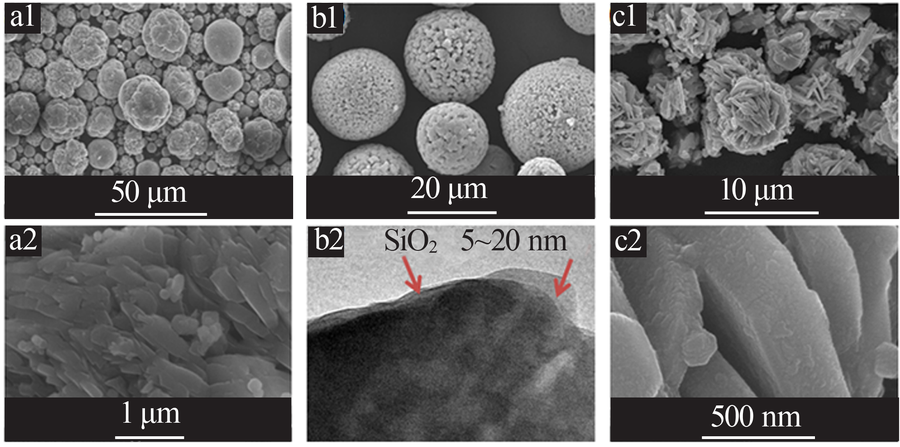
PANG W K, LIN H F, PETERSON V K, et al. Enhanced rate-capa-bility and cycling-stability of 5 V SiO2 and polyimide-coated ca-tion ordered LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 lithium-ion battery positive electrod-es[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121:3680-3689.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b10743 |
| [29] |
KUENZEL M, KIM G T, ZARRABEITIA M, et al. Crystal engine-ering of TMPOx-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes for high-performa-nce lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2020, 39:127-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2020.04.003 |
| [30] | XU T, LI Y, WANG D, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performa-nce of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material by YPO4 surface modifica-tion[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(5):5818-5825. |
| [31] |
CHU C T, MONDAL A, KOSOVA N V, et al. Improved high-tem-perature cycliablity of AlF3 modified spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 530:147169-147177.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147169 |
| [32] |
TIURIN O, SOLOMATIN N, AUINAT M, et al. Atomic layer depo-sition(ALD) of lithium fluoride(LiF) protective film on Li-ion ba-ttery LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 cathode powder material[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448:227373-227386.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227373 |
| [33] | 孙健铭, 谭毅, 王凯, 等. Al3+掺杂对LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4材料性能的影响[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(3):500-506. |
| [34] |
CHEN A, KONG L, SHU Y, et al. Role of Al-doping with different sites upon the structure and electrochemical performance of spheri-cal LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(22):12656-12666.
doi: 10.1039/C9RA00374F |
| [35] | LI X, ZHANG Y, LI W, et al. The synergetic effect of LiMg0.5Mn1.5O4 coating and Mg2+ doping on improving electrochemi-cal performances of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by sol-gel self-co-combustion method[J]. Chemistry Select, 2020, 5(8):2593-2601. |
| [36] |
GAO Y, YU H, SANDINENI P, et al. Fe doping in LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 by atomic layer deposition followed by annealing:Depths and occupa-tion sites[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(14):7560-7567.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c00225 |
| [37] |
AKLALOUCH M, BOUADDI H, GARHI G, et al. Environmentally friendly 5 V cathode based on Fe-doped LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinel for Li-ion batteries[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2021, 37:3951-3957.
doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.232 |
| [38] | SUN H, KONG X, FENG S, et al. Effects of Zn doping amount on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 lithium-ion cathode materials[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2019, 14:11391-11405. |
| [39] |
LIU G Y, KONG X, LUO T B, et al. Cu doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5-xCuxO4 (x=0,0.03,0.05,0.10,0.15) with significant improved electroche-mical performance prepared by a modified low temperature solu-tion combustion synjournal method[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44:4603-4610.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.112 |
| [40] | 李嘉雯, 王海龙, 余俏滟. Co3+掺杂对LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4导电性和倍率性能的影响研究[J]. 广州化工, 2018, 46(22):38-40. |
| [41] |
XU D, YANG F, LIU Z, et al. Effects of Co doping sites on the elec-trochemical performance of LiNi0.5MnO4 as a cathode material[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(8):1-7.
doi: 10.1007/s11581-019-03224-w |
| [42] | LI F, MA J, LIN J, et al. Exploring the origin of electrochemical per-formance of Cr-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4[J]. Physical Chemistry Che-mical Physics, 2020, 22(7):2831-2838. |
| [43] |
OH S W, PARK S H, KIM J H, et al. Improvement of electrochemi-cal properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel material by fluorine substitu-tion[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 157:464-470.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.07.056 |
| [44] |
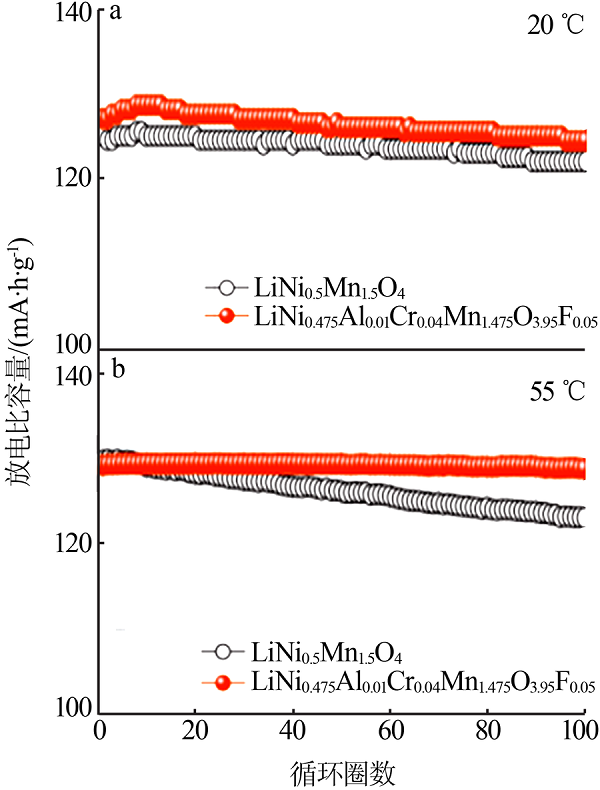
SHA O, TANG Z, WANG S, et al. The multi-substituted LiNi0.475Al0.01Cr0.04Mn1.475O3.95F0.05 cathode material with excellent rate capability and cycle life[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 77:250-255.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.05.096 |
| [1] | Li Wang,Zhou Lan,Liu Jiali. Latest development of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials and adaptive electrolytes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(6): 5-10. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||