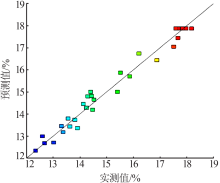
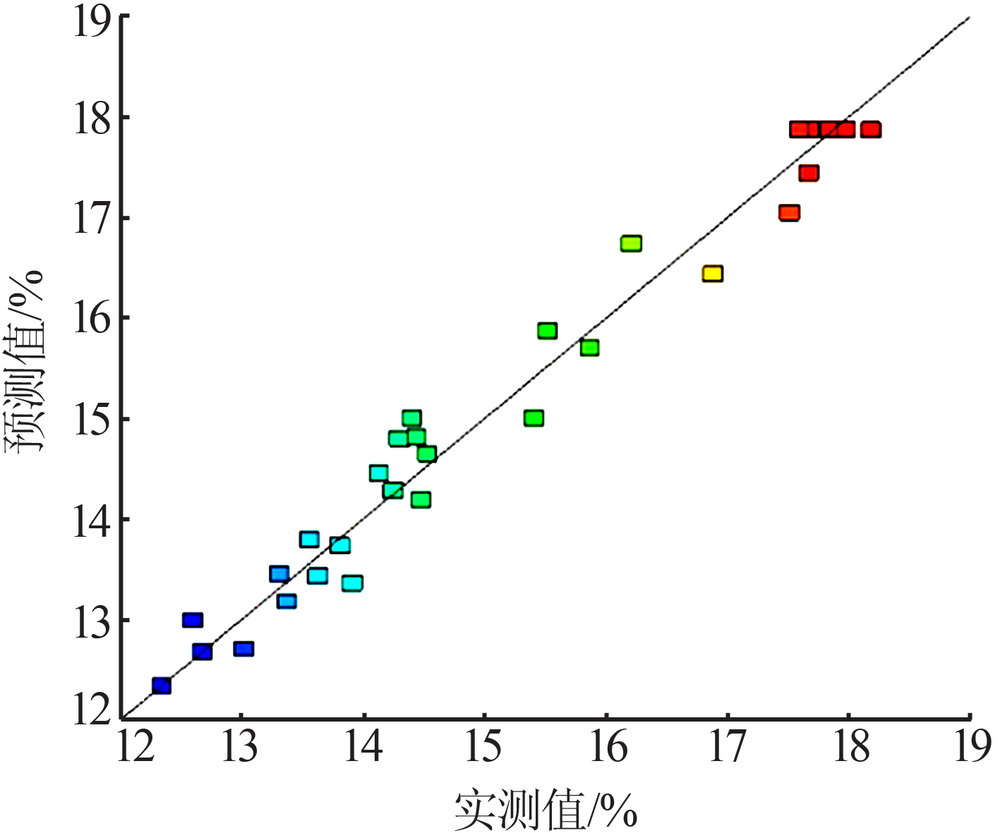
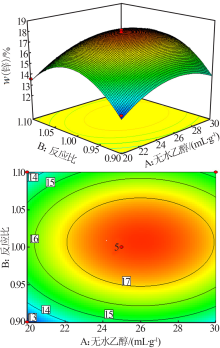
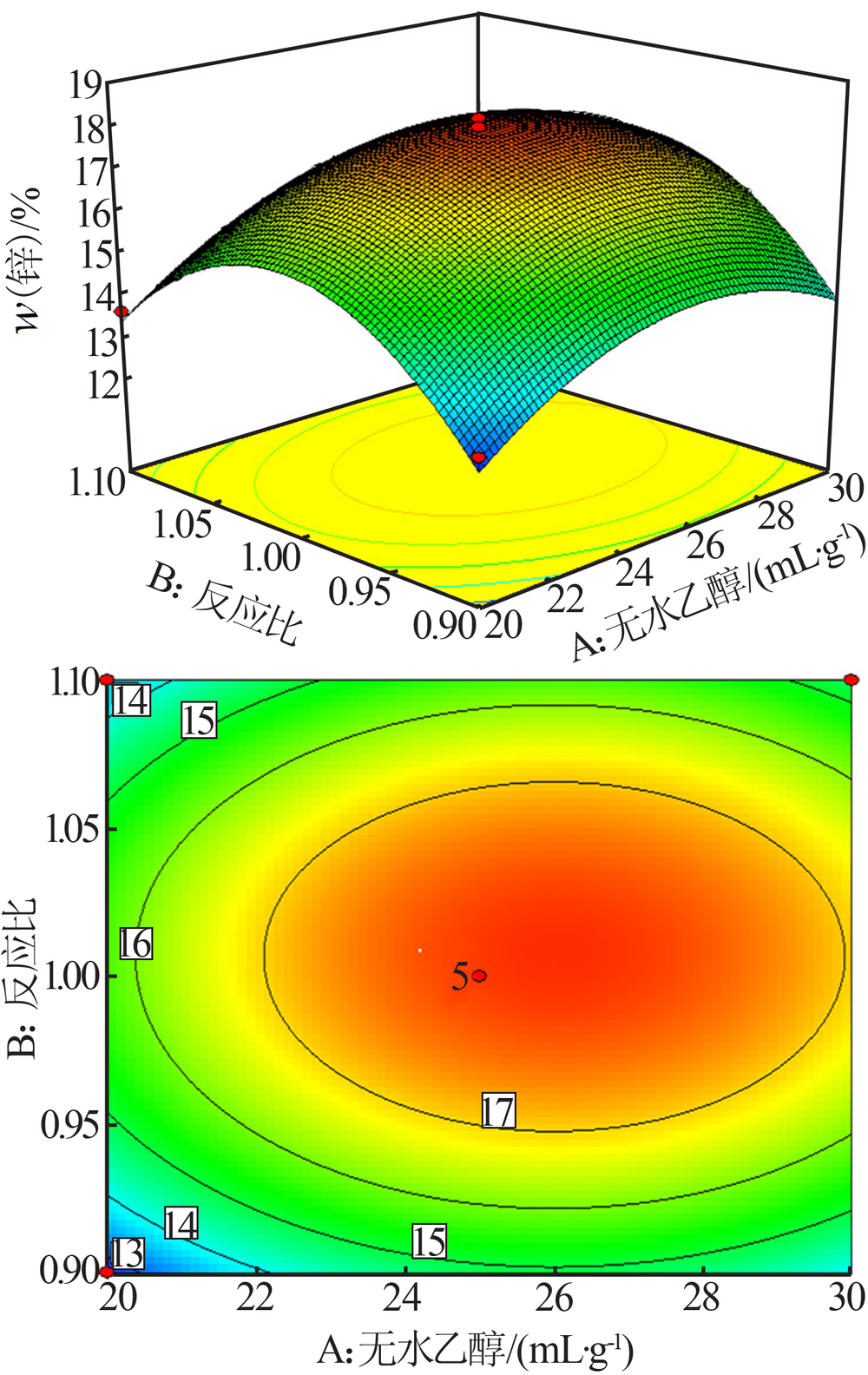
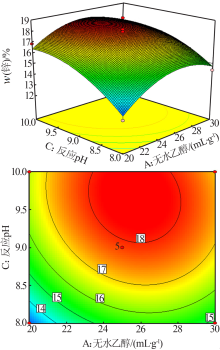
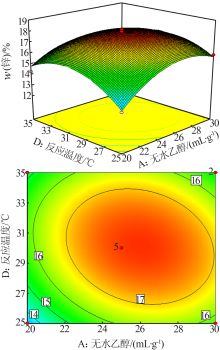
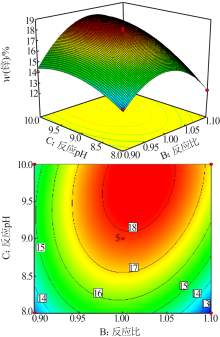
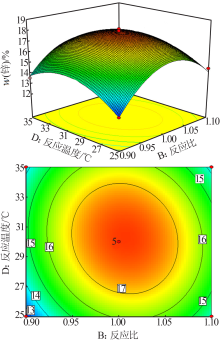
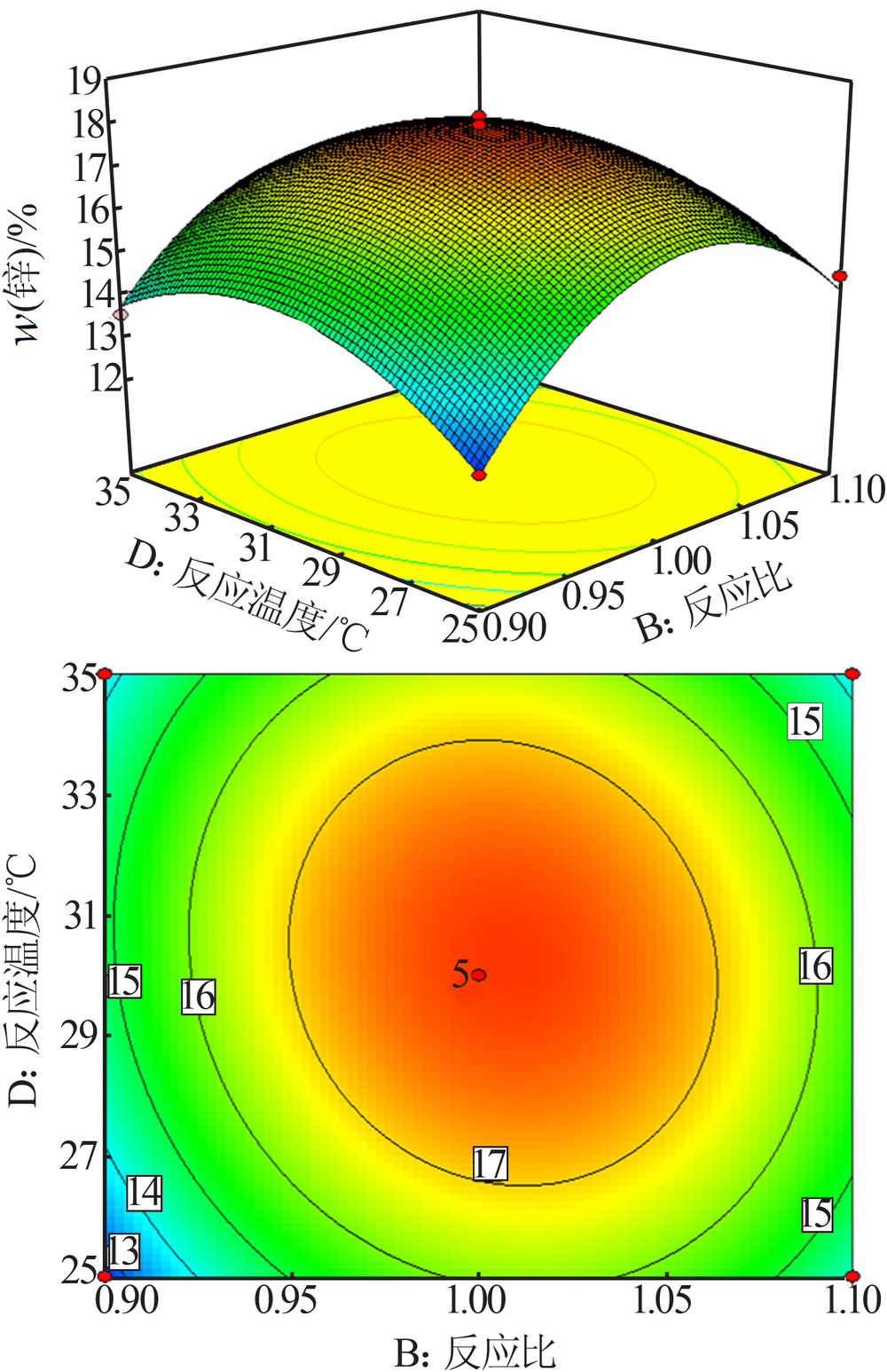
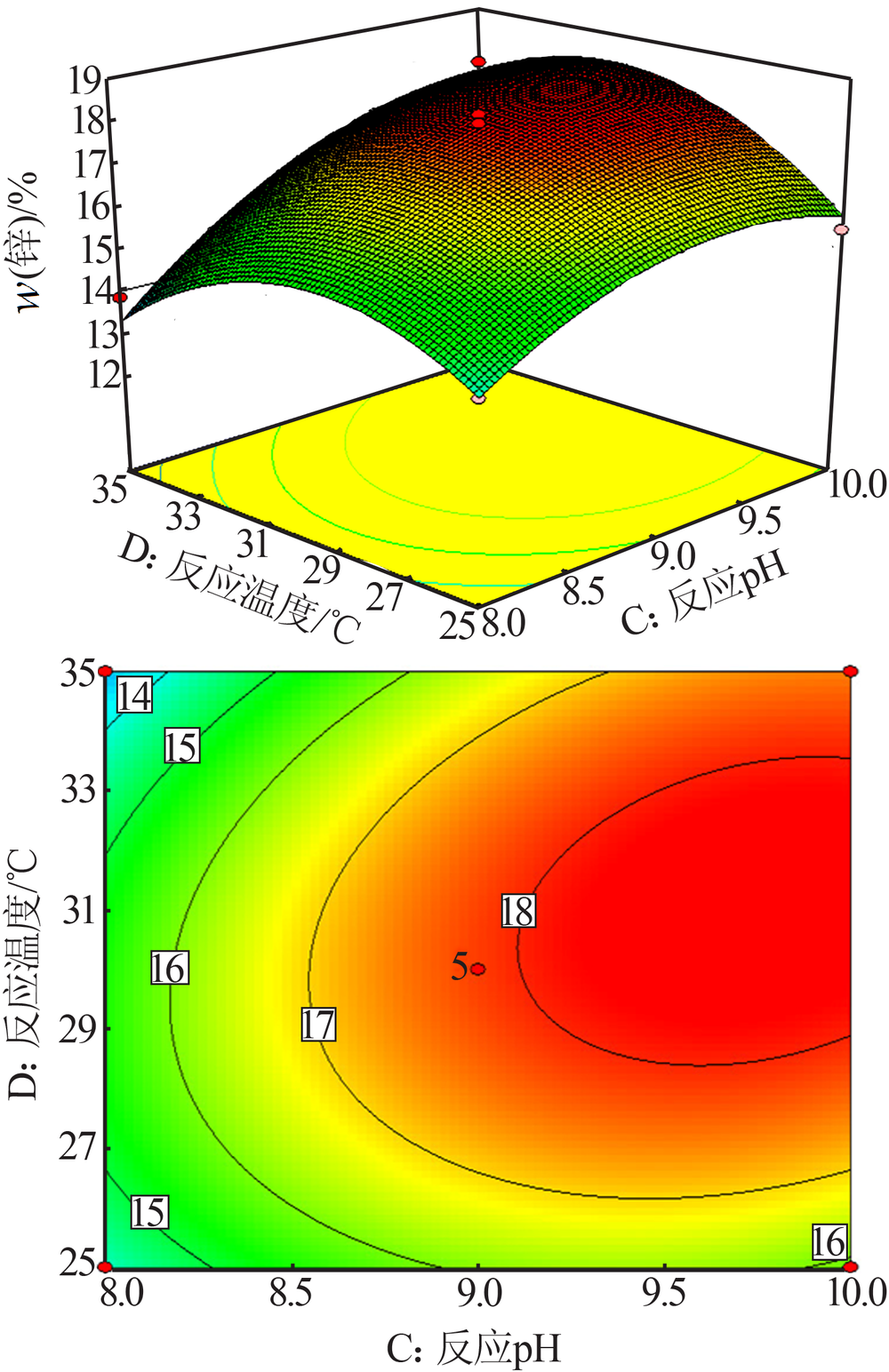
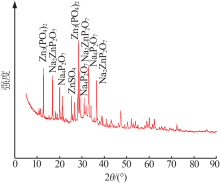
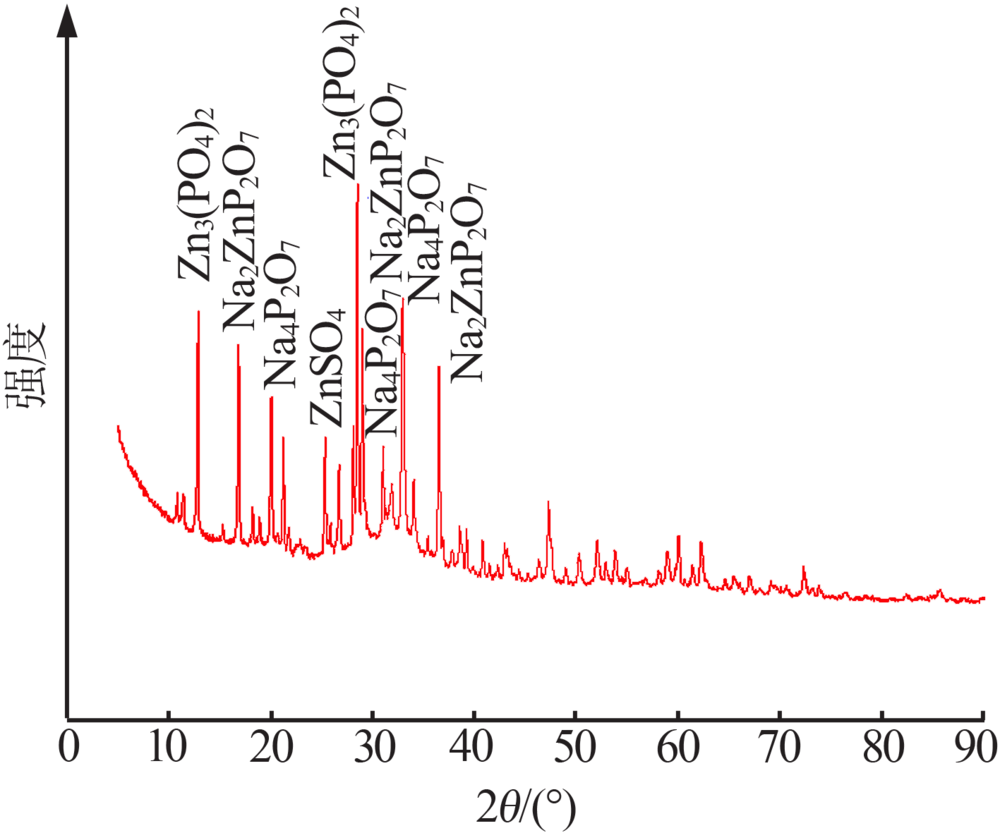
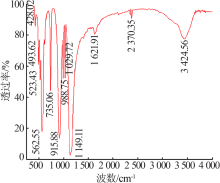
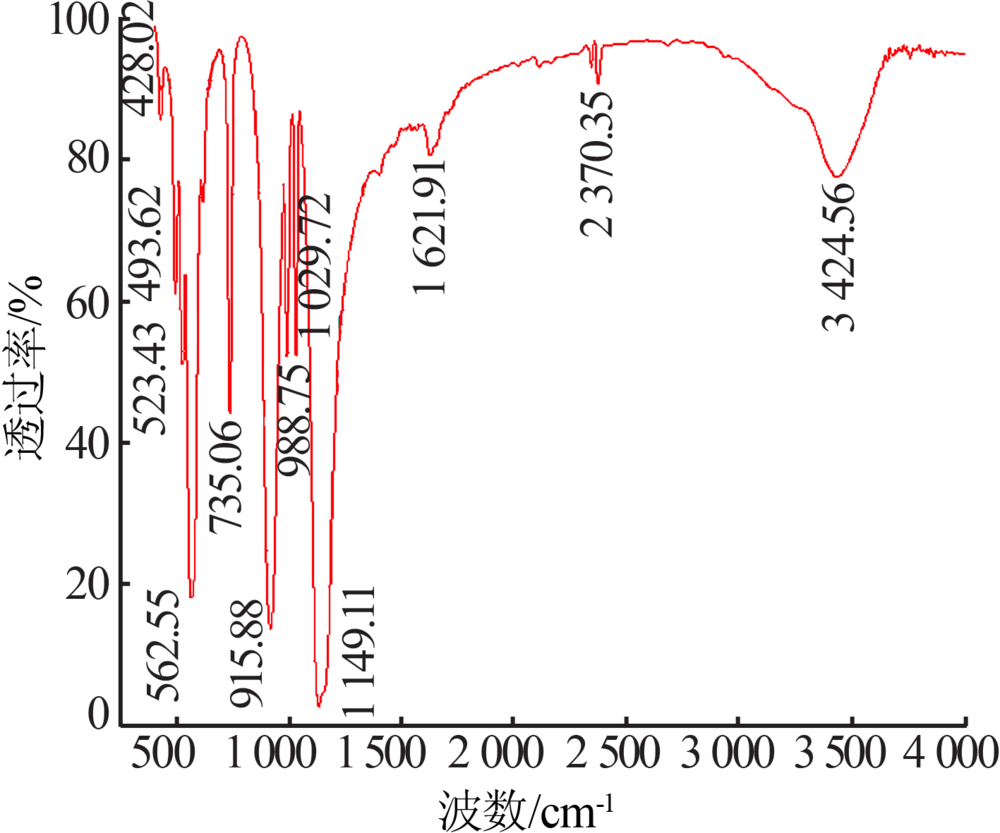
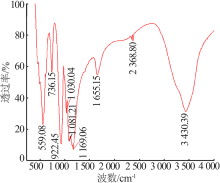
| [1] |
赵玉芬, 赵秉强, 侯翠红, 等. 适应农业新需求,构建我国肥料领域创新体系——中国科学院学部咨询报告[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018,24(2):561-568.
|
| [2] |
侯翠红, 苗俊艳, 谷守玉, 等. 以钙镁磷肥产品创新促进产业发展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019,25(12):2162-2169.
|
| [3] |
Bettger W J, O′dell B L. A critical physiological role of zinc in the structure and function of biomembranes[J]. Life Sciences, 1981,28(13):1425-1438.
pmid: 7017326
|
| [4] |
Gibson R S. Zinc deficiency and human health:etiology,health consequences,and future solutions[J]. Plant and Soil, 2012(1/2):291-299.
|
| [5] |
凌浩瀚, 王辛龙, 许德华, 等. 不同聚合度水溶性聚磷酸铵螯合镁离子的研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019,51(12):20-22,34.
|
| [6] |
黄祖根. 锌肥的施用及效果[J]. 无机盐工业, 1982(3):35-38.
|
| [7] |
马强. 微量金属元素螯合肥制备方法研究[D]. 郑州:郑州大学, 2018.
|
| [8] |
何其明, 刘文涛, 黄廷伟, 等. 高含量液体螯合锌肥及其制备方法及应用:中国,104446678B[P]. 2017-11-14.
|
| [9] |
夏中梅, 侯勇, 曾显斌, 等. 高浓度有机锌肥及其制备方法:中国,1944350[P]. 2007-04-11.
|
| [10] |
郭洪辉, 洪专. 响应面法优化河豚鱼皮胶原寡肽螯合锌的制备工艺[J]. 中国海洋药物, 2017,36(3):47-54.
|
| [11] |
桂明生, 彭惠, 郭亮, 等. 乙二胺四乙酸螯合铁钠微肥的合成[J]. 化肥设计, 2017,55(5):11-13.
|
| [12] |
GB/T 14540—2003 复合肥料中铜铁锰锌硼钼含量的测定[S].
|
| [13] |
Wu Y, Cui S W, Tang J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of crude polysaccharides from boat-fruited sterculia seeds by response urface methodology[J]. Food Chemistry, 2007,105(4):1599-1605.
|
| [14] |
Povilaitis D, Venskutonis P R. Optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of rye bran using response surface methodology and evaluation of extract properties[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2015,100:194-200.
|
| [15] |
梁文, 王辛龙, 陈建钧, 等. 水溶性聚磷酸铵螯合锌的规律研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019,51(11):20-22.
|
| [16] |
李莉, 张赛, 何强, 等. 响应面法在试验设计与优化中的应用[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2015,34(8):41-45.
|
| [17] |
孙克岩, 张志胜, 佟海菊, 等. 响应面法优化牡蛎复合氨基酸螯合锌制备工艺研究[J]. 食品科技, 2011,36(7):107-109,113.
|
| [18] |
谷薇薇. Box-Behnken响应面法优化芒果苷凝胶处方的研究[J]. 中药材, 2019(10):2364-2367.
|
 ),Wang Haobin,Li Luyi
),Wang Haobin,Li Luyi