Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 13-20.doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2020-0579
• Reviews and Special Topics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation,surface functionalization and photoelectrocatalysis of two-dimensional black phosphorus
Yang Huanhuan1,2( ),Yu Binlu1,Wang Jiahong1,2,Yu Xuefeng1,2(
),Yu Binlu1,Wang Jiahong1,2,Yu Xuefeng1,2( )
)
- 1. Shenzhen Engineering Center for the Fabrication of Two-dimensional Atomic Crystals,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
-
Received:2020-10-26Online:2021-05-10Published:2021-05-12 -
Contact:Yu Xuefeng E-mail:hh.yang@siat.ac.cn;xf.yu@siat.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Huanhuan,Yu Binlu,Wang Jiahong,Yu Xuefeng. Preparation,surface functionalization and photoelectrocatalysis of two-dimensional black phosphorus[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(5): 13-20.
share this article
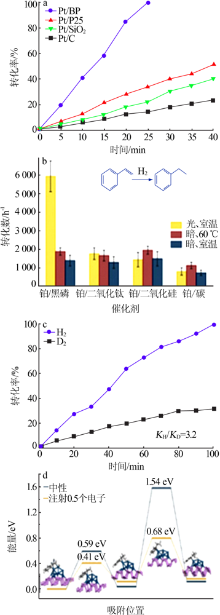
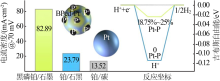
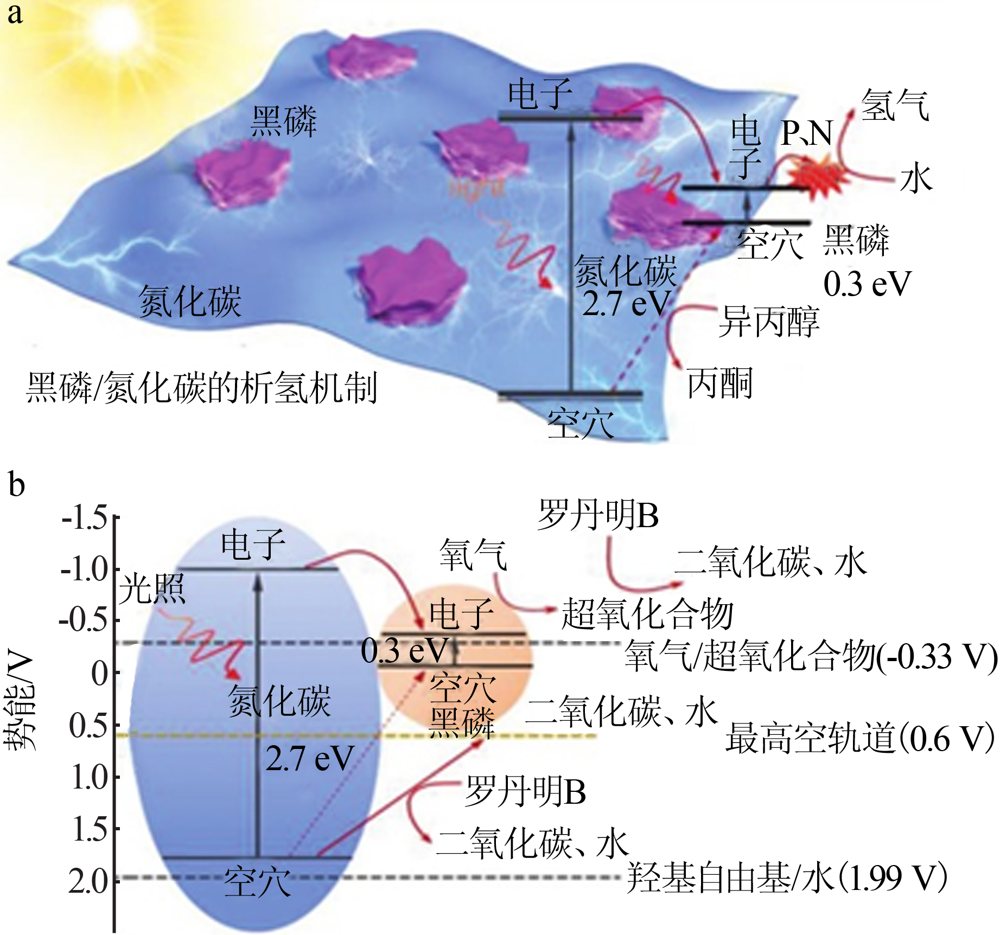
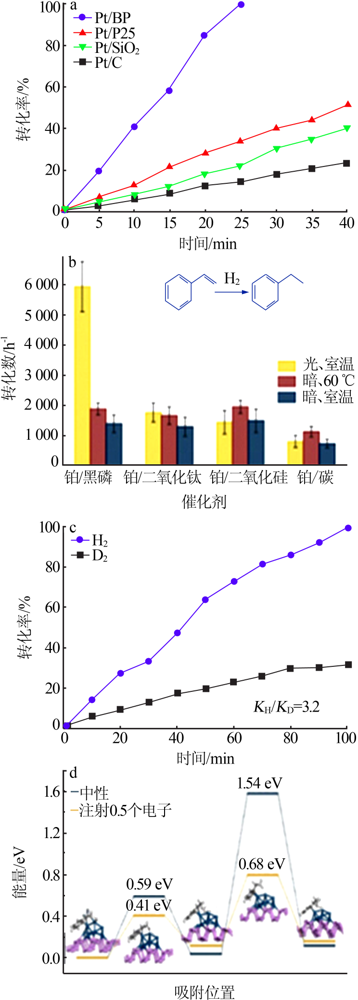
Fig.7
Comparsion of conversion rate of different photocatalysts for styrene hydrogenation(a);comparison of conversion rate of different catalysts for styrene hydrogenation under light and heat(b);isotopic effect of black phosphorus/platinum in styrene hydrogenation(c);effect of photoelectron on energy barrier of styrene hydrogenation(d)[52]"
| [1] |
Li L, Yu Y, Ye G J, et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014,9(5):372-378.
doi: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.35 |
| [2] |
Liu H, Neal A T, Zhu Z, et al. Phosphorene:An unexplored 2D semi-conductor with a high hole mobility[J]. ACS Nano, 2014,8(4):4033-4041.
doi: 10.1021/nn501226z |
| [3] |
Butler S Z, Hollen S M, Cao L, et al. Progress,challenges,and oppo-rtunities in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene[J]. ACS Nano, 2013,7(4):2898-2926.
doi: 10.1021/nn400280c |
| [4] | Liu H, Du Y, Deng Y, et al. Semicon ducting black phosphorus:Syn-journal,transport properties and electronic applications[J]. Chemi-cal Society Reviews, 2015,46(27):2732-2743. |
| [5] | Qiao J, Kong X, Hu Z X, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus[J]. Nature Communications, 2014,5(1):1-7. |
| [6] |
Peng R, Khaliji K, Youngblood N, et al. Mid-infrared electro-optic modulation in few-layer black phosphorus[J]. Nano Letters, 2017,17(10):6315-6320.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b03050 |
| [7] |
Zhang Y, Zheng Y, Rui K, et al. 2D black phosphorus for energy sto-rage and thermoelectric applications[J]. Small, 2017.Doi: 10.1002/smll.201700661.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201700661 |
| [8] |
Zhao Y, Tong L, Li Z, et al. Stable and multifunctional dye-modified black phosphorus nanosheets for near-infrared imaging-guided pho-tothermal therapy[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017,29(17):7131-7139.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b01106 |
| [9] |
Pang J, Bachmatiuk A, Yin Y, et al. Applications of phosphorene and black phosphorus in energy conversion and storage devices[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018,8(8):1702093-1702136.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.8 |
| [10] | Zhu W, Yogeesh M N, Yang S, et al. Flexible black phosphorus ambipolar transistors,circuits and AM demodulator[J]. Nano Let-ters, 2015,15(3):1883-1890. |
| [11] |
Tan C, Cao X, Wu X J, et al. Recent advances in ultrathin two-di-mensional nanomaterials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017,117(9):6225-6331.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00558 |
| [12] |
Castellanos-Gomez A, Vicarelli L, Prada E, et al. Isolation and ch-aracterization of few-layer black phosphorus[J]. 2d Materials, 2014,1(2):025001.
doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/1/2/025001 |
| [13] | Guo Z, Zhang H, Lu S, et al. From black phosphorus to phospho-rene:Basic solvent exfoliation,evolution of raman scattering,and applications to ultrafast photonics[J]. Advanced Functional Mate-rials, 2016,25(45):6996-7002. |
| [14] |
Luo W, Yang R, Liu J, et al. Thermal sublimation:A scalable and controllable thinning method for the fabrication of few-layer black phosphorus[J]. Nanotechnology, 2017,28(28):285301-285388.
doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa76ae |
| [15] | Huang H, Gao M, Kang Y, et al. Rapid and scalable production of high-quality phosphorene by plasma-liquid technology[J]. Chemi-cal Communications, 2019,56:221-224. |
| [16] |
Xu Y J, Shi X Y, Zhang Y S, et al. Epitaxial nucleation and lateral growth of high-crystalline black phosphorus films on silicon[J]. Nature Communications, 2020,11:1330-1338.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14902-z |
| [17] | Wu L, Bian S, Huang H, et al. Black phosphorus:An effective feeds-tock for the synjournal of phosphorus-based chemicals[J]. CCS Che-mistry, 2019,1(2):166-172. |
| [18] |
Liu S, Huang Z, Ren X, et al. P25/black phosphorus/graphene hy-brid for enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Materials Science:Materials in Electronics, 2017,29(6):4441-4448.
doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-8391-3 |
| [19] |
Lei W, Liu G, Zhang J, et al. Black phosphorus nanostructures:Re-cent advances in hybridization,doping and functionalization[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017,46(12):3492-3509.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00021A |
| [20] |
Qiu P X, Xu C M, Zhou N, et al. Metal-free black phosphorus nano-sheets-decorated graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets with CP bon-ds for excellent photocatalytic nitrogen fixation[J]. Applied Cat-alysis B:Environmental, 2017.Doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.010 |
| [21] |
Chen Y, Jiang G, Chen S, et al. Mechanically exfoliated black phos-phorus as a new saturable absorber for both Q-switching and bodelocking laser operation[J]. Optics Express, 2015,23(10):12823-12833.
doi: 10.1364/OE.23.012823 pmid: 26074536 |
| [22] | Sun Z B, Xie H H, Tang S Y, et al. Ultrasmall black phosphorus qu-antum dots:Synjournal and use as photothermal aents[J]. Angewan-dte Chemie International Edition, 2015,54(39):11526-11530. |
| [23] |
Woomer A H, Farnsworth T W, Hu J, et al. Phosphorene:Synthe-sis,scale-up,and quantitative optical spectroscopy[J]. ACS Nano, 2015,9(9):8869-8884.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02599 pmid: 26256770 |
| [24] |
Ambrosi A, Sofer Z, Pumera M, Electrochemical exfoliation of lay-ered black phosphorus into phosphorene[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017,56(35):10443-10445.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.35 |
| [25] | Wen M, Liu D, Kang Y, et al. Synjournal of high-quality black phos-phorus sponges for all-solid-state supercapacitors[J]. Materials Ho-rizons, 2019,6(1):176-181. |
| [26] | Li Q, Zhou Q, Shi L, et al. Recent advances in oxidation and degra-dation mechanisms of ultrathin 2d materials under ambient condi-tions and their passivation strategies[J]. Journal of Materials Che-mistry A, 2019,7(9):4291-4312. |
| [27] | Zhou Q, Chen Q, Tong Y, et al. Light-induced ambient degradation of few-layer black phosphorus:Mechanism and protection[J]. An-gewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016,55(38):11437-11441. |
| [28] |
Tayari V, Hemsworth N, Fakih I, et al. Two-dimensional magneto-transport in a black phosphorus naked quantum well[J]. Nature Communications, 2015,6:7702-7709.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8702 pmid: 26151889 |
| [29] | Artel V, Guo Q, Cohen H, et al. Protective molecular passivation of black phosphorous[J]. Npj 2D Materials & Applications, 2017,1(1):27-32. |
| [30] |
Liu H, Lian P, Tang Y, et al. Facile synjournal of an air-stable 3D re-duced graphene oxide-phosphorene composite by sonication[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019.Doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.248 .
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.248 |
| [31] | Chen X, Wu Y, Wu Z, et al. High quality sandwiched black phos-phorus heterostructure and its quantum oscillations[J]. Nature Co-mmunications, 2015,6:7315-7321. |
| [32] |
Pei J, Gai X, Yang J, et al. Producing air-stable monolayers of pho-sphorene and their defect engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2016,7:10450-10456.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms10450 |
| [33] |
Huang H, He L, Zhou W, et al. Stable black phosphorus/Bi2O3 he-terostructures for synergistic cancer radiotherapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2018,171:12-22.
doi: S0142-9612(18)30278-3 pmid: 29677520 |
| [34] | Zhao Y, Wang H, Huang H, et al. Surface coordination of black phosphorus for robust air and water stability[J]. Angewandte Che-mie International Edition, 2016,128(16):5087-5091. |
| [35] |
Wu L, Wang J, Lu J, et al. Lanthanide-coordinated black phospho-rus[J]. Small, 2018,14(29):1801405.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v14.29 |
| [36] | Guo Z, Chen S, Wang Z, et al. Metal-ion-modified black phospho-rus with enhanced stability and transistor performance[J]. Advan-ced Materials, 2017,29(42):1703811-1703819. |
| [37] |
Yang B, Wan B, Zhou Q, et al. Te-doped black phosphorus field-effect transistors[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016,28(42):9408-9415.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201603723 |
| [38] |
Liu D, Wang J, Lu J, et al. Metal doped phosphorene:Direct synjournal of metal-doped phosphorene with enhanced electro-catalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Small Methods, 2019.Doi: 10.1002/smtd.201970021.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.201970021 |
| [39] | Wang L, Sofer Z, Pumera M. Voltammetry of layered black phosp-horus:Electrochemistry of multilayer phosphorene[J]. Chemelec-trochem, 2015,2(3):324-327. |
| [40] |
Lin Y, Pan Y, Zhang J. In-situ grown of Ni2P nanoparticles on 2D bl-ack phosphorus as a novel hybrid catalyst for hydrogen evolution[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(12):7951-7956.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.030 |
| [41] |
He R, Hua J, Zhang A, et al. Molybdenum disulfide-black phos-phorus hybrid nanosheets as a superior catalyst for electrochemi-cal hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Letters, 2017,17(7):4311-4316.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01334 |
| [42] | Wang J, Liu D, Huang H, et al. In-plane black phosphorus/dicobalt phosphide heterostructure for efficient electrocatalysis[J]. Ange-wandte Chemie International Edition, 2018,57(10):2600-2604. |
| [43] | Wang X, Bai L, Lu J, et al. Rapid activation of platinum with black phosphorus for efficient hydrogen evolution[J]. Angewandte Che-mie International Edition, 2019,58(52):19060-19066. |
| [44] |
Zhu M, Sun Z, Fujitsuka M, et al. Z-scheme photocatalytic water splitting on a 2D heterostructure of black phosphorus/bismuth va-nadate using visible light[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018,57(8):2160-2164.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.8 |
| [45] |
Cai X, Mao L, Yang S, et al. Ultrafast charge separation for full so-lar spectrum activated photocatalytic H2 generation in BP-Au-CdS heterostructure[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018,3(4):932-939.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00126 |
| [46] |
Bian S, Wen M, Wang J, et al. Edge-rich black phosphorus for pho-tocatalytic nitrogen fixation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020,11(3):1052-1058.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b03507 |
| [47] | Liu Y T, Li D, Yu J, et al. Stable confinement of black phosphorus quantum dots on black tin oxide nanotubes:A robust,double-active electrocatalyst toward efficient nitrogen fixation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019,131(46):16591-16596. |
| [48] |
Liu D, Wang J, Bian S, et al. Photoelectrochemical synjournal of am-monia with black phosphorus[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020.Doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002731.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002731 |
| [49] | Shen Z R, Sun S T, Wang W J, et al. A black-red phosphorus het-erostructure for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysis[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015(7):3285-3288. |
| [50] |
Zheng Y, Yu Z, Ou H, et al. Black phosphorus and polymeric car-bon nitride heterostructure for photoinduced molecular oxygen activation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018,28(10). Doi: 10.1002/adfm.201705407.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201705407 |
| [51] |
Wen M, Wang J, Tong R, et al. A low cost metal-free photocatalyst based on black phosphorus[J]. Advanced Science, 2019.Doi: 10.1002/advs.201801321.
doi: 10.1002/advs.201801321 |
| [52] |
Bai L, Wang X, Tang S, et al. Black phosphorus/platinum hetero-structure:A highly efficient photocatalyst for solar-driven chemi-cal reactions[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018.Doi: 10.1002/adma.201803641.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201803641 |
| [1] | LU Xiaomin,LI Xuemei,LIU Lanjun,SHEN Xiaofang,MEI Yi,LIAN Peichao. Research progress in preparation of black phosphorus by liquid phase method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(3): 31-37. |
| [2] | LIU Chang,DUAN Zunbin,WANG Jiannan,MA Huijuan,WANG Jiahong,YU Xuefeng. Research progress on new inorganic phosphorus-based flame retardants [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(11): 8-17. |
| [3] | Jiang Yuncai,Li Xuemei,Wu Zhaoxian,Cao Changdie,Mei Yi,Lian Peichao. Research progress on preparation and application in energy storage of black phosphorus [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(6): 59-71. |
| [4] | Hou Ranran,Cao Changdie,Liu Lanjun,Li Guangneng,Mei Yi,Lian Peichao. Research progress on the preparation of nano-black phosphorus by electrochemical exfoliation from black phosphorus [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(6): 95-100. |
| [5] | DU Miao,MOU Yujin,WANG Shihao,QIU Xinjian,WANG Li,JI Changjian. Research progress on preparation technology of two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks materials [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12): 49-53. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|
||